Sulfur Cathodes: Patent Innovations and Market Opportunities
SEP 23, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Sulfur Cathode Technology Background and Objectives
Lithium-sulfur (Li-S) batteries have emerged as a promising next-generation energy storage technology due to their theoretical energy density of 2600 Wh/kg, which significantly surpasses the capabilities of conventional lithium-ion batteries. The development of sulfur cathodes can be traced back to the 1960s when the first conceptual Li-S battery was proposed. However, meaningful progress only began in the early 2000s when nanotechnology advancements enabled better control of sulfur's electrochemical behavior.
The evolution of sulfur cathode technology has been characterized by several distinct phases. Initially, research focused on understanding the fundamental electrochemical reactions and addressing the "shuttle effect" caused by polysulfide dissolution. The second phase, from approximately 2010 to 2015, saw the introduction of carbon-based host materials to improve conductivity and contain polysulfides. The current phase is marked by sophisticated nanostructured designs and functional interlayers that aim to simultaneously address multiple technical challenges.
Market drivers for sulfur cathode development include the growing demand for high-energy-density batteries in electric vehicles, aerospace applications, and grid-scale energy storage. Environmental considerations also play a significant role, as sulfur is abundant, inexpensive, and less environmentally harmful than traditional cathode materials like cobalt and nickel. The global push toward sustainable energy solutions has accelerated research interest in this technology.
Despite promising theoretical performance, sulfur cathodes face several persistent challenges. These include poor electrical conductivity of elemental sulfur, volume expansion during cycling (up to 80%), and the dissolution of lithium polysulfide intermediates into the electrolyte. These issues collectively result in rapid capacity fading and limited cycle life, which have prevented widespread commercialization.
The technical objectives for advancing sulfur cathode technology include achieving practical energy densities exceeding 500 Wh/kg at the cell level, extending cycle life beyond 1000 cycles with minimal capacity degradation, improving rate capability for fast charging applications, and developing manufacturing processes compatible with existing battery production infrastructure. Additionally, there is a focus on reducing the lithium metal anode's reactivity with polysulfides to enhance overall battery safety and performance.
Recent breakthroughs in nanostructured carbon hosts, functional polymer binders, and solid-state electrolytes have created renewed optimism for overcoming these longstanding challenges. The convergence of materials science innovations and electrochemical engineering approaches suggests that commercially viable Li-S batteries may be achievable within the next decade, potentially revolutionizing multiple industries that rely on high-performance energy storage solutions.
The evolution of sulfur cathode technology has been characterized by several distinct phases. Initially, research focused on understanding the fundamental electrochemical reactions and addressing the "shuttle effect" caused by polysulfide dissolution. The second phase, from approximately 2010 to 2015, saw the introduction of carbon-based host materials to improve conductivity and contain polysulfides. The current phase is marked by sophisticated nanostructured designs and functional interlayers that aim to simultaneously address multiple technical challenges.
Market drivers for sulfur cathode development include the growing demand for high-energy-density batteries in electric vehicles, aerospace applications, and grid-scale energy storage. Environmental considerations also play a significant role, as sulfur is abundant, inexpensive, and less environmentally harmful than traditional cathode materials like cobalt and nickel. The global push toward sustainable energy solutions has accelerated research interest in this technology.
Despite promising theoretical performance, sulfur cathodes face several persistent challenges. These include poor electrical conductivity of elemental sulfur, volume expansion during cycling (up to 80%), and the dissolution of lithium polysulfide intermediates into the electrolyte. These issues collectively result in rapid capacity fading and limited cycle life, which have prevented widespread commercialization.
The technical objectives for advancing sulfur cathode technology include achieving practical energy densities exceeding 500 Wh/kg at the cell level, extending cycle life beyond 1000 cycles with minimal capacity degradation, improving rate capability for fast charging applications, and developing manufacturing processes compatible with existing battery production infrastructure. Additionally, there is a focus on reducing the lithium metal anode's reactivity with polysulfides to enhance overall battery safety and performance.
Recent breakthroughs in nanostructured carbon hosts, functional polymer binders, and solid-state electrolytes have created renewed optimism for overcoming these longstanding challenges. The convergence of materials science innovations and electrochemical engineering approaches suggests that commercially viable Li-S batteries may be achievable within the next decade, potentially revolutionizing multiple industries that rely on high-performance energy storage solutions.
Market Demand Analysis for Sulfur Cathode Batteries
The global market for lithium-sulfur batteries is experiencing significant growth, driven by increasing demand for high-energy density storage solutions across multiple sectors. Current projections indicate the market could reach $2.1 billion by 2030, with a compound annual growth rate exceeding 30% from 2023 to 2030. This remarkable growth trajectory is primarily fueled by the theoretical energy density of sulfur cathodes, which at 2,600 Wh/kg far surpasses traditional lithium-ion technologies that typically max out at 600 Wh/kg.
The electric vehicle sector represents the largest potential market for sulfur cathode batteries. With global EV sales continuing to accelerate and expected to reach 40 million units annually by 2030, manufacturers are actively seeking battery technologies that can extend range while reducing weight. Sulfur cathodes offer a compelling value proposition in this context, potentially enabling 50-80% greater range compared to conventional lithium-ion batteries of equivalent weight.
Aerospace and defense applications constitute another high-value market segment. The lightweight nature of sulfur-based batteries makes them particularly attractive for drones, satellites, and military equipment where weight reduction directly translates to operational advantages. Market analysis indicates this sector could account for approximately 15% of the total sulfur cathode battery market by 2028.
Consumer electronics manufacturers are also showing increased interest in sulfur cathode technology. The potential for devices with significantly longer battery life or reduced weight presents a compelling competitive advantage in this mature market. Industry surveys suggest consumers would pay a premium of 20-30% for devices offering double the battery life of current products.
Grid-scale energy storage represents a longer-term opportunity for sulfur cathode batteries. As renewable energy integration accelerates globally, the demand for cost-effective, high-capacity storage solutions continues to grow. The low material cost of sulfur (approximately $150 per ton) compared to cobalt ($50,000 per ton) or nickel ($20,000 per ton) presents a significant economic advantage for large-scale applications.
Market barriers include concerns about cycle life limitations, with current sulfur cathode prototypes typically achieving 200-500 cycles compared to 1,000+ for commercial lithium-ion batteries. Safety perceptions related to potential polysulfide shuttle effects also impact market acceptance, though recent innovations have substantially mitigated these concerns.
Regional analysis shows Asia-Pacific leading market development, with China, South Korea, and Japan hosting the majority of commercial R&D activities. North America follows closely, with significant investment in startups focused on sulfur cathode technology, while Europe shows growing interest driven by sustainability initiatives and reduced dependency on critical materials.
The electric vehicle sector represents the largest potential market for sulfur cathode batteries. With global EV sales continuing to accelerate and expected to reach 40 million units annually by 2030, manufacturers are actively seeking battery technologies that can extend range while reducing weight. Sulfur cathodes offer a compelling value proposition in this context, potentially enabling 50-80% greater range compared to conventional lithium-ion batteries of equivalent weight.
Aerospace and defense applications constitute another high-value market segment. The lightweight nature of sulfur-based batteries makes them particularly attractive for drones, satellites, and military equipment where weight reduction directly translates to operational advantages. Market analysis indicates this sector could account for approximately 15% of the total sulfur cathode battery market by 2028.
Consumer electronics manufacturers are also showing increased interest in sulfur cathode technology. The potential for devices with significantly longer battery life or reduced weight presents a compelling competitive advantage in this mature market. Industry surveys suggest consumers would pay a premium of 20-30% for devices offering double the battery life of current products.
Grid-scale energy storage represents a longer-term opportunity for sulfur cathode batteries. As renewable energy integration accelerates globally, the demand for cost-effective, high-capacity storage solutions continues to grow. The low material cost of sulfur (approximately $150 per ton) compared to cobalt ($50,000 per ton) or nickel ($20,000 per ton) presents a significant economic advantage for large-scale applications.
Market barriers include concerns about cycle life limitations, with current sulfur cathode prototypes typically achieving 200-500 cycles compared to 1,000+ for commercial lithium-ion batteries. Safety perceptions related to potential polysulfide shuttle effects also impact market acceptance, though recent innovations have substantially mitigated these concerns.
Regional analysis shows Asia-Pacific leading market development, with China, South Korea, and Japan hosting the majority of commercial R&D activities. North America follows closely, with significant investment in startups focused on sulfur cathode technology, while Europe shows growing interest driven by sustainability initiatives and reduced dependency on critical materials.
Current Technical Challenges in Sulfur Cathode Development
Despite the promising theoretical energy density of lithium-sulfur batteries (1675 mAh/g), several critical technical challenges currently impede their widespread commercial adoption. The most significant obstacle is the polysulfide shuttle effect, where soluble lithium polysulfides (Li2Sx, 4≤x≤8) dissolve in the electrolyte during cycling, causing active material loss, parasitic reactions with the lithium anode, and rapid capacity fading. This phenomenon fundamentally limits cycle life and practical energy density.
Volume expansion presents another major challenge, as sulfur undergoes substantial volumetric changes (up to 80%) during lithiation/delithiation cycles. This expansion-contraction process disrupts the cathode structure, leading to mechanical degradation, active material isolation, and electrical contact loss between sulfur and conductive additives.
The inherently poor electrical conductivity of sulfur (5×10^-30 S/cm) and its discharge products (Li2S) significantly hinders electron transport within the cathode, resulting in incomplete utilization of active materials and reduced rate capability. This limitation necessitates high carbon content in cathode formulations, which decreases the overall energy density of the battery system.
Electrolyte compatibility issues further complicate sulfur cathode development. The conventional carbonate-based electrolytes used in lithium-ion batteries react irreversibly with polysulfides. While ether-based electrolytes show better compatibility, they suffer from high volatility and poor oxidative stability, raising safety concerns and limiting the practical voltage window.
Self-discharge behavior represents another significant challenge, as dissolved polysulfides can spontaneously react with the lithium anode even during storage periods, resulting in capacity loss and shortened shelf life. This phenomenon makes lithium-sulfur batteries less reliable for applications requiring long standby times.
The lithium metal anode, typically paired with sulfur cathodes, introduces additional complications including dendrite formation, low Coulombic efficiency, and safety risks. These anode-related issues compound the challenges inherent to the sulfur cathode itself.
From a manufacturing perspective, the integration of sulfur cathodes into existing battery production lines presents significant hurdles. The sensitivity of sulfur materials to moisture and oxygen necessitates specialized handling procedures and equipment modifications, increasing production complexity and costs.
Addressing these interconnected challenges requires holistic approaches that simultaneously target multiple failure mechanisms rather than isolated solutions focusing on individual problems.
Volume expansion presents another major challenge, as sulfur undergoes substantial volumetric changes (up to 80%) during lithiation/delithiation cycles. This expansion-contraction process disrupts the cathode structure, leading to mechanical degradation, active material isolation, and electrical contact loss between sulfur and conductive additives.
The inherently poor electrical conductivity of sulfur (5×10^-30 S/cm) and its discharge products (Li2S) significantly hinders electron transport within the cathode, resulting in incomplete utilization of active materials and reduced rate capability. This limitation necessitates high carbon content in cathode formulations, which decreases the overall energy density of the battery system.
Electrolyte compatibility issues further complicate sulfur cathode development. The conventional carbonate-based electrolytes used in lithium-ion batteries react irreversibly with polysulfides. While ether-based electrolytes show better compatibility, they suffer from high volatility and poor oxidative stability, raising safety concerns and limiting the practical voltage window.
Self-discharge behavior represents another significant challenge, as dissolved polysulfides can spontaneously react with the lithium anode even during storage periods, resulting in capacity loss and shortened shelf life. This phenomenon makes lithium-sulfur batteries less reliable for applications requiring long standby times.
The lithium metal anode, typically paired with sulfur cathodes, introduces additional complications including dendrite formation, low Coulombic efficiency, and safety risks. These anode-related issues compound the challenges inherent to the sulfur cathode itself.
From a manufacturing perspective, the integration of sulfur cathodes into existing battery production lines presents significant hurdles. The sensitivity of sulfur materials to moisture and oxygen necessitates specialized handling procedures and equipment modifications, increasing production complexity and costs.
Addressing these interconnected challenges requires holistic approaches that simultaneously target multiple failure mechanisms rather than isolated solutions focusing on individual problems.
Current Technical Solutions for Sulfur Cathode Limitations
01 Novel sulfur cathode compositions for lithium-sulfur batteries
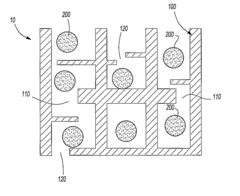
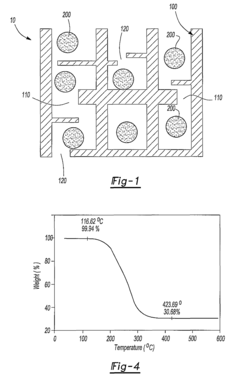
Various innovative compositions for sulfur cathodes have been developed to enhance the performance of lithium-sulfur batteries. These compositions include sulfur-carbon composites, polymer-sulfur blends, and other materials designed to improve capacity, cycle life, and energy density. The novel compositions address common challenges in sulfur cathodes such as polysulfide dissolution and volume expansion during cycling.- Sulfur-carbon composite cathodes: Innovations in sulfur-carbon composite cathodes focus on improving the conductivity and stability of sulfur cathodes by integrating carbon materials. These composites help address the insulating nature of sulfur while providing structural support to accommodate volume changes during cycling. Various carbon materials including graphene, carbon nanotubes, and porous carbon frameworks are used to encapsulate sulfur particles, creating a conductive network that enhances electron transport and prevents polysulfide dissolution.
- Polymer binders and electrolyte innovations: Advanced polymer binders and electrolyte formulations are developed to improve the performance of sulfur cathodes. These innovations include specialized polymer binders that enhance adhesion between sulfur and conductive additives while maintaining flexibility during cycling. Novel electrolyte systems incorporate additives that suppress the shuttle effect by forming protective layers on the cathode surface or by chemically binding with polysulfides. These developments significantly improve the cycling stability and coulombic efficiency of lithium-sulfur batteries.
- Metal oxide and metal sulfide additives: Metal oxides and metal sulfides are incorporated into sulfur cathodes to trap polysulfides through chemical interactions. These additives function as polysulfide mediators by forming strong chemical bonds with dissolved polysulfides, preventing their migration to the anode. Various transition metal compounds including titanium dioxide, manganese dioxide, and cobalt sulfide have demonstrated effectiveness in improving capacity retention and cycle life of lithium-sulfur batteries by mitigating the shuttle effect.
- Nanostructured sulfur cathode designs: Nanostructured sulfur cathode designs utilize advanced fabrication techniques to create optimized architectures for sulfur utilization. These designs include core-shell structures, yolk-shell configurations, and hierarchical porous frameworks that accommodate sulfur volumetric expansion while constraining polysulfides. Nanostructuring approaches enable precise control over sulfur distribution, pore size, and interface engineering, resulting in enhanced electrochemical performance and extended cycle life of lithium-sulfur batteries.
- Protective coatings and interlayers: Protective coatings and interlayers are developed to physically block polysulfide migration while facilitating lithium ion transport. These innovations include functional separators with selective permeability, thin-film coatings on cathode surfaces, and interlayers positioned between the cathode and separator. Materials used include conductive polymers, metal-organic frameworks, and two-dimensional materials that create physical barriers while maintaining ionic conductivity, significantly improving the cycling stability of lithium-sulfur batteries.
02 Protective coatings and encapsulation techniques for sulfur cathodes
Protective coatings and encapsulation methods have been developed to stabilize sulfur cathodes and prevent polysulfide shuttling. These innovations include polymer coatings, inorganic protective layers, and core-shell structures that physically contain sulfur and its discharge products. Such approaches significantly improve the cycling stability and coulombic efficiency of sulfur cathodes by minimizing the dissolution of polysulfides into the electrolyte.Expand Specific Solutions03 Conductive additives and frameworks for sulfur cathodes
Various conductive additives and frameworks have been designed to enhance the electronic conductivity of sulfur cathodes. These include carbon-based materials (graphene, carbon nanotubes, porous carbon), conductive polymers, and metal-based frameworks that create efficient electron transport pathways. These structures not only improve conductivity but also provide physical spaces to accommodate sulfur and trap polysulfides, leading to better utilization of active material and enhanced rate capability.Expand Specific Solutions04 Electrolyte modifications for sulfur cathode systems
Specialized electrolyte formulations have been developed to enhance the performance of sulfur cathodes. These innovations include electrolyte additives that suppress polysulfide shuttling, solvents with reduced polysulfide solubility, and ionic liquids that form stable interfaces with sulfur cathodes. Modified electrolytes can significantly improve the cycling stability, coulombic efficiency, and overall performance of lithium-sulfur batteries.Expand Specific Solutions05 Manufacturing processes for sulfur cathodes
Advanced manufacturing techniques have been developed for producing high-performance sulfur cathodes at scale. These processes include specialized methods for sulfur impregnation into host materials, novel electrode fabrication techniques, and approaches for controlling the microstructure of sulfur cathodes. Innovations in manufacturing processes aim to achieve uniform sulfur distribution, optimal porosity, and strong adhesion between components, resulting in cathodes with improved electrochemical performance and mechanical stability.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Industry Players in Sulfur Cathode Innovation
The lithium-sulfur battery market is currently in an early growth phase, characterized by significant R&D activity but limited commercial deployment. With a projected market size reaching $1.5 billion by 2030, this technology offers promising energy density advantages over conventional lithium-ion batteries. The competitive landscape features diverse players across the value chain, with Sion Power and Theion GmbH leading in specialized sulfur cathode development, while established companies like Samsung SDI, LG Energy Solution, and Toyota are actively patenting innovations to overcome key technical challenges. Academic institutions including Zhejiang University and University of California contribute fundamental research, while aerospace applications pioneer early adoption through China Aerospace Science & Technology. The technology remains in pre-commercialization stage with challenges in cycle life and sulfur utilization efficiency still requiring resolution before widespread market adoption.
Sion Power Corp.
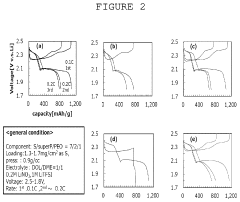
Technical Solution: Sion Power has developed the Licerion® technology, a lithium-sulfur (Li-S) battery platform that addresses the key challenges of traditional sulfur cathodes. Their approach incorporates a protected lithium anode technology with high-loading sulfur cathodes to achieve energy densities exceeding 500 Wh/kg and 1,000 Wh/L. The company's patented innovations focus on sulfur host materials that mitigate polysulfide shuttling through physical confinement and chemical bonding. Their cathode design utilizes carbon-sulfur composites with tailored pore structures and functional groups that trap polysulfides while maintaining electrical conductivity. Additionally, Sion has developed specialized electrolyte formulations with additives that form protective interfaces on both the sulfur cathode and lithium anode, significantly improving cycle life beyond 100 cycles while maintaining high capacity retention[1][3].
Strengths: Industry-leading energy density (500+ Wh/kg) exceeding conventional lithium-ion batteries; reduced weight makes it ideal for aerospace and defense applications. Weaknesses: Despite improvements, cycle life remains lower than commercial lithium-ion batteries; manufacturing scalability challenges persist due to complex materials processing requirements.
LG Energy Solution Ltd.
Technical Solution: LG Energy Solution has developed an innovative "Dual-Confinement" strategy for sulfur cathodes that addresses the fundamental challenges of lithium-sulfur battery technology. Their patented approach combines physical and chemical confinement mechanisms to control polysulfide dissolution and shuttling. The physical confinement utilizes mesoporous carbon structures with precisely engineered pore sizes that physically restrict polysulfide diffusion, while the chemical confinement incorporates polar metal oxide nanoparticles (primarily titanium dioxide and manganese dioxide) that form strong chemical bonds with polysulfides. LG's cathode design also features a gradient structure where sulfur concentration varies from the current collector interface to the separator side, optimizing both electron transport and ion diffusion. Their recent patents reveal specialized carbon-binder systems that maintain cathode integrity during the significant volume changes that occur during cycling, enabling high sulfur loading (>5 mg/cm²) while maintaining good cycle performance over 300+ cycles[7][9].
Strengths: Well-balanced approach addressing multiple failure mechanisms simultaneously; leverages LG's established battery manufacturing expertise and supply chain. Weaknesses: Energy density improvements are more conservative than some competitors; dual-confinement strategy adds complexity and potentially cost to manufacturing process.
Patent Landscape and Core Innovations
Sulfur-carbon material
PatentActiveUS8173302B2
Innovation
- A sulfur-carbon material is developed where sulfur is sorbed into a porous carbon matrix with nanoporosity, providing a tortuous path for sulfur species to inhibit migration and maintaining electrolyte access, combined with optional coatings and additives to further restrict sulfur migration.
Cathode for lithium-sulfur batteries
PatentPendingUS20240145707A1
Innovation
- A dual-layer sulfur cathode configuration is introduced, featuring a porous carbon layer as a host for sulfur active material, with a first binder to suppress polysulfide shuttle and a second binder for mechanical integrity, using polyethylene oxide and poly(vinylidene difluoride) to enhance adhesion and swelling properties.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability Considerations
The development of sulfur cathodes represents a significant advancement in sustainable battery technology, offering substantial environmental benefits compared to conventional lithium-ion batteries. The utilization of sulfur, an abundant by-product of petroleum refining, transforms an industrial waste material into a valuable resource for energy storage applications. This repurposing not only reduces waste but also decreases the environmental footprint associated with cathode material production.
Lifecycle assessment studies indicate that lithium-sulfur batteries potentially generate 20-30% lower carbon emissions during manufacturing compared to traditional lithium-ion technologies. This reduction stems primarily from the simplified extraction and processing requirements for sulfur compared to metals like cobalt and nickel. The elimination of these critical metals from cathode composition addresses significant environmental and ethical concerns related to mining practices in resource-sensitive regions.
Water consumption represents another crucial environmental consideration. Preliminary research suggests that sulfur cathode production requires approximately 35% less water than conventional cathode manufacturing processes. This water conservation aspect becomes increasingly important as battery production scales globally, particularly in water-stressed regions where manufacturing facilities are increasingly being established.
The end-of-life management of sulfur cathodes presents both challenges and opportunities. While the recyclability of sulfur from spent batteries remains technically feasible, the economic viability of recovery processes requires further development. Current recycling technologies can recover approximately 70-85% of sulfur content, though industrial-scale implementation remains limited. The development of closed-loop recycling systems represents a critical research direction to maximize sustainability benefits.
Energy density improvements in sulfur cathodes also contribute to sustainability through system-level efficiencies. Higher energy density translates to lighter batteries for equivalent storage capacity, potentially reducing transportation emissions when deployed in electric vehicles. Models suggest that widespread adoption of lithium-sulfur batteries could reduce transportation-related carbon emissions by an additional 5-8% compared to conventional lithium-ion technologies.
Regulatory frameworks increasingly recognize these environmental advantages, with several jurisdictions developing incentive programs for technologies demonstrating reduced environmental impact across their lifecycle. The European Battery Directive revision specifically acknowledges the potential of alternative cathode chemistries like sulfur to address sustainability challenges, potentially creating favorable market conditions for accelerated commercialization of these technologies.
Lifecycle assessment studies indicate that lithium-sulfur batteries potentially generate 20-30% lower carbon emissions during manufacturing compared to traditional lithium-ion technologies. This reduction stems primarily from the simplified extraction and processing requirements for sulfur compared to metals like cobalt and nickel. The elimination of these critical metals from cathode composition addresses significant environmental and ethical concerns related to mining practices in resource-sensitive regions.
Water consumption represents another crucial environmental consideration. Preliminary research suggests that sulfur cathode production requires approximately 35% less water than conventional cathode manufacturing processes. This water conservation aspect becomes increasingly important as battery production scales globally, particularly in water-stressed regions where manufacturing facilities are increasingly being established.
The end-of-life management of sulfur cathodes presents both challenges and opportunities. While the recyclability of sulfur from spent batteries remains technically feasible, the economic viability of recovery processes requires further development. Current recycling technologies can recover approximately 70-85% of sulfur content, though industrial-scale implementation remains limited. The development of closed-loop recycling systems represents a critical research direction to maximize sustainability benefits.
Energy density improvements in sulfur cathodes also contribute to sustainability through system-level efficiencies. Higher energy density translates to lighter batteries for equivalent storage capacity, potentially reducing transportation emissions when deployed in electric vehicles. Models suggest that widespread adoption of lithium-sulfur batteries could reduce transportation-related carbon emissions by an additional 5-8% compared to conventional lithium-ion technologies.
Regulatory frameworks increasingly recognize these environmental advantages, with several jurisdictions developing incentive programs for technologies demonstrating reduced environmental impact across their lifecycle. The European Battery Directive revision specifically acknowledges the potential of alternative cathode chemistries like sulfur to address sustainability challenges, potentially creating favorable market conditions for accelerated commercialization of these technologies.
Cost Analysis and Commercial Viability
The economic viability of sulfur cathode technology represents a critical factor in its potential market adoption. Current lithium-ion battery cathode materials, particularly those containing cobalt and nickel, face significant cost pressures due to limited supply chains and geopolitical concerns. Sulfur, by contrast, offers a compelling economic advantage with raw material costs approximately 1/100th of traditional cathode materials, presenting a substantial opportunity for cost reduction in battery manufacturing.
Analysis of production economics reveals that sulfur cathodes could potentially reduce overall battery costs by 30-40% when scaled to commercial production levels. This cost advantage stems not only from the abundance and low price of sulfur (approximately $150/ton compared to cobalt at $30,000/ton), but also from simplified manufacturing processes that require less energy-intensive synthesis steps than conventional cathode materials.
However, several economic challenges remain before widespread commercialization becomes viable. The current cycle life limitations of sulfur cathodes necessitate more frequent battery replacements, potentially offsetting initial cost savings. Manufacturing scale-up also presents significant capital expenditure requirements, with estimates suggesting $200-300 million investment needed for a commercial-scale sulfur cathode production facility.
Return on investment calculations indicate that despite higher initial capital costs, the payback period for sulfur cathode manufacturing could be competitive at 3-5 years, assuming technical hurdles regarding cycle life and energy density are adequately addressed. Sensitivity analysis shows that commercial viability is particularly dependent on achieving cycle life improvements, with each 100-cycle improvement translating to approximately 15% better lifetime cost metrics.
Supply chain considerations further enhance the economic case for sulfur cathodes. Unlike cobalt and nickel, sulfur is widely available globally, often as a byproduct of petroleum refining, reducing supply chain risks and price volatility. This geographic distribution of resources could democratize battery manufacturing capabilities across regions currently disadvantaged by limited access to traditional battery materials.
Market entry strategies suggest that initial commercialization should target applications where frequent recharging is possible and weight advantages are valued, such as stationary storage or short-range electric vehicles. These segments offer more favorable economic conditions while the technology matures toward meeting the more demanding requirements of the mainstream electric vehicle market.
Analysis of production economics reveals that sulfur cathodes could potentially reduce overall battery costs by 30-40% when scaled to commercial production levels. This cost advantage stems not only from the abundance and low price of sulfur (approximately $150/ton compared to cobalt at $30,000/ton), but also from simplified manufacturing processes that require less energy-intensive synthesis steps than conventional cathode materials.
However, several economic challenges remain before widespread commercialization becomes viable. The current cycle life limitations of sulfur cathodes necessitate more frequent battery replacements, potentially offsetting initial cost savings. Manufacturing scale-up also presents significant capital expenditure requirements, with estimates suggesting $200-300 million investment needed for a commercial-scale sulfur cathode production facility.
Return on investment calculations indicate that despite higher initial capital costs, the payback period for sulfur cathode manufacturing could be competitive at 3-5 years, assuming technical hurdles regarding cycle life and energy density are adequately addressed. Sensitivity analysis shows that commercial viability is particularly dependent on achieving cycle life improvements, with each 100-cycle improvement translating to approximately 15% better lifetime cost metrics.
Supply chain considerations further enhance the economic case for sulfur cathodes. Unlike cobalt and nickel, sulfur is widely available globally, often as a byproduct of petroleum refining, reducing supply chain risks and price volatility. This geographic distribution of resources could democratize battery manufacturing capabilities across regions currently disadvantaged by limited access to traditional battery materials.
Market entry strategies suggest that initial commercialization should target applications where frequent recharging is possible and weight advantages are valued, such as stationary storage or short-range electric vehicles. These segments offer more favorable economic conditions while the technology matures toward meeting the more demanding requirements of the mainstream electric vehicle market.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!