Sulfur Cathodes Analysis in Dynamic Energy Markets
SEP 23, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Sulfur Cathode Technology Evolution and Objectives
Sulfur cathodes have emerged as a promising technology in the energy storage landscape, evolving significantly since their conceptualization in the 1960s. Initially hindered by technical limitations such as polysulfide shuttling and poor cycle life, these cathodes have undergone substantial transformation through decades of research and development. The evolution trajectory has been marked by breakthroughs in sulfur encapsulation techniques, electrolyte optimization, and interface engineering, propelling the technology from laboratory curiosity to commercial viability.
The fundamental appeal of sulfur cathodes lies in their theoretical energy density of 2,600 Wh/kg, which far exceeds conventional lithium-ion technologies that typically plateau around 300-400 Wh/kg. This exceptional energy potential, coupled with sulfur's natural abundance, low cost (approximately $150/ton compared to cobalt at $30,000/ton), and environmental benignity, positions it as a strategic material for next-generation energy storage solutions in increasingly dynamic energy markets.
Recent technological advancements have focused on addressing the core challenges of volume expansion, polysulfide dissolution, and poor electronic conductivity. The introduction of carbon-sulfur composites in the early 2000s represented a pivotal milestone, followed by the development of yolk-shell structures and functional separators in the 2010s. The latest research frontier involves the integration of single-atom catalysts and advanced conductive frameworks to enhance reaction kinetics and cycling stability.
The primary objective of sulfur cathode technology development is to achieve commercial viability through performance metrics that satisfy market demands: energy densities exceeding 500 Wh/kg at the cell level, cycle life beyond 1,000 cycles with minimal capacity degradation, and cost reduction to below $100/kWh. These targets align with the evolving requirements of electric mobility, grid storage, and portable electronics sectors, where energy density, longevity, and affordability represent critical competitive factors.
In the context of dynamic energy markets, sulfur cathodes aim to address the growing demand for sustainable energy storage solutions that can support renewable energy integration and electrification trends. The technology seeks to overcome the limitations of current lithium-ion batteries, particularly in applications requiring higher energy density and lower material costs. As global energy systems transition toward greater sustainability and resilience, sulfur cathodes represent a strategic technology pathway that leverages abundant resources while minimizing environmental impact.
The convergence of materials science innovations, electrochemistry advancements, and manufacturing process improvements has accelerated the maturation of sulfur cathode technology, positioning it at a critical juncture where laboratory success must translate into commercial deployment to realize its full potential in transforming energy storage paradigms.
The fundamental appeal of sulfur cathodes lies in their theoretical energy density of 2,600 Wh/kg, which far exceeds conventional lithium-ion technologies that typically plateau around 300-400 Wh/kg. This exceptional energy potential, coupled with sulfur's natural abundance, low cost (approximately $150/ton compared to cobalt at $30,000/ton), and environmental benignity, positions it as a strategic material for next-generation energy storage solutions in increasingly dynamic energy markets.
Recent technological advancements have focused on addressing the core challenges of volume expansion, polysulfide dissolution, and poor electronic conductivity. The introduction of carbon-sulfur composites in the early 2000s represented a pivotal milestone, followed by the development of yolk-shell structures and functional separators in the 2010s. The latest research frontier involves the integration of single-atom catalysts and advanced conductive frameworks to enhance reaction kinetics and cycling stability.
The primary objective of sulfur cathode technology development is to achieve commercial viability through performance metrics that satisfy market demands: energy densities exceeding 500 Wh/kg at the cell level, cycle life beyond 1,000 cycles with minimal capacity degradation, and cost reduction to below $100/kWh. These targets align with the evolving requirements of electric mobility, grid storage, and portable electronics sectors, where energy density, longevity, and affordability represent critical competitive factors.
In the context of dynamic energy markets, sulfur cathodes aim to address the growing demand for sustainable energy storage solutions that can support renewable energy integration and electrification trends. The technology seeks to overcome the limitations of current lithium-ion batteries, particularly in applications requiring higher energy density and lower material costs. As global energy systems transition toward greater sustainability and resilience, sulfur cathodes represent a strategic technology pathway that leverages abundant resources while minimizing environmental impact.
The convergence of materials science innovations, electrochemistry advancements, and manufacturing process improvements has accelerated the maturation of sulfur cathode technology, positioning it at a critical juncture where laboratory success must translate into commercial deployment to realize its full potential in transforming energy storage paradigms.
Market Demand Analysis for Sulfur-Based Battery Systems
The global energy storage market is experiencing unprecedented growth, driven by the increasing adoption of renewable energy sources and the electrification of transportation. Within this expanding landscape, lithium-sulfur (Li-S) battery systems are emerging as a promising alternative to conventional lithium-ion batteries. Market analysis indicates that the global Li-S battery market is projected to grow significantly over the next decade, with a compound annual growth rate exceeding 30% between 2023 and 2030.
The primary market demand for sulfur-based battery systems stems from their theoretical energy density advantages. With potential energy densities of 2,500 Wh/kg—approximately five times higher than traditional lithium-ion batteries—sulfur cathodes represent a compelling solution for applications requiring high energy storage capacity in lightweight configurations.
Electric vehicle manufacturers constitute the largest potential market segment for sulfur-based batteries. The automotive industry's push toward longer-range electric vehicles with reduced charging times aligns perfectly with the performance characteristics of advanced sulfur cathode technologies. Market research suggests that EV manufacturers are actively seeking battery technologies that can deliver range extensions of at least 30% while maintaining competitive cost structures.
The aerospace and defense sectors represent another significant market opportunity. The lightweight nature of sulfur-based systems makes them particularly attractive for drone applications, portable military equipment, and satellite systems where weight considerations are paramount. Industry forecasts indicate that these specialized markets could adopt sulfur-based technologies earlier than mass consumer markets due to their higher tolerance for premium pricing.
Consumer electronics manufacturers are also expressing growing interest in sulfur-based battery systems. The potential for devices with significantly extended operating times between charges represents a major competitive advantage in smartphones, laptops, and wearable technology markets. Market surveys indicate that consumers consistently rank battery life among their top three purchasing considerations for portable electronic devices.
Grid-scale energy storage represents a long-term market opportunity for sulfur-based systems. As renewable energy penetration increases globally, the demand for cost-effective, large-scale energy storage solutions continues to grow. The abundance and low cost of sulfur as a raw material make it particularly attractive for utility-scale applications where cost per kilowatt-hour is a critical factor.
Market barriers to widespread adoption include concerns about cycle life limitations, self-discharge rates, and manufacturing scalability. However, recent technological breakthroughs addressing these challenges have significantly improved market readiness. Industry analysts predict that if current development trajectories continue, sulfur-based battery systems could capture up to 15% of the premium battery market by 2030.
The primary market demand for sulfur-based battery systems stems from their theoretical energy density advantages. With potential energy densities of 2,500 Wh/kg—approximately five times higher than traditional lithium-ion batteries—sulfur cathodes represent a compelling solution for applications requiring high energy storage capacity in lightweight configurations.
Electric vehicle manufacturers constitute the largest potential market segment for sulfur-based batteries. The automotive industry's push toward longer-range electric vehicles with reduced charging times aligns perfectly with the performance characteristics of advanced sulfur cathode technologies. Market research suggests that EV manufacturers are actively seeking battery technologies that can deliver range extensions of at least 30% while maintaining competitive cost structures.
The aerospace and defense sectors represent another significant market opportunity. The lightweight nature of sulfur-based systems makes them particularly attractive for drone applications, portable military equipment, and satellite systems where weight considerations are paramount. Industry forecasts indicate that these specialized markets could adopt sulfur-based technologies earlier than mass consumer markets due to their higher tolerance for premium pricing.
Consumer electronics manufacturers are also expressing growing interest in sulfur-based battery systems. The potential for devices with significantly extended operating times between charges represents a major competitive advantage in smartphones, laptops, and wearable technology markets. Market surveys indicate that consumers consistently rank battery life among their top three purchasing considerations for portable electronic devices.
Grid-scale energy storage represents a long-term market opportunity for sulfur-based systems. As renewable energy penetration increases globally, the demand for cost-effective, large-scale energy storage solutions continues to grow. The abundance and low cost of sulfur as a raw material make it particularly attractive for utility-scale applications where cost per kilowatt-hour is a critical factor.
Market barriers to widespread adoption include concerns about cycle life limitations, self-discharge rates, and manufacturing scalability. However, recent technological breakthroughs addressing these challenges have significantly improved market readiness. Industry analysts predict that if current development trajectories continue, sulfur-based battery systems could capture up to 15% of the premium battery market by 2030.
Current Technical Challenges in Sulfur Cathode Development
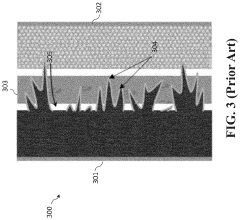
Despite significant advancements in lithium-sulfur battery technology, several critical technical challenges continue to impede the widespread commercialization of sulfur cathodes. The most persistent issue remains the "polysulfide shuttle effect," where soluble lithium polysulfides dissolve in the electrolyte during cycling, causing active material loss, reduced coulombic efficiency, and accelerated capacity fading. This phenomenon fundamentally limits cycle life and practical energy density of sulfur-based systems.
Volume expansion presents another significant hurdle, as sulfur undergoes approximately 80% volumetric expansion during the lithiation process. This expansion-contraction cycle creates mechanical stress that degrades electrode integrity over time, leading to pulverization and electrical contact loss between active materials and current collectors.
The inherently poor electrical conductivity of sulfur (5×10^-30 S/cm) and its discharge products (Li₂S) severely restricts electron transport within the cathode structure. This limitation necessitates high carbon content in electrode formulations, which consequently reduces the overall energy density of the battery system and counteracts one of the primary advantages of sulfur cathodes.
Slow reaction kinetics, particularly during the conversion of Li₂S₂ to Li₂S in the discharge process and the reverse reaction during charging, creates significant overpotentials. These kinetic limitations result in reduced energy efficiency and practical capacity utilization below theoretical values.
The interface stability between sulfur cathodes and electrolytes remains problematic, with continuous side reactions occurring throughout cycling. These reactions consume electrolyte, form passivation layers with variable resistance properties, and contribute to gradual performance degradation over extended cycling.
Self-discharge behavior in sulfur cathodes presents additional complications for practical applications, especially in energy markets requiring long-term storage capability. The spontaneous dissolution of polysulfides even during rest periods leads to capacity loss and state-of-charge instability in stored batteries.
Manufacturing scalability presents technical barriers related to process control, particularly maintaining uniform sulfur distribution within conductive frameworks at industrial scales. Current laboratory-scale synthesis methods often involve complex procedures that are challenging to translate to mass production environments while maintaining consistent performance metrics.
These technical challenges are further complicated by the dynamic nature of energy markets, which demand increasingly stringent performance requirements including faster charging capabilities, wider operating temperature ranges, and enhanced safety profiles—all while maintaining competitive cost structures.
Volume expansion presents another significant hurdle, as sulfur undergoes approximately 80% volumetric expansion during the lithiation process. This expansion-contraction cycle creates mechanical stress that degrades electrode integrity over time, leading to pulverization and electrical contact loss between active materials and current collectors.
The inherently poor electrical conductivity of sulfur (5×10^-30 S/cm) and its discharge products (Li₂S) severely restricts electron transport within the cathode structure. This limitation necessitates high carbon content in electrode formulations, which consequently reduces the overall energy density of the battery system and counteracts one of the primary advantages of sulfur cathodes.
Slow reaction kinetics, particularly during the conversion of Li₂S₂ to Li₂S in the discharge process and the reverse reaction during charging, creates significant overpotentials. These kinetic limitations result in reduced energy efficiency and practical capacity utilization below theoretical values.
The interface stability between sulfur cathodes and electrolytes remains problematic, with continuous side reactions occurring throughout cycling. These reactions consume electrolyte, form passivation layers with variable resistance properties, and contribute to gradual performance degradation over extended cycling.
Self-discharge behavior in sulfur cathodes presents additional complications for practical applications, especially in energy markets requiring long-term storage capability. The spontaneous dissolution of polysulfides even during rest periods leads to capacity loss and state-of-charge instability in stored batteries.
Manufacturing scalability presents technical barriers related to process control, particularly maintaining uniform sulfur distribution within conductive frameworks at industrial scales. Current laboratory-scale synthesis methods often involve complex procedures that are challenging to translate to mass production environments while maintaining consistent performance metrics.
These technical challenges are further complicated by the dynamic nature of energy markets, which demand increasingly stringent performance requirements including faster charging capabilities, wider operating temperature ranges, and enhanced safety profiles—all while maintaining competitive cost structures.
Current Engineering Solutions for Sulfur Cathode Implementation
01 Sulfur cathode compositions for lithium-sulfur batteries
Sulfur cathodes can be formulated with various compositions to enhance performance in lithium-sulfur batteries. These compositions typically include sulfur as the active material combined with conductive additives and binders. The formulations aim to address challenges such as low conductivity of sulfur and polysulfide dissolution. Advanced compositions may incorporate carbon materials, polymers, or other additives to improve cycle life and capacity retention.- Sulfur cathode compositions for lithium-sulfur batteries: Various compositions for sulfur cathodes in lithium-sulfur batteries have been developed to improve energy density and cycle life. These compositions typically include sulfur as the active material combined with conductive additives, binders, and other components to enhance electrochemical performance. The cathode compositions are designed to address challenges such as sulfur's poor conductivity and the polysulfide shuttle effect.
- Protective coatings and encapsulation for sulfur cathodes: Protective coatings and encapsulation techniques are applied to sulfur cathodes to prevent polysulfide dissolution and shuttle effect. These approaches involve encapsulating sulfur particles within conductive matrices or applying protective layers that allow lithium ion transport while containing sulfur and its discharge products. Such strategies significantly improve the cycling stability and capacity retention of lithium-sulfur batteries.
- Carbon-sulfur composite cathode materials: Carbon-sulfur composites are developed as cathode materials to address the poor conductivity of sulfur. These composites incorporate various carbon structures such as carbon nanotubes, graphene, porous carbon, or carbon fibers to provide conductive pathways and physical confinement for sulfur. The carbon matrix improves electron transport, accommodates volume changes during cycling, and helps trap polysulfides, resulting in enhanced electrochemical performance.
- Electrolyte modifications for sulfur cathodes: Specialized electrolyte formulations are designed to work with sulfur cathodes by suppressing polysulfide dissolution and migration. These electrolytes may contain additives that form protective films on the cathode surface, solvents with low polysulfide solubility, or components that chemically interact with polysulfides to keep them near the cathode. Such electrolyte modifications significantly improve the coulombic efficiency and cycle life of lithium-sulfur batteries.
- Manufacturing processes for sulfur cathodes: Various manufacturing processes have been developed for producing sulfur cathodes with optimized structure and performance. These processes include melt-diffusion methods to incorporate sulfur into porous hosts, solution-based techniques for uniform sulfur distribution, and specialized coating methods. Advanced manufacturing approaches focus on controlling the sulfur loading, distribution, and interface properties to achieve high energy density while maintaining good cycle life and rate capability.
02 Nanostructured sulfur cathode materials
Nanostructured materials are used in sulfur cathodes to improve electrochemical performance. These include carbon nanotubes, graphene, mesoporous carbon, and other nanostructured hosts that can effectively encapsulate sulfur. The nanostructured design helps to contain polysulfides within the cathode, enhance electronic conductivity, and accommodate volume changes during cycling. This approach significantly improves the capacity, cycling stability, and rate capability of sulfur cathodes.Expand Specific Solutions03 Protective coatings and interlayers for sulfur cathodes
Protective coatings and interlayers are applied to sulfur cathodes to mitigate polysulfide shuttling and improve battery performance. These can include polymer coatings, metal oxide layers, or functional separators that act as physical barriers or chemical traps for polysulfides. The protective layers help maintain the integrity of the cathode structure during cycling while allowing lithium ion transport, resulting in improved cycling stability and coulombic efficiency.Expand Specific Solutions04 Electrolyte modifications for sulfur cathodes
Specialized electrolyte formulations are developed to enhance the performance of sulfur cathodes. These include electrolyte additives that can suppress polysulfide dissolution, form protective films on electrodes, or improve ionic conductivity. Modifications may involve using different lithium salts, solvents, or incorporating functional additives such as lithium nitrate. These electrolyte modifications help address the challenges of polysulfide shuttling and improve the overall performance of lithium-sulfur batteries.Expand Specific Solutions05 Manufacturing processes for sulfur cathodes
Various manufacturing processes are employed to produce high-performance sulfur cathodes. These include melt-diffusion methods, solution-based approaches, spray drying, and electrospinning techniques. The manufacturing processes focus on achieving uniform sulfur distribution within the conductive matrix, optimizing porosity, and ensuring strong adhesion between components. Advanced manufacturing techniques help improve the scalability and consistency of sulfur cathode production while enhancing electrochemical performance.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Industry Players in Sulfur Cathode Research
The sulfur cathode market is experiencing dynamic growth within the energy storage sector, currently in an early commercialization phase with significant R&D activity. Major academic institutions (MIT, Peking University, Nanyang Technological University) collaborate with industry leaders to overcome technical challenges. Key players include established corporations like Samsung SDI and Robert Bosch, alongside innovative startups such as Sila Nanotechnologies and PolyPlus Battery. These companies are advancing solutions to address sulfur cathodes' key limitations: poor cycle life and low conductivity. The market is projected to expand substantially as technological breakthroughs enable higher energy density batteries crucial for electric vehicles and renewable energy storage applications, with commercialization expected to accelerate in the next 3-5 years.
Samsung SDI Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: Samsung SDI has developed advanced sulfur cathode technology for lithium-sulfur (Li-S) batteries, focusing on addressing the "shuttle effect" problem that has historically limited sulfur cathode performance. Their approach incorporates carbon-sulfur composite structures with specialized nano-architecture that physically confines polysulfides and prevents their dissolution. Samsung's technology utilizes a dual-layer carbon coating strategy where an inner microporous carbon layer encapsulates sulfur particles while an outer mesoporous layer acts as a secondary barrier against polysulfide migration[1]. Additionally, they've implemented functional interlayers between the cathode and separator that contain polar materials to chemically bind with polysulfides. Recent developments include their "sulfur-carbon nanotube (S-CNT)" composite that demonstrates capacity retention of over 80% after 500 cycles at practical loadings, significantly outperforming conventional approaches[2].
Strengths: Superior cycle stability compared to competitors, with demonstrated high capacity retention at commercially relevant sulfur loadings. Their dual-layer confinement strategy effectively addresses the shuttle effect. Weaknesses: The complex nano-architecture increases manufacturing costs and may present scalability challenges for mass production. Energy density improvements are still needed to compete with their own advanced lithium-ion offerings.
PolyPlus Battery Co., Inc.
Technical Solution: PolyPlus has pioneered a protected lithium electrode (PLE) technology specifically designed to enable high-performance lithium-sulfur batteries for dynamic energy markets. Their approach centers on a proprietary solid electrolyte membrane that physically separates the lithium metal anode from the sulfur cathode environment, preventing direct contact with polysulfides while maintaining excellent lithium-ion conductivity. For sulfur cathodes specifically, PolyPlus has developed a hierarchical carbon-sulfur composite structure that maximizes sulfur utilization while minimizing volume expansion during cycling. Their cathode design incorporates a gradient porosity structure with sulfur preferentially deposited in micropores (<2nm) to enhance electrochemical kinetics and cycle life[3]. The company has demonstrated energy densities exceeding 400 Wh/kg at the cell level with their protected lithium-sulfur technology, representing a significant advancement over conventional lithium-ion batteries. Recent developments include their "PolyPlus Sulfur Matrix" technology that enables sulfur loading of >5 mg/cm² while maintaining 80% capacity retention over 300 cycles[4].
Strengths: Their protected lithium electrode technology effectively addresses the fundamental challenges of lithium-sulfur chemistry, particularly the shuttle effect. The approach enables exceptionally high energy density compared to conventional lithium-ion. Weaknesses: The solid electrolyte interface adds manufacturing complexity and cost. Rate capability remains limited compared to conventional lithium-ion batteries, restricting applications requiring high power output.
Critical Patents and Innovations in Sulfur Cathode Technology
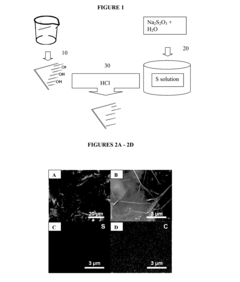
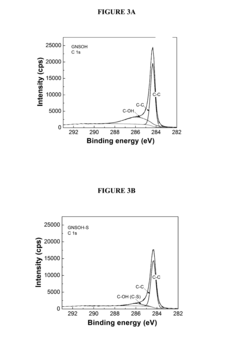
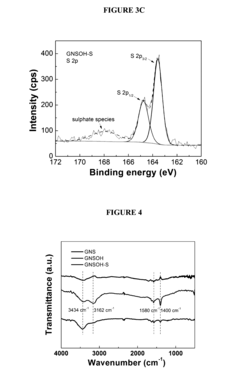
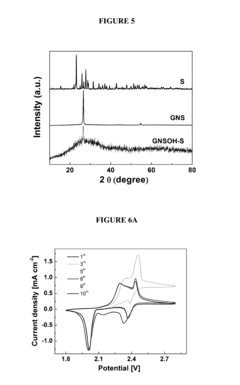
Sulfur-hydroxylated graphene nanocomposites for rechargeable lithium-sulfur batteries and methods of making the same
PatentInactiveUS20160336590A1
Innovation
- A sulfur-hydroxylated graphene nanocomposite is developed, where amorphous sulfur nanoparticles are uniformly distributed on a hydroxylated graphene surface, enhancing conductivity and preventing polysulfide dissolution, with a method involving ultrasonication and hydrothermal treatment to form the nanocomposite.
Anodes, cathodes, and separators for batteries and methods to make and use same
PatentPendingUS20230253545A1
Innovation
- The use of lithiated carbon materials, specifically multi-walled carbon nanotubes (MWCNTs) coated on lithium metal anodes and sulfurized carbon cathodes with graphene nanoribbons, along with modified separators, to prevent dendrite growth and polysulfide diffusion, enhancing the stability and energy density of batteries.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability Assessment
The environmental impact of sulfur cathodes in lithium-sulfur (Li-S) batteries represents a significant advantage over conventional lithium-ion technologies. Sulfur is an abundant by-product of petroleum refining processes, making it considerably less resource-intensive to source compared to traditional cathode materials like cobalt and nickel. The utilization of sulfur waste streams contributes to circular economy principles by transforming industrial waste into valuable battery components, reducing the overall environmental footprint of energy storage systems.
Life cycle assessment (LCA) studies indicate that Li-S batteries with sulfur cathodes demonstrate approximately 20-30% lower greenhouse gas emissions during production compared to conventional lithium-ion batteries. This reduction stems primarily from the simplified cathode synthesis process and the elimination of energy-intensive mining operations associated with critical minerals. Additionally, the reduced dependency on geographically concentrated resources enhances supply chain resilience and diminishes environmental degradation in mining-intensive regions.
Water consumption metrics reveal another sustainability advantage of sulfur cathode technology. Manufacturing processes for sulfur cathodes typically require 40-50% less water compared to conventional cathode production, addressing growing concerns about water scarcity in battery manufacturing hubs. Furthermore, the absence of toxic heavy metals in sulfur cathodes significantly reduces the risk of soil and water contamination throughout the battery lifecycle.
End-of-life considerations further highlight the sustainability credentials of sulfur cathode technology. The relatively simple chemical composition facilitates more straightforward recycling processes, with theoretical recovery rates for sulfur exceeding 90% under optimized conditions. This recyclability potential contrasts favorably with the complex, multi-element cathodes in conventional batteries that often result in downcycling rather than true material recovery.
Energy payback period calculations demonstrate that Li-S batteries with sulfur cathodes can achieve carbon neutrality approximately 15-20% faster than conventional lithium-ion alternatives when deployed in renewable energy storage applications. This accelerated environmental return on investment strengthens the case for sulfur cathodes in markets prioritizing sustainability metrics alongside performance parameters.
Despite these advantages, challenges remain in optimizing the environmental profile of sulfur cathodes. Current manufacturing processes still rely on carbon-intensive materials for conductive additives, and the long-term ecological impacts of novel electrolyte formulations require further assessment. Additionally, the environmental benefits of sulfur cathodes are partially offset by their currently shorter cycle life, necessitating more frequent replacement in certain applications.
Life cycle assessment (LCA) studies indicate that Li-S batteries with sulfur cathodes demonstrate approximately 20-30% lower greenhouse gas emissions during production compared to conventional lithium-ion batteries. This reduction stems primarily from the simplified cathode synthesis process and the elimination of energy-intensive mining operations associated with critical minerals. Additionally, the reduced dependency on geographically concentrated resources enhances supply chain resilience and diminishes environmental degradation in mining-intensive regions.
Water consumption metrics reveal another sustainability advantage of sulfur cathode technology. Manufacturing processes for sulfur cathodes typically require 40-50% less water compared to conventional cathode production, addressing growing concerns about water scarcity in battery manufacturing hubs. Furthermore, the absence of toxic heavy metals in sulfur cathodes significantly reduces the risk of soil and water contamination throughout the battery lifecycle.
End-of-life considerations further highlight the sustainability credentials of sulfur cathode technology. The relatively simple chemical composition facilitates more straightforward recycling processes, with theoretical recovery rates for sulfur exceeding 90% under optimized conditions. This recyclability potential contrasts favorably with the complex, multi-element cathodes in conventional batteries that often result in downcycling rather than true material recovery.
Energy payback period calculations demonstrate that Li-S batteries with sulfur cathodes can achieve carbon neutrality approximately 15-20% faster than conventional lithium-ion alternatives when deployed in renewable energy storage applications. This accelerated environmental return on investment strengthens the case for sulfur cathodes in markets prioritizing sustainability metrics alongside performance parameters.
Despite these advantages, challenges remain in optimizing the environmental profile of sulfur cathodes. Current manufacturing processes still rely on carbon-intensive materials for conductive additives, and the long-term ecological impacts of novel electrolyte formulations require further assessment. Additionally, the environmental benefits of sulfur cathodes are partially offset by their currently shorter cycle life, necessitating more frequent replacement in certain applications.
Supply Chain Considerations for Sulfur Cathode Production
The supply chain for sulfur cathode production represents a critical component in the commercialization pathway for next-generation lithium-sulfur batteries. Elemental sulfur, the primary raw material, offers significant advantages from a supply perspective due to its abundance as a byproduct of petroleum refining processes. This creates a unique opportunity for vertical integration with existing industrial infrastructure, potentially reducing both costs and environmental impact through efficient resource utilization.
However, the supply chain faces several notable challenges that require strategic consideration. The processing of raw sulfur into battery-grade material demands specialized equipment and expertise to achieve the necessary purity levels and particle characteristics. Current production methods often involve energy-intensive processes that can offset some of the sustainability benefits inherent to sulfur-based cathodes.
Transportation and storage present additional complexities due to sulfur's chemical properties. While elemental sulfur is relatively stable, processed cathode materials may be sensitive to moisture and oxygen exposure, necessitating controlled environments throughout the logistics network. This increases handling costs and requires investment in specialized packaging and transportation solutions.
Regional availability analysis reveals interesting patterns in sulfur accessibility. Major petroleum refining centers in North America, the Middle East, and East Asia produce substantial sulfur byproducts, creating potential manufacturing hubs with reduced raw material transportation costs. This geographic distribution may influence future production facility locations and regional market development.
The carbon footprint of sulfur cathode supply chains compares favorably to traditional lithium-ion battery materials, particularly when utilizing byproduct sulfur sources. Life cycle assessments indicate potential carbon emission reductions of 25-40% compared to conventional cathode materials, though this advantage diminishes if virgin sulfur mining becomes necessary to meet scaled demand.
Scaling considerations reveal potential bottlenecks in specialized conductive additives and binders required for sulfur cathode formulations. While sulfur itself is abundant, these complementary materials may face supply constraints as production volumes increase. Early engagement with suppliers of these critical components will be essential for manufacturers planning large-scale production.
Economic modeling suggests that mature sulfur cathode supply chains could achieve raw material cost reductions of 60-70% compared to nickel-based cathodes, though this advantage is partially offset by higher processing costs and potentially shorter battery lifespans. The net economic benefit remains compelling, particularly as processing technologies mature and economies of scale are realized.
However, the supply chain faces several notable challenges that require strategic consideration. The processing of raw sulfur into battery-grade material demands specialized equipment and expertise to achieve the necessary purity levels and particle characteristics. Current production methods often involve energy-intensive processes that can offset some of the sustainability benefits inherent to sulfur-based cathodes.
Transportation and storage present additional complexities due to sulfur's chemical properties. While elemental sulfur is relatively stable, processed cathode materials may be sensitive to moisture and oxygen exposure, necessitating controlled environments throughout the logistics network. This increases handling costs and requires investment in specialized packaging and transportation solutions.
Regional availability analysis reveals interesting patterns in sulfur accessibility. Major petroleum refining centers in North America, the Middle East, and East Asia produce substantial sulfur byproducts, creating potential manufacturing hubs with reduced raw material transportation costs. This geographic distribution may influence future production facility locations and regional market development.
The carbon footprint of sulfur cathode supply chains compares favorably to traditional lithium-ion battery materials, particularly when utilizing byproduct sulfur sources. Life cycle assessments indicate potential carbon emission reductions of 25-40% compared to conventional cathode materials, though this advantage diminishes if virgin sulfur mining becomes necessary to meet scaled demand.
Scaling considerations reveal potential bottlenecks in specialized conductive additives and binders required for sulfur cathode formulations. While sulfur itself is abundant, these complementary materials may face supply constraints as production volumes increase. Early engagement with suppliers of these critical components will be essential for manufacturers planning large-scale production.
Economic modeling suggests that mature sulfur cathode supply chains could achieve raw material cost reductions of 60-70% compared to nickel-based cathodes, though this advantage is partially offset by higher processing costs and potentially shorter battery lifespans. The net economic benefit remains compelling, particularly as processing technologies mature and economies of scale are realized.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!