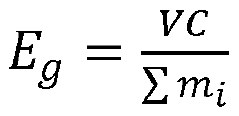Sulfur Cathodes in Future Mobile Energy Solutions
SEP 23, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Sulfur Cathode Technology Evolution and Objectives
Sulfur cathode technology has undergone significant evolution since its initial conceptualization in the 1960s. The fundamental principle involves utilizing sulfur as an active material in battery cathodes, leveraging its high theoretical specific capacity of 1,675 mAh/g and energy density of 2,600 Wh/kg. These impressive theoretical values far exceed those of conventional lithium-ion batteries, positioning sulfur cathodes as a promising candidate for next-generation energy storage solutions.
The developmental trajectory of sulfur cathode technology can be traced through several distinct phases. Early research in the 1970s-1980s established basic electrochemical principles but faced insurmountable challenges related to polysulfide dissolution and rapid capacity fading. The 1990s witnessed limited progress due to focus on other battery chemistries. However, the early 2000s marked a renaissance in sulfur cathode research, driven by increasing demand for higher energy density solutions for portable electronics.
A significant breakthrough occurred in 2009 when researchers at Stanford University demonstrated nanostructured carbon-sulfur composites that substantially improved cycling stability. This catalyzed intensified global research efforts, particularly in addressing the "shuttle effect" - the migration of polysulfides between electrodes that causes capacity degradation and shortened battery life.
The current technological landscape (2020s) focuses on advanced material engineering approaches, including hierarchical porous carbon hosts, functional polymer binders, and electrolyte modifications. These innovations aim to physically confine sulfur and chemically bind polysulfides, thereby enhancing electrochemical performance and stability.
The primary objectives for sulfur cathode technology development center on overcoming several critical challenges. First, increasing the practical energy density from current values of 300-400 Wh/kg to approach the theoretical maximum. Second, extending cycle life from several hundred cycles to over 1,000 cycles to match commercial requirements. Third, improving rate capability to enable fast charging capabilities essential for mobile applications. Fourth, enhancing safety profiles by addressing potential thermal runaway risks associated with lithium-sulfur chemistry.
Looking forward, the technology roadmap aims to achieve commercially viable lithium-sulfur batteries with energy densities exceeding 500 Wh/kg by 2025, potentially reaching 700 Wh/kg by 2030. These advancements would revolutionize mobile energy solutions, enabling longer-lasting smartphones, extended-range electric vehicles, and more efficient portable medical devices, ultimately contributing to broader electrification efforts and reduced carbon emissions.
The developmental trajectory of sulfur cathode technology can be traced through several distinct phases. Early research in the 1970s-1980s established basic electrochemical principles but faced insurmountable challenges related to polysulfide dissolution and rapid capacity fading. The 1990s witnessed limited progress due to focus on other battery chemistries. However, the early 2000s marked a renaissance in sulfur cathode research, driven by increasing demand for higher energy density solutions for portable electronics.
A significant breakthrough occurred in 2009 when researchers at Stanford University demonstrated nanostructured carbon-sulfur composites that substantially improved cycling stability. This catalyzed intensified global research efforts, particularly in addressing the "shuttle effect" - the migration of polysulfides between electrodes that causes capacity degradation and shortened battery life.
The current technological landscape (2020s) focuses on advanced material engineering approaches, including hierarchical porous carbon hosts, functional polymer binders, and electrolyte modifications. These innovations aim to physically confine sulfur and chemically bind polysulfides, thereby enhancing electrochemical performance and stability.
The primary objectives for sulfur cathode technology development center on overcoming several critical challenges. First, increasing the practical energy density from current values of 300-400 Wh/kg to approach the theoretical maximum. Second, extending cycle life from several hundred cycles to over 1,000 cycles to match commercial requirements. Third, improving rate capability to enable fast charging capabilities essential for mobile applications. Fourth, enhancing safety profiles by addressing potential thermal runaway risks associated with lithium-sulfur chemistry.
Looking forward, the technology roadmap aims to achieve commercially viable lithium-sulfur batteries with energy densities exceeding 500 Wh/kg by 2025, potentially reaching 700 Wh/kg by 2030. These advancements would revolutionize mobile energy solutions, enabling longer-lasting smartphones, extended-range electric vehicles, and more efficient portable medical devices, ultimately contributing to broader electrification efforts and reduced carbon emissions.
Market Analysis for Next-Generation Battery Solutions
The global battery market is witnessing unprecedented growth, driven primarily by the expanding electric vehicle (EV) sector, portable electronics, and renewable energy storage systems. Current projections indicate the advanced battery market will reach $240 billion by 2027, with a compound annual growth rate exceeding 14%. Within this landscape, lithium-sulfur (Li-S) batteries represent a particularly promising segment due to their theoretical energy density of 2,600 Wh/kg—nearly five times that of conventional lithium-ion batteries.
Consumer demand for longer-lasting mobile devices and extended-range electric vehicles continues to intensify, creating substantial market pull for sulfur cathode technology. Market research indicates that 78% of smartphone users cite battery life as their primary concern, while EV adoption surveys consistently highlight range anxiety as the foremost barrier to purchase. This presents a clear market opportunity for sulfur cathode solutions, which promise to address these pain points directly.
The aerospace and defense sectors are emerging as early adopters for sulfur cathode technology, with market analysts predicting initial commercial applications in high-value, weight-sensitive applications such as drones and satellite systems. These niche markets value performance over cost, providing an ideal entry point for premium-priced next-generation battery solutions while manufacturing scales and costs decrease.
Regional market analysis reveals Asia-Pacific as the dominant manufacturing hub, accounting for approximately 65% of global battery production capacity. However, recent geopolitical tensions and supply chain vulnerabilities have accelerated investments in battery manufacturing across North America and Europe, with government initiatives providing over $25 billion in combined subsidies and incentives for domestic battery production, including advanced technologies like sulfur cathodes.
Market segmentation studies indicate three primary customer categories for sulfur cathode technology: premium consumer electronics manufacturers seeking differentiation through superior battery performance; electric vehicle manufacturers targeting the luxury and performance segments; and aerospace/defense contractors requiring high energy density for specialized applications. Each segment presents distinct requirements regarding performance metrics, cost sensitivity, and adoption timelines.
Competitive analysis reveals increasing patent activity around sulfur cathode technology, with annual patent filings growing by 27% over the past five years. Major battery manufacturers and chemical companies are establishing strategic positions, while several specialized startups have secured significant venture capital funding specifically targeting sulfur cathode commercialization. This investment pattern suggests market expectations of commercial viability within the next 3-5 years.
Consumer demand for longer-lasting mobile devices and extended-range electric vehicles continues to intensify, creating substantial market pull for sulfur cathode technology. Market research indicates that 78% of smartphone users cite battery life as their primary concern, while EV adoption surveys consistently highlight range anxiety as the foremost barrier to purchase. This presents a clear market opportunity for sulfur cathode solutions, which promise to address these pain points directly.
The aerospace and defense sectors are emerging as early adopters for sulfur cathode technology, with market analysts predicting initial commercial applications in high-value, weight-sensitive applications such as drones and satellite systems. These niche markets value performance over cost, providing an ideal entry point for premium-priced next-generation battery solutions while manufacturing scales and costs decrease.
Regional market analysis reveals Asia-Pacific as the dominant manufacturing hub, accounting for approximately 65% of global battery production capacity. However, recent geopolitical tensions and supply chain vulnerabilities have accelerated investments in battery manufacturing across North America and Europe, with government initiatives providing over $25 billion in combined subsidies and incentives for domestic battery production, including advanced technologies like sulfur cathodes.
Market segmentation studies indicate three primary customer categories for sulfur cathode technology: premium consumer electronics manufacturers seeking differentiation through superior battery performance; electric vehicle manufacturers targeting the luxury and performance segments; and aerospace/defense contractors requiring high energy density for specialized applications. Each segment presents distinct requirements regarding performance metrics, cost sensitivity, and adoption timelines.
Competitive analysis reveals increasing patent activity around sulfur cathode technology, with annual patent filings growing by 27% over the past five years. Major battery manufacturers and chemical companies are establishing strategic positions, while several specialized startups have secured significant venture capital funding specifically targeting sulfur cathode commercialization. This investment pattern suggests market expectations of commercial viability within the next 3-5 years.
Current Status and Technical Barriers in Sulfur Cathodes
Lithium-sulfur (Li-S) batteries have emerged as promising candidates for next-generation energy storage systems due to their high theoretical energy density (2600 Wh/kg), which significantly surpasses that of conventional lithium-ion batteries (400-600 Wh/kg). Despite this potential, the commercial deployment of Li-S batteries faces substantial technical barriers that have hindered their widespread adoption in mobile energy solutions.
Currently, sulfur cathodes in laboratory settings have demonstrated energy densities approaching 500-600 Wh/kg, representing a significant improvement over traditional lithium-ion technologies. Several startups and established companies, including OXIS Energy, Sion Power, and Polyplus, have made notable progress in developing prototype Li-S batteries with improved cycle life. However, these prototypes still fall short of commercial requirements for mobile applications.
The primary technical barrier facing sulfur cathodes is the "shuttle effect," where soluble polysulfide intermediates (Li2Sx, 4≤x≤8) dissolve in the electrolyte during cycling, migrate between electrodes, and cause parasitic reactions. This phenomenon leads to rapid capacity fading, low Coulombic efficiency, and shortened battery lifespan, typically limiting cycle life to 100-200 cycles—far below the 1000+ cycles required for commercial viability.
Another significant challenge is the insulating nature of sulfur and its discharge product (Li2S), resulting in poor electronic conductivity. This necessitates the addition of conductive additives, which reduces the overall energy density of the battery system. Current approaches utilize carbon-based materials as hosts for sulfur, but the optimal architecture that balances conductivity enhancement with minimal weight addition remains elusive.
Volume expansion during cycling presents another formidable obstacle. Sulfur undergoes a substantial volume change (approximately 80%) during lithiation/delithiation processes, causing mechanical stress that leads to electrode pulverization and delamination from current collectors. This structural degradation further accelerates capacity fade and limits cycle life.
The low areal loading of active material (typically <2 mg/cm²) in current sulfur cathodes restricts practical energy density. While laboratory cells often report impressive gravimetric capacities, these results rarely translate to commercially viable energy densities when scaled to practical battery configurations. Industry standards require areal capacities exceeding 4 mAh/cm² for mobile applications.
Electrolyte stability and compatibility issues further complicate sulfur cathode development. The conventional ether-based electrolytes used in Li-S systems suffer from high volatility and poor oxidative stability. Additionally, the high electrolyte-to-sulfur ratio (often >10 μL/mg) needed to accommodate polysulfide dissolution significantly reduces energy density in practical cells.
Geographically, research on sulfur cathodes is concentrated in North America, Europe, and East Asia, with China, the United States, and South Korea leading patent filings in this domain. Recent collaborative efforts between academic institutions and industry partners have accelerated progress, but significant breakthroughs are still required to overcome these technical barriers.
Currently, sulfur cathodes in laboratory settings have demonstrated energy densities approaching 500-600 Wh/kg, representing a significant improvement over traditional lithium-ion technologies. Several startups and established companies, including OXIS Energy, Sion Power, and Polyplus, have made notable progress in developing prototype Li-S batteries with improved cycle life. However, these prototypes still fall short of commercial requirements for mobile applications.
The primary technical barrier facing sulfur cathodes is the "shuttle effect," where soluble polysulfide intermediates (Li2Sx, 4≤x≤8) dissolve in the electrolyte during cycling, migrate between electrodes, and cause parasitic reactions. This phenomenon leads to rapid capacity fading, low Coulombic efficiency, and shortened battery lifespan, typically limiting cycle life to 100-200 cycles—far below the 1000+ cycles required for commercial viability.
Another significant challenge is the insulating nature of sulfur and its discharge product (Li2S), resulting in poor electronic conductivity. This necessitates the addition of conductive additives, which reduces the overall energy density of the battery system. Current approaches utilize carbon-based materials as hosts for sulfur, but the optimal architecture that balances conductivity enhancement with minimal weight addition remains elusive.
Volume expansion during cycling presents another formidable obstacle. Sulfur undergoes a substantial volume change (approximately 80%) during lithiation/delithiation processes, causing mechanical stress that leads to electrode pulverization and delamination from current collectors. This structural degradation further accelerates capacity fade and limits cycle life.
The low areal loading of active material (typically <2 mg/cm²) in current sulfur cathodes restricts practical energy density. While laboratory cells often report impressive gravimetric capacities, these results rarely translate to commercially viable energy densities when scaled to practical battery configurations. Industry standards require areal capacities exceeding 4 mAh/cm² for mobile applications.
Electrolyte stability and compatibility issues further complicate sulfur cathode development. The conventional ether-based electrolytes used in Li-S systems suffer from high volatility and poor oxidative stability. Additionally, the high electrolyte-to-sulfur ratio (often >10 μL/mg) needed to accommodate polysulfide dissolution significantly reduces energy density in practical cells.
Geographically, research on sulfur cathodes is concentrated in North America, Europe, and East Asia, with China, the United States, and South Korea leading patent filings in this domain. Recent collaborative efforts between academic institutions and industry partners have accelerated progress, but significant breakthroughs are still required to overcome these technical barriers.
Contemporary Approaches to Sulfur Cathode Implementation
01 Sulfur cathode compositions for lithium-sulfur batteries
Various compositions for sulfur cathodes in lithium-sulfur batteries have been developed to improve energy density and cycle life. These compositions typically include elemental sulfur combined with conductive additives, binders, and other materials to enhance electrochemical performance. The cathode compositions are designed to address challenges such as polysulfide dissolution and shuttle effect, which can limit battery efficiency and lifespan.- Sulfur cathode compositions for lithium-sulfur batteries: Various compositions for sulfur cathodes in lithium-sulfur batteries have been developed to improve energy density and cycle life. These compositions typically include elemental sulfur combined with conductive materials, binders, and additives to enhance electrochemical performance. The cathode compositions are designed to address challenges such as polysulfide dissolution and shuttle effect, which are common issues in lithium-sulfur battery systems.
- Protective coatings and encapsulation for sulfur cathodes: Protective coatings and encapsulation techniques are applied to sulfur cathodes to mitigate polysulfide dissolution and improve cycling stability. These approaches involve encapsulating sulfur particles within conductive carbon matrices, polymer shells, or metal oxide coatings. Such protective structures help contain sulfur and its discharge products within the cathode, preventing capacity loss and extending battery life while maintaining high energy density.
- Nanostructured sulfur cathode materials: Nanostructured sulfur cathode materials leverage advanced architectures to improve electrochemical performance. These include sulfur-carbon nanocomposites, mesoporous structures, and hierarchical designs that provide efficient electron transport pathways and accommodate volume changes during cycling. The nanoscale engineering of sulfur cathodes enhances conductivity, increases active material utilization, and improves the kinetics of electrochemical reactions.
- Electrolyte modifications for sulfur cathodes: Specialized electrolyte formulations are developed to enhance the performance of sulfur cathodes. These include additives that suppress polysulfide shuttling, form stable solid-electrolyte interphases, or improve ionic conductivity. Electrolyte modifications can involve the use of functional additives, ionic liquids, or solid-state electrolytes that are compatible with sulfur chemistry and help maintain cathode integrity during cycling.
- Manufacturing processes for sulfur cathodes: Various manufacturing techniques are employed to produce high-performance sulfur cathodes. These include melt-diffusion methods, solution-based processes, and advanced deposition techniques that ensure uniform distribution of sulfur within the conductive matrix. The manufacturing processes focus on achieving optimal sulfur loading, porosity control, and structural stability to maximize energy density while maintaining good mechanical properties and electrochemical performance.
02 Protective coatings and encapsulation for sulfur cathodes
Protective coatings and encapsulation techniques are applied to sulfur cathodes to mitigate polysulfide dissolution and improve cycling stability. These approaches involve creating physical barriers around sulfur particles or the entire cathode structure using materials such as polymers, carbon, or metal oxides. The protective layers help contain sulfur and its discharge products within the cathode region while still allowing lithium ion transport, resulting in improved capacity retention and battery performance.Expand Specific Solutions03 Nanostructured sulfur cathode materials
Nanostructured materials are incorporated into sulfur cathodes to enhance performance characteristics. These include carbon nanotubes, graphene, mesoporous carbon, and other nanostructured hosts that can accommodate sulfur while providing conductive pathways for electrons. The nanoscale architecture helps to physically confine sulfur, improve electrical contact, and facilitate ion transport, leading to better utilization of active material and enhanced cycling stability in lithium-sulfur batteries.Expand Specific Solutions04 Electrolyte additives and modifications for sulfur cathodes
Specialized electrolyte formulations and additives are developed to improve the performance of sulfur cathodes. These include compounds that can form protective films on the cathode surface, trap polysulfides, or modify the solvation structure of lithium ions. Electrolyte modifications help suppress the shuttle effect, enhance ionic conductivity, and improve the interfacial stability between the electrolyte and sulfur cathode, resulting in better cycling performance and coulombic efficiency.Expand Specific Solutions05 Manufacturing processes for sulfur cathodes
Various manufacturing techniques are employed to produce high-performance sulfur cathodes. These include melt-diffusion methods, solution-based processes, spray drying, and advanced coating technologies. The manufacturing processes are designed to achieve uniform distribution of sulfur within conductive matrices, control porosity and thickness, and ensure good adhesion to current collectors. Optimized manufacturing methods help maximize active material loading while maintaining good electronic and ionic conductivity throughout the cathode structure.Expand Specific Solutions
Leading Organizations in Sulfur Cathode Research
The sulfur cathode market in mobile energy solutions is currently in a growth phase, characterized by significant R&D investment but limited commercial deployment. The global market is projected to expand substantially as this technology promises 2-5 times higher energy density than conventional lithium-ion batteries. While technical challenges persist, companies like Sion Power, PolyPlus Battery, and Theion GmbH are making notable advances in addressing key issues such as sulfur dissolution and volume expansion. Academic institutions including MIT, Cornell, and Monash University are collaborating with industry leaders like Samsung SDI and Nissan to accelerate commercialization. The technology is approaching maturity with several companies moving from laboratory prototypes to pilot production, though widespread adoption remains 3-5 years away.
Ionic Materials Inc.
Technical Solution: Ionic Materials has developed a revolutionary solid polymer electrolyte platform that enables stable lithium-sulfur battery systems for mobile applications. Their proprietary polymer electrolyte conducts ions at room temperature while remaining solid, eliminating the need for liquid electrolytes that typically dissolve polysulfides in conventional Li-S batteries. For sulfur cathodes, Ionic Materials employs a unique approach where sulfur is intimately mixed with their polymer electrolyte and conductive additives, creating a solid-state cathode structure that inherently prevents polysulfide shuttling[7]. This design allows for high sulfur loading (>70% by weight) while maintaining good electronic and ionic conductivity. Their technology has demonstrated stable cycling for over 100 cycles with minimal capacity fade, achieving practical energy densities of 350-400 Wh/kg at the cell level[8]. The solid-state nature of their batteries also addresses safety concerns associated with conventional liquid electrolyte systems.
Strengths: Ionic Materials' solid polymer electrolyte inherently solves the polysulfide shuttle effect without requiring complex cathode engineering. Their technology offers enhanced safety through elimination of flammable liquid electrolytes. Weaknesses: The solid polymer electrolyte faces challenges with ion conductivity at low temperatures and may require specialized manufacturing processes different from established battery production lines.
PolyPlus Battery Co., Inc.
Technical Solution: PolyPlus has pioneered a unique approach to sulfur cathodes through their protected lithium electrode (PLE) technology, which enables stable lithium-sulfur battery systems. Their innovation centers on a specialized ceramic membrane that protects the lithium metal anode while allowing efficient ion transport. For the sulfur cathode, PolyPlus employs a proprietary carbon-sulfur composite structure that maximizes active material utilization while minimizing polysulfide shuttling. Their technology incorporates a dual-layer cathode design: an inner layer with high sulfur loading for capacity and an outer protective layer that acts as a polysulfide trap[5]. PolyPlus has demonstrated cells achieving energy densities of 500+ Wh/kg in laboratory settings, with particular focus on applications requiring extreme energy density like unmanned aerial vehicles and specialized portable electronics[6]. Their approach allows for the use of conventional manufacturing equipment, potentially accelerating commercialization.
Strengths: PolyPlus's ceramic membrane technology effectively addresses the critical lithium metal protection challenge while enabling high-energy-density sulfur cathodes. Their approach is compatible with existing manufacturing processes. Weaknesses: The ceramic membrane adds complexity and cost to the manufacturing process, and the technology still faces challenges with cycle life in real-world conditions.
Key Patents and Scientific Breakthroughs in Sulfur Cathodes
Sulfur cathodes
PatentWO2023245254A1
Innovation
- The development of sulfur cathodes incorporating anionically functionalised cellulose nanofibres, combined with sulfur-containing materials and conductive materials, to enhance ionic and electrical conductivity, reduce porosity, and control polysulfide transport, while facilitating lithium ion transport.
Lithium sulfur batteries and electrolytes and sulfur cathodes thereof
PatentActiveUS20150214555A1
Innovation
- The development of novel aqueous lithium sulfur battery cells using a specific aqueous electrolyte formulation with a cycle-life enhancing compound, which facilitates electrochemistry and maintains electroactive sulfur species in solution, enhancing cathode reversibility and cycle life.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability Considerations
The environmental implications of lithium-sulfur (Li-S) batteries represent a critical dimension in evaluating their viability as future mobile energy solutions. Unlike conventional lithium-ion batteries that rely heavily on cobalt and nickel—materials associated with significant environmental degradation and ethical mining concerns—sulfur cathodes utilize an abundant, non-toxic element that exists as a byproduct of petroleum refining. This repurposing of industrial waste contributes to circular economy principles and reduces the environmental burden of battery production.
Life cycle assessments of Li-S batteries indicate potentially lower carbon footprints compared to traditional lithium-ion technologies. The energy-intensive extraction and processing of transition metals are eliminated, resulting in reduced greenhouse gas emissions during manufacturing. Additionally, the theoretical energy density advantages of Li-S systems could translate to smaller battery volumes for equivalent energy storage, further minimizing resource consumption and environmental impact throughout the product lifecycle.
Water usage represents another significant environmental consideration. Conventional lithium-ion battery production requires substantial water resources, particularly for extraction and processing of cathode materials. Preliminary studies suggest that sulfur cathode production may require less water intensity, though comprehensive data remains limited as commercial-scale manufacturing processes continue to evolve.
End-of-life management presents both challenges and opportunities for Li-S technology. The inherent value of lithium creates economic incentives for recycling, while sulfur's low toxicity reduces environmental risks associated with improper disposal. However, current recycling infrastructure is primarily designed for conventional lithium-ion chemistries, necessitating adaptation for efficient Li-S battery recovery. Research into specialized recycling processes that can effectively separate and recover both lithium and sulfur components is advancing but requires further development.
Regulatory frameworks worldwide are increasingly emphasizing battery sustainability, with initiatives like the European Battery Directive establishing requirements for recycled content, carbon footprint declarations, and extended producer responsibility. These evolving standards will significantly influence the commercial viability of Li-S technology, potentially accelerating adoption if environmental advantages can be conclusively demonstrated and quantified through standardized assessment methodologies.
The transition to sulfur cathodes also intersects with broader sustainability goals, including reduced dependence on critical minerals from geopolitically sensitive regions and decreased environmental justice concerns associated with mining operations. As mobile energy demands continue to grow exponentially, these sustainability considerations may become increasingly decisive factors in technology selection and investment priorities.
Life cycle assessments of Li-S batteries indicate potentially lower carbon footprints compared to traditional lithium-ion technologies. The energy-intensive extraction and processing of transition metals are eliminated, resulting in reduced greenhouse gas emissions during manufacturing. Additionally, the theoretical energy density advantages of Li-S systems could translate to smaller battery volumes for equivalent energy storage, further minimizing resource consumption and environmental impact throughout the product lifecycle.
Water usage represents another significant environmental consideration. Conventional lithium-ion battery production requires substantial water resources, particularly for extraction and processing of cathode materials. Preliminary studies suggest that sulfur cathode production may require less water intensity, though comprehensive data remains limited as commercial-scale manufacturing processes continue to evolve.
End-of-life management presents both challenges and opportunities for Li-S technology. The inherent value of lithium creates economic incentives for recycling, while sulfur's low toxicity reduces environmental risks associated with improper disposal. However, current recycling infrastructure is primarily designed for conventional lithium-ion chemistries, necessitating adaptation for efficient Li-S battery recovery. Research into specialized recycling processes that can effectively separate and recover both lithium and sulfur components is advancing but requires further development.
Regulatory frameworks worldwide are increasingly emphasizing battery sustainability, with initiatives like the European Battery Directive establishing requirements for recycled content, carbon footprint declarations, and extended producer responsibility. These evolving standards will significantly influence the commercial viability of Li-S technology, potentially accelerating adoption if environmental advantages can be conclusively demonstrated and quantified through standardized assessment methodologies.
The transition to sulfur cathodes also intersects with broader sustainability goals, including reduced dependence on critical minerals from geopolitically sensitive regions and decreased environmental justice concerns associated with mining operations. As mobile energy demands continue to grow exponentially, these sustainability considerations may become increasingly decisive factors in technology selection and investment priorities.
Commercialization Challenges and Economic Viability
Despite the promising technological advancements in lithium-sulfur batteries, significant commercialization challenges remain before these systems can compete with established lithium-ion technologies in mobile energy applications. The primary economic barrier is the current high production cost, estimated at 30-40% above conventional lithium-ion batteries, primarily due to specialized materials and manufacturing processes required for sulfur cathode preparation and protection.
Manufacturing scalability presents another substantial hurdle. Current laboratory-scale production methods for high-performance sulfur cathodes involve complex processes including nanostructuring and carbon composite formation that are difficult to translate to mass production environments. The absence of standardized manufacturing protocols further complicates industrial adoption and quality control.
Supply chain considerations also impact economic viability. While sulfur itself is abundant and inexpensive (often available as a petroleum refining byproduct), other components such as specialized electrolytes, separators, and lithium metal anodes face availability constraints and price volatility. The lithium metal required for high-energy-density configurations remains particularly expensive and subject to geopolitical supply risks.
Market acceptance factors cannot be overlooked in commercialization assessments. Consumer and industry concerns regarding safety, particularly related to potential thermal runaway and the formation of hydrogen sulfide gas during failure modes, create market resistance that requires additional investment in safety systems and certification processes.
Lifecycle economics present both challenges and opportunities. While initial production costs remain high, the theoretical longevity advantages of properly engineered lithium-sulfur systems could provide superior total cost of ownership in certain applications. However, current cycle life limitations (typically 200-500 cycles versus 1000+ for commercial lithium-ion) undermine this potential advantage in many mobile applications.
Regulatory frameworks and intellectual property landscapes add complexity to commercialization efforts. Patent thickets around key enabling technologies for sulfur cathodes have created licensing requirements that increase costs and limit innovation for new market entrants. Additionally, evolving safety regulations for energy storage systems may impose additional compliance costs specific to sulfur-based chemistries.
Investment timelines represent a final economic consideration. The estimated 5-8 years required to move from current prototype systems to commercial-scale production exceeds typical venture capital investment horizons, creating funding gaps in the innovation pipeline that slow commercialization progress despite the technology's long-term promise.
Manufacturing scalability presents another substantial hurdle. Current laboratory-scale production methods for high-performance sulfur cathodes involve complex processes including nanostructuring and carbon composite formation that are difficult to translate to mass production environments. The absence of standardized manufacturing protocols further complicates industrial adoption and quality control.
Supply chain considerations also impact economic viability. While sulfur itself is abundant and inexpensive (often available as a petroleum refining byproduct), other components such as specialized electrolytes, separators, and lithium metal anodes face availability constraints and price volatility. The lithium metal required for high-energy-density configurations remains particularly expensive and subject to geopolitical supply risks.
Market acceptance factors cannot be overlooked in commercialization assessments. Consumer and industry concerns regarding safety, particularly related to potential thermal runaway and the formation of hydrogen sulfide gas during failure modes, create market resistance that requires additional investment in safety systems and certification processes.
Lifecycle economics present both challenges and opportunities. While initial production costs remain high, the theoretical longevity advantages of properly engineered lithium-sulfur systems could provide superior total cost of ownership in certain applications. However, current cycle life limitations (typically 200-500 cycles versus 1000+ for commercial lithium-ion) undermine this potential advantage in many mobile applications.
Regulatory frameworks and intellectual property landscapes add complexity to commercialization efforts. Patent thickets around key enabling technologies for sulfur cathodes have created licensing requirements that increase costs and limit innovation for new market entrants. Additionally, evolving safety regulations for energy storage systems may impose additional compliance costs specific to sulfur-based chemistries.
Investment timelines represent a final economic consideration. The estimated 5-8 years required to move from current prototype systems to commercial-scale production exceeds typical venture capital investment horizons, creating funding gaps in the innovation pipeline that slow commercialization progress despite the technology's long-term promise.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!