Market Analysis of Sulfur Cathodes in Energy Applications
SEP 23, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Sulfur Cathode Technology Evolution and Objectives
Sulfur cathode technology has undergone significant evolution since its initial conceptualization in the 1960s. The journey began with rudimentary lithium-sulfur battery designs that demonstrated the theoretical potential of sulfur as a cathode material but suffered from severe practical limitations. The 1980s and 1990s saw incremental improvements in understanding the complex electrochemistry of sulfur cathodes, particularly the polysulfide shuttle effect that hampered early designs.
A pivotal shift occurred in the early 2000s when nanotechnology advancements enabled researchers to address key challenges in sulfur cathode design. The introduction of carbon-sulfur composites marked a significant milestone, improving both conductivity and sulfur utilization. By 2010, the development of mesoporous carbon structures and conductive polymers further enhanced the performance metrics of sulfur cathodes, pushing energy densities closer to theoretical limits.
The current technological landscape is characterized by multifaceted approaches to overcome persistent challenges. Advanced material engineering techniques focus on nanostructured sulfur hosts, electrolyte modifications, and protective layers to mitigate polysulfide dissolution. Recent breakthroughs in 2020-2023 include the development of lithiophilic interfaces, single-atom catalysts, and functional separators that collectively address cycle life limitations.
The primary objective of sulfur cathode technology development is to harness its theoretical energy density of 2,600 Wh/kg, which significantly exceeds current lithium-ion technologies (250-300 Wh/kg). This represents a potential tenfold increase in energy storage capacity, making it a compelling candidate for next-generation energy storage solutions.
Secondary objectives include extending cycle life beyond 1,000 cycles, improving rate capability for fast-charging applications, and enhancing safety profiles through stable electrolyte systems. Cost reduction remains a critical goal, with sulfur's natural abundance ($150/ton compared to cobalt at $30,000/ton) offering a pathway to more economical energy storage solutions.
The technology evolution trajectory suggests convergence toward hybrid approaches that combine multiple mitigation strategies rather than singular solutions. Research trends indicate growing interest in solid-state sulfur batteries and semi-solid systems that fundamentally alter the reaction mechanisms to bypass traditional limitations.
Looking forward, the field is moving toward practical commercialization with several startups and established companies announcing pilot production lines. The technology roadmap projects commercial viability for specific applications by 2025-2027, with broader market penetration anticipated in the 2030 timeframe as manufacturing processes mature and performance metrics stabilize.
A pivotal shift occurred in the early 2000s when nanotechnology advancements enabled researchers to address key challenges in sulfur cathode design. The introduction of carbon-sulfur composites marked a significant milestone, improving both conductivity and sulfur utilization. By 2010, the development of mesoporous carbon structures and conductive polymers further enhanced the performance metrics of sulfur cathodes, pushing energy densities closer to theoretical limits.
The current technological landscape is characterized by multifaceted approaches to overcome persistent challenges. Advanced material engineering techniques focus on nanostructured sulfur hosts, electrolyte modifications, and protective layers to mitigate polysulfide dissolution. Recent breakthroughs in 2020-2023 include the development of lithiophilic interfaces, single-atom catalysts, and functional separators that collectively address cycle life limitations.
The primary objective of sulfur cathode technology development is to harness its theoretical energy density of 2,600 Wh/kg, which significantly exceeds current lithium-ion technologies (250-300 Wh/kg). This represents a potential tenfold increase in energy storage capacity, making it a compelling candidate for next-generation energy storage solutions.
Secondary objectives include extending cycle life beyond 1,000 cycles, improving rate capability for fast-charging applications, and enhancing safety profiles through stable electrolyte systems. Cost reduction remains a critical goal, with sulfur's natural abundance ($150/ton compared to cobalt at $30,000/ton) offering a pathway to more economical energy storage solutions.
The technology evolution trajectory suggests convergence toward hybrid approaches that combine multiple mitigation strategies rather than singular solutions. Research trends indicate growing interest in solid-state sulfur batteries and semi-solid systems that fundamentally alter the reaction mechanisms to bypass traditional limitations.
Looking forward, the field is moving toward practical commercialization with several startups and established companies announcing pilot production lines. The technology roadmap projects commercial viability for specific applications by 2025-2027, with broader market penetration anticipated in the 2030 timeframe as manufacturing processes mature and performance metrics stabilize.
Market Demand Analysis for Sulfur-Based Energy Storage
The global energy storage market is witnessing unprecedented growth, with projections indicating a compound annual growth rate of 20-25% through 2030. Within this expanding landscape, sulfur-based energy storage technologies, particularly lithium-sulfur (Li-S) batteries, are emerging as promising alternatives to conventional lithium-ion batteries. Market research indicates that the Li-S battery segment could capture 5-7% of the total energy storage market by 2028, representing a significant opportunity for early movers in this technology space.
The primary market drivers for sulfur-based energy storage include the increasing demand for high-energy-density solutions in electric vehicles, growing concerns about the sustainability and environmental impact of current battery technologies, and the favorable economics of sulfur as an abundant and low-cost cathode material. The theoretical energy density of Li-S batteries (2,600 Wh/kg) far exceeds that of conventional lithium-ion batteries (250-300 Wh/kg), making them particularly attractive for applications where weight and space constraints are critical factors.
Consumer electronics represents another substantial market segment for sulfur-based energy storage, with manufacturers actively seeking battery technologies that can extend device operation time while reducing weight. Market surveys indicate that consumers are willing to pay a 15-20% premium for devices with significantly improved battery performance, creating a viable entry point for sulfur-based technologies.
The aerospace and defense sectors are showing strong interest in advanced energy storage solutions, with several major contractors investing in research partnerships focused on sulfur cathode technology. These high-value niche applications could serve as important early markets, allowing for technology refinement before broader commercial deployment.
Regionally, Asia-Pacific dominates the current market landscape for battery production, but North America and Europe are making strategic investments to reduce dependency on foreign supply chains. Government initiatives supporting domestic battery production, particularly those emphasizing sustainable materials, are creating favorable conditions for sulfur-based technologies in these regions.
Market challenges include competition from other emerging battery technologies, such as solid-state batteries and sodium-ion systems, as well as the technical hurdles that still limit the commercial viability of sulfur cathodes. Consumer and industry concerns about the safety and longevity of new battery technologies also represent significant market barriers that must be addressed through rigorous testing and certification.
The market for stationary energy storage systems represents another significant opportunity, with grid-scale applications projected to grow at 30% annually through 2028. Sulfur-based systems could capture a meaningful share of this market if they can demonstrate competitive lifecycle costs and reliability metrics.
The primary market drivers for sulfur-based energy storage include the increasing demand for high-energy-density solutions in electric vehicles, growing concerns about the sustainability and environmental impact of current battery technologies, and the favorable economics of sulfur as an abundant and low-cost cathode material. The theoretical energy density of Li-S batteries (2,600 Wh/kg) far exceeds that of conventional lithium-ion batteries (250-300 Wh/kg), making them particularly attractive for applications where weight and space constraints are critical factors.
Consumer electronics represents another substantial market segment for sulfur-based energy storage, with manufacturers actively seeking battery technologies that can extend device operation time while reducing weight. Market surveys indicate that consumers are willing to pay a 15-20% premium for devices with significantly improved battery performance, creating a viable entry point for sulfur-based technologies.
The aerospace and defense sectors are showing strong interest in advanced energy storage solutions, with several major contractors investing in research partnerships focused on sulfur cathode technology. These high-value niche applications could serve as important early markets, allowing for technology refinement before broader commercial deployment.
Regionally, Asia-Pacific dominates the current market landscape for battery production, but North America and Europe are making strategic investments to reduce dependency on foreign supply chains. Government initiatives supporting domestic battery production, particularly those emphasizing sustainable materials, are creating favorable conditions for sulfur-based technologies in these regions.
Market challenges include competition from other emerging battery technologies, such as solid-state batteries and sodium-ion systems, as well as the technical hurdles that still limit the commercial viability of sulfur cathodes. Consumer and industry concerns about the safety and longevity of new battery technologies also represent significant market barriers that must be addressed through rigorous testing and certification.
The market for stationary energy storage systems represents another significant opportunity, with grid-scale applications projected to grow at 30% annually through 2028. Sulfur-based systems could capture a meaningful share of this market if they can demonstrate competitive lifecycle costs and reliability metrics.
Technical Challenges and Global Development Status
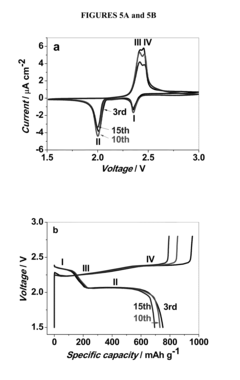
Sulfur cathodes represent one of the most promising yet challenging technologies in next-generation energy storage systems. Despite their theoretical energy density of 2,600 Wh/kg—nearly five times that of conventional lithium-ion batteries—several critical technical challenges have impeded their widespread commercialization. The most significant obstacle remains the "shuttle effect," where soluble polysulfide intermediates migrate between electrodes during cycling, causing rapid capacity fading and shortened battery lifespan. This phenomenon has proven particularly difficult to overcome despite extensive research efforts globally.
Material stability presents another major challenge, as sulfur undergoes substantial volume expansion (approximately 80%) during lithium insertion, leading to mechanical degradation of the electrode structure. This expansion-contraction cycle creates stress that compromises the integrity of the cathode over multiple charge-discharge cycles, resulting in poor cycling performance and reduced battery longevity.
The low electrical conductivity of sulfur (5×10^-30 S/cm) necessitates the incorporation of conductive additives, which reduces the overall energy density of the battery system. Additionally, the slow reaction kinetics between lithium and sulfur limits power capability, making sulfur cathodes less suitable for high-power applications where rapid charging and discharging are required.
From a global development perspective, research on sulfur cathodes exhibits distinct regional characteristics. North America, particularly the United States, leads in fundamental research and intellectual property development, with significant contributions from national laboratories and universities such as Stanford, MIT, and Argonne National Laboratory. The U.S. Department of Energy has allocated substantial funding through its Battery500 Consortium specifically targeting lithium-sulfur technology advancement.
In Asia, China has emerged as the dominant force in sulfur cathode development, with both academic institutions and industrial players making significant strides. Companies like CATL and BYD have established dedicated research divisions for sulfur-based energy storage. South Korea and Japan maintain strong positions through companies such as Samsung SDI and Toyota, which have published numerous patents on sulfur cathode technologies in recent years.
European efforts are characterized by collaborative research initiatives, with the European Union funding several large-scale projects through Horizon Europe. Notable contributions come from German research institutions and automotive manufacturers, who view sulfur cathodes as a potential solution for electric vehicle range extension.
Recent technological breakthroughs include novel electrolyte formulations, advanced carbon hosts for sulfur encapsulation, and protective coatings that mitigate the shuttle effect. However, these solutions often address individual challenges rather than providing comprehensive approaches to all technical barriers simultaneously.
Material stability presents another major challenge, as sulfur undergoes substantial volume expansion (approximately 80%) during lithium insertion, leading to mechanical degradation of the electrode structure. This expansion-contraction cycle creates stress that compromises the integrity of the cathode over multiple charge-discharge cycles, resulting in poor cycling performance and reduced battery longevity.
The low electrical conductivity of sulfur (5×10^-30 S/cm) necessitates the incorporation of conductive additives, which reduces the overall energy density of the battery system. Additionally, the slow reaction kinetics between lithium and sulfur limits power capability, making sulfur cathodes less suitable for high-power applications where rapid charging and discharging are required.
From a global development perspective, research on sulfur cathodes exhibits distinct regional characteristics. North America, particularly the United States, leads in fundamental research and intellectual property development, with significant contributions from national laboratories and universities such as Stanford, MIT, and Argonne National Laboratory. The U.S. Department of Energy has allocated substantial funding through its Battery500 Consortium specifically targeting lithium-sulfur technology advancement.
In Asia, China has emerged as the dominant force in sulfur cathode development, with both academic institutions and industrial players making significant strides. Companies like CATL and BYD have established dedicated research divisions for sulfur-based energy storage. South Korea and Japan maintain strong positions through companies such as Samsung SDI and Toyota, which have published numerous patents on sulfur cathode technologies in recent years.
European efforts are characterized by collaborative research initiatives, with the European Union funding several large-scale projects through Horizon Europe. Notable contributions come from German research institutions and automotive manufacturers, who view sulfur cathodes as a potential solution for electric vehicle range extension.
Recent technological breakthroughs include novel electrolyte formulations, advanced carbon hosts for sulfur encapsulation, and protective coatings that mitigate the shuttle effect. However, these solutions often address individual challenges rather than providing comprehensive approaches to all technical barriers simultaneously.
Current Technical Solutions for Sulfur Cathodes
01 Sulfur cathode compositions for lithium-sulfur batteries
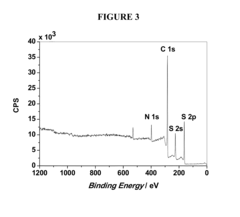
Various compositions for sulfur cathodes in lithium-sulfur batteries have been developed to improve energy density and cycle life. These compositions typically include sulfur as the active material combined with conductive additives and binders. The cathodes may incorporate carbon materials, polymers, or metal oxides to enhance conductivity and contain sulfur within the electrode structure, preventing dissolution into the electrolyte and improving overall battery performance.- Sulfur cathode compositions for lithium-sulfur batteries: Various compositions for sulfur cathodes in lithium-sulfur batteries have been developed to improve energy density and cycle life. These compositions typically include elemental sulfur combined with conductive additives, binders, and other materials to enhance electrochemical performance. The cathode compositions are designed to address challenges such as sulfur's poor conductivity and the polysulfide shuttle effect that can reduce battery efficiency.
- Protective coatings and encapsulation for sulfur cathodes: Protective coatings and encapsulation techniques are applied to sulfur cathodes to mitigate polysulfide dissolution and shuttle effect. These approaches involve encapsulating sulfur particles within conductive or polymeric shells, or applying protective layers to the cathode surface. Such strategies help contain sulfur and its discharge products within the cathode structure, preventing capacity loss and extending battery life.
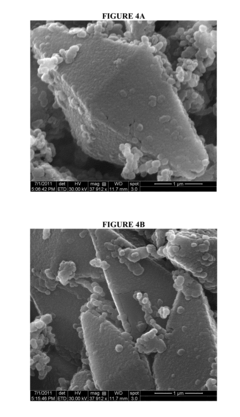
- Carbon-sulfur composite structures for cathodes: Carbon-sulfur composite structures are designed to improve the conductivity and stability of sulfur cathodes. These composites typically incorporate sulfur into various carbon matrices such as carbon nanotubes, graphene, porous carbon, or carbon fibers. The carbon framework provides electrical conductivity while physically constraining sulfur and its discharge products, leading to improved cycling performance and capacity retention.
- Electrolyte modifications for sulfur cathode systems: Specialized electrolyte formulations are developed to work synergistically with sulfur cathodes. These electrolytes often contain additives that suppress polysulfide dissolution or promote the formation of stable interfaces on the cathode surface. Modifications may include using high-concentration electrolytes, incorporating polysulfide scavengers, or employing ionic liquids to enhance the electrochemical stability and performance of sulfur cathode systems.
- Manufacturing methods for sulfur cathodes: Various manufacturing techniques have been developed for producing high-performance sulfur cathodes. These methods include melt-diffusion processes, chemical vapor deposition, solution-based approaches, and advanced coating techniques. The manufacturing processes are designed to achieve uniform sulfur distribution, optimal pore structure, and strong bonding between sulfur and conductive matrices, which are critical for maximizing the utilization of active material and battery performance.
02 Protective coatings and encapsulation for sulfur cathodes
Protective coatings and encapsulation techniques are applied to sulfur cathodes to mitigate polysulfide dissolution and shuttle effect. These approaches involve creating physical barriers around sulfur particles using polymers, carbon materials, or metal compounds. The encapsulation helps contain sulfur and its discharge products within the cathode structure during cycling, significantly improving capacity retention and extending battery life while maintaining high energy density.Expand Specific Solutions03 Nanostructured sulfur cathode materials
Nanostructured materials for sulfur cathodes offer improved performance through enhanced surface area and controlled sulfur distribution. These include carbon nanotubes, graphene, mesoporous carbon, and other nanostructured hosts that accommodate volume changes during cycling and provide conductive pathways. The nanoscale architecture helps contain polysulfides, improves electron transport, and enables faster reaction kinetics, resulting in better rate capability and cycling stability for lithium-sulfur batteries.Expand Specific Solutions04 Electrolyte additives and modifications for sulfur cathodes
Specialized electrolyte formulations and additives are designed to work with sulfur cathodes to suppress polysulfide shuttling and enhance electrochemical performance. These include lithium salts, solvents, and functional additives that form protective interfaces on the cathode surface or chemically interact with polysulfides. Modified electrolytes can improve the stability of sulfur cathodes, enhance ionic conductivity, and create favorable solid-electrolyte interfaces, leading to better cycling performance and coulombic efficiency.Expand Specific Solutions05 Manufacturing processes for sulfur cathodes
Advanced manufacturing techniques for sulfur cathodes focus on achieving uniform sulfur distribution, optimal porosity, and strong structural integrity. These processes include melt-diffusion methods, solution-based approaches, spray drying, and electrospinning to incorporate sulfur into conductive hosts. Novel fabrication methods aim to maximize sulfur loading while maintaining electronic conductivity and mechanical stability, addressing key challenges in scaling up lithium-sulfur battery technology for commercial applications.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Industry Players and Competitive Landscape
The sulfur cathode market in energy applications is in an early growth phase, characterized by significant R&D investment but limited commercial deployment. The global market size is projected to expand substantially as lithium-sulfur battery technology matures, driven by demands for higher energy density storage solutions. Technical challenges around cycle life and sulfur utilization are being addressed by key players across the value chain. Companies like Sion Power and PolyPlus Battery are pioneering lithium-sulfur technologies, while established players such as Samsung SDI and LG Energy Solution are incorporating sulfur-based materials into their roadmaps. Academic institutions including Cornell University and Nanyang Technological University are advancing fundamental research, while materials innovators like Conamix and Wildcat Discovery Technologies are developing practical solutions to overcome performance limitations.
PolyPlus Battery Co., Inc.
Technical Solution: PolyPlus Battery has pioneered a revolutionary approach to lithium-sulfur battery technology through their protected lithium electrode (PLE) technology. Their proprietary ceramic membrane technology creates a solid-state interface that physically separates the lithium metal anode from the sulfur cathode environment, effectively eliminating the polysulfide shuttle effect at its source. For sulfur cathodes specifically, PolyPlus has developed nanostructured carbon-sulfur composites with tailored pore architectures that maximize active material utilization while accommodating volume expansion. Their cathode design incorporates specialized conductive additives and binders that maintain electrical connectivity throughout cycling. The company's latest prototypes have demonstrated energy densities exceeding 500 Wh/kg with significantly improved cycle life compared to conventional lithium-sulfur designs. PolyPlus has also developed aqueous-compatible lithium-sulfur systems using their protected electrode technology, opening potential applications in marine and underwater environments where conventional batteries face limitations. Their technology roadmap includes scaling production of their ceramic membranes for larger format cells suitable for electric vehicles and grid storage applications.
Strengths: Unique protected electrode technology effectively addresses the fundamental polysulfide shuttle problem; potential for extremely high energy density systems; versatility for both conventional and aqueous electrolyte systems. Weaknesses: Manufacturing challenges for ceramic membrane components at scale; higher production costs compared to conventional approaches; integration complexities with existing battery manufacturing processes.
Samsung SDI Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: Samsung SDI has developed a multi-faceted approach to sulfur cathode technology for next-generation energy storage. Their research focuses on hierarchical carbon-sulfur composite structures that effectively encapsulate sulfur within mesoporous carbon frameworks, significantly reducing polysulfide dissolution. Samsung's proprietary cathode design incorporates graphene-wrapped sulfur particles with functional interlayers that act as physical barriers to polysulfide migration. The company has also engineered specialized electrolyte additives that form stable solid-electrolyte interphases on both electrodes. Their latest prototypes demonstrate energy densities approaching 400-450 Wh/kg with improved cycle stability of 300+ cycles at 80% capacity retention. Samsung SDI has integrated these advances with their existing battery manufacturing infrastructure, positioning them for potential commercial scale-up of lithium-sulfur batteries for electric vehicles and grid storage applications. The company has also explored hybrid lithium-ion/sulfur systems as a transitional technology to leverage existing manufacturing capabilities.
Strengths: Strong manufacturing infrastructure and supply chain integration capabilities; balanced approach to performance and practicality; significant R&D resources and intellectual property portfolio in battery technologies. Weaknesses: More conservative energy density targets compared to pure Li-S startups; still facing challenges with cycle life for automotive applications; competing internal priorities with established lithium-ion technology roadmaps.
Critical Patents and Research Breakthroughs
Sulfur-hydroxylated graphene nanocomposites for rechargeable lithium-sulfur batteries and methods of making the same
PatentInactiveUS20160336590A1
Innovation
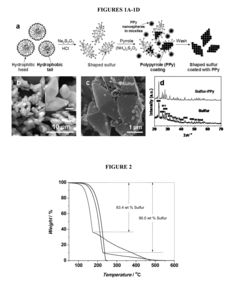
- A sulfur-hydroxylated graphene nanocomposite is developed, where amorphous sulfur nanoparticles are uniformly distributed on a hydroxylated graphene surface, enhancing conductivity and preventing polysulfide dissolution, with a method involving ultrasonication and hydrothermal treatment to form the nanocomposite.
Conductive polymer-coated, shaped sulfur-nanocomposite cathodes for rechargeable lithium-sulfur batteries and methods of making the same
PatentInactiveUS20150349323A1
Innovation
- A polymer-coated, shaped sulfur-nanocomposite is synthesized by forming shaped sulfur particles in an aqueous solution with a micelle-forming agent and nucleating agent, followed by coating with a nano-sized polymer layer, which improves electrical conductivity and confinement of sulfur, inhibiting polysulfide dissolution and enhancing electrode stability.
Supply Chain Analysis and Material Sourcing
The sulfur cathode supply chain presents unique challenges and opportunities within the energy storage sector. Elemental sulfur, the primary raw material, benefits from abundant availability as a byproduct of petroleum refining and natural gas processing. Global annual production exceeds 70 million tons, with significant reserves concentrated in North America, the Middle East, and China. This abundance translates to exceptionally low material costs, typically below $0.10 per kilogram, representing a substantial cost advantage over traditional cathode materials like cobalt and nickel compounds.
Despite this abundance, the sulfur cathode supply chain faces several critical bottlenecks. The processing of raw sulfur into battery-grade material requires specialized equipment and techniques to achieve the necessary purity levels and particle morphology. Currently, only a limited number of manufacturers possess this capability at scale, creating potential supply constraints as demand increases. Additionally, the carbon additives and conductive polymers essential for sulfur cathode functionality often rely on specialized suppliers, introducing vulnerability to supply disruptions.
Regional distribution of sulfur cathode manufacturing capacity shows significant imbalance. China dominates early-stage production with approximately 65% of global capacity, followed by South Korea and Japan. North American and European production remains limited despite growing interest in lithium-sulfur technology. This geographic concentration creates potential geopolitical vulnerabilities in the supply chain, particularly as energy storage becomes increasingly strategic.
Material sourcing strategies for sulfur cathodes must address several key considerations. The quality and consistency of sulfur feedstock vary significantly depending on the source, with petroleum-derived sulfur generally offering higher purity than mining-sourced material. Establishing reliable quality control protocols throughout the supply chain is essential for battery performance consistency. Furthermore, the environmental footprint of sulfur sourcing must be considered, as extraction methods and transportation logistics significantly impact the overall sustainability profile of sulfur cathode technologies.
The emerging circular economy for sulfur presents promising opportunities. As a waste product from multiple industrial processes, sulfur cathode production can potentially create value from materials that would otherwise require disposal. Several innovative companies are developing processes to directly convert industrial sulfur waste streams into battery-grade materials, potentially reducing both costs and environmental impact. These circular approaches may become increasingly important as regulatory frameworks around waste management and carbon emissions continue to evolve globally.
Despite this abundance, the sulfur cathode supply chain faces several critical bottlenecks. The processing of raw sulfur into battery-grade material requires specialized equipment and techniques to achieve the necessary purity levels and particle morphology. Currently, only a limited number of manufacturers possess this capability at scale, creating potential supply constraints as demand increases. Additionally, the carbon additives and conductive polymers essential for sulfur cathode functionality often rely on specialized suppliers, introducing vulnerability to supply disruptions.
Regional distribution of sulfur cathode manufacturing capacity shows significant imbalance. China dominates early-stage production with approximately 65% of global capacity, followed by South Korea and Japan. North American and European production remains limited despite growing interest in lithium-sulfur technology. This geographic concentration creates potential geopolitical vulnerabilities in the supply chain, particularly as energy storage becomes increasingly strategic.
Material sourcing strategies for sulfur cathodes must address several key considerations. The quality and consistency of sulfur feedstock vary significantly depending on the source, with petroleum-derived sulfur generally offering higher purity than mining-sourced material. Establishing reliable quality control protocols throughout the supply chain is essential for battery performance consistency. Furthermore, the environmental footprint of sulfur sourcing must be considered, as extraction methods and transportation logistics significantly impact the overall sustainability profile of sulfur cathode technologies.
The emerging circular economy for sulfur presents promising opportunities. As a waste product from multiple industrial processes, sulfur cathode production can potentially create value from materials that would otherwise require disposal. Several innovative companies are developing processes to directly convert industrial sulfur waste streams into battery-grade materials, potentially reducing both costs and environmental impact. These circular approaches may become increasingly important as regulatory frameworks around waste management and carbon emissions continue to evolve globally.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability Assessment
The environmental impact of sulfur cathode technologies extends far beyond their energy storage capabilities, representing a critical dimension in their market viability. Sulfur cathodes offer significant environmental advantages compared to conventional lithium-ion battery technologies, primarily due to the abundance and low toxicity of sulfur as a raw material. The extraction of sulfur generates substantially lower environmental footprints than mining operations for cobalt, nickel, and other critical materials used in traditional cathodes.
Life cycle assessments of sulfur cathode batteries demonstrate potential reductions in greenhouse gas emissions by 25-30% compared to conventional lithium-ion technologies when considering the entire production chain. This reduction stems from simplified manufacturing processes and decreased reliance on energy-intensive material refinement. Additionally, the carbon footprint associated with transportation of raw materials is minimized due to sulfur's widespread geographical availability, eliminating the need for long-distance shipping from limited extraction sites.
Water consumption metrics also favor sulfur cathode technologies, with preliminary studies indicating up to 40% reduction in process water requirements compared to conventional cathode production. This advantage becomes particularly significant in water-stressed regions where battery manufacturing facilities might be located. Furthermore, the absence of toxic heavy metals in sulfur cathodes substantially reduces the risk of soil and groundwater contamination during both manufacturing and end-of-life stages.
End-of-life management presents both challenges and opportunities for sulfur cathode technologies. While the recycling infrastructure for these newer battery chemistries remains underdeveloped, the inherent material composition offers promising recyclability pathways. Theoretical recovery rates for sulfur from spent batteries exceed 90%, though commercial-scale processes have yet to achieve these efficiencies consistently. The development of closed-loop recycling systems specifically designed for sulfur cathodes represents a critical area for future investment.
Regulatory frameworks worldwide are increasingly incorporating sustainability metrics into energy storage technology assessments. The European Union's Battery Directive revision and similar initiatives in North America and Asia are establishing more stringent environmental performance requirements that may accelerate market adoption of sulfur cathode technologies. Companies demonstrating superior environmental credentials through reduced carbon emissions, water usage, and toxic material elimination will likely gain competitive advantages as these regulations mature.
Life cycle assessments of sulfur cathode batteries demonstrate potential reductions in greenhouse gas emissions by 25-30% compared to conventional lithium-ion technologies when considering the entire production chain. This reduction stems from simplified manufacturing processes and decreased reliance on energy-intensive material refinement. Additionally, the carbon footprint associated with transportation of raw materials is minimized due to sulfur's widespread geographical availability, eliminating the need for long-distance shipping from limited extraction sites.
Water consumption metrics also favor sulfur cathode technologies, with preliminary studies indicating up to 40% reduction in process water requirements compared to conventional cathode production. This advantage becomes particularly significant in water-stressed regions where battery manufacturing facilities might be located. Furthermore, the absence of toxic heavy metals in sulfur cathodes substantially reduces the risk of soil and groundwater contamination during both manufacturing and end-of-life stages.
End-of-life management presents both challenges and opportunities for sulfur cathode technologies. While the recycling infrastructure for these newer battery chemistries remains underdeveloped, the inherent material composition offers promising recyclability pathways. Theoretical recovery rates for sulfur from spent batteries exceed 90%, though commercial-scale processes have yet to achieve these efficiencies consistently. The development of closed-loop recycling systems specifically designed for sulfur cathodes represents a critical area for future investment.
Regulatory frameworks worldwide are increasingly incorporating sustainability metrics into energy storage technology assessments. The European Union's Battery Directive revision and similar initiatives in North America and Asia are establishing more stringent environmental performance requirements that may accelerate market adoption of sulfur cathode technologies. Companies demonstrating superior environmental credentials through reduced carbon emissions, water usage, and toxic material elimination will likely gain competitive advantages as these regulations mature.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!