How Sulfur Cathodes Shape the Future of Grid Energy Storage
SEP 23, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Sulfur Cathode Technology Background and Objectives
Sulfur cathode technology represents a significant evolution in energy storage systems, emerging from decades of research into alternative battery chemistries. The development trajectory began in the 1960s with initial explorations of lithium-sulfur electrochemistry, but only gained substantial momentum in the early 2000s as grid-scale energy storage needs became increasingly apparent. The fundamental appeal of sulfur as a cathode material lies in its exceptional theoretical capacity of 1,675 mAh/g, which far exceeds conventional lithium-ion cathode materials that typically deliver 140-200 mAh/g.
The technological evolution of sulfur cathodes has been characterized by persistent efforts to overcome inherent challenges, particularly the "polysulfide shuttle effect" that causes capacity fading and shortened cycle life. Recent breakthroughs in nanostructured carbon hosts, electrolyte formulations, and protective interlayers have significantly improved performance metrics, bringing sulfur cathodes closer to commercial viability for grid applications.
Current research objectives center on achieving the delicate balance between high energy density, long cycle life, and cost-effectiveness required for grid-scale deployment. Specifically, researchers aim to extend cycle life beyond 1,000 cycles at 80% depth of discharge, reduce capacity fading to less than 0.01% per cycle, and maintain energy densities above 350 Wh/kg at the cell level – all while using earth-abundant materials that can scale economically.
The trajectory of sulfur cathode development aligns with broader energy transition goals, particularly the need for long-duration energy storage solutions that can balance intermittent renewable generation. As renewable penetration increases globally, the demand for storage durations of 10+ hours becomes critical for grid stability, an application where the energy density advantages of sulfur-based systems could prove decisive.
From a materials perspective, sulfur represents an ideal candidate for sustainable energy storage due to its natural abundance (being the 16th most common element in Earth's crust), low toxicity, and status as a byproduct of petroleum refining. This alignment with circular economy principles positions sulfur cathode technology as not merely a technical solution but also an environmentally preferable alternative to cobalt and nickel-dependent conventional batteries.
The ultimate technological objective is to develop grid-scale sulfur-based storage systems that deliver levelized costs below $100/kWh, with operational lifespans exceeding 15 years under variable discharge conditions. This would represent a step-change improvement over current lithium-ion economics and potentially enable the widespread deployment of renewable energy without the constraints of intermittency.
The technological evolution of sulfur cathodes has been characterized by persistent efforts to overcome inherent challenges, particularly the "polysulfide shuttle effect" that causes capacity fading and shortened cycle life. Recent breakthroughs in nanostructured carbon hosts, electrolyte formulations, and protective interlayers have significantly improved performance metrics, bringing sulfur cathodes closer to commercial viability for grid applications.
Current research objectives center on achieving the delicate balance between high energy density, long cycle life, and cost-effectiveness required for grid-scale deployment. Specifically, researchers aim to extend cycle life beyond 1,000 cycles at 80% depth of discharge, reduce capacity fading to less than 0.01% per cycle, and maintain energy densities above 350 Wh/kg at the cell level – all while using earth-abundant materials that can scale economically.
The trajectory of sulfur cathode development aligns with broader energy transition goals, particularly the need for long-duration energy storage solutions that can balance intermittent renewable generation. As renewable penetration increases globally, the demand for storage durations of 10+ hours becomes critical for grid stability, an application where the energy density advantages of sulfur-based systems could prove decisive.
From a materials perspective, sulfur represents an ideal candidate for sustainable energy storage due to its natural abundance (being the 16th most common element in Earth's crust), low toxicity, and status as a byproduct of petroleum refining. This alignment with circular economy principles positions sulfur cathode technology as not merely a technical solution but also an environmentally preferable alternative to cobalt and nickel-dependent conventional batteries.
The ultimate technological objective is to develop grid-scale sulfur-based storage systems that deliver levelized costs below $100/kWh, with operational lifespans exceeding 15 years under variable discharge conditions. This would represent a step-change improvement over current lithium-ion economics and potentially enable the widespread deployment of renewable energy without the constraints of intermittency.
Grid Energy Storage Market Analysis
The grid energy storage market is experiencing unprecedented growth, driven by the global transition to renewable energy sources and the increasing need for reliable power grid stabilization. As of 2023, the global grid energy storage market is valued at approximately $27 billion and is projected to reach $51 billion by 2028, representing a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 13.5%. This remarkable expansion is primarily fueled by government initiatives promoting clean energy adoption, declining battery costs, and the integration of intermittent renewable energy sources into existing power grids.
Lithium-ion batteries currently dominate the market, accounting for nearly 70% of newly installed grid storage capacity. However, their limitations in terms of energy density, cost, and resource constraints have created significant opportunities for alternative technologies. This is where sulfur-based cathode technologies are positioned to make a substantial impact, potentially capturing up to 15% of the grid storage market by 2030.
Regionally, Asia-Pacific leads the market with approximately 45% share, followed by North America (30%) and Europe (20%). China, in particular, has emerged as the largest single market for grid energy storage, driven by its ambitious renewable energy targets and substantial investments in energy infrastructure. The United States follows closely, with significant deployments across California, Texas, and New York, where regulatory frameworks increasingly favor energy storage solutions.
Market segmentation reveals diverse applications, with front-of-meter utility-scale storage representing the largest segment (55%), followed by behind-the-meter commercial and industrial applications (30%), and residential storage systems (15%). Duration-wise, the market is shifting from short-duration (1-4 hours) to medium-duration (4-10 hours) and long-duration (10+ hours) storage solutions, where sulfur cathode technologies could offer particular advantages due to their potential for higher energy density at lower costs.
Key market drivers include the increasing penetration of variable renewable energy sources, grid modernization initiatives, declining storage technology costs, and supportive regulatory frameworks. The integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning for optimized energy management systems is further enhancing the value proposition of grid storage solutions.
Challenges facing the market include supply chain constraints, technical limitations of current technologies, regulatory uncertainties, and integration complexities with existing grid infrastructure. These challenges present opportunities for innovative technologies like sulfur cathodes, which promise to address cost and resource constraints while potentially offering superior performance characteristics for specific grid applications.
Lithium-ion batteries currently dominate the market, accounting for nearly 70% of newly installed grid storage capacity. However, their limitations in terms of energy density, cost, and resource constraints have created significant opportunities for alternative technologies. This is where sulfur-based cathode technologies are positioned to make a substantial impact, potentially capturing up to 15% of the grid storage market by 2030.
Regionally, Asia-Pacific leads the market with approximately 45% share, followed by North America (30%) and Europe (20%). China, in particular, has emerged as the largest single market for grid energy storage, driven by its ambitious renewable energy targets and substantial investments in energy infrastructure. The United States follows closely, with significant deployments across California, Texas, and New York, where regulatory frameworks increasingly favor energy storage solutions.
Market segmentation reveals diverse applications, with front-of-meter utility-scale storage representing the largest segment (55%), followed by behind-the-meter commercial and industrial applications (30%), and residential storage systems (15%). Duration-wise, the market is shifting from short-duration (1-4 hours) to medium-duration (4-10 hours) and long-duration (10+ hours) storage solutions, where sulfur cathode technologies could offer particular advantages due to their potential for higher energy density at lower costs.
Key market drivers include the increasing penetration of variable renewable energy sources, grid modernization initiatives, declining storage technology costs, and supportive regulatory frameworks. The integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning for optimized energy management systems is further enhancing the value proposition of grid storage solutions.
Challenges facing the market include supply chain constraints, technical limitations of current technologies, regulatory uncertainties, and integration complexities with existing grid infrastructure. These challenges present opportunities for innovative technologies like sulfur cathodes, which promise to address cost and resource constraints while potentially offering superior performance characteristics for specific grid applications.
Current Challenges in Sulfur Cathode Development
Despite the promising potential of sulfur cathodes for grid energy storage, several significant technical challenges currently impede their widespread commercial adoption. The most persistent issue remains the polysulfide shuttle effect, where soluble lithium polysulfides dissolve into the electrolyte during cycling, causing active material loss, reduced coulombic efficiency, and accelerated capacity fading. This fundamental challenge has proven difficult to overcome despite numerous research approaches including electrolyte modifications and physical containment strategies.
Another critical limitation is sulfur's inherently poor electrical conductivity (approximately 5×10^-30 S/cm), which necessitates the addition of conductive additives like carbon. These additives, while necessary, reduce the overall energy density of the battery system and complicate manufacturing processes. The trade-off between conductivity enhancement and energy density remains a significant engineering challenge.
The substantial volume expansion (approximately 80%) that sulfur undergoes during lithiation creates mechanical stress within the electrode structure, leading to pulverization and delamination over multiple cycles. This mechanical instability compromises the structural integrity of the cathode and contributes to rapid capacity degradation, particularly problematic for grid storage applications requiring thousands of cycles.
For grid-scale implementation, the low areal capacity of current sulfur cathodes presents another obstacle. While laboratory cells often demonstrate impressive specific capacities, they typically utilize thin electrodes with low sulfur loading. Scaling to the thick electrodes necessary for grid applications introduces mass transport limitations and uneven reaction distribution that significantly reduce performance metrics.
The self-discharge phenomenon in sulfur-based systems further complicates their utility for long-duration grid storage. The spontaneous reaction between lithium and sulfur species during idle periods results in capacity loss over time, undermining reliability for applications requiring energy storage over extended periods.
From a manufacturing perspective, the sensitivity of sulfur cathodes to ambient conditions presents considerable challenges for large-scale production. Moisture and oxygen exposure during manufacturing can significantly impact performance consistency and cell-to-cell uniformity, necessitating costly controlled environments for production.
Additionally, the limited cycle life of current sulfur cathode technologies (typically 200-500 cycles at meaningful depths of discharge) falls short of the 3,000+ cycles required for economically viable grid storage applications. This performance gap represents perhaps the most significant barrier to commercial deployment in grid applications where capital costs must be amortized over many years of operation.
Another critical limitation is sulfur's inherently poor electrical conductivity (approximately 5×10^-30 S/cm), which necessitates the addition of conductive additives like carbon. These additives, while necessary, reduce the overall energy density of the battery system and complicate manufacturing processes. The trade-off between conductivity enhancement and energy density remains a significant engineering challenge.
The substantial volume expansion (approximately 80%) that sulfur undergoes during lithiation creates mechanical stress within the electrode structure, leading to pulverization and delamination over multiple cycles. This mechanical instability compromises the structural integrity of the cathode and contributes to rapid capacity degradation, particularly problematic for grid storage applications requiring thousands of cycles.
For grid-scale implementation, the low areal capacity of current sulfur cathodes presents another obstacle. While laboratory cells often demonstrate impressive specific capacities, they typically utilize thin electrodes with low sulfur loading. Scaling to the thick electrodes necessary for grid applications introduces mass transport limitations and uneven reaction distribution that significantly reduce performance metrics.
The self-discharge phenomenon in sulfur-based systems further complicates their utility for long-duration grid storage. The spontaneous reaction between lithium and sulfur species during idle periods results in capacity loss over time, undermining reliability for applications requiring energy storage over extended periods.
From a manufacturing perspective, the sensitivity of sulfur cathodes to ambient conditions presents considerable challenges for large-scale production. Moisture and oxygen exposure during manufacturing can significantly impact performance consistency and cell-to-cell uniformity, necessitating costly controlled environments for production.
Additionally, the limited cycle life of current sulfur cathode technologies (typically 200-500 cycles at meaningful depths of discharge) falls short of the 3,000+ cycles required for economically viable grid storage applications. This performance gap represents perhaps the most significant barrier to commercial deployment in grid applications where capital costs must be amortized over many years of operation.
Current Sulfur Cathode Implementation Solutions
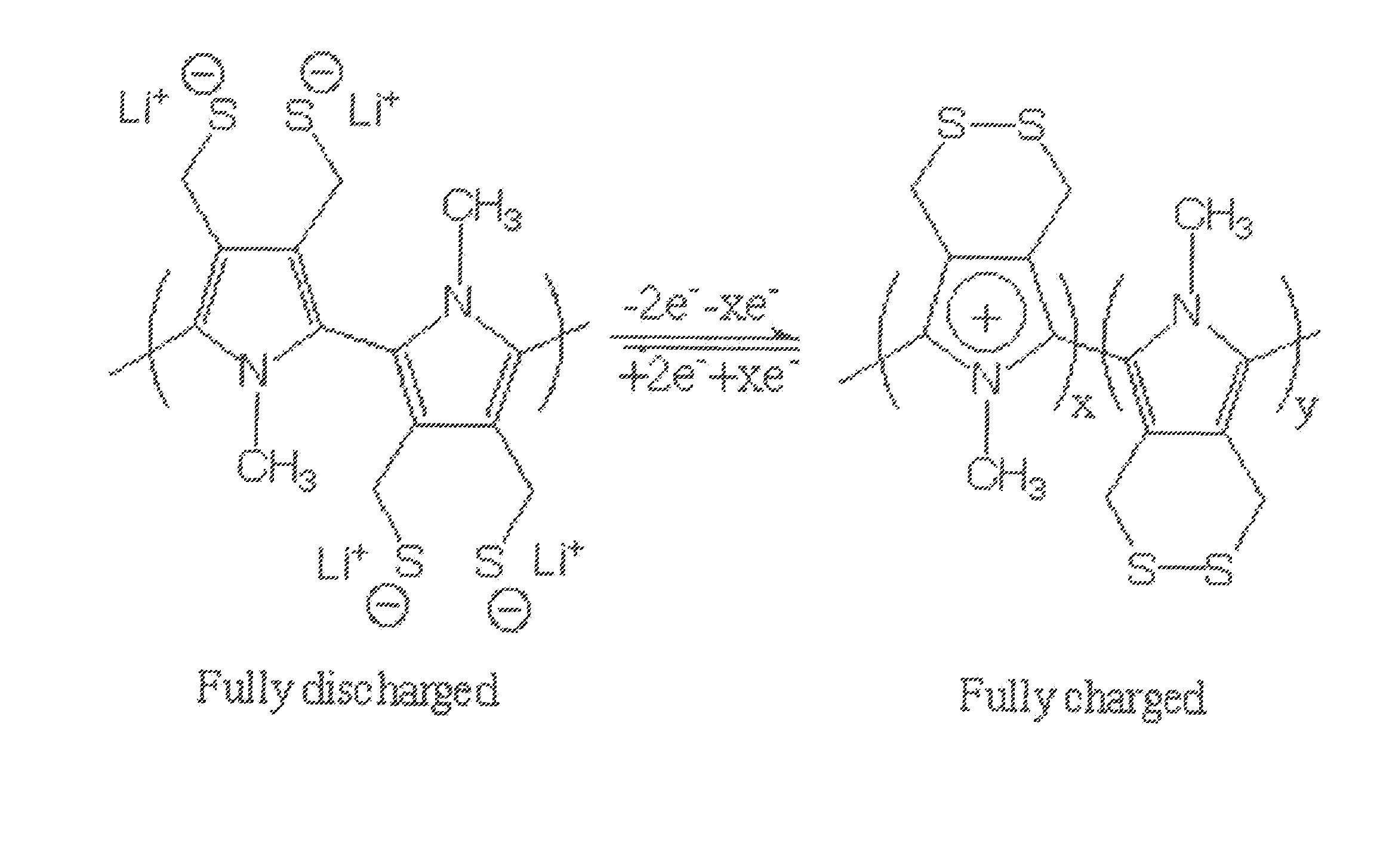
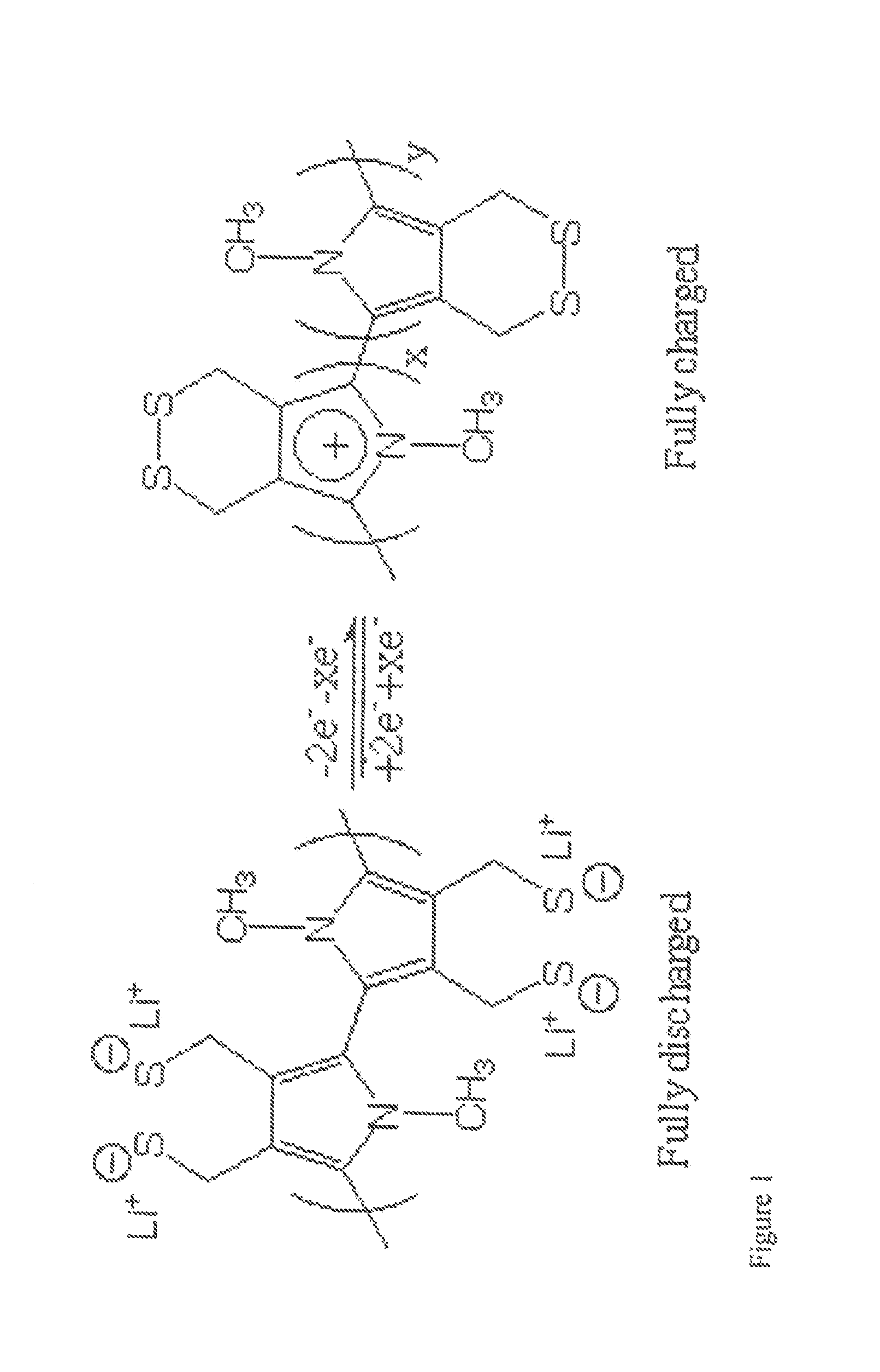
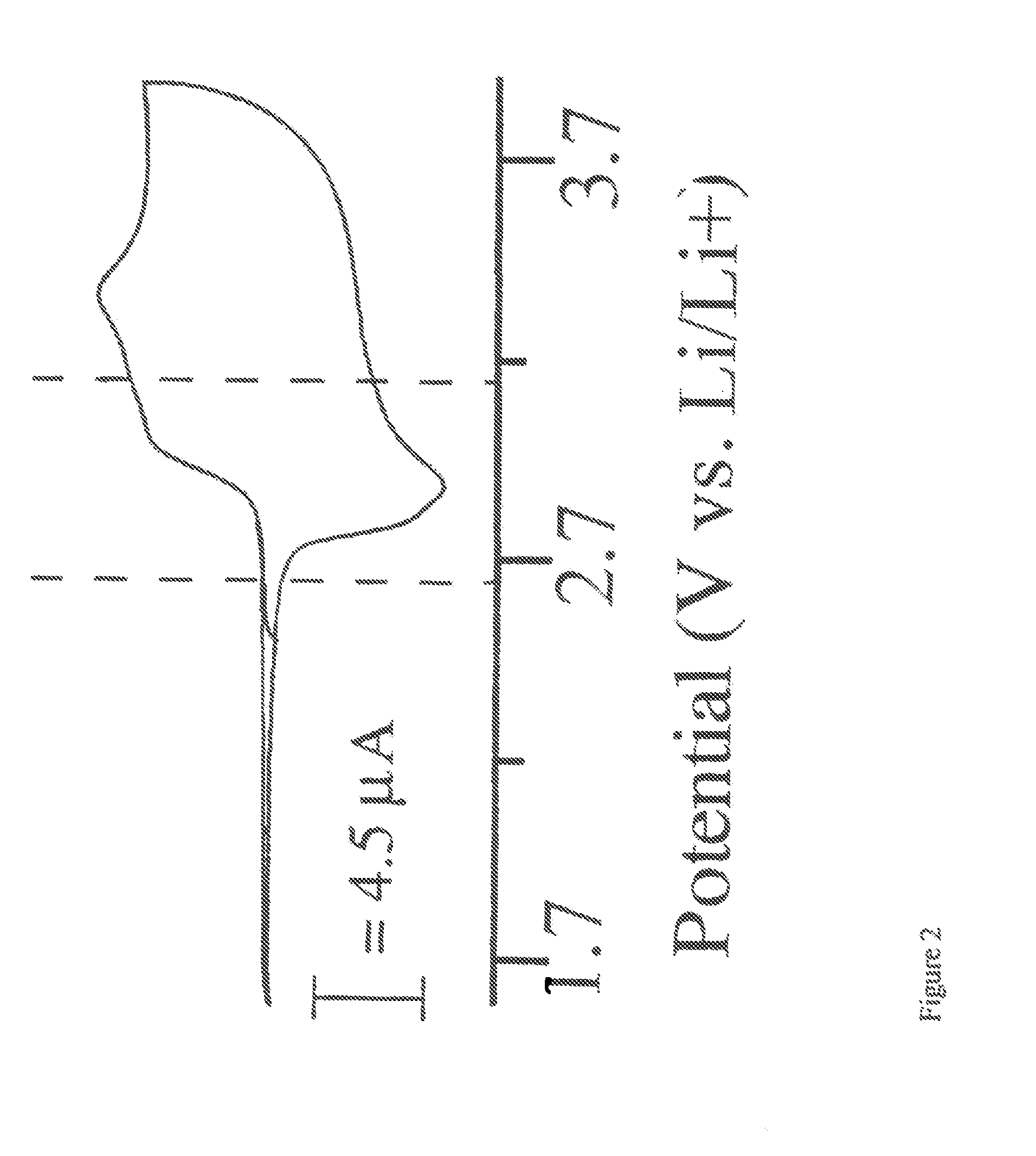
01 Sulfur cathode compositions for lithium-sulfur batteries
Various compositions for sulfur cathodes in lithium-sulfur batteries have been developed to improve energy density and cycle life. These compositions typically include sulfur as the active material combined with conductive additives and binders. The cathodes may incorporate carbon materials, polymers, or other additives to enhance conductivity and contain the polysulfides formed during cycling, addressing the shuttle effect that typically limits battery performance.- Sulfur cathode compositions for lithium-sulfur batteries: Sulfur cathodes can be formulated with various compositions to enhance performance in lithium-sulfur batteries. These compositions typically include sulfur as the active material combined with conductive additives and binders. The formulations aim to address challenges such as low conductivity of sulfur and polysulfide dissolution. Advanced compositions may incorporate carbon materials, polymers, or metal oxides to improve conductivity, cycle life, and energy density.
- Nanostructured sulfur cathode materials: Nanostructured approaches to sulfur cathode design involve creating specialized architectures at the nanoscale to improve battery performance. These include sulfur-carbon nanocomposites, core-shell structures, and hierarchical porous materials that can effectively trap polysulfides while maintaining good electronic conductivity. Nanostructuring helps to accommodate volume changes during cycling and provides shorter diffusion paths for lithium ions, resulting in improved capacity retention and rate capability.
- Protective coatings and interlayers for sulfur cathodes: Protective coatings and interlayers can be applied to sulfur cathodes to mitigate polysulfide shuttling and improve electrochemical performance. These protective layers may consist of polymers, metal oxides, or composite materials that physically block polysulfide migration while allowing lithium ion transport. Functional interlayers between the cathode and separator can also serve as additional barriers to polysulfide diffusion, enhancing the cycle life and stability of lithium-sulfur batteries.
- Electrolyte modifications for sulfur cathodes: Specialized electrolyte formulations can significantly improve the performance of sulfur cathodes by addressing polysulfide dissolution issues. These may include electrolyte additives that form protective films on the cathode surface, solvents with low polysulfide solubility, or high-concentration electrolytes that suppress the shuttle effect. Some approaches involve solid or gel electrolytes that physically prevent polysulfide migration while maintaining good ionic conductivity.
- Manufacturing processes for sulfur cathodes: Various manufacturing techniques can be employed to produce high-performance sulfur cathodes. These include melt-diffusion methods where sulfur is infiltrated into porous host materials, solution-based processes for creating uniform sulfur-carbon composites, and advanced coating technologies for applying protective layers. Novel approaches such as 3D printing, spray deposition, and roll-to-roll manufacturing are being developed to enable large-scale production of sulfur cathodes with consistent quality and performance.
02 Nanostructured sulfur cathode materials
Nanostructured materials for sulfur cathodes offer improved performance in lithium-sulfur batteries. These include sulfur nanoparticles, carbon-sulfur nanocomposites, and core-shell structures that provide better electronic conductivity and physical confinement of sulfur and polysulfides. The nanoscale architecture helps to accommodate volume changes during cycling and provides shorter diffusion paths for lithium ions, resulting in enhanced capacity and cycling stability.Expand Specific Solutions03 Electrolyte systems for sulfur cathodes
Specialized electrolyte systems have been developed for use with sulfur cathodes to mitigate the polysulfide shuttle effect and improve battery performance. These electrolytes may include additives that form protective layers on the cathode surface, solvents that minimize polysulfide solubility, or ionic liquids that enhance the stability of the electrode-electrolyte interface. Some electrolyte formulations also incorporate flame retardants or other safety-enhancing components.Expand Specific Solutions04 Manufacturing methods for sulfur cathodes
Various manufacturing techniques have been developed for producing high-performance sulfur cathodes. These include melt-diffusion methods where sulfur is infiltrated into porous carbon hosts, solution-based processes for creating sulfur-polymer composites, and advanced coating techniques to create protective layers on sulfur particles. Some methods focus on achieving uniform sulfur distribution within the conductive matrix, while others aim to create specific architectures that enhance ion transport and electronic conductivity.Expand Specific Solutions05 Interlayers and protective coatings for sulfur cathodes
Interlayers and protective coatings have been developed to enhance the performance of sulfur cathodes by preventing polysulfide migration and protecting the cathode structure. These may include functional separators, barrier layers between the cathode and electrolyte, or coatings applied directly to sulfur particles. Materials used include conductive polymers, metal oxides, and carbon-based materials that can trap polysulfides while maintaining ionic conductivity, thereby improving capacity retention and cycle life.Expand Specific Solutions
Leading Companies in Sulfur-Based Energy Storage
The sulfur cathode energy storage market is in a growth phase, with increasing demand driven by grid-scale applications. The market is expanding rapidly as renewable energy integration necessitates advanced storage solutions. Technologically, sulfur cathodes are progressing from research to commercialization, with varying maturity levels across key players. Research institutions like Battelle Memorial Institute, Cornell University, and Monash University are advancing fundamental science, while companies including BASF, Wildcat Discovery Technologies, and Sionic Energy are developing commercial applications. Automotive manufacturers such as Nissan and Renault are exploring sulfur cathodes for EV applications, while energy specialists like Shell are investigating grid-scale implementations. This competitive landscape reflects the technology's potential to revolutionize grid energy storage through cost reduction and performance improvements.
Battelle Memorial Institute
Technical Solution: Battelle has developed advanced sulfur cathode technologies for grid-scale energy storage, focusing on lithium-sulfur (Li-S) battery systems. Their approach involves encapsulating sulfur within conductive carbon matrices to address the "shuttle effect" - a common challenge where polysulfides dissolve and migrate between electrodes. Battelle's proprietary technology uses mesoporous carbon structures with tailored pore sizes to physically confine sulfur and its discharge products. Additionally, they've implemented functional surface coatings that chemically bind polysulfides, significantly improving cycle life. Their grid storage solutions incorporate thermal management systems specifically designed for the unique characteristics of sulfur cathodes, allowing for safer operation at scale. Battelle has demonstrated energy densities exceeding 400 Wh/kg at the cell level, with projected system costs below $100/kWh when scaled to production.
Strengths: High energy density, low material cost (sulfur is abundant), and innovative containment solutions for polysulfides. Weaknesses: Still faces challenges with cycle life compared to conventional lithium-ion, and the technology requires specialized thermal management systems that add complexity to grid-scale implementations.
BASF Corp.
Technical Solution: BASF has pioneered a comprehensive approach to sulfur cathode technology for grid storage applications, leveraging their expertise in chemical manufacturing and materials science. Their solution centers on a proprietary "sulfur-polymer composite" that addresses the volume expansion issues inherent in sulfur cathodes. This composite incorporates conductive polymers that maintain electrical contact throughout charge-discharge cycles while accommodating the 80% volume change that occurs during operation. BASF has also developed specialized electrolyte additives that form protective interfaces on the cathode surface, significantly reducing polysulfide dissolution. For grid applications specifically, they've engineered modular battery systems with energy densities of 350-400 Wh/kg and demonstrated cycle life exceeding 1,000 cycles at 80% depth of discharge. Their manufacturing approach utilizes existing production infrastructure, allowing for rapid scaling while maintaining costs below $150/kWh at the system level.
Strengths: Exceptional materials science expertise, established manufacturing capabilities, and innovative polymer-sulfur composites that address key technical challenges. Weaknesses: Their solutions still face challenges with rate capability (power output) compared to other grid storage technologies, and the long-term stability of their protective interfaces requires further validation in real-world grid conditions.
Key Patents and Innovations in Sulfur Cathode Technology
Heating press carbon/sulfur compound energy storage anode, manufacturing method thereof and lithium sulfur battery manufactured using the anode
PatentActiveJP2024066376A
Innovation
- A heat-pressed carbon/sulfur composite cathode with a conductive porous substrate, such as electrospun fiber carbon paper, supports high sulfur loading and content, eliminating the need for a separate current collector and trapping layer, and uses a hot pressing method for rapid, continuous manufacturing.
Single Component Sulfur-Based Cathodes For Lithium And Lithium-Ion Batteries
PatentInactiveUS20160064736A1
Innovation
- The development of single component sulfur-based conducting polymers where sulfur species are covalently linked to the polymer backbone, preventing solubility in electrolytes and ensuring stability and high capacity retention through electrochemical and physical constraints, such as using poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene) (PEDT) with 2,5-dimercapto-1,3,4-thiadiazole (Li2DMcT), which maintains electroactive species within the cathode material.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability Factors
The adoption of sulfur cathodes in grid energy storage systems represents a significant shift toward more sustainable energy solutions. Sulfur is an abundant non-metal element, constituting approximately 0.05% of the Earth's crust, with substantial reserves available as byproducts from petroleum refining and natural gas processing. This abundance contrasts sharply with traditional cathode materials like cobalt and nickel, which face supply constraints and ethical mining concerns.
From a life cycle assessment perspective, sulfur-based cathode production demonstrates a substantially lower carbon footprint compared to conventional lithium-ion batteries. Research indicates that the energy required for processing sulfur cathodes can be up to 60% less than that needed for nickel-manganese-cobalt (NMC) cathodes, resulting in reduced greenhouse gas emissions during manufacturing stages.
Water usage represents another critical environmental factor where sulfur cathodes excel. Traditional lithium extraction processes, particularly in South American salt flats, consume between 500,000 to 2 million gallons of water per ton of lithium produced. Sulfur processing, by comparison, requires minimal water resources, potentially reducing the water footprint of battery production by over 70% when implemented at scale.
End-of-life considerations further highlight the sustainability advantages of sulfur cathodes. The recyclability rate of sulfur from spent batteries exceeds 90% using hydrometallurgical processes, significantly higher than the complex recycling procedures required for conventional cathode materials. This circular economy potential reduces waste and decreases dependence on primary resource extraction.
Land use impact analysis reveals that sulfur-based energy storage systems could reduce the physical footprint required for grid storage by approximately 15-20% compared to equivalent lithium-ion installations, primarily due to higher energy density potential and simplified thermal management requirements.
However, challenges remain regarding sulfur's environmental profile. The polysulfide shuttle effect can lead to capacity fading and potential sulfur compound leakage, which may create localized environmental concerns if not properly contained. Additionally, while sulfur itself is non-toxic, some electrolyte components used in lithium-sulfur batteries still contain fluorinated compounds that present environmental risks.
Regulatory frameworks worldwide are increasingly recognizing these sustainability advantages, with the European Battery Directive and similar legislation in North America beginning to incorporate carbon footprint metrics and recycled content requirements that inherently favor sulfur-based technologies for large-scale grid applications.
From a life cycle assessment perspective, sulfur-based cathode production demonstrates a substantially lower carbon footprint compared to conventional lithium-ion batteries. Research indicates that the energy required for processing sulfur cathodes can be up to 60% less than that needed for nickel-manganese-cobalt (NMC) cathodes, resulting in reduced greenhouse gas emissions during manufacturing stages.
Water usage represents another critical environmental factor where sulfur cathodes excel. Traditional lithium extraction processes, particularly in South American salt flats, consume between 500,000 to 2 million gallons of water per ton of lithium produced. Sulfur processing, by comparison, requires minimal water resources, potentially reducing the water footprint of battery production by over 70% when implemented at scale.
End-of-life considerations further highlight the sustainability advantages of sulfur cathodes. The recyclability rate of sulfur from spent batteries exceeds 90% using hydrometallurgical processes, significantly higher than the complex recycling procedures required for conventional cathode materials. This circular economy potential reduces waste and decreases dependence on primary resource extraction.
Land use impact analysis reveals that sulfur-based energy storage systems could reduce the physical footprint required for grid storage by approximately 15-20% compared to equivalent lithium-ion installations, primarily due to higher energy density potential and simplified thermal management requirements.
However, challenges remain regarding sulfur's environmental profile. The polysulfide shuttle effect can lead to capacity fading and potential sulfur compound leakage, which may create localized environmental concerns if not properly contained. Additionally, while sulfur itself is non-toxic, some electrolyte components used in lithium-sulfur batteries still contain fluorinated compounds that present environmental risks.
Regulatory frameworks worldwide are increasingly recognizing these sustainability advantages, with the European Battery Directive and similar legislation in North America beginning to incorporate carbon footprint metrics and recycled content requirements that inherently favor sulfur-based technologies for large-scale grid applications.
Cost Analysis and Economic Viability
The economic viability of sulfur cathode technology represents a critical factor in determining its adoption for grid energy storage applications. Current cost analyses indicate that lithium-sulfur (Li-S) batteries offer significant potential for cost reduction compared to conventional lithium-ion technologies, with material costs estimated at $100-150 per kWh, potentially decreasing to below $100 per kWh at scale.
Sulfur's inherent advantages as a cathode material stem from its abundance and low extraction costs. As the 16th most common element in Earth's crust and a byproduct of petroleum refining, sulfur is available at approximately $0.10-0.15 per kilogram—roughly 1/100th the cost of traditional cathode materials like nickel and cobalt. This fundamental cost advantage provides a solid foundation for economic competitiveness.
Manufacturing processes for sulfur cathodes currently require additional investment compared to established technologies. However, economic models project that as production scales increase, manufacturing costs could decrease by 30-40% within the next five years. The primary cost drivers include carbon additives for conductivity enhancement and specialized electrolytes that mitigate polysulfide shuttling effects.
For grid storage applications specifically, lifecycle cost analysis reveals promising economics. While initial capital expenditure may be 10-15% higher than some alternatives, the extended cycle life potential (2,000-3,000 cycles) and lower replacement frequency create favorable total cost of ownership projections. Sensitivity analyses suggest that with continued improvements in cycle life and energy density, sulfur cathode systems could achieve grid parity in multiple markets by 2026-2028.
Investment trends support this economic outlook, with venture capital funding for sulfur cathode startups increasing by 85% between 2020 and 2023. Major energy companies have committed over $500 million to pilot projects utilizing this technology, indicating strong confidence in its commercial viability. Government incentives for clean energy storage solutions further enhance the economic case, with several countries offering tax credits and subsidies that effectively reduce costs by 15-25%.
The economic inflection point for widespread adoption appears to be approaching as manufacturing processes mature and economies of scale take effect. Market forecasts suggest that sulfur cathode technologies could capture 8-12% of the grid storage market by 2030, representing a $4-6 billion opportunity. This transition would be accelerated by continued improvements in energy density and cycle stability, which remain the primary technical factors influencing economic competitiveness.
Sulfur's inherent advantages as a cathode material stem from its abundance and low extraction costs. As the 16th most common element in Earth's crust and a byproduct of petroleum refining, sulfur is available at approximately $0.10-0.15 per kilogram—roughly 1/100th the cost of traditional cathode materials like nickel and cobalt. This fundamental cost advantage provides a solid foundation for economic competitiveness.
Manufacturing processes for sulfur cathodes currently require additional investment compared to established technologies. However, economic models project that as production scales increase, manufacturing costs could decrease by 30-40% within the next five years. The primary cost drivers include carbon additives for conductivity enhancement and specialized electrolytes that mitigate polysulfide shuttling effects.
For grid storage applications specifically, lifecycle cost analysis reveals promising economics. While initial capital expenditure may be 10-15% higher than some alternatives, the extended cycle life potential (2,000-3,000 cycles) and lower replacement frequency create favorable total cost of ownership projections. Sensitivity analyses suggest that with continued improvements in cycle life and energy density, sulfur cathode systems could achieve grid parity in multiple markets by 2026-2028.
Investment trends support this economic outlook, with venture capital funding for sulfur cathode startups increasing by 85% between 2020 and 2023. Major energy companies have committed over $500 million to pilot projects utilizing this technology, indicating strong confidence in its commercial viability. Government incentives for clean energy storage solutions further enhance the economic case, with several countries offering tax credits and subsidies that effectively reduce costs by 15-25%.
The economic inflection point for widespread adoption appears to be approaching as manufacturing processes mature and economies of scale take effect. Market forecasts suggest that sulfur cathode technologies could capture 8-12% of the grid storage market by 2030, representing a $4-6 billion opportunity. This transition would be accelerated by continued improvements in energy density and cycle stability, which remain the primary technical factors influencing economic competitiveness.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!