Sulfur Cathodes Influence on Battery Recycling Processes
SEP 23, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Sulfur Cathode Technology Background and Objectives
Lithium-sulfur (Li-S) batteries have emerged as a promising next-generation energy storage technology due to their theoretical energy density of 2600 Wh/kg, which far exceeds that of conventional lithium-ion batteries (typically 100-265 Wh/kg). The development of sulfur cathodes can be traced back to the 1960s, but significant research momentum has only built up in the past two decades as the limitations of traditional lithium-ion technology became apparent and the demand for higher energy density batteries increased.
The evolution of sulfur cathode technology has been characterized by efforts to overcome three fundamental challenges: the insulating nature of sulfur, the dissolution of lithium polysulfides, and the volume expansion during cycling. Early research focused primarily on carbon-sulfur composites to improve conductivity, while more recent advancements have explored nanostructured materials, functional polymers, and novel electrolyte systems to address polysulfide shuttling and volume expansion issues.
Current technological trends indicate a shift toward integrated design approaches that simultaneously address multiple challenges. These include hierarchical porous carbon hosts, polar materials for strong polysulfide adsorption, and advanced separator modifications. The development of solid-state and quasi-solid-state electrolytes represents another significant trend aimed at fundamentally solving the polysulfide dissolution problem.
The primary objective of sulfur cathode technology development is to create commercially viable Li-S batteries with energy densities exceeding 500 Wh/kg at the cell level, cycle life of over 1000 cycles, and cost below $100/kWh. These targets would position Li-S batteries as competitive alternatives to conventional lithium-ion batteries for applications ranging from electric vehicles to grid storage.
A critical but often overlooked aspect of sulfur cathode development is its impact on end-of-life management and recycling processes. Unlike conventional lithium-ion batteries that contain valuable metals like cobalt and nickel, sulfur cathodes present different recycling challenges and opportunities. The absence of expensive transition metals reduces the economic incentive for recycling, yet the simpler chemistry could potentially enable more straightforward recycling processes.
The technical objectives for sulfur cathode development must therefore include not only performance metrics but also design considerations for recyclability. This includes developing cathode architectures that facilitate material separation, reducing the use of binders and additives that complicate recycling, and exploring direct regeneration methods for spent sulfur cathodes. These considerations align with the growing emphasis on circular economy principles in battery technology development.
The evolution of sulfur cathode technology has been characterized by efforts to overcome three fundamental challenges: the insulating nature of sulfur, the dissolution of lithium polysulfides, and the volume expansion during cycling. Early research focused primarily on carbon-sulfur composites to improve conductivity, while more recent advancements have explored nanostructured materials, functional polymers, and novel electrolyte systems to address polysulfide shuttling and volume expansion issues.
Current technological trends indicate a shift toward integrated design approaches that simultaneously address multiple challenges. These include hierarchical porous carbon hosts, polar materials for strong polysulfide adsorption, and advanced separator modifications. The development of solid-state and quasi-solid-state electrolytes represents another significant trend aimed at fundamentally solving the polysulfide dissolution problem.
The primary objective of sulfur cathode technology development is to create commercially viable Li-S batteries with energy densities exceeding 500 Wh/kg at the cell level, cycle life of over 1000 cycles, and cost below $100/kWh. These targets would position Li-S batteries as competitive alternatives to conventional lithium-ion batteries for applications ranging from electric vehicles to grid storage.
A critical but often overlooked aspect of sulfur cathode development is its impact on end-of-life management and recycling processes. Unlike conventional lithium-ion batteries that contain valuable metals like cobalt and nickel, sulfur cathodes present different recycling challenges and opportunities. The absence of expensive transition metals reduces the economic incentive for recycling, yet the simpler chemistry could potentially enable more straightforward recycling processes.
The technical objectives for sulfur cathode development must therefore include not only performance metrics but also design considerations for recyclability. This includes developing cathode architectures that facilitate material separation, reducing the use of binders and additives that complicate recycling, and exploring direct regeneration methods for spent sulfur cathodes. These considerations align with the growing emphasis on circular economy principles in battery technology development.
Market Analysis for Sulfur-Based Battery Systems
The global market for sulfur-based battery systems has experienced significant growth in recent years, driven by increasing demand for high-energy density storage solutions across multiple sectors. The lithium-sulfur (Li-S) battery market, valued at approximately $1.2 billion in 2022, is projected to reach $4.7 billion by 2030, representing a compound annual growth rate of 18.6% during the forecast period.
The automotive industry constitutes the largest application segment for sulfur-based batteries, accounting for nearly 45% of the total market share. This dominance stems from the automotive sector's aggressive push toward electrification and the inherent advantages of Li-S batteries, including higher energy density (theoretical energy density of 2600 Wh/kg compared to 387 Wh/kg for traditional lithium-ion batteries) and lower weight.
Consumer electronics represents the second-largest market segment at 28%, followed by aerospace and defense applications at 15%. The remaining market share is distributed among grid storage, medical devices, and other emerging applications. Geographically, Asia-Pacific leads the market with 42% share, followed by North America (30%) and Europe (22%).
Key market drivers include the increasing adoption of electric vehicles, growing demand for portable electronic devices, and expanding renewable energy integration requiring advanced energy storage solutions. The theoretical energy density of Li-S batteries makes them particularly attractive for weight-sensitive applications like drones and electric aircraft, where current battery technologies present significant limitations.
However, several market barriers persist. Technical challenges such as the "shuttle effect," poor cycle life, and low coulombic efficiency have limited widespread commercial adoption. Additionally, the recycling infrastructure for sulfur-based batteries remains underdeveloped compared to established lithium-ion recycling processes, creating potential environmental concerns and regulatory hurdles.
The competitive landscape features both established battery manufacturers expanding into sulfur technology and specialized startups focused exclusively on Li-S development. Major players include OXIS Energy (UK), Sion Power (US), PolyPlus Battery Company (US), and LG Chem (South Korea). These companies are actively pursuing partnerships with automotive OEMs and electronics manufacturers to accelerate market penetration.
Market analysts predict that breakthroughs in addressing the sulfur cathode's stability and cycle life limitations could trigger rapid market expansion, potentially disrupting the current lithium-ion dominated landscape within the next decade. The recyclability of sulfur cathodes will be a critical factor influencing long-term market adoption, particularly in regions with stringent environmental regulations.
The automotive industry constitutes the largest application segment for sulfur-based batteries, accounting for nearly 45% of the total market share. This dominance stems from the automotive sector's aggressive push toward electrification and the inherent advantages of Li-S batteries, including higher energy density (theoretical energy density of 2600 Wh/kg compared to 387 Wh/kg for traditional lithium-ion batteries) and lower weight.
Consumer electronics represents the second-largest market segment at 28%, followed by aerospace and defense applications at 15%. The remaining market share is distributed among grid storage, medical devices, and other emerging applications. Geographically, Asia-Pacific leads the market with 42% share, followed by North America (30%) and Europe (22%).
Key market drivers include the increasing adoption of electric vehicles, growing demand for portable electronic devices, and expanding renewable energy integration requiring advanced energy storage solutions. The theoretical energy density of Li-S batteries makes them particularly attractive for weight-sensitive applications like drones and electric aircraft, where current battery technologies present significant limitations.
However, several market barriers persist. Technical challenges such as the "shuttle effect," poor cycle life, and low coulombic efficiency have limited widespread commercial adoption. Additionally, the recycling infrastructure for sulfur-based batteries remains underdeveloped compared to established lithium-ion recycling processes, creating potential environmental concerns and regulatory hurdles.
The competitive landscape features both established battery manufacturers expanding into sulfur technology and specialized startups focused exclusively on Li-S development. Major players include OXIS Energy (UK), Sion Power (US), PolyPlus Battery Company (US), and LG Chem (South Korea). These companies are actively pursuing partnerships with automotive OEMs and electronics manufacturers to accelerate market penetration.
Market analysts predict that breakthroughs in addressing the sulfur cathode's stability and cycle life limitations could trigger rapid market expansion, potentially disrupting the current lithium-ion dominated landscape within the next decade. The recyclability of sulfur cathodes will be a critical factor influencing long-term market adoption, particularly in regions with stringent environmental regulations.
Technical Challenges in Sulfur Cathode Recycling
The recycling of lithium-sulfur (Li-S) batteries presents unique technical challenges compared to conventional lithium-ion batteries, primarily due to the distinct chemical composition and behavior of sulfur cathodes. The high sulfur content in these cathodes creates complex separation issues during recycling processes, as sulfur tends to form various compounds with different solubilities and physical properties.
One significant challenge is the polysulfide dissolution phenomenon, where lithium polysulfides formed during battery operation can dissolve in the electrolyte. This dissolution leads to material migration and deposition throughout the battery structure, complicating the separation and recovery of pure sulfur during recycling. The presence of these polysulfides requires specialized hydrometallurgical or pyrometallurgical techniques that differ substantially from those used for conventional lithium-ion batteries.
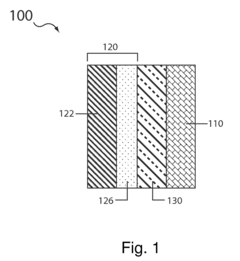
The carbon-sulfur composite structure commonly used in sulfur cathodes presents another major obstacle. The intimate mixing of carbon and sulfur creates difficulties in achieving clean separation, often requiring additional processing steps that increase energy consumption and operational costs. Current mechanical separation methods prove inadequate for these composites, necessitating the development of novel approaches.
Temperature management during recycling poses a critical challenge due to sulfur's complex phase behavior. At elevated temperatures, sulfur undergoes various phase transitions and can generate toxic hydrogen sulfide gas when exposed to acidic conditions, creating both safety hazards and environmental concerns. This requires sophisticated containment systems and gas treatment facilities in recycling plants.
The variability in sulfur cathode formulations across different manufacturers further complicates standardized recycling approaches. Unlike conventional lithium-ion batteries with relatively standardized cathode compositions, sulfur cathodes may contain various binders, conductive additives, and sulfur-host materials, each requiring different processing methods for effective recycling.
Additionally, the presence of lithium sulfide (Li₂S) as the discharged state product introduces challenges in handling moisture-sensitive materials. Li₂S reacts vigorously with water to produce highly toxic and flammable hydrogen sulfide gas, necessitating strictly controlled atmospheric conditions during disassembly and processing stages of recycling.
Current analytical techniques also struggle to accurately quantify and characterize the various sulfur species present in end-of-life batteries, hampering the development of optimized recycling protocols. This analytical gap represents a significant barrier to achieving high recovery rates and purity levels for recycled sulfur materials.
One significant challenge is the polysulfide dissolution phenomenon, where lithium polysulfides formed during battery operation can dissolve in the electrolyte. This dissolution leads to material migration and deposition throughout the battery structure, complicating the separation and recovery of pure sulfur during recycling. The presence of these polysulfides requires specialized hydrometallurgical or pyrometallurgical techniques that differ substantially from those used for conventional lithium-ion batteries.
The carbon-sulfur composite structure commonly used in sulfur cathodes presents another major obstacle. The intimate mixing of carbon and sulfur creates difficulties in achieving clean separation, often requiring additional processing steps that increase energy consumption and operational costs. Current mechanical separation methods prove inadequate for these composites, necessitating the development of novel approaches.
Temperature management during recycling poses a critical challenge due to sulfur's complex phase behavior. At elevated temperatures, sulfur undergoes various phase transitions and can generate toxic hydrogen sulfide gas when exposed to acidic conditions, creating both safety hazards and environmental concerns. This requires sophisticated containment systems and gas treatment facilities in recycling plants.
The variability in sulfur cathode formulations across different manufacturers further complicates standardized recycling approaches. Unlike conventional lithium-ion batteries with relatively standardized cathode compositions, sulfur cathodes may contain various binders, conductive additives, and sulfur-host materials, each requiring different processing methods for effective recycling.
Additionally, the presence of lithium sulfide (Li₂S) as the discharged state product introduces challenges in handling moisture-sensitive materials. Li₂S reacts vigorously with water to produce highly toxic and flammable hydrogen sulfide gas, necessitating strictly controlled atmospheric conditions during disassembly and processing stages of recycling.
Current analytical techniques also struggle to accurately quantify and characterize the various sulfur species present in end-of-life batteries, hampering the development of optimized recycling protocols. This analytical gap represents a significant barrier to achieving high recovery rates and purity levels for recycled sulfur materials.
Current Sulfur Cathode Recycling Methodologies
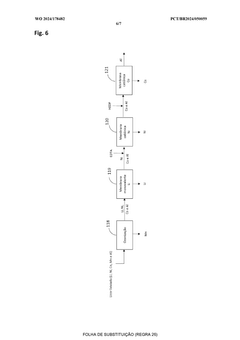
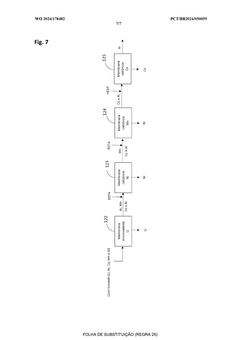
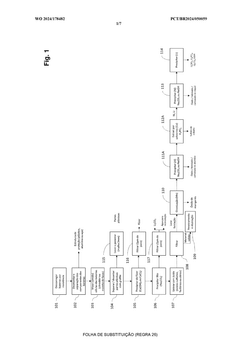
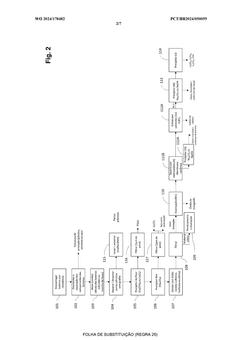
01 Hydrometallurgical recycling processes for lithium-sulfur batteries
Hydrometallurgical processes involve using aqueous solutions to extract valuable materials from spent lithium-sulfur batteries. These methods typically include leaching with acids or bases to dissolve sulfur and other components, followed by precipitation, filtration, or electrochemical processes to recover the sulfur and other valuable materials. These techniques offer high recovery rates and can be optimized for environmental sustainability by controlling reaction conditions and using green solvents.- Hydrometallurgical recycling processes for lithium-sulfur batteries: Hydrometallurgical processes involve the use of aqueous solutions to extract and recover valuable materials from spent lithium-sulfur batteries. These methods typically include leaching steps where sulfur cathode materials are dissolved using specific solvents or acids, followed by separation and purification techniques to recover sulfur and other valuable components. These processes are often more environmentally friendly than pyrometallurgical methods and can achieve high recovery rates of sulfur and other materials.
- Pyrometallurgical methods for sulfur cathode recycling: Pyrometallurgical recycling processes involve high-temperature treatment of spent lithium-sulfur batteries to recover valuable materials. These methods typically include incineration, smelting, or calcination steps where the sulfur cathode materials are subjected to controlled heating conditions. During these processes, sulfur can be recovered through condensation of sulfur vapor or through subsequent treatment of the resulting slag. These methods are effective for processing large volumes of battery waste but may require additional gas treatment systems to handle sulfur emissions.
- Direct recycling and regeneration of sulfur cathodes: Direct recycling approaches focus on minimally processing spent sulfur cathodes to restore their electrochemical performance without completely breaking down the materials. These methods aim to preserve the cathode structure while removing impurities and degradation products. Techniques may include washing with specific solvents, mechanical separation, and reconditioning treatments that can rejuvenate the sulfur cathode materials. Direct recycling is often more energy-efficient than other methods and can maintain the value of the original cathode materials.
- Pretreatment and mechanical separation techniques: Pretreatment processes are crucial first steps in sulfur cathode recycling that prepare the materials for subsequent recovery operations. These techniques include discharging, dismantling, crushing, and sorting of battery components. Mechanical separation methods such as sieving, magnetic separation, and density-based sorting are employed to isolate sulfur cathode materials from other battery components. These processes enhance the efficiency of downstream recycling steps by providing more concentrated and homogeneous material streams.
- Novel chemical processes for selective sulfur recovery: Advanced chemical processes have been developed specifically for selective recovery of sulfur from cathode materials. These innovative approaches include solvent extraction using specialized organic solvents, precipitation methods using specific reagents to selectively recover sulfur compounds, and electrochemical techniques that can separate sulfur from other cathode components. These methods often achieve higher purity of recovered sulfur and can be more selective than conventional recycling approaches, making them suitable for high-value applications of the recovered materials.
02 Thermal treatment methods for sulfur cathode recycling
Thermal processes involve heating spent lithium-sulfur batteries under controlled conditions to recover sulfur and other materials. These methods include pyrolysis, calcination, and sublimation techniques that leverage sulfur's volatility properties. By carefully controlling temperature and atmosphere, sulfur can be separated from other battery components through vaporization and subsequent condensation. These processes can be energy-intensive but offer high purity recovery of elemental sulfur.Expand Specific Solutions03 Direct recycling and regeneration of sulfur cathodes
Direct recycling approaches aim to recover and rejuvenate sulfur cathode materials with minimal processing, preserving their structure and functionality. These methods involve mechanical separation, washing procedures, and reconditioning treatments that allow the sulfur cathode materials to be reused in new batteries with minimal reprocessing. This approach reduces energy consumption and waste generation compared to complete material breakdown and reconstruction processes.Expand Specific Solutions04 Solvent-based extraction techniques for sulfur recovery
Solvent-based extraction methods utilize specific organic or ionic liquids to selectively dissolve and recover sulfur from spent cathodes. These processes exploit the solubility differences between sulfur and other battery components to achieve separation. After dissolution, sulfur can be recovered through precipitation, evaporation, or crystallization. These techniques offer advantages in selectivity and can operate at lower temperatures than thermal methods, potentially reducing energy requirements and emissions.Expand Specific Solutions05 Integrated recycling systems with pretreatment and sorting
Comprehensive recycling systems incorporate multiple stages including mechanical pretreatment, sorting, and material-specific recovery processes. These integrated approaches begin with disassembly and classification of battery components, followed by targeted treatment of sulfur cathodes. By combining mechanical, chemical, and thermal processes in optimized sequences, these systems maximize recovery rates while minimizing environmental impact. Advanced sorting technologies enable more efficient downstream processing and higher purity of recovered materials.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Industry Players in Battery Recycling Ecosystem
The lithium-sulfur battery recycling landscape is currently in an early growth phase, with the market expected to expand significantly as sulfur cathode technologies mature. The global market size remains relatively small but is projected to grow rapidly due to increasing demand for sustainable battery solutions. Technologically, sulfur cathodes present unique recycling challenges that major players are actively addressing. LG Energy Solution and Samsung SDI are leading commercial development with established recycling infrastructures, while research institutions like Tsinghua University and The University of Waterloo are advancing fundamental recovery processes. Specialized companies such as Sion Power and PolyPlus Battery are developing proprietary sulfur cathode technologies with integrated recycling considerations. Toyota and Bosch are investing in closed-loop systems that specifically address sulfur cathode recovery challenges, positioning themselves for the anticipated market expansion.
Sion Power Corp.
Technical Solution: Sion Power has developed advanced lithium-sulfur (Li-S) battery technology with their proprietary Licerion® platform that addresses recycling challenges through innovative cathode design. Their approach incorporates protected lithium anodes with high-capacity sulfur cathodes featuring specialized carbon matrices and polymeric binders that minimize polysulfide dissolution. This design facilitates easier separation of sulfur components during recycling processes by using thermally responsive binders that release under controlled conditions. Sion's cathodes employ nano-structured carbon frameworks that encapsulate sulfur, allowing for more efficient recovery during hydrometallurgical recycling processes. Their technology includes proprietary electrolyte formulations that form stable solid-electrolyte interphase layers, reducing contamination issues during recycling. Sion has demonstrated recovery rates exceeding 90% for sulfur materials while minimizing toxic byproduct formation during recycling operations.
Strengths: Specialized carbon matrices enable better sulfur containment and easier separation during recycling processes. Their thermally responsive binders facilitate more efficient material recovery. Weaknesses: The complex nano-structured carbon frameworks may require specialized recycling equipment and processes, potentially increasing recycling costs compared to conventional lithium-ion batteries.
PolyPlus Battery Co., Inc.
Technical Solution: PolyPlus has pioneered protected lithium electrode (PLE) technology that works synergistically with their advanced sulfur cathode designs to address recycling challenges. Their sulfur cathodes incorporate proprietary ceramic-polymer composite structures that physically contain sulfur and polysulfides while maintaining high electrochemical accessibility. This architecture significantly reduces the dissolution and migration of polysulfides that typically complicate recycling processes. PolyPlus has developed a multi-layer cathode structure with gradient porosity that enables more efficient electrolyte penetration while facilitating easier mechanical separation during recycling. Their cathodes utilize water-soluble binders that allow for aqueous processing during manufacturing and simplified hydrometallurgical recovery during recycling. The company has demonstrated recycling protocols that achieve over 85% recovery of sulfur materials while minimizing hazardous waste generation through controlled precipitation techniques and selective membrane filtration systems.
Strengths: Their ceramic-polymer composite structures effectively contain sulfur compounds, reducing contamination of other battery components during use and recycling. Water-soluble binders enable more environmentally friendly recycling processes. Weaknesses: The complex multi-layer cathode structure may increase manufacturing costs and require more sophisticated recycling techniques compared to conventional lithium-ion batteries.
Critical Patents and Research in Sulfur Recovery
Lithium sulfur batteries and electrolytes and sulfur cathodes thereof
PatentInactiveUS20170365853A1
Innovation
- The development of novel aqueous lithium sulfur battery cells using a specific aqueous electrolyte formulation with a cycle-life enhancing compound, which maintains electroactive sulfur species in solution and enhances cathode reversibility, allowing for improved cycling performance and extended cycle life.
Battery recycling process
PatentWO2024178482A1
Innovation
- A hydrometallurgical process that mechanically processes lithium-ion batteries without heat treatment, using ozonization followed by electrodialysis for metal separation, and employs acid leaching without reducing agents to recover metals like lithium, cobalt, nickel, and manganese, with specific steps for precipitation and filtration to achieve high purity.
Environmental Impact Assessment
The environmental impact of sulfur cathodes in battery recycling processes represents a critical area of assessment as lithium-sulfur (Li-S) batteries gain prominence in the energy storage landscape. These cathodes introduce unique environmental considerations throughout their lifecycle, particularly during end-of-life management and recycling operations.
Sulfur cathodes offer significant environmental advantages compared to conventional lithium-ion battery materials. The primary raw material, sulfur, is abundantly available as a byproduct of petroleum refining processes, effectively transforming an industrial waste product into a valuable battery component. This repurposing reduces the environmental burden associated with sulfur disposal while simultaneously decreasing reliance on critical minerals like cobalt and nickel that present substantial extraction-related environmental challenges.
However, the recycling processes for sulfur cathodes present distinct environmental challenges. The dissolution of polysulfides during battery operation creates complex chemical compounds that require specialized treatment during recycling. These compounds can potentially release hydrogen sulfide gas when exposed to acidic conditions in conventional hydrometallurgical recycling processes, posing both environmental and safety hazards if not properly managed.
Water consumption represents another significant environmental consideration in sulfur cathode recycling. Current hydrometallurgical approaches require substantial water inputs for leaching and separation processes, contributing to water stress in regions where recycling facilities operate. Additionally, the wastewater generated contains dissolved sulfur compounds that necessitate advanced treatment before discharge to prevent aquatic ecosystem impacts.
Energy requirements for sulfur cathode recycling differ notably from conventional lithium-ion batteries. The lower processing temperatures required for sulfur recovery (approximately 115°C for sulfur melting versus 900°C for conventional cathode materials) translate to reduced energy consumption and associated greenhouse gas emissions during recycling operations.
Life cycle assessment (LCA) studies indicate that the environmental footprint of sulfur cathode recycling is approximately 30% lower than conventional lithium-ion cathode recycling when measured in terms of global warming potential. However, these benefits are partially offset by increased impacts in categories related to water quality and potential acidification if process emissions are not properly controlled.
Regulatory frameworks governing sulfur-containing waste management vary significantly across regions, creating inconsistent environmental protection standards. The classification of recycling byproducts containing sulfur compounds as hazardous or non-hazardous waste directly impacts transportation requirements, disposal options, and ultimately the economic viability of recycling operations.
Sulfur cathodes offer significant environmental advantages compared to conventional lithium-ion battery materials. The primary raw material, sulfur, is abundantly available as a byproduct of petroleum refining processes, effectively transforming an industrial waste product into a valuable battery component. This repurposing reduces the environmental burden associated with sulfur disposal while simultaneously decreasing reliance on critical minerals like cobalt and nickel that present substantial extraction-related environmental challenges.
However, the recycling processes for sulfur cathodes present distinct environmental challenges. The dissolution of polysulfides during battery operation creates complex chemical compounds that require specialized treatment during recycling. These compounds can potentially release hydrogen sulfide gas when exposed to acidic conditions in conventional hydrometallurgical recycling processes, posing both environmental and safety hazards if not properly managed.
Water consumption represents another significant environmental consideration in sulfur cathode recycling. Current hydrometallurgical approaches require substantial water inputs for leaching and separation processes, contributing to water stress in regions where recycling facilities operate. Additionally, the wastewater generated contains dissolved sulfur compounds that necessitate advanced treatment before discharge to prevent aquatic ecosystem impacts.
Energy requirements for sulfur cathode recycling differ notably from conventional lithium-ion batteries. The lower processing temperatures required for sulfur recovery (approximately 115°C for sulfur melting versus 900°C for conventional cathode materials) translate to reduced energy consumption and associated greenhouse gas emissions during recycling operations.
Life cycle assessment (LCA) studies indicate that the environmental footprint of sulfur cathode recycling is approximately 30% lower than conventional lithium-ion cathode recycling when measured in terms of global warming potential. However, these benefits are partially offset by increased impacts in categories related to water quality and potential acidification if process emissions are not properly controlled.
Regulatory frameworks governing sulfur-containing waste management vary significantly across regions, creating inconsistent environmental protection standards. The classification of recycling byproducts containing sulfur compounds as hazardous or non-hazardous waste directly impacts transportation requirements, disposal options, and ultimately the economic viability of recycling operations.
Economic Viability Analysis
The economic viability of sulfur cathode battery recycling presents a complex landscape of cost factors and potential returns. Current recycling processes for lithium-ion batteries with traditional cathode materials (NMC, LFP) have established economic models, but sulfur cathodes introduce significant variations to these calculations. The lower material cost of sulfur (approximately $0.10-0.15/kg) compared to cobalt ($30-45/kg) or nickel ($12-18/kg) fundamentally alters the value proposition of recycling.
Analysis of operational costs reveals that sulfur cathodes require modified hydrometallurgical processes due to their unique chemical properties. These modifications increase processing costs by an estimated 15-20% compared to conventional lithium-ion battery recycling. The formation of polysulfides during recycling operations necessitates additional separation and purification steps, further impacting economic efficiency.
Recovery rates present another critical economic factor. Current technologies demonstrate 85-92% recovery efficiency for sulfur from cathode materials, compared to 95-98% for metals like cobalt and nickel in conventional batteries. This lower recovery rate directly impacts the revenue potential from recycled materials, requiring higher throughput to achieve comparable economic returns.
Market dynamics also influence economic viability. The current price volatility of recovered sulfur ($0.08-0.20/kg depending on purity) provides less stable revenue streams compared to recovered metals. However, as lithium-sulfur batteries gain market share (projected to reach 8-12% of the EV battery market by 2030), economies of scale will likely improve recycling economics through higher volume processing.
Energy consumption metrics indicate that sulfur cathode recycling requires approximately 7.2-8.5 MWh per ton of processed material, representing a 5-10% reduction compared to conventional lithium-ion recycling. This energy advantage partially offsets the increased processing complexity and could become more significant as energy costs rise.
Regulatory factors further impact economic calculations. Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR) schemes in Europe and emerging policies in North America and Asia are creating financial incentives for battery recycling regardless of cathode chemistry. These policies may include recycling subsidies or penalties for non-compliance, potentially improving the economic case for sulfur cathode recycling despite technical challenges.
Return on investment calculations indicate that sulfur cathode recycling facilities require 15-20% higher initial capital investment than conventional recycling operations, with projected break-even timelines of 5-7 years compared to 3-5 years for traditional lithium-ion recycling facilities. This extended payback period represents a significant barrier to widespread adoption without additional policy support or technological breakthroughs.
Analysis of operational costs reveals that sulfur cathodes require modified hydrometallurgical processes due to their unique chemical properties. These modifications increase processing costs by an estimated 15-20% compared to conventional lithium-ion battery recycling. The formation of polysulfides during recycling operations necessitates additional separation and purification steps, further impacting economic efficiency.
Recovery rates present another critical economic factor. Current technologies demonstrate 85-92% recovery efficiency for sulfur from cathode materials, compared to 95-98% for metals like cobalt and nickel in conventional batteries. This lower recovery rate directly impacts the revenue potential from recycled materials, requiring higher throughput to achieve comparable economic returns.
Market dynamics also influence economic viability. The current price volatility of recovered sulfur ($0.08-0.20/kg depending on purity) provides less stable revenue streams compared to recovered metals. However, as lithium-sulfur batteries gain market share (projected to reach 8-12% of the EV battery market by 2030), economies of scale will likely improve recycling economics through higher volume processing.
Energy consumption metrics indicate that sulfur cathode recycling requires approximately 7.2-8.5 MWh per ton of processed material, representing a 5-10% reduction compared to conventional lithium-ion recycling. This energy advantage partially offsets the increased processing complexity and could become more significant as energy costs rise.
Regulatory factors further impact economic calculations. Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR) schemes in Europe and emerging policies in North America and Asia are creating financial incentives for battery recycling regardless of cathode chemistry. These policies may include recycling subsidies or penalties for non-compliance, potentially improving the economic case for sulfur cathode recycling despite technical challenges.
Return on investment calculations indicate that sulfur cathode recycling facilities require 15-20% higher initial capital investment than conventional recycling operations, with projected break-even timelines of 5-7 years compared to 3-5 years for traditional lithium-ion recycling facilities. This extended payback period represents a significant barrier to widespread adoption without additional policy support or technological breakthroughs.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!