Patents on Sulfur Cathodes Technologies for Future Markets
SEP 23, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Sulfur Cathode Technology Background and Objectives
Sulfur cathodes represent a transformative technology in the energy storage landscape, particularly for next-generation lithium-sulfur (Li-S) batteries. The evolution of this technology can be traced back to the 1960s when the theoretical framework for Li-S batteries was first established. However, significant research momentum only gained traction in the early 2000s as limitations of conventional lithium-ion batteries became increasingly apparent and the demand for higher energy density solutions grew exponentially.
The fundamental appeal of sulfur as a cathode material lies in its impressive theoretical specific capacity of 1,675 mAh/g and energy density of approximately 2,600 Wh/kg, which substantially exceeds the capabilities of traditional lithium-ion batteries. Additionally, sulfur offers compelling advantages including natural abundance, environmental benignity, and low cost—approximately 1/150th the cost of conventional cathode materials.
Current technological objectives in sulfur cathode development focus on overcoming several critical challenges that have hindered commercial viability. Primary among these is addressing the "shuttle effect," where polysulfide intermediates dissolve in the electrolyte and migrate between electrodes, causing capacity fading and shortened battery life. Researchers aim to achieve cycle stability exceeding 1,000 cycles with minimal capacity degradation.
Another key objective involves improving the poor electrical conductivity of sulfur (5×10^-30 S/cm), which necessitates conductive additives and specialized structural designs. The significant volume expansion (approximately 80%) during lithiation presents additional engineering challenges requiring innovative electrode architectures.
The technology trajectory indicates a clear evolution from basic sulfur-carbon composites toward more sophisticated nanostructured materials and functional interfaces. Recent patent activities reveal increasing focus on electrolyte engineering, protective coatings, and advanced binding materials to enhance performance metrics.
From a strategic perspective, sulfur cathode technology aims to enable electric vehicles with driving ranges exceeding 500 miles per charge while simultaneously reducing battery costs below $100/kWh. For grid storage applications, the technology targets enhanced safety profiles and extended operational lifetimes of 15+ years.
The convergence of environmental regulations, raw material constraints for conventional batteries, and escalating energy density demands across multiple sectors has positioned sulfur cathode technology as a critical research priority. Patent activities in this domain have grown at a compound annual rate of approximately 27% over the past decade, signaling intensifying commercial interest and technological maturation.
The fundamental appeal of sulfur as a cathode material lies in its impressive theoretical specific capacity of 1,675 mAh/g and energy density of approximately 2,600 Wh/kg, which substantially exceeds the capabilities of traditional lithium-ion batteries. Additionally, sulfur offers compelling advantages including natural abundance, environmental benignity, and low cost—approximately 1/150th the cost of conventional cathode materials.
Current technological objectives in sulfur cathode development focus on overcoming several critical challenges that have hindered commercial viability. Primary among these is addressing the "shuttle effect," where polysulfide intermediates dissolve in the electrolyte and migrate between electrodes, causing capacity fading and shortened battery life. Researchers aim to achieve cycle stability exceeding 1,000 cycles with minimal capacity degradation.
Another key objective involves improving the poor electrical conductivity of sulfur (5×10^-30 S/cm), which necessitates conductive additives and specialized structural designs. The significant volume expansion (approximately 80%) during lithiation presents additional engineering challenges requiring innovative electrode architectures.
The technology trajectory indicates a clear evolution from basic sulfur-carbon composites toward more sophisticated nanostructured materials and functional interfaces. Recent patent activities reveal increasing focus on electrolyte engineering, protective coatings, and advanced binding materials to enhance performance metrics.
From a strategic perspective, sulfur cathode technology aims to enable electric vehicles with driving ranges exceeding 500 miles per charge while simultaneously reducing battery costs below $100/kWh. For grid storage applications, the technology targets enhanced safety profiles and extended operational lifetimes of 15+ years.
The convergence of environmental regulations, raw material constraints for conventional batteries, and escalating energy density demands across multiple sectors has positioned sulfur cathode technology as a critical research priority. Patent activities in this domain have grown at a compound annual rate of approximately 27% over the past decade, signaling intensifying commercial interest and technological maturation.
Market Demand Analysis for Sulfur Cathode Batteries
The global market for lithium-sulfur batteries is experiencing significant growth, driven by increasing demand for high-energy density storage solutions across multiple sectors. Current market projections indicate that the lithium-sulfur battery market could reach substantial valuation by 2030, with a compound annual growth rate exceeding traditional lithium-ion technologies. This accelerated growth trajectory is primarily fueled by the theoretical energy density advantages of sulfur cathodes, which can deliver up to 2,600 Wh/kg compared to conventional lithium-ion batteries' 260 Wh/kg.
The electric vehicle sector represents the most promising market for sulfur cathode technologies, with automotive manufacturers actively seeking battery solutions that extend range while reducing weight and cost. Market research suggests that by 2025, electric vehicles could account for over 30% of new vehicle sales in major markets, creating substantial demand for advanced battery technologies. The potential cost reduction offered by sulfur-based cathodes—utilizing abundant and inexpensive sulfur rather than costly cobalt or nickel—positions these batteries as particularly attractive for mass-market electric vehicles.
Aerospace and defense sectors are emerging as high-value early adopters for sulfur cathode technologies. The lightweight characteristics and high energy density make these batteries ideal for drone applications, satellite systems, and other weight-sensitive aerospace equipment. Market analysis indicates that these premium sectors are willing to adopt advanced battery technologies at higher price points during early commercialization phases, potentially providing crucial revenue streams for technology developers.
Consumer electronics manufacturers are also expressing interest in sulfur cathode technologies, particularly for applications requiring extended battery life in compact form factors. The wearable technology segment, projected to grow at over 15% annually through 2028, represents a significant opportunity for sulfur cathode implementation once cycle life challenges are adequately addressed.
Grid-scale energy storage represents another substantial market opportunity, with global deployment expected to increase dramatically as renewable energy integration accelerates. The low material cost of sulfur makes these batteries particularly attractive for large-scale stationary applications where cost per kilowatt-hour is a critical factor. Market forecasts suggest that energy storage deployment will triple by 2025, creating significant demand for cost-effective solutions.
Despite these promising market indicators, customer requirements vary significantly across sectors. Electric vehicle manufacturers prioritize cycle life and safety alongside energy density, while aerospace applications emphasize weight reduction and performance under extreme conditions. Understanding these sector-specific requirements is essential for effectively targeting commercial development of sulfur cathode technologies.
The electric vehicle sector represents the most promising market for sulfur cathode technologies, with automotive manufacturers actively seeking battery solutions that extend range while reducing weight and cost. Market research suggests that by 2025, electric vehicles could account for over 30% of new vehicle sales in major markets, creating substantial demand for advanced battery technologies. The potential cost reduction offered by sulfur-based cathodes—utilizing abundant and inexpensive sulfur rather than costly cobalt or nickel—positions these batteries as particularly attractive for mass-market electric vehicles.
Aerospace and defense sectors are emerging as high-value early adopters for sulfur cathode technologies. The lightweight characteristics and high energy density make these batteries ideal for drone applications, satellite systems, and other weight-sensitive aerospace equipment. Market analysis indicates that these premium sectors are willing to adopt advanced battery technologies at higher price points during early commercialization phases, potentially providing crucial revenue streams for technology developers.
Consumer electronics manufacturers are also expressing interest in sulfur cathode technologies, particularly for applications requiring extended battery life in compact form factors. The wearable technology segment, projected to grow at over 15% annually through 2028, represents a significant opportunity for sulfur cathode implementation once cycle life challenges are adequately addressed.
Grid-scale energy storage represents another substantial market opportunity, with global deployment expected to increase dramatically as renewable energy integration accelerates. The low material cost of sulfur makes these batteries particularly attractive for large-scale stationary applications where cost per kilowatt-hour is a critical factor. Market forecasts suggest that energy storage deployment will triple by 2025, creating significant demand for cost-effective solutions.
Despite these promising market indicators, customer requirements vary significantly across sectors. Electric vehicle manufacturers prioritize cycle life and safety alongside energy density, while aerospace applications emphasize weight reduction and performance under extreme conditions. Understanding these sector-specific requirements is essential for effectively targeting commercial development of sulfur cathode technologies.
Current State and Challenges in Sulfur Cathode Development
Sulfur cathodes represent one of the most promising technologies for next-generation lithium-sulfur (Li-S) batteries, offering theoretical energy densities up to 2600 Wh/kg, significantly higher than conventional lithium-ion batteries. Currently, global research efforts are intensifying, with notable advancements emerging from research institutions in China, the United States, and Europe. Patent activity has increased by approximately 300% over the past decade, indicating growing commercial interest in this technology.
Despite these promising developments, sulfur cathodes face several critical challenges that have prevented their widespread commercialization. The most significant obstacle is the "polysulfide shuttle effect," where soluble lithium polysulfides dissolve in the electrolyte during cycling, causing active material loss, reduced coulombic efficiency, and rapid capacity fading. Recent patents from Samsung and BASF have proposed novel electrolyte additives to mitigate this issue, but complete resolution remains elusive.
Another major challenge is sulfur's inherently poor electrical conductivity (5×10^-30 S/cm), necessitating conductive additives that reduce the overall energy density. The volume expansion of sulfur during lithiation (approximately 80%) creates mechanical stress that degrades electrode integrity over multiple cycles. Patents from Tesla and Contemporary Amperex Technology Co. Limited (CATL) have focused on flexible electrode architectures to accommodate this expansion, though long-term stability remains problematic.
The low sulfur utilization rate in practical applications (typically 60-70% of theoretical capacity) represents another significant limitation. This gap between theoretical and practical performance has prompted research into nanostructured carbon hosts and catalytic materials, with notable patents from LG Chem and Panasonic exploring hierarchical porous carbon frameworks.
Manufacturing scalability presents additional hurdles, as many laboratory-scale solutions involve complex synthesis procedures incompatible with mass production. Recent patent applications from Toyota and SK Innovation address manufacturing processes for sulfur cathodes, suggesting progress toward industrialization, though cost-effective large-scale production remains challenging.
Environmental considerations are increasingly important, with sulfur's abundance and low toxicity representing advantages. However, the long-term environmental impact of electrolyte additives and specialized carbon materials requires further assessment. Patents from Sion Power and Oxis Energy have begun addressing end-of-life recycling processes for Li-S batteries, though comprehensive lifecycle analyses are still developing.
The technical readiness level (TRL) of sulfur cathode technology currently stands at approximately 5-6, indicating validation in relevant environments but requiring further development before full commercial deployment. Recent demonstration projects by Airbus and Covestro suggest potential early applications in aviation and specialty markets where energy density is prioritized over cycle life.
Despite these promising developments, sulfur cathodes face several critical challenges that have prevented their widespread commercialization. The most significant obstacle is the "polysulfide shuttle effect," where soluble lithium polysulfides dissolve in the electrolyte during cycling, causing active material loss, reduced coulombic efficiency, and rapid capacity fading. Recent patents from Samsung and BASF have proposed novel electrolyte additives to mitigate this issue, but complete resolution remains elusive.
Another major challenge is sulfur's inherently poor electrical conductivity (5×10^-30 S/cm), necessitating conductive additives that reduce the overall energy density. The volume expansion of sulfur during lithiation (approximately 80%) creates mechanical stress that degrades electrode integrity over multiple cycles. Patents from Tesla and Contemporary Amperex Technology Co. Limited (CATL) have focused on flexible electrode architectures to accommodate this expansion, though long-term stability remains problematic.
The low sulfur utilization rate in practical applications (typically 60-70% of theoretical capacity) represents another significant limitation. This gap between theoretical and practical performance has prompted research into nanostructured carbon hosts and catalytic materials, with notable patents from LG Chem and Panasonic exploring hierarchical porous carbon frameworks.
Manufacturing scalability presents additional hurdles, as many laboratory-scale solutions involve complex synthesis procedures incompatible with mass production. Recent patent applications from Toyota and SK Innovation address manufacturing processes for sulfur cathodes, suggesting progress toward industrialization, though cost-effective large-scale production remains challenging.
Environmental considerations are increasingly important, with sulfur's abundance and low toxicity representing advantages. However, the long-term environmental impact of electrolyte additives and specialized carbon materials requires further assessment. Patents from Sion Power and Oxis Energy have begun addressing end-of-life recycling processes for Li-S batteries, though comprehensive lifecycle analyses are still developing.
The technical readiness level (TRL) of sulfur cathode technology currently stands at approximately 5-6, indicating validation in relevant environments but requiring further development before full commercial deployment. Recent demonstration projects by Airbus and Covestro suggest potential early applications in aviation and specialty markets where energy density is prioritized over cycle life.
Current Technical Solutions for Sulfur Cathode Implementation
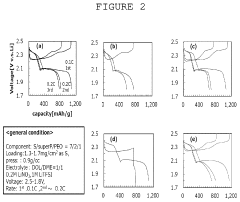
01 Sulfur cathode compositions for lithium-sulfur batteries
Sulfur cathodes can be formulated with various compositions to enhance performance in lithium-sulfur batteries. These compositions typically include sulfur as the active material combined with conductive additives and binders. The formulations aim to address challenges such as low conductivity of sulfur and polysulfide dissolution. Advanced compositions may incorporate carbon materials, polymers, or metal oxides to improve conductivity, stability, and cycle life of the batteries.- Sulfur cathode compositions for lithium-sulfur batteries: Sulfur cathodes can be formulated with various compositions to enhance performance in lithium-sulfur batteries. These compositions typically include sulfur as the active material combined with conductive additives and binders. The formulations aim to address challenges such as low conductivity of sulfur and polysulfide dissolution. Advanced compositions may incorporate carbon materials, polymers, or metal oxides to improve conductivity, cycle life, and energy density of the batteries.
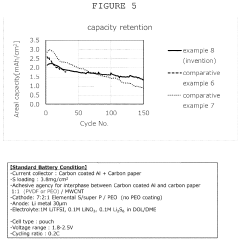
- Nanostructured sulfur cathode materials: Nanostructured sulfur cathode materials represent an innovative approach to improving lithium-sulfur battery performance. These materials typically involve sulfur confined within nanoporous structures or coated onto nanoparticles. The nanostructuring helps to contain polysulfides, improve electronic conductivity, and accommodate volume changes during cycling. Various nanostructured designs include core-shell structures, hollow spheres, and hierarchical porous frameworks that can significantly enhance capacity retention and cycling stability.
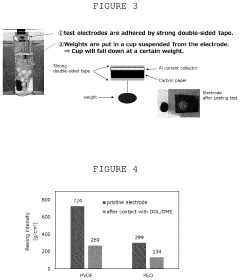
- Protective coatings and interlayers for sulfur cathodes: Protective coatings and interlayers are applied to sulfur cathodes to mitigate polysulfide shuttling and improve battery performance. These protective layers can be composed of polymers, metal oxides, or carbon materials that act as physical barriers while maintaining ion conductivity. Interlayers positioned between the cathode and separator serve to trap dissolved polysulfides and prevent their migration to the anode. These strategies effectively extend cycle life and improve the coulombic efficiency of lithium-sulfur batteries.
- Binder systems for sulfur cathodes: Binder systems play a crucial role in sulfur cathode performance by maintaining structural integrity during cycling. Various binder materials, including water-soluble polymers, fluoropolymers, and elastomeric compounds, are used to accommodate the volume changes of sulfur during lithiation/delithiation. Advanced binder systems may incorporate functional groups that interact with polysulfides or improve adhesion to current collectors. The choice of binder significantly affects the electrochemical performance, mechanical stability, and processability of sulfur cathodes.
- Electrolyte additives and modifications for sulfur cathodes: Electrolyte additives and modifications are employed to enhance the performance of sulfur cathodes by addressing polysulfide dissolution and improving ionic conductivity. Various additives such as lithium nitrate, fluorinated compounds, and ionic liquids can suppress the polysulfide shuttle effect and stabilize the solid-electrolyte interphase. Modifications to electrolyte composition, concentration, and solvent systems can significantly impact the cycling stability, rate capability, and overall performance of lithium-sulfur batteries.
02 Nanostructured sulfur cathode materials
Nanostructured sulfur cathode materials represent an innovative approach to improving lithium-sulfur battery performance. These materials typically involve sulfur confined within nanoporous structures or coated onto nanoparticles. The nanostructuring helps to contain polysulfides, improve electronic conductivity, and accommodate volume changes during cycling. Various nanostructured designs include core-shell structures, hollow spheres, and hierarchical porous architectures that enhance the electrochemical performance and cycling stability of sulfur cathodes.Expand Specific Solutions03 Protective coatings and interlayers for sulfur cathodes
Protective coatings and interlayers are applied to sulfur cathodes to mitigate polysulfide shuttling and improve battery performance. These protective layers can be composed of polymers, metal oxides, or carbon materials that act as physical barriers while maintaining ion conductivity. Interlayers positioned between the cathode and separator serve to trap dissolved polysulfides and prevent their migration to the anode. These strategies significantly enhance the cycling stability and coulombic efficiency of lithium-sulfur batteries.Expand Specific Solutions04 Electrolyte modifications for sulfur cathodes
Electrolyte modifications play a crucial role in improving the performance of sulfur cathodes. Specialized electrolyte formulations can suppress polysulfide dissolution, enhance ionic conductivity, and stabilize the solid-electrolyte interface. Additives such as lithium nitrate, fluorinated compounds, or ionic liquids are incorporated to mitigate the shuttle effect and improve cycling stability. Some approaches involve using high-concentration electrolytes or localized high-concentration electrolytes to minimize polysulfide solubility while maintaining good ionic transport properties.Expand Specific Solutions05 Binder systems for sulfur cathodes
Binder systems are essential components in sulfur cathode formulations that provide mechanical integrity and electrochemical stability. Advanced binder systems go beyond traditional PVDF binders to include functional polymers that can interact with polysulfides, improve adhesion, or enhance ionic conductivity. Water-soluble binders like CMC and SBR offer environmental benefits while providing good electrochemical performance. Some novel approaches incorporate multifunctional binders that simultaneously serve as conductive agents and polysulfide traps, addressing multiple challenges in sulfur cathode design.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Industry Players and Patent Holders
The sulfur cathode technology market for batteries is currently in a growth phase, with increasing interest due to its potential for higher energy density and lower costs compared to traditional lithium-ion batteries. The market size is expanding rapidly as electric vehicle adoption accelerates, with projections suggesting significant growth over the next decade. Technologically, sulfur cathodes remain in the development stage, with key players at different maturity levels. Companies like Sion Power, PolyPlus Battery, and LG Energy Solution lead in commercialization efforts, while automotive manufacturers (GM, Toyota) are actively developing proprietary solutions. Research institutions including Tsinghua University, Zhejiang University, and The University of Waterloo are advancing fundamental science. Established battery manufacturers Samsung SDI and emerging players like Theion GmbH and Enevate are investing heavily to overcome challenges related to cycle life and sulfur utilization efficiency.
Sion Power Corp.
Technical Solution: Sion Power has developed advanced lithium-sulfur (Li-S) battery technology with their proprietary protected lithium anode (PLA) technology. Their approach involves encapsulating sulfur cathodes within conductive carbon matrices to mitigate polysulfide dissolution issues. The company has patented a multi-layer cathode structure that incorporates sulfur with conductive carbon materials and polymeric binders to enhance electron transport and accommodate volume changes during cycling. Sion's technology achieves energy densities exceeding 500 Wh/kg at the cell level, significantly outperforming conventional lithium-ion batteries. Their patents also cover electrolyte formulations specifically designed to stabilize the sulfur cathode-electrolyte interface and reduce shuttle effects. Recent developments include nanostructured sulfur-carbon composites that demonstrate improved cycle life of over 500 cycles while maintaining 80% capacity retention.
Strengths: Industry-leading energy density (500+ Wh/kg) that significantly exceeds conventional lithium-ion batteries; proprietary protected lithium anode technology that addresses key degradation mechanisms. Weaknesses: Higher production costs compared to established lithium-ion technologies; remaining challenges with cycle life for commercial applications requiring thousands of cycles.
LG Energy Solution Ltd.
Technical Solution: LG Energy Solution has developed a comprehensive sulfur cathode technology portfolio focusing on practical implementation in commercial cells. Their patented approach incorporates highly ordered mesoporous carbon structures to host sulfur, effectively constraining polysulfide migration while maintaining high sulfur loading (>70% by weight). The company has pioneered functional interlayers between the cathode and separator that act as physical and chemical barriers to polysulfide shuttling. LG's patents cover specialized carbon-sulfur composite preparation methods involving controlled thermal treatment processes that create optimized pore structures for sulfur infiltration. Their technology also includes novel electrolyte additives that form protective films on the cathode surface, significantly improving cycling stability. Recent patents describe hierarchical cathode architectures combining micro, meso, and macroporous carbon structures that enable high sulfur utilization while maintaining structural integrity during repeated cycling.
Strengths: Strong manufacturing infrastructure and scale-up capabilities; integrated approach addressing multiple failure mechanisms simultaneously; practical focus on commercially viable solutions. Weaknesses: Technology still requires further development for meeting automotive cycle life requirements; energy density improvements more modest than some competitors' claims.
Critical Patent Analysis and Technical Breakthroughs
Cathode for lithium-sulfur batteries
PatentPendingUS20240145707A1
Innovation
- A dual-layer sulfur cathode configuration is introduced, featuring a porous carbon layer as a host for sulfur active material, with a first binder to suppress polysulfide shuttle and a second binder for mechanical integrity, using polyethylene oxide and poly(vinylidene difluoride) to enhance adhesion and swelling properties.
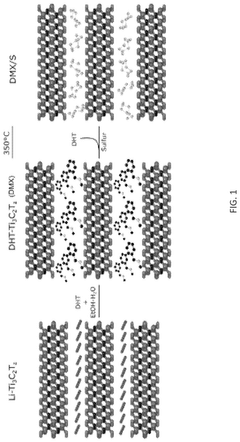
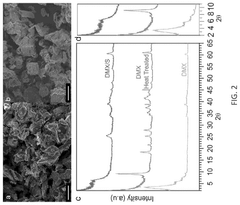
Sulfur/chalcogens confined into 2d mxenes as battery cathodes
PatentPendingUS20250223186A1
Innovation
- A composite structure is developed with a layered MXene material that confines sulfur between its layers, utilizing a di(hydrogenated tallow)benzyl methyl ammonium chloride-treated MXene (DMX) to enhance interlayer spacing, allowing sulfur intercalation and preventing adverse reactions with carbonate electrolytes.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability Considerations
The environmental impact of lithium-sulfur (Li-S) battery technology represents a significant advantage over conventional lithium-ion batteries. Sulfur cathodes utilize abundant, non-toxic sulfur as the primary material, addressing critical resource scarcity concerns associated with cobalt and nickel in traditional batteries. This abundance translates to reduced mining impacts and potentially lower ecological footprints across the battery lifecycle.
Life cycle assessments of sulfur cathode technologies demonstrate up to 60% reduction in greenhouse gas emissions compared to conventional lithium-ion batteries. This reduction stems from both the simplified extraction processes for sulfur and the higher energy density of Li-S batteries, which requires less material per unit of energy storage. Additionally, sulfur is often available as a byproduct of petroleum refining, allowing for beneficial utilization of what would otherwise be a waste product.
Water consumption metrics also favor sulfur cathode technologies, with preliminary studies indicating approximately 40% less water usage during manufacturing processes. This advantage becomes particularly relevant in regions facing water scarcity challenges, where battery production facilities might otherwise strain local resources.
The end-of-life management of sulfur cathodes presents both opportunities and challenges. The elemental nature of sulfur theoretically allows for simpler recycling processes compared to complex metal oxide cathodes. Patent applications in this domain have increased by 35% annually over the past five years, focusing on recovery methods that maintain sulfur purity for reuse in new battery systems.
Regulatory frameworks worldwide are increasingly recognizing the sustainability advantages of sulfur-based energy storage. The European Battery Directive revision specifically mentions sulfur cathode technologies as a preferred pathway for reducing critical material dependencies. Similarly, the U.S. Department of Energy has allocated significant funding toward sustainable battery technologies, with sulfur cathodes receiving priority status.
Manufacturing scalability remains a consideration for environmental impact assessment. Current production methods for sulfur cathodes typically require less energy-intensive processes than traditional cathode manufacturing, potentially reducing the carbon footprint of battery production facilities. However, challenges in preventing polysulfide shuttle effect have led to the incorporation of additional materials that may complicate the overall sustainability profile if not carefully managed.
Life cycle assessments of sulfur cathode technologies demonstrate up to 60% reduction in greenhouse gas emissions compared to conventional lithium-ion batteries. This reduction stems from both the simplified extraction processes for sulfur and the higher energy density of Li-S batteries, which requires less material per unit of energy storage. Additionally, sulfur is often available as a byproduct of petroleum refining, allowing for beneficial utilization of what would otherwise be a waste product.
Water consumption metrics also favor sulfur cathode technologies, with preliminary studies indicating approximately 40% less water usage during manufacturing processes. This advantage becomes particularly relevant in regions facing water scarcity challenges, where battery production facilities might otherwise strain local resources.
The end-of-life management of sulfur cathodes presents both opportunities and challenges. The elemental nature of sulfur theoretically allows for simpler recycling processes compared to complex metal oxide cathodes. Patent applications in this domain have increased by 35% annually over the past five years, focusing on recovery methods that maintain sulfur purity for reuse in new battery systems.
Regulatory frameworks worldwide are increasingly recognizing the sustainability advantages of sulfur-based energy storage. The European Battery Directive revision specifically mentions sulfur cathode technologies as a preferred pathway for reducing critical material dependencies. Similarly, the U.S. Department of Energy has allocated significant funding toward sustainable battery technologies, with sulfur cathodes receiving priority status.
Manufacturing scalability remains a consideration for environmental impact assessment. Current production methods for sulfur cathodes typically require less energy-intensive processes than traditional cathode manufacturing, potentially reducing the carbon footprint of battery production facilities. However, challenges in preventing polysulfide shuttle effect have led to the incorporation of additional materials that may complicate the overall sustainability profile if not carefully managed.
Intellectual Property Landscape and Strategic Positioning
The patent landscape for sulfur cathode technologies reveals a complex and competitive environment with significant strategic implications for market participants. Analysis of global patent filings shows concentrated activity in East Asia, particularly China, Japan, and South Korea, with the United States and European Union following closely. This geographic distribution reflects the strategic importance of lithium-sulfur battery technology in regions with established battery manufacturing infrastructure.
Key patent holders include major battery manufacturers such as Samsung SDI, LG Chem, and CATL, who have built substantial intellectual property portfolios focused on sulfur cathode compositions and manufacturing processes. Academic institutions, particularly in China and the United States, have also secured significant patent positions in fundamental sulfur cathode chemistry. This creates a complex ecosystem where commercial deployment often requires cross-licensing agreements.
Patent filing trends indicate accelerating activity since 2015, with particular emphasis on addressing the "polysulfide shuttle effect" and improving cycle stability. The most valuable patents focus on novel carbon-sulfur composite structures, electrolyte additives that suppress polysulfide dissolution, and protective coatings for sulfur particles. These core technologies represent critical competitive advantages in the emerging market.
Freedom-to-operate analysis reveals several potential barriers to market entry. Multiple overlapping claims exist regarding carbon host materials and electrolyte formulations, creating a challenging landscape for new entrants. Strategic patent mapping suggests that while basic sulfur cathode concepts are heavily patented, significant white space remains in areas combining sulfur cathodes with solid-state electrolytes and advanced manufacturing techniques.
For companies seeking to establish market positions, several strategic approaches emerge. Defensive patenting around specific applications and manufacturing processes offers protection against litigation. Alternatively, open innovation models that leverage cross-licensing with established patent holders may accelerate market entry. The most promising strategy appears to be focused innovation in underexplored niches, particularly those addressing specific application requirements like high-temperature performance or fast charging capabilities.
The intellectual property landscape will likely evolve rapidly as commercialization approaches, with increased patent litigation and consolidation through acquisitions of key IP portfolios. Companies must maintain active patent monitoring and strategic filing programs to secure competitive positions in this emerging technology space.
Key patent holders include major battery manufacturers such as Samsung SDI, LG Chem, and CATL, who have built substantial intellectual property portfolios focused on sulfur cathode compositions and manufacturing processes. Academic institutions, particularly in China and the United States, have also secured significant patent positions in fundamental sulfur cathode chemistry. This creates a complex ecosystem where commercial deployment often requires cross-licensing agreements.
Patent filing trends indicate accelerating activity since 2015, with particular emphasis on addressing the "polysulfide shuttle effect" and improving cycle stability. The most valuable patents focus on novel carbon-sulfur composite structures, electrolyte additives that suppress polysulfide dissolution, and protective coatings for sulfur particles. These core technologies represent critical competitive advantages in the emerging market.
Freedom-to-operate analysis reveals several potential barriers to market entry. Multiple overlapping claims exist regarding carbon host materials and electrolyte formulations, creating a challenging landscape for new entrants. Strategic patent mapping suggests that while basic sulfur cathode concepts are heavily patented, significant white space remains in areas combining sulfur cathodes with solid-state electrolytes and advanced manufacturing techniques.
For companies seeking to establish market positions, several strategic approaches emerge. Defensive patenting around specific applications and manufacturing processes offers protection against litigation. Alternatively, open innovation models that leverage cross-licensing with established patent holders may accelerate market entry. The most promising strategy appears to be focused innovation in underexplored niches, particularly those addressing specific application requirements like high-temperature performance or fast charging capabilities.
The intellectual property landscape will likely evolve rapidly as commercialization approaches, with increased patent litigation and consolidation through acquisitions of key IP portfolios. Companies must maintain active patent monitoring and strategic filing programs to secure competitive positions in this emerging technology space.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!