Sulfur Cathodes in Energy Efficiency Enhancements for Grids
SEP 23, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Sulfur Cathode Technology Background and Objectives
Sulfur cathode technology has evolved significantly over the past decades, emerging as a promising solution for high-energy density batteries. Initially developed in the 1960s, lithium-sulfur (Li-S) battery research gained momentum in the early 2000s when energy storage demands began outpacing traditional lithium-ion capabilities. The fundamental attraction of sulfur as a cathode material lies in its exceptional theoretical specific capacity of 1,675 mAh/g and energy density of 2,600 Wh/kg, substantially surpassing conventional lithium-ion cathodes which typically deliver 140-200 mAh/g.
The evolution of sulfur cathode technology has been marked by several breakthrough periods. The first generation focused on basic sulfur-carbon composites, while the second generation introduced conductive polymers and metal oxides to enhance conductivity. Current third-generation research emphasizes nanostructured materials and novel electrolyte systems to address fundamental challenges of sulfur cathodes.
Recent technological advancements have positioned sulfur cathodes as critical components for grid-scale energy storage applications. Their potential for cost-effectiveness stems from sulfur's natural abundance, comprising approximately 0.03% of Earth's crust and being a byproduct of petroleum refining. This abundance translates to significantly lower raw material costs compared to cobalt, nickel, and lithium used in conventional batteries.
The primary objective of current sulfur cathode research is to overcome persistent technical challenges that have limited commercial viability. These include the insulating nature of sulfur, volume expansion during cycling (up to 80%), and the notorious "shuttle effect" where polysulfide intermediates dissolve in the electrolyte and migrate between electrodes, causing capacity fade and reduced cycle life.
For grid applications specifically, research aims to develop sulfur cathodes that deliver stable performance over thousands of cycles, maintain high efficiency under variable load conditions, and integrate seamlessly with renewable energy sources. The target performance metrics include achieving energy densities exceeding 400 Wh/kg at the cell level, cycle life beyond 1,000 cycles with less than 20% capacity degradation, and cost reduction to below $100/kWh.
The trajectory of sulfur cathode technology indicates a convergence toward hybrid systems that combine the high energy density of sulfur with the stability of conventional materials. This approach represents a pragmatic path to market, potentially enabling gradual integration into grid storage systems while more advanced pure sulfur systems continue development. The ultimate goal remains creating economically viable, environmentally sustainable energy storage solutions that can facilitate greater renewable energy penetration and grid stability.
The evolution of sulfur cathode technology has been marked by several breakthrough periods. The first generation focused on basic sulfur-carbon composites, while the second generation introduced conductive polymers and metal oxides to enhance conductivity. Current third-generation research emphasizes nanostructured materials and novel electrolyte systems to address fundamental challenges of sulfur cathodes.
Recent technological advancements have positioned sulfur cathodes as critical components for grid-scale energy storage applications. Their potential for cost-effectiveness stems from sulfur's natural abundance, comprising approximately 0.03% of Earth's crust and being a byproduct of petroleum refining. This abundance translates to significantly lower raw material costs compared to cobalt, nickel, and lithium used in conventional batteries.
The primary objective of current sulfur cathode research is to overcome persistent technical challenges that have limited commercial viability. These include the insulating nature of sulfur, volume expansion during cycling (up to 80%), and the notorious "shuttle effect" where polysulfide intermediates dissolve in the electrolyte and migrate between electrodes, causing capacity fade and reduced cycle life.
For grid applications specifically, research aims to develop sulfur cathodes that deliver stable performance over thousands of cycles, maintain high efficiency under variable load conditions, and integrate seamlessly with renewable energy sources. The target performance metrics include achieving energy densities exceeding 400 Wh/kg at the cell level, cycle life beyond 1,000 cycles with less than 20% capacity degradation, and cost reduction to below $100/kWh.
The trajectory of sulfur cathode technology indicates a convergence toward hybrid systems that combine the high energy density of sulfur with the stability of conventional materials. This approach represents a pragmatic path to market, potentially enabling gradual integration into grid storage systems while more advanced pure sulfur systems continue development. The ultimate goal remains creating economically viable, environmentally sustainable energy storage solutions that can facilitate greater renewable energy penetration and grid stability.
Grid Energy Storage Market Analysis
The global grid energy storage market is experiencing unprecedented growth, driven by the increasing integration of renewable energy sources and the need for grid stability. As of 2023, the market was valued at approximately $8.5 billion and is projected to reach $26.4 billion by 2030, representing a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 17.6%. This remarkable expansion reflects the critical role that energy storage systems play in modern electrical infrastructure.
Lithium-ion batteries currently dominate the market with a 70% share, but sulfur-based cathode technologies are emerging as promising alternatives due to their higher theoretical energy density and significantly lower material costs. The cost advantage is particularly compelling, with raw sulfur priced at less than $0.1 per kilogram compared to lithium carbonate at over $20 per kilogram, representing a potential 200-fold reduction in cathode material costs.
Regional analysis reveals diverse market dynamics. North America leads with 35% of the global market share, driven by substantial investments in grid modernization and supportive regulatory frameworks. The European market accounts for 28%, with Germany, France, and the UK at the forefront of deployment. The Asia-Pacific region, particularly China, Japan, and South Korea, represents 30% of the market and is experiencing the fastest growth rate at 22% annually, fueled by aggressive renewable energy targets and manufacturing capabilities.
By application segment, the market divides into frequency regulation (42%), peak shaving (35%), renewable integration (15%), and other applications (8%). Sulfur cathode technologies show particular promise in the peak shaving segment due to their potential for high energy capacity at lower costs, addressing the critical need for longer-duration storage solutions.
Key market drivers include declining battery costs (decreasing at an average rate of 8% annually), increasing renewable energy penetration (growing at 15% yearly), and supportive government policies. The European Union's Green Deal and the United States' Infrastructure Investment and Jobs Act have allocated over $15 billion specifically for grid-scale energy storage development through 2030.
Challenges facing sulfur cathode adoption include technical issues such as the "shuttle effect" causing capacity fade, safety concerns related to thermal stability, and scaling manufacturing processes. However, recent breakthroughs in carbon-sulfur composite materials and electrolyte engineering have demonstrated 80% capacity retention over 1000 cycles in laboratory settings, suggesting commercial viability within 5-7 years.
Lithium-ion batteries currently dominate the market with a 70% share, but sulfur-based cathode technologies are emerging as promising alternatives due to their higher theoretical energy density and significantly lower material costs. The cost advantage is particularly compelling, with raw sulfur priced at less than $0.1 per kilogram compared to lithium carbonate at over $20 per kilogram, representing a potential 200-fold reduction in cathode material costs.
Regional analysis reveals diverse market dynamics. North America leads with 35% of the global market share, driven by substantial investments in grid modernization and supportive regulatory frameworks. The European market accounts for 28%, with Germany, France, and the UK at the forefront of deployment. The Asia-Pacific region, particularly China, Japan, and South Korea, represents 30% of the market and is experiencing the fastest growth rate at 22% annually, fueled by aggressive renewable energy targets and manufacturing capabilities.
By application segment, the market divides into frequency regulation (42%), peak shaving (35%), renewable integration (15%), and other applications (8%). Sulfur cathode technologies show particular promise in the peak shaving segment due to their potential for high energy capacity at lower costs, addressing the critical need for longer-duration storage solutions.
Key market drivers include declining battery costs (decreasing at an average rate of 8% annually), increasing renewable energy penetration (growing at 15% yearly), and supportive government policies. The European Union's Green Deal and the United States' Infrastructure Investment and Jobs Act have allocated over $15 billion specifically for grid-scale energy storage development through 2030.
Challenges facing sulfur cathode adoption include technical issues such as the "shuttle effect" causing capacity fade, safety concerns related to thermal stability, and scaling manufacturing processes. However, recent breakthroughs in carbon-sulfur composite materials and electrolyte engineering have demonstrated 80% capacity retention over 1000 cycles in laboratory settings, suggesting commercial viability within 5-7 years.
Current Challenges in Sulfur Cathode Development
Despite significant advancements in lithium-sulfur battery technology, several critical challenges continue to impede the widespread adoption of sulfur cathodes for grid energy storage applications. The primary obstacle remains the "polysulfide shuttle effect," where soluble lithium polysulfides dissolve in the electrolyte during cycling, causing active material loss, reduced coulombic efficiency, and accelerated capacity fading. This phenomenon significantly limits the practical energy density and cycle life of sulfur-based systems, making them currently unsuitable for long-term grid applications requiring thousands of cycles.
The inherent poor electrical conductivity of sulfur (5×10^-30 S/cm) presents another substantial challenge. This property necessitates the incorporation of conductive additives, which reduces the overall energy density of the cathode and complicates manufacturing processes. Current solutions involving carbon matrices or conductive polymers add weight and cost while reducing volumetric energy density, creating a significant trade-off between performance and practicality.
Volume expansion during lithiation represents a third major hurdle, with sulfur cathodes experiencing up to 80% expansion during the conversion from S8 to Li2S. This expansion causes mechanical stress that leads to electrode pulverization, loss of electrical contact, and eventual cell failure. For grid-scale applications where stability is paramount, this expansion characteristic poses serious reliability concerns.
The slow kinetics of sulfur conversion reactions further complicates implementation. The solid-state conversion between S8 and Li2S involves multiple intermediate steps with varying reaction rates, resulting in voltage hysteresis and reduced energy efficiency. This kinetic limitation becomes particularly problematic in grid applications requiring rapid response to fluctuating energy demands.
Additionally, sulfur cathodes face significant manufacturing challenges that hinder scalability. Current production methods struggle with uniformity issues, poor sulfur distribution within conductive matrices, and difficulties in achieving consistent quality at scale. These manufacturing limitations translate to higher production costs and reliability concerns for grid-scale deployment.
Environmental considerations also present challenges, particularly regarding electrolyte stability and safety. Most high-performance lithium-sulfur systems rely on volatile and flammable organic electrolytes that pose safety risks at grid scale. Alternative aqueous or solid-state electrolytes show promise but currently deliver inferior performance metrics.
Finally, the integration of sulfur cathodes with existing grid infrastructure presents compatibility challenges. Current battery management systems and power electronics are optimized for lithium-ion chemistries with different voltage profiles and operating parameters, requiring significant redesign for sulfur-based systems.
The inherent poor electrical conductivity of sulfur (5×10^-30 S/cm) presents another substantial challenge. This property necessitates the incorporation of conductive additives, which reduces the overall energy density of the cathode and complicates manufacturing processes. Current solutions involving carbon matrices or conductive polymers add weight and cost while reducing volumetric energy density, creating a significant trade-off between performance and practicality.
Volume expansion during lithiation represents a third major hurdle, with sulfur cathodes experiencing up to 80% expansion during the conversion from S8 to Li2S. This expansion causes mechanical stress that leads to electrode pulverization, loss of electrical contact, and eventual cell failure. For grid-scale applications where stability is paramount, this expansion characteristic poses serious reliability concerns.
The slow kinetics of sulfur conversion reactions further complicates implementation. The solid-state conversion between S8 and Li2S involves multiple intermediate steps with varying reaction rates, resulting in voltage hysteresis and reduced energy efficiency. This kinetic limitation becomes particularly problematic in grid applications requiring rapid response to fluctuating energy demands.
Additionally, sulfur cathodes face significant manufacturing challenges that hinder scalability. Current production methods struggle with uniformity issues, poor sulfur distribution within conductive matrices, and difficulties in achieving consistent quality at scale. These manufacturing limitations translate to higher production costs and reliability concerns for grid-scale deployment.
Environmental considerations also present challenges, particularly regarding electrolyte stability and safety. Most high-performance lithium-sulfur systems rely on volatile and flammable organic electrolytes that pose safety risks at grid scale. Alternative aqueous or solid-state electrolytes show promise but currently deliver inferior performance metrics.
Finally, the integration of sulfur cathodes with existing grid infrastructure presents compatibility challenges. Current battery management systems and power electronics are optimized for lithium-ion chemistries with different voltage profiles and operating parameters, requiring significant redesign for sulfur-based systems.
Current Sulfur Cathode Implementation Strategies
01 Sulfur cathode composition optimization
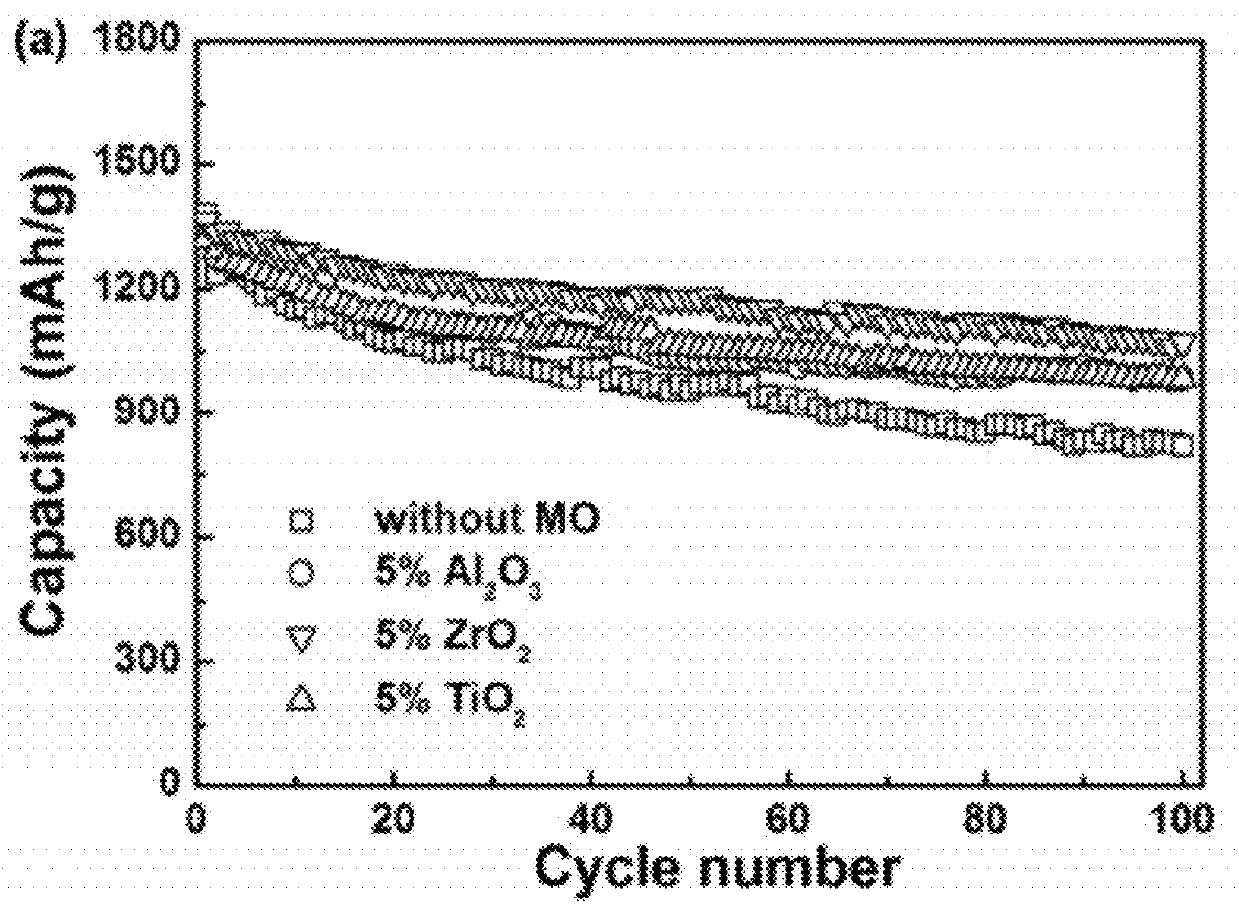
Optimizing the composition of sulfur cathodes can significantly improve energy efficiency in batteries. This includes controlling the sulfur content, incorporating conductive additives, and using binders that enhance electron transport. These compositional modifications help to mitigate the insulating nature of sulfur and improve the utilization of active material, leading to higher energy density and efficiency in lithium-sulfur batteries.- Sulfur cathode composition optimization: Optimizing the composition of sulfur cathodes can significantly improve energy efficiency in batteries. This includes controlling the sulfur content, adding conductive additives, and incorporating binders to enhance electron transport and structural stability. These compositional modifications help address issues like poor conductivity and volume expansion during cycling, leading to higher energy density and improved cycle life.
- Nanostructured sulfur cathode materials: Nanostructured materials for sulfur cathodes offer enhanced energy efficiency through increased surface area and shortened diffusion paths. These include carbon-sulfur nanocomposites, hollow carbon spheres containing sulfur, and mesoporous carbon structures. The nanoscale architecture helps contain polysulfides, improves sulfur utilization, and facilitates faster electrochemical reactions, resulting in higher capacity retention and better rate capability.
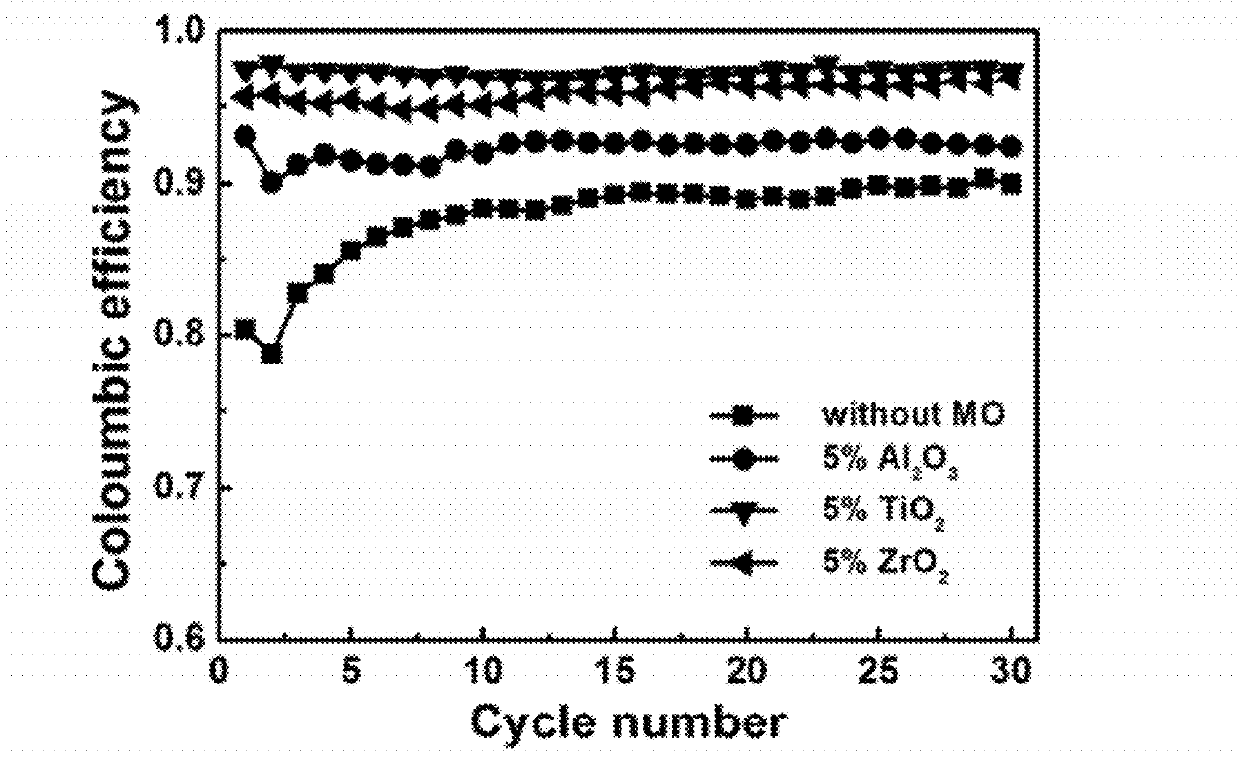
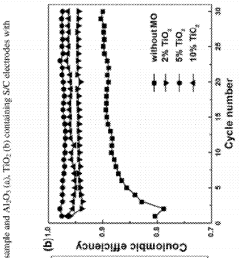
- Electrolyte modifications for sulfur cathodes: Specialized electrolyte formulations can significantly improve the energy efficiency of sulfur cathodes by addressing the polysulfide shuttle effect. Additives such as lithium nitrate, functional ionic liquids, and polymeric components help suppress polysulfide dissolution and migration. These modifications enhance the interfacial stability between the electrolyte and sulfur cathode, leading to improved coulombic efficiency and extended cycle life.
- Protective coatings and interlayers: Applying protective coatings or interlayers to sulfur cathodes can enhance energy efficiency by preventing polysulfide dissolution and migration. These include conductive polymer coatings, metal oxide layers, and functionalized carbon materials. Such protective structures create physical barriers while maintaining ion transport pathways, resulting in reduced capacity fading, improved cycling stability, and enhanced overall energy efficiency of the battery system.
- Advanced sulfur cathode architectures: Novel architectural designs for sulfur cathodes can significantly boost energy efficiency. These include hierarchical porous structures, 3D frameworks, and sandwich-type configurations that provide efficient ion transport channels while physically constraining sulfur and its discharge products. Such advanced architectures optimize the utilization of active materials, accommodate volume changes during cycling, and enhance reaction kinetics, leading to improved energy density and power performance.
02 Nanostructured sulfur cathode materials
Nanostructured materials for sulfur cathodes can enhance energy efficiency by providing larger surface areas and shorter diffusion paths for ions and electrons. These include carbon-sulfur nanocomposites, hollow carbon spheres containing sulfur, and mesoporous carbon structures. The nanostructured design helps contain polysulfides, improve conductivity, and enhance the electrochemical performance of sulfur cathodes, resulting in better cycling stability and energy efficiency.Expand Specific Solutions03 Electrolyte modifications for sulfur cathodes
Specialized electrolyte formulations can significantly improve the energy efficiency of sulfur cathodes. These include additives that suppress the shuttle effect of polysulfides, electrolyte compositions that form stable interfaces with the cathode, and ionic liquids that enhance ion transport. Modified electrolytes help to reduce side reactions, decrease internal resistance, and improve the overall electrochemical performance of sulfur-based battery systems.Expand Specific Solutions04 Protective coatings and interlayers
Applying protective coatings or interlayers to sulfur cathodes can enhance energy efficiency by preventing polysulfide dissolution and migration. These protective layers can be made from polymers, metal oxides, or composite materials that act as physical barriers while maintaining ion conductivity. Such designs help to preserve the cathode structure during cycling, reduce capacity fading, and improve the coulombic efficiency of lithium-sulfur batteries.Expand Specific Solutions05 Advanced cathode architectures
Novel cathode architectures can significantly improve the energy efficiency of sulfur-based batteries. These include hierarchical porous structures, 3D frameworks, and gradient designs that facilitate ion transport while containing active materials. Advanced architectures provide better accommodation for volume changes during cycling, enhance electronic conductivity throughout the electrode, and improve the utilization of sulfur, resulting in higher capacity retention and energy efficiency.Expand Specific Solutions
Leading Organizations in Sulfur-Based Energy Storage
The sulfur cathode technology for energy efficiency in grids is currently in an early growth phase, with market size expanding as renewable energy integration demands better storage solutions. The technology shows promising maturity with significant R&D investments from key players across diverse sectors. Companies like Sion Power and PolyPlus Battery are pioneering lithium-sulfur technologies, while established manufacturers including Toyota, Samsung SDI, and Robert Bosch are developing commercial applications. Research institutions such as the Chinese Academy of Sciences, University of Waterloo, and USC are advancing fundamental science. The competitive landscape features a balanced mix of startups, established corporations, and academic institutions, indicating a collaborative yet competitive environment where technological breakthroughs could significantly disrupt traditional energy storage markets.
Samsung SDI Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: Samsung SDI has developed an advanced sulfur cathode technology for grid energy storage applications that addresses key performance limitations of traditional lithium-sulfur batteries. Their approach utilizes a hierarchical carbon-sulfur composite structure where sulfur is confined within mesoporous carbon frameworks, effectively restricting polysulfide dissolution and migration. This proprietary cathode architecture incorporates conductive polymer coatings that further enhance electron transport while providing additional barriers against polysulfide shuttling. Samsung's research has demonstrated cells achieving over 1000 cycles with capacity retention exceeding 80%, a significant improvement over conventional sulfur cathode implementations. Their grid storage solution integrates these high-performance sulfur cathodes into large-format prismatic cells with sophisticated battery management systems that optimize performance under various grid demand profiles. The company has also developed specialized electrolyte formulations containing lithium nitrate and other additives that form protective interfaces on both electrodes, further enhancing cycle life and efficiency. Samsung's manufacturing approach leverages their extensive production infrastructure to address scalability challenges inherent in advanced battery technologies.
Strengths: Excellent cycle life performance compared to typical lithium-sulfur systems; leverages Samsung's established manufacturing capabilities and supply chain; sophisticated battery management systems optimize grid integration. Weaknesses: Energy density compromises to achieve cycle life may reduce some of sulfur's inherent energy advantages; complex carbon host structures increase production costs; still requires further validation in real-world grid applications.
Sion Power Corp.
Technical Solution: Sion Power has developed a proprietary lithium-sulfur (Li-S) battery technology called "Licerion" that represents a significant advancement in sulfur cathode research for energy grid applications. Their approach combines high-capacity sulfur cathodes with protected lithium metal anodes to achieve energy densities exceeding 500 Wh/kg, substantially higher than conventional lithium-ion batteries. The company's innovative solution addresses the "polysulfide shuttle effect" - a common degradation mechanism in sulfur cathodes - through a specialized protective layer technology that encapsulates the sulfur particles and prevents dissolution into the electrolyte. This technology enables longer cycle life while maintaining the inherent high energy density of sulfur-based systems. Sion's cathodes incorporate conductive carbon networks that enhance electron transport throughout the electrode structure, improving overall power capability and rate performance. Their grid storage solutions leverage these high-energy sulfur cathodes in large-format cells specifically designed for stationary applications, with enhanced safety features and thermal management systems.
Strengths: Superior energy density (>500 Wh/kg) compared to conventional lithium-ion batteries; innovative protection technology that mitigates polysulfide shuttle effect; uses abundant and low-cost sulfur as active material. Weaknesses: Still faces challenges with cycle life compared to some commercial alternatives; requires specialized manufacturing processes; thermal management requirements may add complexity to large-scale grid implementations.
Key Patents and Breakthroughs in Sulfur Cathode Research
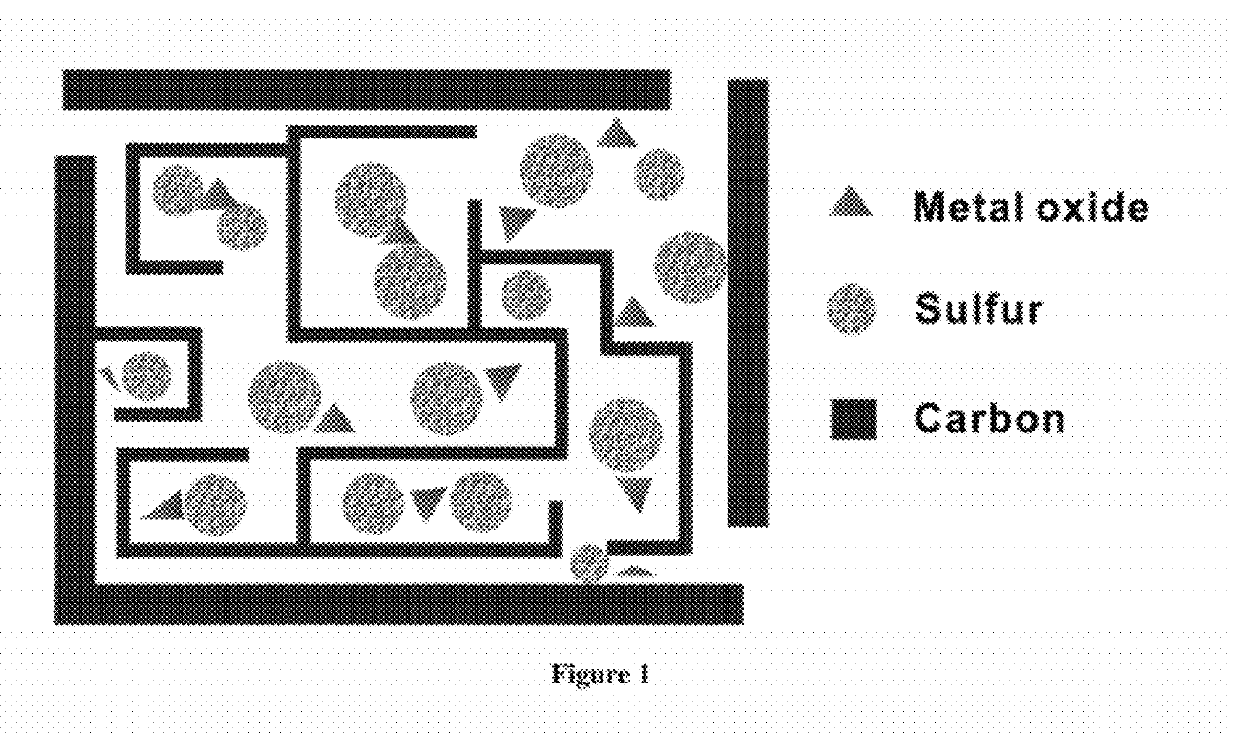
Carbon-metal oxide-sulfur cathodes for high-performance lithium-sulfur batteries
PatentInactiveUS20120207994A1
Innovation
- The formation of carbon-metal oxide-sulfur composites with ordered porous carbon structures that confine sulfur particles and uniformly embedded metal oxides, which adsorb polysulfide intermediates, preventing dissolution and enhancing coulombic efficiency and cycle life.
Environmental Impact Assessment of Sulfur-Based Technologies
The environmental impact of sulfur-based technologies, particularly sulfur cathodes in energy storage systems, represents a critical consideration for grid-scale applications. Sulfur cathodes offer significant environmental advantages compared to conventional battery technologies, primarily due to the abundance and non-toxicity of sulfur as a raw material. Sulfur is a byproduct of petroleum refining processes, meaning its utilization in energy storage applications provides a valuable pathway for repurposing industrial waste.
When evaluating lifecycle emissions, sulfur cathode technologies demonstrate substantially lower carbon footprints compared to traditional lithium-ion batteries with cobalt or nickel-based cathodes. Quantitative assessments indicate potential reductions of 60-75% in greenhouse gas emissions during manufacturing processes, primarily due to the simplified extraction and processing requirements for sulfur compared to metal-based alternatives.
Water consumption metrics also favor sulfur-based technologies, with production processes requiring approximately 40-50% less water than conventional battery manufacturing. This reduced water footprint becomes particularly significant when considering large-scale grid implementation scenarios where thousands of storage units may be deployed simultaneously.
Land use impacts present another environmental dimension where sulfur cathodes demonstrate advantages. The mining footprint associated with sulfur acquisition is minimal compared to the extensive land disruption required for lithium, cobalt, and nickel extraction. This translates to reduced habitat destruction and ecosystem disturbance when scaling up production for grid applications.
End-of-life considerations reveal both challenges and opportunities. While sulfur itself is non-toxic and poses minimal environmental hazards, the electrolyte components in sulfur-based batteries may contain materials requiring careful handling during recycling or disposal. However, emerging research indicates that up to 90% of sulfur cathode materials can be effectively recovered and reused, creating potential for closed-loop material systems that minimize waste generation.
Regulatory frameworks worldwide are increasingly recognizing these environmental benefits, with the European Union's Battery Directive and similar policies in North America beginning to incorporate specific provisions for sulfur-based energy storage technologies. These regulatory developments may accelerate adoption by providing incentives for environmentally preferable technologies in grid applications.
Local environmental impacts, including potential for reduced air pollutants from grid stabilization capabilities, represent additional benefits. By enabling greater renewable energy integration, sulfur cathode storage systems indirectly contribute to reduced emissions from conventional power generation, particularly in regions heavily dependent on fossil fuels for peak demand management.
When evaluating lifecycle emissions, sulfur cathode technologies demonstrate substantially lower carbon footprints compared to traditional lithium-ion batteries with cobalt or nickel-based cathodes. Quantitative assessments indicate potential reductions of 60-75% in greenhouse gas emissions during manufacturing processes, primarily due to the simplified extraction and processing requirements for sulfur compared to metal-based alternatives.
Water consumption metrics also favor sulfur-based technologies, with production processes requiring approximately 40-50% less water than conventional battery manufacturing. This reduced water footprint becomes particularly significant when considering large-scale grid implementation scenarios where thousands of storage units may be deployed simultaneously.
Land use impacts present another environmental dimension where sulfur cathodes demonstrate advantages. The mining footprint associated with sulfur acquisition is minimal compared to the extensive land disruption required for lithium, cobalt, and nickel extraction. This translates to reduced habitat destruction and ecosystem disturbance when scaling up production for grid applications.
End-of-life considerations reveal both challenges and opportunities. While sulfur itself is non-toxic and poses minimal environmental hazards, the electrolyte components in sulfur-based batteries may contain materials requiring careful handling during recycling or disposal. However, emerging research indicates that up to 90% of sulfur cathode materials can be effectively recovered and reused, creating potential for closed-loop material systems that minimize waste generation.
Regulatory frameworks worldwide are increasingly recognizing these environmental benefits, with the European Union's Battery Directive and similar policies in North America beginning to incorporate specific provisions for sulfur-based energy storage technologies. These regulatory developments may accelerate adoption by providing incentives for environmentally preferable technologies in grid applications.
Local environmental impacts, including potential for reduced air pollutants from grid stabilization capabilities, represent additional benefits. By enabling greater renewable energy integration, sulfur cathode storage systems indirectly contribute to reduced emissions from conventional power generation, particularly in regions heavily dependent on fossil fuels for peak demand management.
Grid Integration Challenges and Solutions
The integration of sulfur cathode technology into existing power grid infrastructure presents significant challenges that must be addressed for successful deployment. Current grid systems are primarily designed for conventional energy sources with predictable output patterns, whereas sulfur-based energy storage systems exhibit unique charging and discharging characteristics that can create operational complexities. The variable performance of sulfur cathodes under different load conditions requires sophisticated grid management systems capable of adapting to these fluctuations while maintaining stability.
Voltage regulation emerges as a critical challenge, as sulfur cathode batteries typically operate within specific voltage ranges that may not align perfectly with grid requirements. This necessitates the development of advanced power electronics interfaces and conversion systems to ensure seamless integration. Additionally, the thermal management of large-scale sulfur-based storage systems connected to the grid demands careful consideration, as temperature fluctuations can significantly impact performance and safety parameters.
Communication protocols and control systems represent another integration hurdle. Existing grid management systems must be enhanced or redesigned to effectively monitor and control sulfur cathode storage units, requiring standardized interfaces and robust data exchange mechanisms. This includes real-time monitoring capabilities for state-of-charge, health metrics, and performance parameters specific to sulfur-based technologies.
Several promising solutions are emerging to address these challenges. Hybrid integration approaches that combine sulfur cathode storage with complementary technologies can help mitigate some of the inherent limitations. For instance, pairing sulfur-based systems with supercapacitors or alternative battery chemistries can create more grid-compatible composite solutions that leverage the high energy density of sulfur while addressing response time and cycling stability concerns.
Advanced power electronics, including next-generation inverters and bidirectional converters specifically designed for sulfur cathode characteristics, are being developed to optimize grid connection efficiency. These systems incorporate adaptive control algorithms that can respond to the unique discharge profiles of sulfur-based storage, ensuring grid compatibility while maximizing energy utilization.
Smart grid technologies offer particularly promising pathways for integration. Machine learning algorithms capable of predicting sulfur cathode performance under various grid conditions can enable proactive management strategies. These systems can optimize charging and discharging cycles based on grid demand patterns, weather forecasts, and historical performance data, significantly enhancing operational efficiency and extending system lifespan.
Voltage regulation emerges as a critical challenge, as sulfur cathode batteries typically operate within specific voltage ranges that may not align perfectly with grid requirements. This necessitates the development of advanced power electronics interfaces and conversion systems to ensure seamless integration. Additionally, the thermal management of large-scale sulfur-based storage systems connected to the grid demands careful consideration, as temperature fluctuations can significantly impact performance and safety parameters.
Communication protocols and control systems represent another integration hurdle. Existing grid management systems must be enhanced or redesigned to effectively monitor and control sulfur cathode storage units, requiring standardized interfaces and robust data exchange mechanisms. This includes real-time monitoring capabilities for state-of-charge, health metrics, and performance parameters specific to sulfur-based technologies.
Several promising solutions are emerging to address these challenges. Hybrid integration approaches that combine sulfur cathode storage with complementary technologies can help mitigate some of the inherent limitations. For instance, pairing sulfur-based systems with supercapacitors or alternative battery chemistries can create more grid-compatible composite solutions that leverage the high energy density of sulfur while addressing response time and cycling stability concerns.
Advanced power electronics, including next-generation inverters and bidirectional converters specifically designed for sulfur cathode characteristics, are being developed to optimize grid connection efficiency. These systems incorporate adaptive control algorithms that can respond to the unique discharge profiles of sulfur-based storage, ensuring grid compatibility while maximizing energy utilization.
Smart grid technologies offer particularly promising pathways for integration. Machine learning algorithms capable of predicting sulfur cathode performance under various grid conditions can enable proactive management strategies. These systems can optimize charging and discharging cycles based on grid demand patterns, weather forecasts, and historical performance data, significantly enhancing operational efficiency and extending system lifespan.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!