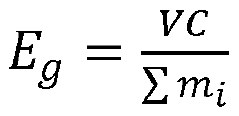Sulfur Cathodes Potentials in Autonomous Vehicle Systems
SEP 23, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Sulfur Cathode Technology Background and Objectives
Lithium-sulfur (Li-S) batteries have emerged as a promising energy storage technology over the past two decades, with their development trajectory closely aligned with the evolution of electric and autonomous vehicle systems. The fundamental attraction of sulfur cathodes lies in their theoretical energy density of 2,600 Wh/kg, which significantly surpasses the 387 Wh/kg limit of conventional lithium-ion batteries with intercalation cathodes. This substantial energy density advantage positions sulfur cathodes as a potentially transformative technology for next-generation autonomous vehicle power systems.
The historical development of sulfur cathodes can be traced back to the 1960s, though significant research momentum only began building in the early 2000s when the limitations of conventional lithium-ion technology became apparent for advanced transportation applications. The technological evolution has been characterized by progressive improvements in cycle life, capacity retention, and practical energy density, with major breakthroughs occurring in electrolyte formulations and cathode architectures around 2009-2013.
Current research objectives for sulfur cathodes in autonomous vehicle applications focus on several critical parameters. Primary among these is extending cycle life beyond 1,000 cycles while maintaining high capacity retention—a necessity for the intensive duty cycles of autonomous vehicle operations. Additionally, researchers aim to mitigate the "shuttle effect" of polysulfide dissolution, which has historically limited the commercial viability of Li-S technology.
Another key objective involves improving the volumetric energy density, as autonomous vehicles require compact power sources that do not compromise interior space or vehicle design. Current targets seek to achieve practical volumetric energy densities exceeding 500 Wh/L, representing a significant improvement over existing lithium-ion solutions while leveraging sulfur's inherent advantages.
Temperature performance represents another critical research direction, as autonomous vehicles must operate reliably across diverse environmental conditions. Current sulfur cathode technologies exhibit suboptimal performance at low temperatures, necessitating innovations in electrolyte composition and cathode structure to ensure consistent power delivery in cold environments.
The integration of sulfur cathodes with autonomous vehicle systems also presents unique objectives related to fast charging capabilities and safety profiles. The high power demands during rapid acceleration and the potential for extended idle periods in autonomous fleet operations create specific performance requirements that differ from conventional electric vehicles.
Looking forward, the technology roadmap for sulfur cathodes in autonomous vehicles aims to achieve commercial viability by 2025-2027, with incremental improvements in energy density, cycle life, and manufacturing scalability. This timeline aligns with industry projections for widespread autonomous vehicle deployment, positioning sulfur cathode technology as a potential enabler for extended-range autonomous operations.
The historical development of sulfur cathodes can be traced back to the 1960s, though significant research momentum only began building in the early 2000s when the limitations of conventional lithium-ion technology became apparent for advanced transportation applications. The technological evolution has been characterized by progressive improvements in cycle life, capacity retention, and practical energy density, with major breakthroughs occurring in electrolyte formulations and cathode architectures around 2009-2013.
Current research objectives for sulfur cathodes in autonomous vehicle applications focus on several critical parameters. Primary among these is extending cycle life beyond 1,000 cycles while maintaining high capacity retention—a necessity for the intensive duty cycles of autonomous vehicle operations. Additionally, researchers aim to mitigate the "shuttle effect" of polysulfide dissolution, which has historically limited the commercial viability of Li-S technology.
Another key objective involves improving the volumetric energy density, as autonomous vehicles require compact power sources that do not compromise interior space or vehicle design. Current targets seek to achieve practical volumetric energy densities exceeding 500 Wh/L, representing a significant improvement over existing lithium-ion solutions while leveraging sulfur's inherent advantages.
Temperature performance represents another critical research direction, as autonomous vehicles must operate reliably across diverse environmental conditions. Current sulfur cathode technologies exhibit suboptimal performance at low temperatures, necessitating innovations in electrolyte composition and cathode structure to ensure consistent power delivery in cold environments.
The integration of sulfur cathodes with autonomous vehicle systems also presents unique objectives related to fast charging capabilities and safety profiles. The high power demands during rapid acceleration and the potential for extended idle periods in autonomous fleet operations create specific performance requirements that differ from conventional electric vehicles.
Looking forward, the technology roadmap for sulfur cathodes in autonomous vehicles aims to achieve commercial viability by 2025-2027, with incremental improvements in energy density, cycle life, and manufacturing scalability. This timeline aligns with industry projections for widespread autonomous vehicle deployment, positioning sulfur cathode technology as a potential enabler for extended-range autonomous operations.
Market Analysis for Sulfur-Based Battery Applications in EVs
The electric vehicle (EV) market has experienced unprecedented growth over the past decade, with global sales reaching 10.5 million units in 2022, representing a 55% increase from the previous year. This surge has intensified the demand for more efficient, cost-effective, and sustainable battery technologies. Within this context, sulfur-based cathodes have emerged as a promising alternative to conventional lithium-ion batteries, particularly for applications in autonomous vehicle systems where energy density and range requirements are critical factors.
Market research indicates that the global lithium-sulfur battery market is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate of 35.2% from 2023 to 2030, reaching a market value of $1.8 billion by the end of the forecast period. This growth is primarily driven by the superior theoretical energy density of sulfur cathodes (approximately 2,600 Wh/kg) compared to traditional lithium-ion batteries (250-300 Wh/kg), which could potentially extend EV range by up to 80%.
Consumer demand patterns reveal increasing preference for EVs with longer ranges and shorter charging times. A recent survey conducted across major automotive markets showed that 78% of potential EV buyers consider range anxiety as their primary concern, while 65% prioritize charging speed. Sulfur-based batteries address both concerns through higher energy density and potentially faster charging capabilities, positioning them as a highly attractive solution for next-generation EVs.
The commercial landscape for sulfur-based battery applications in EVs is currently dominated by startups and research institutions, with major battery manufacturers increasingly investing in R&D partnerships. Notable market entrants include OXIS Energy, Sion Power, and PolyPlus, who have demonstrated prototype sulfur-based batteries with energy densities exceeding 400 Wh/kg in controlled environments.
Regional analysis shows that Asia-Pacific currently leads in sulfur-based battery research and production capacity, with China, South Korea, and Japan accounting for approximately 65% of global patents in this technology. However, North America and Europe are rapidly expanding their capabilities through substantial government funding initiatives aimed at reducing dependency on imported battery technologies.
The economic viability of sulfur-based batteries is further enhanced by the abundance and low cost of sulfur as a raw material. Current estimates suggest that mass-produced lithium-sulfur batteries could potentially reduce battery costs by 30-40% compared to conventional lithium-ion technologies, addressing a critical barrier to widespread EV adoption.
Market research indicates that the global lithium-sulfur battery market is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate of 35.2% from 2023 to 2030, reaching a market value of $1.8 billion by the end of the forecast period. This growth is primarily driven by the superior theoretical energy density of sulfur cathodes (approximately 2,600 Wh/kg) compared to traditional lithium-ion batteries (250-300 Wh/kg), which could potentially extend EV range by up to 80%.
Consumer demand patterns reveal increasing preference for EVs with longer ranges and shorter charging times. A recent survey conducted across major automotive markets showed that 78% of potential EV buyers consider range anxiety as their primary concern, while 65% prioritize charging speed. Sulfur-based batteries address both concerns through higher energy density and potentially faster charging capabilities, positioning them as a highly attractive solution for next-generation EVs.
The commercial landscape for sulfur-based battery applications in EVs is currently dominated by startups and research institutions, with major battery manufacturers increasingly investing in R&D partnerships. Notable market entrants include OXIS Energy, Sion Power, and PolyPlus, who have demonstrated prototype sulfur-based batteries with energy densities exceeding 400 Wh/kg in controlled environments.
Regional analysis shows that Asia-Pacific currently leads in sulfur-based battery research and production capacity, with China, South Korea, and Japan accounting for approximately 65% of global patents in this technology. However, North America and Europe are rapidly expanding their capabilities through substantial government funding initiatives aimed at reducing dependency on imported battery technologies.
The economic viability of sulfur-based batteries is further enhanced by the abundance and low cost of sulfur as a raw material. Current estimates suggest that mass-produced lithium-sulfur batteries could potentially reduce battery costs by 30-40% compared to conventional lithium-ion technologies, addressing a critical barrier to widespread EV adoption.
Current Challenges in Sulfur Cathode Development
Despite the promising potential of lithium-sulfur (Li-S) batteries for autonomous vehicle applications, several significant technical challenges currently impede their widespread commercial adoption. The primary obstacle remains the "shuttle effect," where soluble polysulfide intermediates migrate between electrodes during cycling, causing rapid capacity fading and shortened battery lifespan. This phenomenon is particularly problematic in automotive applications where long-term reliability is essential for autonomous systems.
Material stability presents another critical challenge, as sulfur cathodes undergo substantial volume changes (up to 80%) during charge-discharge cycles, leading to mechanical stress and structural degradation. This expansion-contraction pattern compromises the electrode integrity and accelerates performance deterioration, making current designs unsuitable for the rigorous operational demands of autonomous vehicles.
The low electrical conductivity of sulfur (5×10^-30 S/cm) significantly limits electron transport within the cathode, resulting in poor rate capability and reduced power output. This limitation is particularly problematic for autonomous vehicles that require rapid power delivery during acceleration and high-computation driving scenarios.
Self-discharge issues further complicate Li-S battery implementation in autonomous systems. The dissolution of lithium polysulfides leads to unwanted chemical reactions when the battery is idle, causing energy loss and reducing the practical energy density. For autonomous vehicles that may experience irregular usage patterns or extended parking periods, this self-discharge behavior presents a significant reliability concern.
Temperature sensitivity remains another unresolved challenge, with Li-S batteries showing performance inconsistencies across the wide temperature range experienced by vehicles. Cold-weather performance is particularly problematic, with significant capacity loss and increased internal resistance at lower temperatures affecting system reliability.
Manufacturing scalability also presents substantial hurdles. Current production methods for high-quality sulfur cathodes involve complex processes that are difficult to scale economically. The lack of standardized, cost-effective manufacturing techniques impedes mass production necessary for automotive applications.
Safety concerns persist regarding the potential formation of hydrogen sulfide gas under certain failure conditions. While less prone to thermal runaway than conventional lithium-ion batteries, the unique failure modes of Li-S systems require specialized safety protocols and management systems that have not yet been fully developed for automotive implementation.
Addressing these interconnected challenges requires coordinated research efforts across materials science, electrochemistry, and engineering disciplines to develop viable sulfur cathode solutions capable of meeting the demanding requirements of autonomous vehicle systems.
Material stability presents another critical challenge, as sulfur cathodes undergo substantial volume changes (up to 80%) during charge-discharge cycles, leading to mechanical stress and structural degradation. This expansion-contraction pattern compromises the electrode integrity and accelerates performance deterioration, making current designs unsuitable for the rigorous operational demands of autonomous vehicles.
The low electrical conductivity of sulfur (5×10^-30 S/cm) significantly limits electron transport within the cathode, resulting in poor rate capability and reduced power output. This limitation is particularly problematic for autonomous vehicles that require rapid power delivery during acceleration and high-computation driving scenarios.
Self-discharge issues further complicate Li-S battery implementation in autonomous systems. The dissolution of lithium polysulfides leads to unwanted chemical reactions when the battery is idle, causing energy loss and reducing the practical energy density. For autonomous vehicles that may experience irregular usage patterns or extended parking periods, this self-discharge behavior presents a significant reliability concern.
Temperature sensitivity remains another unresolved challenge, with Li-S batteries showing performance inconsistencies across the wide temperature range experienced by vehicles. Cold-weather performance is particularly problematic, with significant capacity loss and increased internal resistance at lower temperatures affecting system reliability.
Manufacturing scalability also presents substantial hurdles. Current production methods for high-quality sulfur cathodes involve complex processes that are difficult to scale economically. The lack of standardized, cost-effective manufacturing techniques impedes mass production necessary for automotive applications.
Safety concerns persist regarding the potential formation of hydrogen sulfide gas under certain failure conditions. While less prone to thermal runaway than conventional lithium-ion batteries, the unique failure modes of Li-S systems require specialized safety protocols and management systems that have not yet been fully developed for automotive implementation.
Addressing these interconnected challenges requires coordinated research efforts across materials science, electrochemistry, and engineering disciplines to develop viable sulfur cathode solutions capable of meeting the demanding requirements of autonomous vehicle systems.
Current Technical Solutions for Sulfur Cathode Implementation
01 Sulfur cathode compositions for lithium-sulfur batteries
Sulfur cathodes can be formulated with various compositions to enhance performance in lithium-sulfur batteries. These compositions typically include sulfur as the active material combined with conductive additives and binders. The formulations aim to address challenges such as low conductivity of sulfur and polysulfide dissolution. Advanced compositions may incorporate carbon materials, polymers, or other additives to improve conductivity, cycle life, and energy density of the batteries.- Sulfur cathode compositions for lithium-sulfur batteries: Various compositions for sulfur cathodes in lithium-sulfur batteries have been developed to improve energy density and cycle life. These compositions typically include sulfur as the active material combined with conductive additives and binders. The cathodes may incorporate carbon materials, polymers, or other additives to enhance conductivity and contain the polysulfides formed during cycling, addressing the shuttle effect that typically reduces battery performance.
- Nanostructured sulfur cathode materials: Nanostructured approaches to sulfur cathode design involve creating specialized architectures at the nanoscale to improve sulfur utilization and polysulfide containment. These include core-shell structures, nanocomposites, and porous carbon frameworks that encapsulate sulfur. The nanostructured design helps to accommodate volume changes during cycling, improve electronic conductivity, and provide physical barriers to prevent polysulfide dissolution, resulting in enhanced capacity retention and cycle life.
- Protective coatings and interlayers for sulfur cathodes: Protective coatings and interlayers are applied to sulfur cathodes or between the cathode and separator to mitigate polysulfide shuttling. These can include polymer films, inorganic layers, or composite materials that act as physical or chemical barriers. The coatings help to trap polysulfides within the cathode region while still allowing lithium ion transport, thereby improving the coulombic efficiency and extending the cycle life of lithium-sulfur batteries.
- Electrolyte modifications for sulfur cathodes: Specialized electrolyte formulations are developed to work synergistically with sulfur cathodes. These may include additives that form protective films on the cathode surface, solvents with reduced polysulfide solubility, or ionic liquids that modify the electrochemical behavior of the system. The electrolyte modifications aim to suppress the shuttle effect, enhance the stability of the cathode-electrolyte interface, and improve the overall performance of lithium-sulfur batteries.
- Manufacturing processes for sulfur cathodes: Various manufacturing techniques are employed to produce high-performance sulfur cathodes, including melt-diffusion methods, solution-based processes, and advanced deposition techniques. These processes focus on achieving uniform sulfur distribution within the conductive matrix, optimizing the cathode microstructure, and ensuring good adhesion to current collectors. Scalable manufacturing approaches are particularly important for commercial viability of lithium-sulfur batteries.
02 Nanostructured sulfur cathode materials
Nanostructured materials are used in sulfur cathodes to improve electrochemical performance. These include sulfur-carbon nanocomposites, nanoparticles, and other nanostructured architectures that provide better electron transport pathways and accommodate volume changes during cycling. The nanostructured approach helps to contain polysulfides within the cathode structure, reducing the shuttle effect and improving capacity retention. These materials often feature high surface area and controlled pore structures to enhance sulfur utilization.Expand Specific Solutions03 Protective coatings and interlayers for sulfur cathodes
Protective coatings and interlayers are applied to sulfur cathodes to mitigate polysulfide dissolution and improve battery performance. These can include polymer coatings, metal oxide layers, or functional interlayers between the cathode and separator. Such protective structures help to physically contain polysulfides within the cathode region while still allowing lithium ion transport. This approach significantly improves the cycling stability and coulombic efficiency of lithium-sulfur batteries.Expand Specific Solutions04 Binder systems for sulfur cathodes
Specialized binder systems are developed for sulfur cathodes to improve mechanical stability and electrochemical performance. These binders help maintain the structural integrity of the cathode during cycling, which involves significant volume changes. Functional binders may also interact with polysulfides to limit their dissolution. Water-based and fluorine-free binder systems are being developed as environmentally friendly alternatives to traditional PVDF binders, while still providing strong adhesion and electrochemical stability.Expand Specific Solutions05 Electrolyte additives and modifications for sulfur cathodes
Electrolyte additives and modifications are employed to enhance the performance of sulfur cathodes. These additives can form protective films on the cathode surface, suppress polysulfide dissolution, or improve ionic conductivity. Modified electrolyte formulations may include salts, solvents, or functional additives that specifically interact with sulfur species. Some approaches involve the use of high-concentration electrolytes or localized high-concentration electrolytes to minimize polysulfide solubility while maintaining good ionic conductivity.Expand Specific Solutions
Leading Companies and Research Institutions in Sulfur Battery Field
The sulfur cathode market for autonomous vehicle systems is in an early growth phase, characterized by significant R&D investment but limited commercial deployment. Market size is projected to expand rapidly as electric autonomous vehicles gain traction, with estimates suggesting a multi-billion dollar opportunity by 2030. Technologically, sulfur cathodes remain in development with key challenges in cycle life and stability. Leading players demonstrate varying levels of maturity: Sila Nanotechnologies and PolyPlus Battery are advancing commercial applications, while automotive giants like Nissan, Renault, and GM are integrating these technologies into vehicle platforms. Academic institutions (Cornell, Penn State, Zhejiang University) are driving fundamental research, while established players like Robert Bosch are developing systems integration capabilities to bridge laboratory innovations with practical autonomous vehicle applications.
Sila Nanotechnologies, Inc.
Technical Solution: Sila Nanotechnologies has developed a groundbreaking approach to sulfur cathodes for next-generation energy storage in autonomous vehicles. Their technology centers on a silicon-sulfur composite cathode structure that leverages the company's expertise in silicon anode materials. The proprietary "nano-composite framework" consists of sulfur particles embedded within a silicon-carbon matrix that provides both physical confinement and chemical bonding sites to prevent polysulfide shuttling. Sila's approach incorporates a specialized polymer coating that forms a flexible yet protective layer around the sulfur particles, accommodating volume changes during cycling while maintaining structural integrity. The company has engineered a novel electrolyte formulation containing lithium salt additives and flame-retardant components that enhance both performance and safety[5]. For autonomous vehicle applications, Sila has developed an integrated power management system that optimizes battery performance based on vehicle operational demands and environmental conditions. Their sulfur cathode technology delivers energy densities approaching 500 Wh/kg with significantly improved cycle life compared to conventional lithium-sulfur batteries.
Strengths: Industry-leading energy density supporting extended autonomous operation; enhanced safety profile critical for autonomous applications; established manufacturing processes facilitating commercialization. Weaknesses: Higher production costs compared to conventional lithium-ion technologies; performance consistency challenges across varying operational conditions; requires specialized battery management systems for optimal performance.
Robert Bosch GmbH
Technical Solution: Bosch has developed an innovative sulfur cathode technology tailored for autonomous vehicle power systems. Their approach centers on a hierarchical carbon-sulfur composite structure that effectively contains sulfur while providing multiple conductive pathways. The technology employs a proprietary "sulfur encapsulation method" where sulfur is confined within mesoporous carbon spheres with an additional protective carbon coating. This double-confinement strategy significantly reduces polysulfide dissolution. Bosch's system incorporates a specialized ionic liquid electrolyte that forms a stable interface with the sulfur cathode while enhancing lithium-ion transport. For autonomous vehicle applications, Bosch has integrated their sulfur cathode batteries with their vehicle control units through a dedicated Battery Management System (BMS) that provides real-time performance data and predictive analytics[4]. The system includes redundant power pathways to ensure uninterrupted operation of critical autonomous functions even during partial battery degradation. Bosch's solution delivers energy densities of approximately 450 Wh/kg with improved cycle stability compared to conventional lithium-sulfur designs.
Strengths: Seamless integration with existing Bosch autonomous driving platforms; enhanced safety through redundant power systems; superior energy density supporting extended operation. Weaknesses: Higher initial cost compared to traditional lithium-ion solutions; performance variability in extreme temperature conditions; requires specialized manufacturing infrastructure limiting production scaling.
Key Patents and Innovations in Sulfur Cathode Technology
Sulfur cathodes
PatentWO2023245254A1
Innovation
- The development of sulfur cathodes incorporating anionically functionalised cellulose nanofibres, combined with sulfur-containing materials and conductive materials, to enhance ionic and electrical conductivity, reduce porosity, and control polysulfide transport, while facilitating lithium ion transport.
Coating for separator or cathode of lithium-sulfur or silicon-sulfur battery
PatentActiveUS20140272569A1
Innovation
- A cation-exchange membrane layer or coating layer containing a single-lithium ion conductor, such as polymeric lithium salt or inorganic ceramic, is applied to the cathode or separator to prevent or slow the passage of polysulfide anions, enhancing cycling stability and capacity retention.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability Assessment
The integration of sulfur cathodes in autonomous vehicle systems presents significant environmental and sustainability implications that warrant thorough assessment. Lithium-sulfur (Li-S) batteries offer substantial environmental advantages over conventional lithium-ion technologies, primarily due to sulfur's natural abundance, low toxicity, and sustainable sourcing options. Unlike cobalt and nickel used in traditional batteries, sulfur is a byproduct of petroleum refining processes, effectively transforming industrial waste into valuable energy storage material.
Life cycle assessments indicate that sulfur cathode production generates approximately 60% lower carbon emissions compared to conventional cathode materials. This reduction stems from simplified manufacturing processes and decreased energy requirements during material synthesis and battery assembly. Furthermore, the elimination of rare earth elements and heavy metals significantly reduces environmental degradation associated with mining operations, including habitat destruction, water pollution, and soil contamination.
Water consumption metrics reveal another critical advantage, with Li-S battery production requiring up to 40% less water than conventional lithium-ion manufacturing. This resource efficiency becomes increasingly important as autonomous vehicle fleets scale globally, particularly in water-stressed regions where manufacturing facilities may operate.
End-of-life considerations demonstrate additional sustainability benefits. Sulfur cathodes exhibit superior recyclability characteristics, with laboratory studies achieving recovery rates exceeding 90% for sulfur components. The simplified chemical composition facilitates more efficient recycling processes, reducing energy consumption and environmental impact during material recovery operations. This circular economy potential addresses growing concerns regarding battery waste management as autonomous vehicle adoption accelerates.
When evaluating autonomous vehicle systems holistically, the extended range capabilities of sulfur cathodes translate to fewer charging cycles over vehicle lifetime, consequently reducing electricity demand and associated environmental impacts from power generation. Models suggest that a fleet of 10,000 autonomous vehicles equipped with Li-S batteries could reduce lifetime carbon emissions by approximately 15,000 metric tons compared to conventional battery technologies.
However, challenges remain regarding sulfur leakage during recycling processes and potential hydrogen sulfide formation under certain conditions. These issues necessitate careful handling protocols and specialized recycling infrastructure to fully realize the environmental benefits. Ongoing research focuses on encapsulation technologies and advanced recycling methodologies to mitigate these concerns while maximizing sustainability advantages.
Life cycle assessments indicate that sulfur cathode production generates approximately 60% lower carbon emissions compared to conventional cathode materials. This reduction stems from simplified manufacturing processes and decreased energy requirements during material synthesis and battery assembly. Furthermore, the elimination of rare earth elements and heavy metals significantly reduces environmental degradation associated with mining operations, including habitat destruction, water pollution, and soil contamination.
Water consumption metrics reveal another critical advantage, with Li-S battery production requiring up to 40% less water than conventional lithium-ion manufacturing. This resource efficiency becomes increasingly important as autonomous vehicle fleets scale globally, particularly in water-stressed regions where manufacturing facilities may operate.
End-of-life considerations demonstrate additional sustainability benefits. Sulfur cathodes exhibit superior recyclability characteristics, with laboratory studies achieving recovery rates exceeding 90% for sulfur components. The simplified chemical composition facilitates more efficient recycling processes, reducing energy consumption and environmental impact during material recovery operations. This circular economy potential addresses growing concerns regarding battery waste management as autonomous vehicle adoption accelerates.
When evaluating autonomous vehicle systems holistically, the extended range capabilities of sulfur cathodes translate to fewer charging cycles over vehicle lifetime, consequently reducing electricity demand and associated environmental impacts from power generation. Models suggest that a fleet of 10,000 autonomous vehicles equipped with Li-S batteries could reduce lifetime carbon emissions by approximately 15,000 metric tons compared to conventional battery technologies.
However, challenges remain regarding sulfur leakage during recycling processes and potential hydrogen sulfide formation under certain conditions. These issues necessitate careful handling protocols and specialized recycling infrastructure to fully realize the environmental benefits. Ongoing research focuses on encapsulation technologies and advanced recycling methodologies to mitigate these concerns while maximizing sustainability advantages.
Integration Challenges with Autonomous Vehicle Systems
The integration of sulfur cathode technology into autonomous vehicle systems presents significant challenges that require careful consideration. The primary obstacle lies in the compatibility between lithium-sulfur battery systems and the complex electrical architecture of autonomous vehicles. These vehicles demand consistent, reliable power delivery for critical systems including LiDAR, radar arrays, computer vision processors, and decision-making AI components - all of which have varying power requirements and sensitivity to voltage fluctuations.
Thermal management represents another substantial integration challenge. Sulfur cathodes exhibit different thermal characteristics compared to traditional lithium-ion batteries, potentially requiring redesigned cooling systems. Autonomous vehicles operating continuously for ride-sharing or logistics applications generate considerable heat through both battery operation and computational processes, necessitating integrated thermal management solutions that can handle these dual heat sources efficiently.
Safety protocols present additional complexity when integrating sulfur cathode technology. The polysulfide shuttle effect, while increasingly controlled in laboratory settings, requires robust battery management systems (BMS) specifically calibrated for lithium-sulfur chemistry. These systems must interface seamlessly with autonomous vehicles' existing safety architecture while maintaining the redundancy requirements essential for autonomous operation certification.
Weight distribution and physical integration pose engineering challenges that impact vehicle dynamics. While lithium-sulfur batteries offer theoretical weight advantages, their different form factors and structural requirements may necessitate chassis redesign. Autonomous vehicle platforms, already crowded with sensors and computing hardware, must accommodate these new power systems without compromising structural integrity or sensor placement.
Software integration represents perhaps the most sophisticated challenge. Energy management algorithms for autonomous vehicles must be completely recalibrated to account for the different discharge characteristics of sulfur cathodes. These systems must optimize power distribution between propulsion and autonomous functions while accurately predicting remaining range based on the unique discharge curve of lithium-sulfur chemistry.
Regulatory compliance adds another layer of complexity, as autonomous vehicle certification processes have not yet fully addressed alternative battery chemistries. Manufacturers must navigate evolving standards across different jurisdictions while demonstrating that sulfur cathode integration maintains or enhances the safety profile of their autonomous systems.
Thermal management represents another substantial integration challenge. Sulfur cathodes exhibit different thermal characteristics compared to traditional lithium-ion batteries, potentially requiring redesigned cooling systems. Autonomous vehicles operating continuously for ride-sharing or logistics applications generate considerable heat through both battery operation and computational processes, necessitating integrated thermal management solutions that can handle these dual heat sources efficiently.
Safety protocols present additional complexity when integrating sulfur cathode technology. The polysulfide shuttle effect, while increasingly controlled in laboratory settings, requires robust battery management systems (BMS) specifically calibrated for lithium-sulfur chemistry. These systems must interface seamlessly with autonomous vehicles' existing safety architecture while maintaining the redundancy requirements essential for autonomous operation certification.
Weight distribution and physical integration pose engineering challenges that impact vehicle dynamics. While lithium-sulfur batteries offer theoretical weight advantages, their different form factors and structural requirements may necessitate chassis redesign. Autonomous vehicle platforms, already crowded with sensors and computing hardware, must accommodate these new power systems without compromising structural integrity or sensor placement.
Software integration represents perhaps the most sophisticated challenge. Energy management algorithms for autonomous vehicles must be completely recalibrated to account for the different discharge characteristics of sulfur cathodes. These systems must optimize power distribution between propulsion and autonomous functions while accurately predicting remaining range based on the unique discharge curve of lithium-sulfur chemistry.
Regulatory compliance adds another layer of complexity, as autonomous vehicle certification processes have not yet fully addressed alternative battery chemistries. Manufacturers must navigate evolving standards across different jurisdictions while demonstrating that sulfur cathode integration maintains or enhances the safety profile of their autonomous systems.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!