How Sulfur Cathodes Can Lead the Future of Energy Sustainability
SEP 23, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Sulfur Cathode Technology Background and Objectives
Sulfur cathode technology represents a significant advancement in the evolution of energy storage systems, particularly in the realm of lithium-sulfur (Li-S) batteries. The development of this technology can be traced back to the early 1960s when researchers first explored sulfur as a potential cathode material due to its high theoretical energy density of 2,600 Wh/kg, which far exceeds the capabilities of conventional lithium-ion batteries (typically 250-300 Wh/kg). This remarkable energy density potential has positioned sulfur cathodes as a promising candidate for next-generation energy storage solutions.
The technological evolution of sulfur cathodes has been characterized by persistent efforts to overcome inherent challenges, including the "shuttle effect" (polysulfide dissolution), volume expansion during cycling, and poor electrical conductivity. Throughout the 1980s and 1990s, research primarily focused on understanding these fundamental limitations, with limited practical applications. The early 2000s witnessed a resurgence of interest in Li-S technology, driven by the growing demand for higher energy density batteries for electric vehicles and renewable energy storage.
Recent technological breakthroughs have significantly improved the performance and stability of sulfur cathodes. Innovations in carbon-sulfur composite materials, electrolyte formulations, and protective coatings have addressed many of the historical challenges. The development of nanostructured carbon hosts, such as graphene and carbon nanotubes, has enhanced sulfur utilization and mitigated polysulfide shuttling, leading to improved cycle life and efficiency.
The primary objective of sulfur cathode technology development is to create commercially viable energy storage systems that leverage sulfur's abundant nature, low cost, and environmental friendliness. Sulfur is a byproduct of petroleum refining, making it readily available and approximately 1/150th the cost of conventional cathode materials like cobalt oxide. This economic advantage, coupled with its non-toxic nature, aligns perfectly with global sustainability goals.
Looking forward, the technological roadmap for sulfur cathodes aims to achieve energy densities exceeding 500 Wh/kg at the cell level, with cycle lives of over 1,000 cycles and cost reductions of 70-80% compared to current lithium-ion technologies. These ambitious targets are driving research across academic institutions and industrial laboratories worldwide, with significant investments from both public and private sectors.
The successful development and commercialization of sulfur cathode technology could revolutionize multiple sectors, including transportation (enabling longer-range electric vehicles), renewable energy (providing more efficient grid storage solutions), and portable electronics (delivering longer-lasting devices). As global energy demands continue to rise and environmental concerns intensify, sulfur cathodes represent a critical pathway toward sustainable energy storage solutions that balance performance, cost, and environmental impact.
The technological evolution of sulfur cathodes has been characterized by persistent efforts to overcome inherent challenges, including the "shuttle effect" (polysulfide dissolution), volume expansion during cycling, and poor electrical conductivity. Throughout the 1980s and 1990s, research primarily focused on understanding these fundamental limitations, with limited practical applications. The early 2000s witnessed a resurgence of interest in Li-S technology, driven by the growing demand for higher energy density batteries for electric vehicles and renewable energy storage.
Recent technological breakthroughs have significantly improved the performance and stability of sulfur cathodes. Innovations in carbon-sulfur composite materials, electrolyte formulations, and protective coatings have addressed many of the historical challenges. The development of nanostructured carbon hosts, such as graphene and carbon nanotubes, has enhanced sulfur utilization and mitigated polysulfide shuttling, leading to improved cycle life and efficiency.
The primary objective of sulfur cathode technology development is to create commercially viable energy storage systems that leverage sulfur's abundant nature, low cost, and environmental friendliness. Sulfur is a byproduct of petroleum refining, making it readily available and approximately 1/150th the cost of conventional cathode materials like cobalt oxide. This economic advantage, coupled with its non-toxic nature, aligns perfectly with global sustainability goals.
Looking forward, the technological roadmap for sulfur cathodes aims to achieve energy densities exceeding 500 Wh/kg at the cell level, with cycle lives of over 1,000 cycles and cost reductions of 70-80% compared to current lithium-ion technologies. These ambitious targets are driving research across academic institutions and industrial laboratories worldwide, with significant investments from both public and private sectors.
The successful development and commercialization of sulfur cathode technology could revolutionize multiple sectors, including transportation (enabling longer-range electric vehicles), renewable energy (providing more efficient grid storage solutions), and portable electronics (delivering longer-lasting devices). As global energy demands continue to rise and environmental concerns intensify, sulfur cathodes represent a critical pathway toward sustainable energy storage solutions that balance performance, cost, and environmental impact.
Market Analysis for Sustainable Energy Storage Solutions
The global energy storage market is experiencing unprecedented growth, driven by the increasing adoption of renewable energy sources and the pressing need for sustainable power solutions. As of 2023, the market valuation stands at approximately $211 billion, with projections indicating a compound annual growth rate of 8.4% through 2030. Within this expanding landscape, lithium-sulfur (Li-S) batteries represent one of the most promising next-generation energy storage technologies, potentially addressing many limitations of current lithium-ion solutions.
Consumer demand for higher energy density storage solutions continues to rise across multiple sectors. Electric vehicle manufacturers seek batteries that can extend range while reducing weight, with the EV battery market alone expected to reach $95 billion by 2028. Simultaneously, grid-scale storage applications require cost-effective solutions with longer cycle life to accommodate the intermittent nature of renewable energy generation.
Sulfur cathodes offer compelling market advantages that align with these demands. The theoretical energy density of Li-S batteries (2,600 Wh/kg) significantly exceeds that of conventional lithium-ion batteries (387 Wh/kg for LiCoO₂), presenting a transformative opportunity for applications where weight and space constraints are critical. Additionally, sulfur's natural abundance translates to potential cost reductions of 70-80% compared to current cathode materials, addressing a major barrier to widespread energy storage adoption.
Market segmentation analysis reveals varied adoption potential across industries. The transportation sector, particularly aviation and maritime applications, shows the highest immediate interest due to the weight advantages of sulfur-based batteries. Consumer electronics manufacturers are exploring sulfur cathodes for next-generation devices, while utility-scale storage represents a longer-term but potentially larger market opportunity.
Regional market dynamics indicate Asia-Pacific will likely lead manufacturing capacity development, with China investing heavily in sulfur cathode research and production facilities. North America and Europe are focusing on specialized applications and technological refinement, with significant venture capital flowing into startups developing proprietary sulfur cathode technologies.
Customer willingness-to-pay analysis suggests premium pricing potential in specialized markets where performance advantages outweigh cost considerations. However, mass market adoption will require achieving price parity with existing technologies, estimated to be possible within 5-7 years as manufacturing scales and technology matures.
The competitive landscape is evolving rapidly, with both established battery manufacturers and emerging startups securing strategic positions. Recent market entrants have attracted over $2.3 billion in investment funding since 2020, indicating strong financial market confidence in sulfur cathode technology's commercial viability and future growth potential.
Consumer demand for higher energy density storage solutions continues to rise across multiple sectors. Electric vehicle manufacturers seek batteries that can extend range while reducing weight, with the EV battery market alone expected to reach $95 billion by 2028. Simultaneously, grid-scale storage applications require cost-effective solutions with longer cycle life to accommodate the intermittent nature of renewable energy generation.
Sulfur cathodes offer compelling market advantages that align with these demands. The theoretical energy density of Li-S batteries (2,600 Wh/kg) significantly exceeds that of conventional lithium-ion batteries (387 Wh/kg for LiCoO₂), presenting a transformative opportunity for applications where weight and space constraints are critical. Additionally, sulfur's natural abundance translates to potential cost reductions of 70-80% compared to current cathode materials, addressing a major barrier to widespread energy storage adoption.
Market segmentation analysis reveals varied adoption potential across industries. The transportation sector, particularly aviation and maritime applications, shows the highest immediate interest due to the weight advantages of sulfur-based batteries. Consumer electronics manufacturers are exploring sulfur cathodes for next-generation devices, while utility-scale storage represents a longer-term but potentially larger market opportunity.
Regional market dynamics indicate Asia-Pacific will likely lead manufacturing capacity development, with China investing heavily in sulfur cathode research and production facilities. North America and Europe are focusing on specialized applications and technological refinement, with significant venture capital flowing into startups developing proprietary sulfur cathode technologies.
Customer willingness-to-pay analysis suggests premium pricing potential in specialized markets where performance advantages outweigh cost considerations. However, mass market adoption will require achieving price parity with existing technologies, estimated to be possible within 5-7 years as manufacturing scales and technology matures.
The competitive landscape is evolving rapidly, with both established battery manufacturers and emerging startups securing strategic positions. Recent market entrants have attracted over $2.3 billion in investment funding since 2020, indicating strong financial market confidence in sulfur cathode technology's commercial viability and future growth potential.
Current Status and Challenges in Sulfur Cathode Development
Sulfur cathodes represent one of the most promising advancements in battery technology, offering theoretical energy densities up to five times higher than conventional lithium-ion batteries. Currently, research laboratories worldwide have demonstrated lithium-sulfur batteries with energy densities reaching 400-600 Wh/kg, significantly surpassing commercial lithium-ion batteries that typically deliver 250-300 Wh/kg. However, these impressive laboratory results have not yet translated to commercially viable products due to several persistent technical challenges.
The primary obstacle facing sulfur cathode development is the "polysulfide shuttle effect," where soluble lithium polysulfides dissolve in the electrolyte during cycling, causing active material loss, reduced coulombic efficiency, and rapid capacity fading. Most laboratory cells demonstrate significant capacity degradation after just 100-200 cycles, far below the 1,000+ cycles required for commercial applications.
Another critical challenge is sulfur's inherently poor electrical conductivity (approximately 5×10^-30 S/cm), necessitating large amounts of conductive additives that reduce the overall energy density of the battery system. Additionally, sulfur undergoes substantial volume expansion (up to 80%) during lithiation, leading to mechanical stress that can cause electrode pulverization and further capacity loss over repeated cycles.
The development of suitable electrolytes remains problematic, as conventional carbonate-based electrolytes used in lithium-ion batteries react irreversibly with polysulfides. While ether-based electrolytes show better compatibility, they present safety concerns due to their low flash points and limited electrochemical stability windows.
Geographically, research efforts are concentrated in China, the United States, and Europe, with China leading in patent applications and publications. Major research institutions include the Chinese Academy of Sciences, Stanford University, and the Pacific Northwest National Laboratory, each pursuing different approaches to overcome these technical barriers.
Recent advancements include the development of functional interlayers, polysulfide trapping materials, and novel electrolyte formulations. Particularly promising are carbon-sulfur composite materials that physically confine sulfur within nanoporous structures, reducing polysulfide dissolution. However, scaling these laboratory solutions to mass production presents additional challenges related to cost, manufacturing complexity, and quality control.
The sulfur supply chain presents fewer concerns than other battery materials, as sulfur is abundant as a byproduct of petroleum refining. However, high-purity sulfur processing for battery applications requires additional refinement steps that impact overall production costs and environmental footprint.
Despite these challenges, the past three years have seen accelerated progress in addressing the fundamental issues of lithium-sulfur batteries, suggesting that commercial viability may be achievable within the next 5-10 years if current technical hurdles can be overcome.
The primary obstacle facing sulfur cathode development is the "polysulfide shuttle effect," where soluble lithium polysulfides dissolve in the electrolyte during cycling, causing active material loss, reduced coulombic efficiency, and rapid capacity fading. Most laboratory cells demonstrate significant capacity degradation after just 100-200 cycles, far below the 1,000+ cycles required for commercial applications.
Another critical challenge is sulfur's inherently poor electrical conductivity (approximately 5×10^-30 S/cm), necessitating large amounts of conductive additives that reduce the overall energy density of the battery system. Additionally, sulfur undergoes substantial volume expansion (up to 80%) during lithiation, leading to mechanical stress that can cause electrode pulverization and further capacity loss over repeated cycles.
The development of suitable electrolytes remains problematic, as conventional carbonate-based electrolytes used in lithium-ion batteries react irreversibly with polysulfides. While ether-based electrolytes show better compatibility, they present safety concerns due to their low flash points and limited electrochemical stability windows.
Geographically, research efforts are concentrated in China, the United States, and Europe, with China leading in patent applications and publications. Major research institutions include the Chinese Academy of Sciences, Stanford University, and the Pacific Northwest National Laboratory, each pursuing different approaches to overcome these technical barriers.
Recent advancements include the development of functional interlayers, polysulfide trapping materials, and novel electrolyte formulations. Particularly promising are carbon-sulfur composite materials that physically confine sulfur within nanoporous structures, reducing polysulfide dissolution. However, scaling these laboratory solutions to mass production presents additional challenges related to cost, manufacturing complexity, and quality control.
The sulfur supply chain presents fewer concerns than other battery materials, as sulfur is abundant as a byproduct of petroleum refining. However, high-purity sulfur processing for battery applications requires additional refinement steps that impact overall production costs and environmental footprint.
Despite these challenges, the past three years have seen accelerated progress in addressing the fundamental issues of lithium-sulfur batteries, suggesting that commercial viability may be achievable within the next 5-10 years if current technical hurdles can be overcome.
Current Technical Solutions for Sulfur Cathode Implementation
01 Sulfur cathode composition and structure
Innovations in sulfur cathode composition and structure focus on enhancing energy density and cycle life. These include novel sulfur-carbon composites, nanostructured materials, and hierarchical porous structures that accommodate volume changes during cycling. Advanced designs help contain polysulfides and improve electronic conductivity, addressing key challenges in lithium-sulfur battery technology for sustainable energy storage applications.- Sulfur cathode composition and structure: Innovations in sulfur cathode composition and structure focus on enhancing energy density and cycle life. These include novel sulfur-carbon composites, nanostructured materials, and hierarchical porous structures that accommodate volume changes during cycling. Advanced designs help contain polysulfides and improve electronic conductivity, addressing key challenges in lithium-sulfur battery technology.
- Electrolyte systems for sulfur cathodes: Specialized electrolyte formulations are critical for sulfur cathode performance and sustainability. These include ionic liquids, solid-state electrolytes, and additives designed to suppress the polysulfide shuttle effect. Novel electrolyte systems enhance the electrochemical stability, improve sulfur utilization, and extend battery lifespan while reducing environmental impact.
- Binder and conductive additives for sulfur cathodes: Advanced binder systems and conductive additives play crucial roles in sulfur cathode performance. Water-soluble polymers, functional binders with strong affinity to polysulfides, and novel conductive materials help maintain structural integrity during cycling. These components improve electronic connectivity, enhance active material utilization, and contribute to more sustainable battery manufacturing processes.
- Protective coatings and interlayers: Protective coatings and interlayers are designed to enhance sulfur cathode stability and performance. These include functional separators, barrier layers, and surface modifications that prevent polysulfide migration while facilitating lithium-ion transport. Such innovations extend cycle life, improve coulombic efficiency, and enhance the overall energy sustainability of lithium-sulfur batteries.
- Sustainable manufacturing and recycling processes: Environmentally friendly manufacturing and recycling processes are being developed for sulfur cathodes to enhance energy sustainability. These include green synthesis methods, solvent-free processing, recovery of active materials, and closed-loop recycling systems. Such approaches reduce the environmental footprint of battery production, conserve resources, and support the circular economy for energy storage technologies.
02 Electrolyte systems for sulfur cathodes
Specialized electrolyte formulations are critical for sulfur cathode performance and sustainability. These include ionic liquids, solid-state electrolytes, and additives designed to suppress the polysulfide shuttle effect. Novel electrolyte systems enhance the electrochemical stability window, improve sulfur utilization, and extend battery lifespan, contributing to more sustainable energy storage solutions with reduced environmental impact.Expand Specific Solutions03 Binder and conductive additives for sulfur cathodes
Advanced binder systems and conductive additives play crucial roles in sulfur cathode performance. Water-soluble polymers, functional binders with strong polysulfide adsorption capabilities, and environmentally friendly alternatives to traditional PVDF binders enhance mechanical stability and electrochemical performance. Conductive additives like carbon nanotubes and graphene derivatives improve electron transport and enable higher sulfur loading for sustainable high-energy batteries.Expand Specific Solutions04 Manufacturing processes for sustainable sulfur cathodes
Eco-friendly manufacturing processes for sulfur cathodes include solvent-free methods, water-based slurry preparation, and energy-efficient thermal treatments. These approaches reduce toxic solvent usage, lower energy consumption, and minimize waste generation. Advanced manufacturing techniques like 3D printing and roll-to-roll processing enable scalable production of high-performance sulfur cathodes while maintaining sustainability throughout the battery lifecycle.Expand Specific Solutions05 Recycling and circular economy approaches for sulfur batteries
Sustainable end-of-life management for sulfur-based batteries involves innovative recycling processes to recover valuable materials and reduce environmental impact. Direct recycling methods preserve cathode structures, while hydrometallurgical and pyrometallurgical approaches enable efficient material recovery. Designing batteries with recyclability in mind and establishing closed-loop systems contribute to the circular economy of energy storage technologies and reduce dependence on primary resource extraction.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Industry Players in Sulfur Cathode Research and Production
The sulfur cathode technology market is currently in an early growth phase, characterized by significant R&D investments but limited commercial deployment. The global energy storage market, which this technology aims to disrupt, is projected to reach $500 billion by 2035, with sulfur cathodes potentially capturing a substantial segment due to their cost-effectiveness and sustainability advantages. Technologically, development is progressing through collaborative efforts between academic institutions (MIT, Cornell, Peking University) and industry players. Companies like Sila Nanotechnologies, Wildcat Discovery Technologies, and Sionic Energy are advancing commercial applications, while established manufacturers including Nissan, Renault, and Bosch are exploring integration into their energy storage portfolios. The technology's appeal lies in sulfur's abundance, low cost, and high theoretical capacity, though challenges in cycle stability and conductivity remain key focus areas for ongoing research.
Sila Nanotechnologies, Inc.
Technical Solution: Sila Nanotechnologies has developed proprietary silicon-sulfur composite materials for next-generation battery cathodes. Their technology employs a core-shell nanostructure approach where sulfur is encapsulated within silicon-based matrices, creating stable interfaces that prevent polysulfide dissolution. The company's engineered porous silicon framework provides both mechanical stability and efficient ion transport pathways. Their patented manufacturing process enables precise control of nanostructure morphology, resulting in cathode materials with sulfur loading exceeding 70% by weight while maintaining structural integrity over hundreds of cycles. Sila's technology incorporates functional additives that form protective surface films on the cathode, further enhancing cycle life. The company has demonstrated full cells with energy densities approaching 400 Wh/kg using their silicon-sulfur composite cathodes paired with lithium metal anodes.
Strengths: Scalable manufacturing process already proven for silicon anodes that can be adapted to sulfur cathodes; strong industry partnerships for commercialization. Weaknesses: Their silicon-sulfur composites may face challenges with electronic conductivity over long-term cycling, potentially requiring additional conductive additives that reduce energy density.
Ionic Materials Inc.
Technical Solution: Ionic Materials has developed a revolutionary solid polymer electrolyte specifically engineered to enable stable lithium-sulfur battery chemistry. Their proprietary polymer conducts lithium ions at room temperature without liquid components, fundamentally addressing the polysulfide shuttling issue that plagues conventional lithium-sulfur batteries. The company's technology creates a physical barrier preventing sulfur dissolution while maintaining high ionic conductivity (>1 mS/cm at room temperature). Their cathode design incorporates sulfur directly into the polymer matrix, creating a homogeneous distribution that maximizes active material utilization. This approach eliminates the need for heavy current collectors and excess electrolyte, significantly improving gravimetric energy density. Ionic Materials' solid-state design has demonstrated stable cycling for over 500 cycles with minimal capacity fade, even at high sulfur loadings of 5-7 mg/cm².
Strengths: Their solid-state approach eliminates fundamental safety concerns associated with liquid electrolytes while solving the polysulfide shuttling problem. Weaknesses: Solid-state interfaces may present challenges for high-rate performance, potentially limiting applications requiring rapid charging or high power output.
Critical Patents and Innovations in Sulfur Cathode Technology
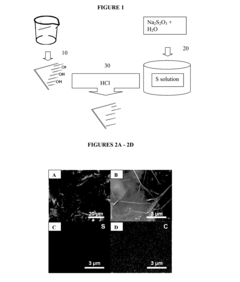
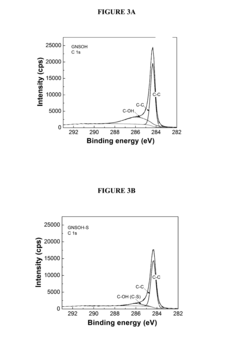
Sulfur-hydroxylated graphene nanocomposites for rechargeable lithium-sulfur batteries and methods of making the same
PatentInactiveUS20160336590A1
Innovation
- A sulfur-hydroxylated graphene nanocomposite is developed, where amorphous sulfur nanoparticles are uniformly distributed on a hydroxylated graphene surface, enhancing conductivity and preventing polysulfide dissolution, with a method involving ultrasonication and hydrothermal treatment to form the nanocomposite.
Sulfur cathodes protected with hybrid solid-electrolyte interfaces for high performance li-s batteries
PatentInactiveEP3772765A1
Innovation
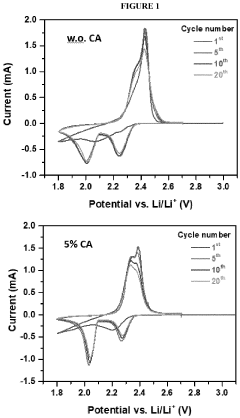
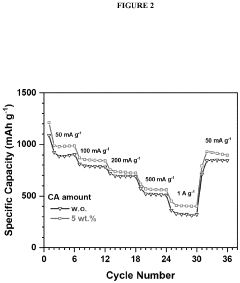
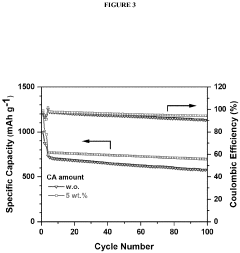
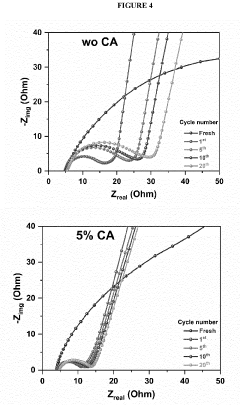
- Incorporating a carboxylic acid or its lithiated form, such as citric acid, at the surface of the cathode to form a lithium carboxylate-based solid electrolyte interphase (SEI) that mitigates the shuttle effect, enhancing capacity retention and efficiency.
Environmental Impact Assessment of Sulfur Cathode Technologies
The environmental implications of sulfur cathode technologies extend far beyond their energy storage capabilities, representing a critical dimension in evaluating their sustainability credentials. Sulfur cathodes offer significant environmental advantages compared to conventional lithium-ion battery technologies, primarily due to the abundance and non-toxicity of sulfur as a raw material. Unlike cobalt and nickel used in traditional cathodes, sulfur is a byproduct of petroleum refining, meaning its utilization in batteries effectively transforms an industrial waste product into a valuable resource, reducing environmental burden.
Life cycle assessments of sulfur cathode batteries demonstrate substantially lower carbon footprints during the production phase. Studies indicate a potential reduction of greenhouse gas emissions by 60-75% compared to conventional lithium-ion batteries, primarily due to the simplified extraction and processing requirements. The elimination of energy-intensive mining operations associated with metals like cobalt significantly reduces habitat destruction, water pollution, and ecosystem disruption in mining regions.
Water consumption metrics also favor sulfur cathode technologies, with manufacturing processes requiring approximately 50% less water than conventional cathode production. This advantage becomes particularly significant in water-stressed regions where battery manufacturing facilities might operate. Additionally, the reduced dependency on critical minerals mitigates geopolitical tensions and supply chain vulnerabilities associated with materials concentrated in politically sensitive regions.
End-of-life considerations reveal further environmental benefits. Sulfur cathode batteries present fewer recycling challenges due to their simpler chemical composition. The absence of toxic heavy metals facilitates safer disposal protocols and more efficient material recovery processes. Preliminary recycling methodologies demonstrate recovery rates exceeding 90% for sulfur components, creating a more circular material economy.
However, certain environmental challenges persist. The production of lithium sulfide intermediates involves hydrogen sulfide, requiring robust safety protocols to prevent accidental releases of this toxic gas. Additionally, the polysulfide shuttle effect can lead to premature degradation, potentially shortening battery lifespans and increasing replacement frequency, which could partially offset the initial environmental benefits.
Scaling considerations must also address potential sulfur supply constraints if deployment reaches massive levels. While currently abundant as a petroleum byproduct, a transition away from fossil fuels could ironically reduce this supply source, necessitating alternative sulfur procurement strategies to maintain the technology's environmental advantages.
Life cycle assessments of sulfur cathode batteries demonstrate substantially lower carbon footprints during the production phase. Studies indicate a potential reduction of greenhouse gas emissions by 60-75% compared to conventional lithium-ion batteries, primarily due to the simplified extraction and processing requirements. The elimination of energy-intensive mining operations associated with metals like cobalt significantly reduces habitat destruction, water pollution, and ecosystem disruption in mining regions.
Water consumption metrics also favor sulfur cathode technologies, with manufacturing processes requiring approximately 50% less water than conventional cathode production. This advantage becomes particularly significant in water-stressed regions where battery manufacturing facilities might operate. Additionally, the reduced dependency on critical minerals mitigates geopolitical tensions and supply chain vulnerabilities associated with materials concentrated in politically sensitive regions.
End-of-life considerations reveal further environmental benefits. Sulfur cathode batteries present fewer recycling challenges due to their simpler chemical composition. The absence of toxic heavy metals facilitates safer disposal protocols and more efficient material recovery processes. Preliminary recycling methodologies demonstrate recovery rates exceeding 90% for sulfur components, creating a more circular material economy.
However, certain environmental challenges persist. The production of lithium sulfide intermediates involves hydrogen sulfide, requiring robust safety protocols to prevent accidental releases of this toxic gas. Additionally, the polysulfide shuttle effect can lead to premature degradation, potentially shortening battery lifespans and increasing replacement frequency, which could partially offset the initial environmental benefits.
Scaling considerations must also address potential sulfur supply constraints if deployment reaches massive levels. While currently abundant as a petroleum byproduct, a transition away from fossil fuels could ironically reduce this supply source, necessitating alternative sulfur procurement strategies to maintain the technology's environmental advantages.
Supply Chain Analysis for Sulfur Cathode Manufacturing
The sulfur cathode supply chain represents a critical component in the advancement of sustainable energy storage technologies. The manufacturing process begins with raw material sourcing, where elemental sulfur offers a significant advantage due to its abundance as a byproduct of petroleum refining and natural gas processing. This creates a circular economy opportunity by utilizing what would otherwise be industrial waste, significantly reducing both environmental impact and production costs compared to traditional cathode materials like cobalt and nickel.
The global distribution of sulfur resources presents both opportunities and challenges. While sulfur is geographically widespread, reducing dependency on specific regions unlike critical battery minerals, the quality and purity levels vary considerably. This necessitates the development of standardized purification processes to ensure consistent performance in battery applications.
Processing infrastructure represents a current bottleneck in the supply chain. The conversion of raw sulfur into battery-grade material requires specialized equipment for purification, carbon-sulfur composite formation, and electrode manufacturing. Currently, this infrastructure is underdeveloped compared to established lithium-ion battery production facilities, creating potential scaling challenges as demand increases.
Transportation and logistics considerations are uniquely favorable for sulfur cathodes. Unlike many battery materials that require specialized handling due to reactivity or toxicity concerns, sulfur is relatively stable and can utilize existing transportation networks with minimal modification. This translates to lower distribution costs and reduced supply chain complexity.
The economic analysis reveals compelling advantages. Production cost modeling indicates that sulfur cathodes could achieve manufacturing costs 30-40% lower than conventional lithium-ion cathodes at scale. This cost advantage stems from both cheaper raw materials and potentially simplified production processes, though initial capital investment for specialized manufacturing equipment remains a barrier to entry.
Supply chain resilience assessment identifies diversification opportunities through the development of regional processing hubs near petroleum refineries and natural gas facilities. This distributed manufacturing approach could mitigate geopolitical risks while reducing transportation emissions and costs. However, the integration with existing battery manufacturing ecosystems requires strategic planning to ensure compatibility with established production lines and quality control systems.
The global distribution of sulfur resources presents both opportunities and challenges. While sulfur is geographically widespread, reducing dependency on specific regions unlike critical battery minerals, the quality and purity levels vary considerably. This necessitates the development of standardized purification processes to ensure consistent performance in battery applications.
Processing infrastructure represents a current bottleneck in the supply chain. The conversion of raw sulfur into battery-grade material requires specialized equipment for purification, carbon-sulfur composite formation, and electrode manufacturing. Currently, this infrastructure is underdeveloped compared to established lithium-ion battery production facilities, creating potential scaling challenges as demand increases.
Transportation and logistics considerations are uniquely favorable for sulfur cathodes. Unlike many battery materials that require specialized handling due to reactivity or toxicity concerns, sulfur is relatively stable and can utilize existing transportation networks with minimal modification. This translates to lower distribution costs and reduced supply chain complexity.
The economic analysis reveals compelling advantages. Production cost modeling indicates that sulfur cathodes could achieve manufacturing costs 30-40% lower than conventional lithium-ion cathodes at scale. This cost advantage stems from both cheaper raw materials and potentially simplified production processes, though initial capital investment for specialized manufacturing equipment remains a barrier to entry.
Supply chain resilience assessment identifies diversification opportunities through the development of regional processing hubs near petroleum refineries and natural gas facilities. This distributed manufacturing approach could mitigate geopolitical risks while reducing transportation emissions and costs. However, the integration with existing battery manufacturing ecosystems requires strategic planning to ensure compatibility with established production lines and quality control systems.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!