Sulfur Cathodes and Advanced Regulatory Frameworks
SEP 23, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Sulfur Cathode Technology Background and Objectives
Lithium-sulfur (Li-S) batteries have emerged as a promising next-generation energy storage technology due to their theoretical energy density of 2600 Wh/kg, which far exceeds the capabilities of conventional lithium-ion batteries. The development of sulfur cathodes can be traced back to the 1960s, but significant research momentum has only built up in the past two decades as global demand for high-energy density storage solutions has intensified. The evolution of this technology has been characterized by incremental improvements addressing fundamental challenges such as the "shuttle effect," poor conductivity, and volume expansion issues.
The current technological landscape is driven by the urgent need for sustainable and high-performance energy storage systems to support renewable energy integration, electric vehicle advancement, and portable electronics. Sulfur, as a cathode material, presents compelling advantages including natural abundance (being the 16th most common element in Earth's crust), low cost (often available as a byproduct of petroleum refining), and environmental friendliness compared to traditional cathode materials containing cobalt or nickel.
Recent technological breakthroughs have focused on nanostructured carbon hosts, functional interlayers, and electrolyte modifications to mitigate the dissolution of lithium polysulfides. These innovations have pushed practical energy densities from below 200 Wh/kg to over 400 Wh/kg in laboratory settings, demonstrating the rapid pace of advancement in this field. However, significant gaps remain between laboratory demonstrations and commercial viability.
The primary technical objectives for sulfur cathode development include achieving high sulfur loading (>5 mg/cm²) while maintaining good cycle stability (>1000 cycles with <0.05% capacity fade per cycle), improving rate capability for fast charging applications, and developing manufacturing processes compatible with existing battery production infrastructure. These targets are essential for Li-S batteries to compete with and eventually surpass conventional lithium-ion technologies.
Regulatory frameworks surrounding battery technologies are simultaneously evolving to address safety concerns, environmental impact, and end-of-life management. The unique chemistry of sulfur cathodes presents both challenges and opportunities within this regulatory landscape. Unlike conventional lithium-ion batteries, Li-S cells contain no heavy metals, potentially simplifying recycling processes and reducing environmental concerns associated with mining.
The convergence of technological advancement and regulatory development represents a critical juncture for sulfur cathode commercialization. Research objectives must therefore extend beyond pure performance metrics to include safety validation, standardization of testing protocols, and life cycle assessment methodologies that can inform appropriate regulatory frameworks. This holistic approach is essential to facilitate the transition of sulfur cathode technology from laboratory curiosity to commercial reality.
The current technological landscape is driven by the urgent need for sustainable and high-performance energy storage systems to support renewable energy integration, electric vehicle advancement, and portable electronics. Sulfur, as a cathode material, presents compelling advantages including natural abundance (being the 16th most common element in Earth's crust), low cost (often available as a byproduct of petroleum refining), and environmental friendliness compared to traditional cathode materials containing cobalt or nickel.
Recent technological breakthroughs have focused on nanostructured carbon hosts, functional interlayers, and electrolyte modifications to mitigate the dissolution of lithium polysulfides. These innovations have pushed practical energy densities from below 200 Wh/kg to over 400 Wh/kg in laboratory settings, demonstrating the rapid pace of advancement in this field. However, significant gaps remain between laboratory demonstrations and commercial viability.
The primary technical objectives for sulfur cathode development include achieving high sulfur loading (>5 mg/cm²) while maintaining good cycle stability (>1000 cycles with <0.05% capacity fade per cycle), improving rate capability for fast charging applications, and developing manufacturing processes compatible with existing battery production infrastructure. These targets are essential for Li-S batteries to compete with and eventually surpass conventional lithium-ion technologies.
Regulatory frameworks surrounding battery technologies are simultaneously evolving to address safety concerns, environmental impact, and end-of-life management. The unique chemistry of sulfur cathodes presents both challenges and opportunities within this regulatory landscape. Unlike conventional lithium-ion batteries, Li-S cells contain no heavy metals, potentially simplifying recycling processes and reducing environmental concerns associated with mining.
The convergence of technological advancement and regulatory development represents a critical juncture for sulfur cathode commercialization. Research objectives must therefore extend beyond pure performance metrics to include safety validation, standardization of testing protocols, and life cycle assessment methodologies that can inform appropriate regulatory frameworks. This holistic approach is essential to facilitate the transition of sulfur cathode technology from laboratory curiosity to commercial reality.
Market Analysis for Sulfur-Based Battery Systems
The global market for sulfur-based battery systems has witnessed significant growth in recent years, driven by increasing demand for high-energy density storage solutions across multiple sectors. The market size for lithium-sulfur batteries was valued at approximately $551 million in 2022 and is projected to reach $2.1 billion by 2030, representing a compound annual growth rate of 18.3% during the forecast period.
The automotive sector constitutes the largest application segment for sulfur-based battery systems, accounting for nearly 40% of the total market share. This dominance is attributed to the growing adoption of electric vehicles (EVs) worldwide and the pressing need for batteries with higher energy density and lower cost. Major automotive manufacturers including Tesla, Volkswagen, and Toyota have shown interest in sulfur cathode technology as a potential successor to conventional lithium-ion batteries.
Consumer electronics represents the second-largest market segment, with a share of 25%. The demand for longer-lasting portable devices continues to drive research and development in this sector. Additionally, grid storage applications are emerging as a rapidly growing segment, expected to register the highest growth rate of 22.7% over the next decade due to increasing renewable energy integration.
Geographically, Asia-Pacific dominates the market with a 45% share, led by China, Japan, and South Korea. These countries have established robust manufacturing capabilities and supportive government policies for advanced battery technologies. North America follows with a 30% market share, while Europe accounts for 20%, with the remaining 5% distributed across other regions.
Key market drivers include the declining cost of sulfur as a cathode material, which is approximately 1/150th the cost of cobalt used in conventional lithium-ion batteries. Environmental regulations limiting the use of heavy metals in batteries have also accelerated interest in sulfur-based alternatives. Furthermore, the theoretical energy density of lithium-sulfur batteries (2,600 Wh/kg) far exceeds that of lithium-ion batteries (387 Wh/kg), presenting a compelling value proposition.
Market challenges primarily revolve around technical limitations such as the "shuttle effect," poor cycle life, and manufacturing scalability. These factors have restricted widespread commercial adoption despite the promising theoretical advantages. However, recent technological breakthroughs in sulfur cathode design and electrolyte formulations have begun to address these limitations, potentially accelerating market penetration in the coming years.
The automotive sector constitutes the largest application segment for sulfur-based battery systems, accounting for nearly 40% of the total market share. This dominance is attributed to the growing adoption of electric vehicles (EVs) worldwide and the pressing need for batteries with higher energy density and lower cost. Major automotive manufacturers including Tesla, Volkswagen, and Toyota have shown interest in sulfur cathode technology as a potential successor to conventional lithium-ion batteries.
Consumer electronics represents the second-largest market segment, with a share of 25%. The demand for longer-lasting portable devices continues to drive research and development in this sector. Additionally, grid storage applications are emerging as a rapidly growing segment, expected to register the highest growth rate of 22.7% over the next decade due to increasing renewable energy integration.
Geographically, Asia-Pacific dominates the market with a 45% share, led by China, Japan, and South Korea. These countries have established robust manufacturing capabilities and supportive government policies for advanced battery technologies. North America follows with a 30% market share, while Europe accounts for 20%, with the remaining 5% distributed across other regions.
Key market drivers include the declining cost of sulfur as a cathode material, which is approximately 1/150th the cost of cobalt used in conventional lithium-ion batteries. Environmental regulations limiting the use of heavy metals in batteries have also accelerated interest in sulfur-based alternatives. Furthermore, the theoretical energy density of lithium-sulfur batteries (2,600 Wh/kg) far exceeds that of lithium-ion batteries (387 Wh/kg), presenting a compelling value proposition.
Market challenges primarily revolve around technical limitations such as the "shuttle effect," poor cycle life, and manufacturing scalability. These factors have restricted widespread commercial adoption despite the promising theoretical advantages. However, recent technological breakthroughs in sulfur cathode design and electrolyte formulations have begun to address these limitations, potentially accelerating market penetration in the coming years.
Current Challenges in Sulfur Cathode Development
Despite significant advancements in lithium-sulfur battery technology, sulfur cathodes continue to face several critical challenges that impede their widespread commercial adoption. The most persistent issue is the "shuttle effect," where soluble lithium polysulfides formed during discharge migrate between electrodes, causing rapid capacity fading and shortened battery lifespan. This phenomenon not only reduces energy density but also compromises the long-term cycling stability essential for practical applications.
Material degradation presents another significant obstacle. The substantial volume expansion (approximately 80%) that sulfur undergoes during lithiation/delithiation cycles leads to mechanical stress and structural disintegration of the cathode. This expansion-contraction process gradually destroys the conductive network within the electrode, resulting in increased internal resistance and diminished performance over time.
The inherently poor electrical conductivity of sulfur (5×10^-30 S/cm) severely limits electron transport within the cathode, necessitating large amounts of conductive additives that reduce the overall energy density of the battery system. This trade-off between conductivity and energy density remains a fundamental design challenge for researchers and engineers.
Low sulfur utilization rates further compound these issues. In many current designs, only a fraction of the theoretical capacity (1675 mAh/g) is practically achievable due to incomplete conversion reactions and inaccessible active material. This utilization gap significantly undermines the theoretical advantages of sulfur as a high-capacity cathode material.
Manufacturing scalability presents additional hurdles. Current laboratory-scale production methods for advanced sulfur cathodes often involve complex synthesis procedures that are difficult to scale up cost-effectively. Techniques such as chemical vapor deposition for carbon host materials or precise nanostructure engineering require specialized equipment and controlled conditions that are challenging to implement in mass production environments.
Safety concerns also persist, particularly regarding the formation of hydrogen sulfide gas during cell failure or improper disposal. The development of robust safety mechanisms and containment strategies remains critical for consumer acceptance and regulatory approval.
Addressing these multifaceted challenges requires interdisciplinary approaches combining materials science, electrochemistry, and engineering innovations. Recent research directions focus on developing novel host materials, electrolyte additives, and cell designs that can simultaneously mitigate multiple failure mechanisms while maintaining the high energy density that makes lithium-sulfur batteries so promising.
Material degradation presents another significant obstacle. The substantial volume expansion (approximately 80%) that sulfur undergoes during lithiation/delithiation cycles leads to mechanical stress and structural disintegration of the cathode. This expansion-contraction process gradually destroys the conductive network within the electrode, resulting in increased internal resistance and diminished performance over time.
The inherently poor electrical conductivity of sulfur (5×10^-30 S/cm) severely limits electron transport within the cathode, necessitating large amounts of conductive additives that reduce the overall energy density of the battery system. This trade-off between conductivity and energy density remains a fundamental design challenge for researchers and engineers.
Low sulfur utilization rates further compound these issues. In many current designs, only a fraction of the theoretical capacity (1675 mAh/g) is practically achievable due to incomplete conversion reactions and inaccessible active material. This utilization gap significantly undermines the theoretical advantages of sulfur as a high-capacity cathode material.
Manufacturing scalability presents additional hurdles. Current laboratory-scale production methods for advanced sulfur cathodes often involve complex synthesis procedures that are difficult to scale up cost-effectively. Techniques such as chemical vapor deposition for carbon host materials or precise nanostructure engineering require specialized equipment and controlled conditions that are challenging to implement in mass production environments.
Safety concerns also persist, particularly regarding the formation of hydrogen sulfide gas during cell failure or improper disposal. The development of robust safety mechanisms and containment strategies remains critical for consumer acceptance and regulatory approval.
Addressing these multifaceted challenges requires interdisciplinary approaches combining materials science, electrochemistry, and engineering innovations. Recent research directions focus on developing novel host materials, electrolyte additives, and cell designs that can simultaneously mitigate multiple failure mechanisms while maintaining the high energy density that makes lithium-sulfur batteries so promising.
Current Technical Solutions for Sulfur Cathodes
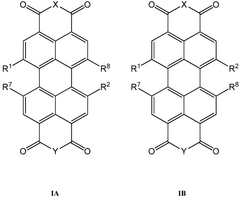
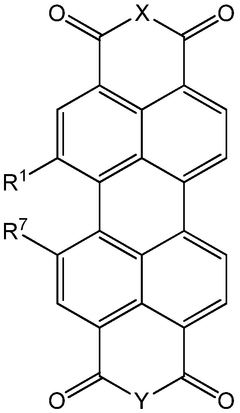
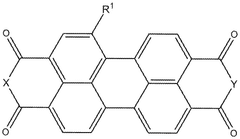
01 Sulfur cathode compositions for lithium-sulfur batteries
Sulfur cathodes can be formulated with various compositions to enhance performance in lithium-sulfur batteries. These compositions typically include sulfur as the active material combined with conductive additives and binders. The formulations aim to address challenges such as low conductivity of sulfur and polysulfide dissolution. Advanced compositions may incorporate carbon materials, polymers, or other additives to improve cycle life and capacity retention.- Sulfur cathode compositions for lithium-sulfur batteries: Sulfur cathodes are widely used in lithium-sulfur batteries due to their high theoretical energy density. These cathodes typically consist of elemental sulfur combined with conductive additives and binders. The compositions are designed to address challenges such as polysulfide dissolution and volume expansion during cycling, which can lead to capacity fading. Various formulations incorporate carbon materials, polymers, and other additives to enhance conductivity and stability.
- Nanostructured sulfur cathode materials: Nanostructured sulfur cathode materials offer improved performance in lithium-sulfur batteries by providing better sulfur utilization and polysulfide confinement. These materials include sulfur-carbon nanocomposites, hollow carbon structures containing sulfur, and mesoporous materials that encapsulate sulfur. The nanostructured approach helps to mitigate the insulating nature of sulfur and provides physical confinement to reduce polysulfide shuttling, thereby enhancing cycling stability and rate capability.
- Protective coatings and interlayers for sulfur cathodes: Protective coatings and interlayers are applied to sulfur cathodes to enhance their electrochemical performance and stability. These include polymer coatings, metal oxide layers, and functional interlayers between the cathode and separator. Such protective structures help to physically contain polysulfides within the cathode region, prevent their migration to the anode, and maintain the integrity of the electrode during cycling. This approach significantly improves the cycle life and capacity retention of lithium-sulfur batteries.
- Binder systems for sulfur cathodes: Specialized binder systems play a crucial role in sulfur cathode performance by improving the mechanical stability and electrochemical properties of the electrode. These binders include water-soluble polymers, conductive polymers, and functional binders with chemical affinity for polysulfides. The binder selection affects electrode adhesion, flexibility, and ionic conductivity. Advanced binder systems can accommodate the volume changes during cycling and help retain active material within the cathode structure.
- Electrolyte additives and modifications for sulfur cathodes: Electrolyte additives and modifications are employed to enhance the performance of sulfur cathodes by addressing the polysulfide shuttle effect and improving the electrode-electrolyte interface. These include lithium salt additives, solvents with high donor numbers, and functional additives that form protective films on the electrode surface. Modified electrolytes can suppress polysulfide dissolution, enhance ionic conductivity, and stabilize the solid-electrolyte interphase, leading to improved cycling performance and coulombic efficiency in lithium-sulfur batteries.
02 Nanostructured sulfur cathode materials
Nanostructured approaches to sulfur cathode design involve creating materials with nanoscale features to improve electrochemical performance. These include sulfur nanoparticles, nanocomposites with carbon materials (such as carbon nanotubes or graphene), and core-shell structures. Nanostructuring helps to contain polysulfides, enhance conductivity, and accommodate volume changes during cycling, leading to improved capacity retention and cycle life in lithium-sulfur batteries.Expand Specific Solutions03 Protective coatings and interlayers for sulfur cathodes
Various protective coatings and interlayers can be applied to sulfur cathodes to mitigate polysulfide shuttling and improve battery performance. These include polymer coatings, metal oxide layers, and functional separators. Such protective measures create physical barriers that prevent polysulfides from dissolving into the electrolyte while still allowing lithium ion transport. This approach significantly improves the cycling stability and coulombic efficiency of lithium-sulfur batteries.Expand Specific Solutions04 Electrolyte systems for sulfur cathodes
Specialized electrolyte systems are developed specifically for use with sulfur cathodes to address the polysulfide dissolution issue. These include solid-state electrolytes, gel polymer electrolytes, ionic liquid electrolytes, and electrolytes with additives that can chemically interact with polysulfides. The electrolyte composition significantly affects the performance of sulfur cathodes by influencing polysulfide solubility, lithium ion transport, and interfacial stability.Expand Specific Solutions05 Manufacturing processes for sulfur cathodes
Various manufacturing processes are employed to produce high-performance sulfur cathodes. These include melt-diffusion methods, solution-based processes, spray drying, and electrospinning techniques. Advanced manufacturing approaches focus on achieving uniform sulfur distribution within conductive matrices, controlling the sulfur loading, and creating optimized pore structures. The manufacturing method significantly impacts the microstructure of the cathode and consequently its electrochemical performance.Expand Specific Solutions
Leading Organizations in Sulfur Battery Research
The sulfur cathode technology market is currently in a growth phase, with increasing research activity and commercial interest. The market size is expanding due to the potential for higher energy density batteries, particularly for electric vehicles and portable electronics. Technologically, sulfur cathodes are advancing from early-stage research toward commercialization, with companies at varying maturity levels. Leading players include established automotive manufacturers (Toyota, Hyundai, GM), battery specialists (Sion Power, Samsung SDI), and innovative startups (Theion, Conamix, Sila Nanotechnologies). Research institutions like Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics and universities (Cornell, Bar-Ilan) are driving fundamental breakthroughs, while regulatory frameworks are evolving to address safety and environmental concerns, creating opportunities for companies developing sustainable battery technologies.
Sion Power Corp.
Technical Solution: Sion Power has pioneered the development of their proprietary Licerion® technology, which combines lithium-sulfur chemistry with protected lithium metal anodes. Their approach focuses on addressing the fundamental challenges of sulfur cathodes through a multi-faceted strategy. Sion's sulfur cathodes utilize a nanostructured carbon framework that provides both physical containment of sulfur and electrical conductivity. The company has developed specialized binders and electrolyte formulations that minimize polysulfide dissolution while maintaining ionic conductivity. Their research has demonstrated energy densities exceeding 500 Wh/kg at the cell level, with projections of reaching 700 Wh/kg in future iterations. Sion Power has also made significant advances in regulatory compliance, working closely with transportation safety authorities to establish protocols for the safe shipping and handling of high-energy lithium-sulfur batteries.
Strengths: Highest demonstrated energy density among commercial Li-S developers; protected intellectual property portfolio; established partnerships with aerospace and defense sectors. Weaknesses: Limited production scale compared to major battery manufacturers; higher costs than conventional lithium-ion; challenges with fast-charging capabilities.
Samsung SDI Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: Samsung SDI has developed advanced sulfur cathode technology utilizing a dual-confinement strategy that addresses the polysulfide shuttle effect. Their approach combines physical confinement through carbon matrices with chemical binding via polar materials. The company has created a hierarchical porous carbon structure that effectively traps sulfur and polysulfides while maintaining high electrical conductivity. Samsung's research has demonstrated lithium-sulfur batteries with initial capacities exceeding 1,200 mAh/g and capacity retention of over 80% after 500 cycles. Their technology incorporates functional interlayers between the cathode and separator that act as additional barriers to polysulfide migration. Samsung has also developed proprietary electrolyte additives that form stable interfaces on lithium metal anodes, addressing another critical challenge in Li-S battery systems.
Strengths: Industry-leading cycle stability and capacity retention; established manufacturing infrastructure for potential commercialization; strong integration with existing battery management systems. Weaknesses: Higher production costs compared to conventional lithium-ion batteries; energy density improvements still needed to reach theoretical potential; temperature sensitivity issues in extreme conditions.
Key Patents and Innovations in Sulfur Cathode Design
A composite comprising carbon nanotubes and uses thereof as a cathode
PatentWO2024201466A1
Innovation
- A composite cathode is developed using a multi-layered structure of multi-walled carbon nanotubes (MWCNT) and single-walled carbon nanotubes (SWCNT) with a weight ratio of 10:1 to 1:10, optionally incorporating aromatic compounds, to enhance conductivity, mechanical strength, and sulfur loading, facilitating efficient lithium-ion diffusion and polysulfide trapping.
Improved sulfur cathodes
PatentWO2025129258A1
Innovation
- The development of a sulfur cathode comprising sulfur-containing materials, conductive materials, metal cations with a valency of two or more, halide anions, polyhalogen anions, and binding polymers capable of binding these species. This configuration enhances the retention and conversion of lithium polysulfides, improving reaction kinetics and mechanical stability.
Regulatory Framework Analysis for Battery Technologies
The regulatory landscape for battery technologies, particularly those involving sulfur cathodes, has evolved significantly in response to environmental concerns, safety requirements, and sustainability goals. Current regulatory frameworks across major markets focus on several key aspects including lifecycle management, safety standards, and environmental impact mitigation. The European Union's Battery Directive and the more recent Battery Regulation proposal establish comprehensive requirements for battery collection, recycling, and material recovery, with specific provisions for hazardous materials management that directly impact sulfur cathode development.
In the United States, regulations are more fragmented, with the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) overseeing waste management aspects under the Resource Conservation and Recovery Act, while the Department of Transportation regulates battery transportation safety. These frameworks increasingly incorporate provisions for emerging battery chemistries, though sulfur-specific regulations remain underdeveloped compared to lithium-ion technologies.
Asian markets, particularly China, Japan, and South Korea, have implemented robust regulatory systems focusing on manufacturing standards and end-of-life management. China's policies on battery recycling and material recovery have become increasingly stringent, creating both challenges and opportunities for sulfur cathode technologies that offer potential environmental advantages.
Safety certification standards represent another critical regulatory dimension, with organizations like UL, IEC, and ISO developing specific protocols for battery testing and certification. The unique properties of sulfur cathodes, including their thermal behavior and potential for polysulfide shuttling, necessitate specialized safety considerations that current standards may not fully address.
Emerging regulatory trends indicate a shift toward more performance-based approaches rather than prescriptive requirements, allowing greater flexibility for innovative technologies like sulfur cathodes. Carbon footprint regulations and extended producer responsibility schemes are increasingly being incorporated into battery regulations, potentially favoring sulfur-based systems due to their abundant and environmentally benign active material.
Regulatory gaps persist in areas specific to sulfur cathode technologies, particularly regarding long-term environmental impact assessment, recycling protocols, and safety standards tailored to sulfur's unique chemical properties. These gaps create uncertainty for manufacturers and may slow commercialization efforts despite the promising performance characteristics of sulfur cathodes.
Harmonization efforts across jurisdictions are gradually addressing regulatory fragmentation, with international bodies working to establish consistent approaches to battery regulation that can accommodate emerging technologies while ensuring safety and environmental protection.
In the United States, regulations are more fragmented, with the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) overseeing waste management aspects under the Resource Conservation and Recovery Act, while the Department of Transportation regulates battery transportation safety. These frameworks increasingly incorporate provisions for emerging battery chemistries, though sulfur-specific regulations remain underdeveloped compared to lithium-ion technologies.
Asian markets, particularly China, Japan, and South Korea, have implemented robust regulatory systems focusing on manufacturing standards and end-of-life management. China's policies on battery recycling and material recovery have become increasingly stringent, creating both challenges and opportunities for sulfur cathode technologies that offer potential environmental advantages.
Safety certification standards represent another critical regulatory dimension, with organizations like UL, IEC, and ISO developing specific protocols for battery testing and certification. The unique properties of sulfur cathodes, including their thermal behavior and potential for polysulfide shuttling, necessitate specialized safety considerations that current standards may not fully address.
Emerging regulatory trends indicate a shift toward more performance-based approaches rather than prescriptive requirements, allowing greater flexibility for innovative technologies like sulfur cathodes. Carbon footprint regulations and extended producer responsibility schemes are increasingly being incorporated into battery regulations, potentially favoring sulfur-based systems due to their abundant and environmentally benign active material.
Regulatory gaps persist in areas specific to sulfur cathode technologies, particularly regarding long-term environmental impact assessment, recycling protocols, and safety standards tailored to sulfur's unique chemical properties. These gaps create uncertainty for manufacturers and may slow commercialization efforts despite the promising performance characteristics of sulfur cathodes.
Harmonization efforts across jurisdictions are gradually addressing regulatory fragmentation, with international bodies working to establish consistent approaches to battery regulation that can accommodate emerging technologies while ensuring safety and environmental protection.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability Considerations
The development of sulfur cathodes for lithium-sulfur batteries represents a significant advancement in energy storage technology, yet their environmental implications require thorough examination. Sulfur cathodes offer a promising alternative to conventional lithium-ion batteries due to their use of abundant, low-cost sulfur—a byproduct of petroleum refining processes. This repurposing of industrial waste contributes to circular economy principles and reduces environmental burden associated with sulfur disposal.
When evaluating the life cycle assessment (LCA) of sulfur cathodes, research indicates a potential reduction in greenhouse gas emissions by 15-20% compared to traditional lithium-ion technologies. This advantage stems from the simplified manufacturing process and reduced energy requirements during production. However, challenges remain regarding the long-term environmental stability of these systems, particularly concerning sulfur leakage and potential groundwater contamination.
Regulatory frameworks worldwide are evolving to address these emerging technologies. The European Union's Battery Directive is currently undergoing revision to incorporate specific provisions for next-generation battery chemistries, including sulfur-based systems. Similarly, the United States Environmental Protection Agency has initiated studies to establish appropriate end-of-life management protocols for these novel energy storage solutions.
Water usage represents another critical sustainability consideration. Conventional lithium extraction processes can consume up to 500,000 gallons of water per ton of lithium produced. In contrast, sulfur cathode production pathways demonstrate approximately 30-40% lower water requirements, offering significant conservation benefits in water-stressed regions where battery manufacturing occurs.
Material recoverability presents both opportunities and challenges. While sulfur itself is highly recoverable and can be reintegrated into new battery systems with minimal processing, other components in lithium-sulfur batteries—particularly specialized electrolytes and separators—may present recycling difficulties. Advanced regulatory frameworks must therefore establish clear guidelines for the responsible recovery of these materials to prevent environmental contamination and resource depletion.
Carbon footprint analyses reveal that transportation impacts of sulfur cathodes benefit from their lighter weight compared to conventional alternatives. This weight reduction translates to fuel savings when implemented in electric vehicles, potentially offsetting the initial manufacturing emissions within the first 30,000-50,000 miles of vehicle operation according to recent industry studies.
When evaluating the life cycle assessment (LCA) of sulfur cathodes, research indicates a potential reduction in greenhouse gas emissions by 15-20% compared to traditional lithium-ion technologies. This advantage stems from the simplified manufacturing process and reduced energy requirements during production. However, challenges remain regarding the long-term environmental stability of these systems, particularly concerning sulfur leakage and potential groundwater contamination.
Regulatory frameworks worldwide are evolving to address these emerging technologies. The European Union's Battery Directive is currently undergoing revision to incorporate specific provisions for next-generation battery chemistries, including sulfur-based systems. Similarly, the United States Environmental Protection Agency has initiated studies to establish appropriate end-of-life management protocols for these novel energy storage solutions.
Water usage represents another critical sustainability consideration. Conventional lithium extraction processes can consume up to 500,000 gallons of water per ton of lithium produced. In contrast, sulfur cathode production pathways demonstrate approximately 30-40% lower water requirements, offering significant conservation benefits in water-stressed regions where battery manufacturing occurs.
Material recoverability presents both opportunities and challenges. While sulfur itself is highly recoverable and can be reintegrated into new battery systems with minimal processing, other components in lithium-sulfur batteries—particularly specialized electrolytes and separators—may present recycling difficulties. Advanced regulatory frameworks must therefore establish clear guidelines for the responsible recovery of these materials to prevent environmental contamination and resource depletion.
Carbon footprint analyses reveal that transportation impacts of sulfur cathodes benefit from their lighter weight compared to conventional alternatives. This weight reduction translates to fuel savings when implemented in electric vehicles, potentially offsetting the initial manufacturing emissions within the first 30,000-50,000 miles of vehicle operation according to recent industry studies.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!