Sulfur Cathodes Role in Battery Electrochemical Performance
SEP 23, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Sulfur Cathode Technology Background and Objectives
Lithium-sulfur (Li-S) batteries have emerged as a promising next-generation energy storage technology due to their theoretical energy density of 2600 Wh/kg, which significantly surpasses that of conventional lithium-ion batteries (typically 100-265 Wh/kg). The development of sulfur cathodes can be traced back to the 1960s when the first Li-S battery concept was proposed. However, meaningful progress only began in the early 2000s when nanotechnology advancements enabled better control of sulfur's electrochemical behavior.
The evolution of sulfur cathode technology has been driven by the increasing demand for high-energy-density batteries in applications ranging from portable electronics to electric vehicles and grid-scale energy storage. The abundance and low cost of sulfur, a byproduct of petroleum refining, further enhance its appeal as a sustainable cathode material. Current global sulfur production exceeds 70 million tons annually, providing a readily available resource for large-scale battery production.
Despite their theoretical advantages, sulfur cathodes face several intrinsic challenges that have hindered their commercial viability. The insulating nature of sulfur (5×10^-30 S/cm at 25°C) necessitates conductive additives for electron transport. Additionally, the formation of soluble lithium polysulfides during cycling leads to the "shuttle effect," causing capacity fading and reduced coulombic efficiency. Volume expansion during lithiation (approximately 80%) also creates mechanical stress that can compromise electrode integrity.
The primary technical objectives in sulfur cathode development include enhancing sulfur utilization, mitigating the shuttle effect, accommodating volume changes, and improving cycle life. Researchers aim to achieve practical energy densities exceeding 500 Wh/kg at the cell level, with cycle life of at least 1000 cycles while maintaining 80% capacity retention. Cost targets of below $100/kWh are essential for commercial competitiveness with conventional lithium-ion technologies.
Recent technological breakthroughs have focused on nanostructured carbon hosts, functional polymer binders, and electrolyte modifications. The development of hierarchical porous carbon matrices has significantly improved sulfur confinement and utilization. Meanwhile, advanced characterization techniques such as in-situ X-ray diffraction and cryo-electron microscopy have provided unprecedented insights into reaction mechanisms and failure modes.
The trajectory of sulfur cathode development is increasingly aligned with sustainable manufacturing principles, emphasizing water-based processing and reduced use of toxic solvents. This alignment with green chemistry principles positions Li-S technology as not only a high-performance alternative but also an environmentally responsible one in the evolving landscape of energy storage solutions.
The evolution of sulfur cathode technology has been driven by the increasing demand for high-energy-density batteries in applications ranging from portable electronics to electric vehicles and grid-scale energy storage. The abundance and low cost of sulfur, a byproduct of petroleum refining, further enhance its appeal as a sustainable cathode material. Current global sulfur production exceeds 70 million tons annually, providing a readily available resource for large-scale battery production.
Despite their theoretical advantages, sulfur cathodes face several intrinsic challenges that have hindered their commercial viability. The insulating nature of sulfur (5×10^-30 S/cm at 25°C) necessitates conductive additives for electron transport. Additionally, the formation of soluble lithium polysulfides during cycling leads to the "shuttle effect," causing capacity fading and reduced coulombic efficiency. Volume expansion during lithiation (approximately 80%) also creates mechanical stress that can compromise electrode integrity.
The primary technical objectives in sulfur cathode development include enhancing sulfur utilization, mitigating the shuttle effect, accommodating volume changes, and improving cycle life. Researchers aim to achieve practical energy densities exceeding 500 Wh/kg at the cell level, with cycle life of at least 1000 cycles while maintaining 80% capacity retention. Cost targets of below $100/kWh are essential for commercial competitiveness with conventional lithium-ion technologies.
Recent technological breakthroughs have focused on nanostructured carbon hosts, functional polymer binders, and electrolyte modifications. The development of hierarchical porous carbon matrices has significantly improved sulfur confinement and utilization. Meanwhile, advanced characterization techniques such as in-situ X-ray diffraction and cryo-electron microscopy have provided unprecedented insights into reaction mechanisms and failure modes.
The trajectory of sulfur cathode development is increasingly aligned with sustainable manufacturing principles, emphasizing water-based processing and reduced use of toxic solvents. This alignment with green chemistry principles positions Li-S technology as not only a high-performance alternative but also an environmentally responsible one in the evolving landscape of energy storage solutions.
Market Analysis for Lithium-Sulfur Battery Applications
The lithium-sulfur (Li-S) battery market is experiencing significant growth potential due to the inherent advantages of sulfur cathodes, including high theoretical energy density (2,600 Wh/kg), abundant sulfur resources, and environmental friendliness. Current market projections indicate that the global Li-S battery market could reach $2.1 billion by 2028, with a compound annual growth rate exceeding 30% from 2023 to 2028.
The primary market segments for Li-S batteries include aerospace and defense, automotive, and consumer electronics. The aerospace sector represents the most immediate commercial opportunity, with companies like Airbus and NASA actively exploring Li-S technology for high-altitude platforms and satellite applications where energy density is paramount. This segment values the weight reduction potential of Li-S batteries, which can be 70% lighter than conventional lithium-ion alternatives.
In the automotive sector, Li-S batteries face stronger competition from established lithium-ion technologies but offer compelling advantages for electric vehicles requiring extended range. Market research indicates that if cycle life challenges are addressed, Li-S batteries could capture up to 15% of the EV battery market by 2030, particularly in premium long-range vehicles where their superior energy density provides a competitive edge.
Consumer electronics represents another promising application area, particularly for devices requiring high energy density in limited space. However, this market segment demands more stringent cycle life requirements, currently limiting immediate adoption until further technological improvements are achieved.
Geographically, North America and Europe lead in Li-S battery research and development investments, while Asia-Pacific dominates in manufacturing capacity development. China has recently increased investments in Li-S technology, recognizing its strategic importance in next-generation energy storage solutions.
Market barriers include competition from rapidly improving lithium-ion technologies, manufacturing scalability challenges, and the need for specialized battery management systems. The cost structure remains higher than conventional batteries, with current production costs approximately 30% above lithium-ion equivalents, though economies of scale are expected to reduce this gap significantly by 2025.
Customer adoption studies indicate that initial markets will prioritize applications where energy density provides critical competitive advantages, with price sensitivity decreasing as performance benefits become more apparent. Strategic partnerships between sulfur material suppliers, battery manufacturers, and end-users are emerging as a key market development strategy to accelerate commercialization and address remaining technical challenges.
The primary market segments for Li-S batteries include aerospace and defense, automotive, and consumer electronics. The aerospace sector represents the most immediate commercial opportunity, with companies like Airbus and NASA actively exploring Li-S technology for high-altitude platforms and satellite applications where energy density is paramount. This segment values the weight reduction potential of Li-S batteries, which can be 70% lighter than conventional lithium-ion alternatives.
In the automotive sector, Li-S batteries face stronger competition from established lithium-ion technologies but offer compelling advantages for electric vehicles requiring extended range. Market research indicates that if cycle life challenges are addressed, Li-S batteries could capture up to 15% of the EV battery market by 2030, particularly in premium long-range vehicles where their superior energy density provides a competitive edge.
Consumer electronics represents another promising application area, particularly for devices requiring high energy density in limited space. However, this market segment demands more stringent cycle life requirements, currently limiting immediate adoption until further technological improvements are achieved.
Geographically, North America and Europe lead in Li-S battery research and development investments, while Asia-Pacific dominates in manufacturing capacity development. China has recently increased investments in Li-S technology, recognizing its strategic importance in next-generation energy storage solutions.
Market barriers include competition from rapidly improving lithium-ion technologies, manufacturing scalability challenges, and the need for specialized battery management systems. The cost structure remains higher than conventional batteries, with current production costs approximately 30% above lithium-ion equivalents, though economies of scale are expected to reduce this gap significantly by 2025.
Customer adoption studies indicate that initial markets will prioritize applications where energy density provides critical competitive advantages, with price sensitivity decreasing as performance benefits become more apparent. Strategic partnerships between sulfur material suppliers, battery manufacturers, and end-users are emerging as a key market development strategy to accelerate commercialization and address remaining technical challenges.
Current Challenges in Sulfur Cathode Development
Despite significant advancements in lithium-sulfur (Li-S) battery technology, several critical challenges continue to impede the widespread commercialization of sulfur cathodes. The most prominent issue remains the "shuttle effect," where soluble lithium polysulfide intermediates (Li2Sx, 4≤x≤8) dissolve in the electrolyte during cycling, shuttling between electrodes. This phenomenon leads to active material loss, parasitic reactions with the lithium anode, and ultimately results in rapid capacity fading and shortened battery lifespan.
The inherently poor electrical conductivity of sulfur (5×10^-30 S/cm) and its discharge product Li2S (10^-13 S/cm) presents another significant barrier. This low conductivity necessitates the addition of substantial amounts of conductive additives, which reduces the overall energy density of the battery system and complicates manufacturing processes.
Volume expansion during lithiation poses an additional challenge, as sulfur undergoes approximately 80% volume expansion when converted to Li2S. This expansion causes mechanical stress within the electrode structure, leading to pulverization, loss of electrical contact, and degradation of the conductive network over repeated cycles.
The slow reaction kinetics of sulfur, particularly the sluggish conversion between soluble polysulfides and insoluble Li2S/Li2S2 during discharge, and the difficult oxidation of Li2S during charging, result in large voltage hysteresis and reduced energy efficiency. This kinetic limitation becomes especially problematic at high current densities, severely restricting the power capability of Li-S batteries.
Electrolyte stability and consumption represent another critical challenge. The high reactivity between polysulfides and conventional electrolytes leads to continuous electrolyte depletion during cycling. Additionally, maintaining an appropriate electrolyte-to-sulfur ratio (E/S) remains difficult; too little electrolyte limits ion transport, while excessive amounts reduce energy density and exacerbate the shuttle effect.
The lithium metal anode used in Li-S batteries introduces further complications, including dendrite formation and continuous SEI layer growth due to reactions with polysulfides, leading to increased internal resistance and safety concerns.
From a manufacturing perspective, the integration of sulfur cathodes into existing lithium-ion battery production lines presents significant challenges due to sulfur's sensitivity to moisture and the need for specialized processing techniques that differ substantially from conventional cathode manufacturing methods.
The inherently poor electrical conductivity of sulfur (5×10^-30 S/cm) and its discharge product Li2S (10^-13 S/cm) presents another significant barrier. This low conductivity necessitates the addition of substantial amounts of conductive additives, which reduces the overall energy density of the battery system and complicates manufacturing processes.
Volume expansion during lithiation poses an additional challenge, as sulfur undergoes approximately 80% volume expansion when converted to Li2S. This expansion causes mechanical stress within the electrode structure, leading to pulverization, loss of electrical contact, and degradation of the conductive network over repeated cycles.
The slow reaction kinetics of sulfur, particularly the sluggish conversion between soluble polysulfides and insoluble Li2S/Li2S2 during discharge, and the difficult oxidation of Li2S during charging, result in large voltage hysteresis and reduced energy efficiency. This kinetic limitation becomes especially problematic at high current densities, severely restricting the power capability of Li-S batteries.
Electrolyte stability and consumption represent another critical challenge. The high reactivity between polysulfides and conventional electrolytes leads to continuous electrolyte depletion during cycling. Additionally, maintaining an appropriate electrolyte-to-sulfur ratio (E/S) remains difficult; too little electrolyte limits ion transport, while excessive amounts reduce energy density and exacerbate the shuttle effect.
The lithium metal anode used in Li-S batteries introduces further complications, including dendrite formation and continuous SEI layer growth due to reactions with polysulfides, leading to increased internal resistance and safety concerns.
From a manufacturing perspective, the integration of sulfur cathodes into existing lithium-ion battery production lines presents significant challenges due to sulfur's sensitivity to moisture and the need for specialized processing techniques that differ substantially from conventional cathode manufacturing methods.
Current Technical Solutions for Sulfur Cathode Implementation
01 Sulfur cathode composition and structure
Various compositions and structures for sulfur cathodes have been developed to enhance electrochemical performance. These include sulfur-carbon composites, nanostructured sulfur materials, and sulfur-polymer composites. The specific structure and composition of the cathode material significantly impacts capacity, cycling stability, and rate capability of lithium-sulfur batteries.- Sulfur cathode composition and structure: The composition and structure of sulfur cathodes significantly impact their electrochemical performance. Various approaches include using sulfur-carbon composites, sulfur-polymer composites, and nanostructured sulfur materials. These compositions help address issues like volume expansion, polysulfide dissolution, and poor electrical conductivity, thereby enhancing capacity, cycling stability, and rate capability of lithium-sulfur batteries.
- Conductive additives and carbon materials: Incorporating conductive additives and carbon materials into sulfur cathodes improves their electrochemical performance. Materials such as carbon nanotubes, graphene, carbon black, and conductive polymers enhance electron transport, provide structural support, and help contain polysulfides. These additives create conductive networks within the cathode, leading to improved capacity retention, higher sulfur utilization, and better rate performance.
- Electrolyte modifications and additives: Modifying electrolytes and incorporating additives can significantly enhance sulfur cathode performance. Approaches include using ionic liquids, solid-state electrolytes, gel polymer electrolytes, and functional additives that suppress polysulfide shuttling. These modifications improve the interface stability between electrolyte and cathode, reduce side reactions, and enhance lithium-ion transport, resulting in better cycling stability and coulombic efficiency.
- Binders and interlayers for sulfur cathodes: Specialized binders and protective interlayers play crucial roles in improving sulfur cathode performance. Water-soluble binders, polymer binders with functional groups, and composite binders help maintain structural integrity during cycling. Interlayers between cathode and separator act as physical barriers to polysulfide migration while facilitating lithium-ion transport, resulting in enhanced cycling stability and reduced capacity fading.
- Novel cathode architectures and manufacturing methods: Advanced cathode architectures and manufacturing methods enhance sulfur cathode performance. Hierarchical structures, core-shell designs, 3D frameworks, and novel fabrication techniques like freeze-drying and template-assisted methods create optimized sulfur distribution and confinement. These approaches provide efficient electron/ion pathways, accommodate volume changes, and trap polysulfides, leading to improved capacity, rate capability, and long-term cycling stability.
02 Conductive additives and carbon materials
Incorporating conductive additives and carbon materials into sulfur cathodes improves electron transport and electrochemical performance. Materials such as carbon nanotubes, graphene, conductive polymers, and carbon black help mitigate the insulating nature of sulfur. These additives create conductive networks within the cathode structure, enhancing utilization of active material and improving rate capability.Expand Specific Solutions03 Electrolyte modifications for sulfur cathodes
Specialized electrolyte formulations can significantly improve sulfur cathode performance by addressing polysulfide dissolution and shuttle effect issues. Additives, ionic liquids, solid-state electrolytes, and electrolyte concentration adjustments help contain sulfur species within the cathode region. These modifications enhance coulombic efficiency, cycling stability, and overall battery lifespan.Expand Specific Solutions04 Binders and interlayers for sulfur cathodes
Specialized binders and protective interlayers improve the mechanical stability and electrochemical performance of sulfur cathodes. Functional binders help maintain structural integrity during cycling while interlayers between cathode and separator act as physical barriers to polysulfide migration. These components enhance cycle life, capacity retention, and rate performance of lithium-sulfur batteries.Expand Specific Solutions05 Sulfur loading and cathode architecture optimization
Optimizing sulfur loading and cathode architecture is crucial for achieving high energy density while maintaining good electrochemical performance. Techniques include hierarchical pore structures, gradient compositions, and three-dimensional architectures that accommodate volume changes during cycling. These design strategies balance high sulfur content with effective ion transport pathways and structural stability.Expand Specific Solutions
Leading Companies and Research Institutions in Sulfur Cathodes
The lithium-sulfur battery market is currently in an early growth phase, characterized by significant R&D investment but limited commercial deployment. With a projected market size of $1-2 billion by 2030, sulfur cathodes represent a promising next-generation battery technology offering theoretical energy densities up to 5x higher than conventional lithium-ion batteries. Key players are pursuing different technological approaches: Samsung SDI and LG Energy Solution are leveraging their manufacturing expertise; Sila Nanotechnologies and Conamix focus on novel materials; while PolyPlus and Sion Power lead in lithium-sulfur specific innovations. Academic-industrial partnerships involving Tsinghua University and Fraunhofer-Gesellschaft are accelerating development to address critical challenges of sulfur cathodes, including polysulfide shuttling and limited cycle life that currently restrict widespread commercialization.
Samsung SDI Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: Samsung SDI has developed advanced sulfur cathode technologies focusing on addressing the "shuttle effect" problem in lithium-sulfur batteries. Their approach involves encapsulating sulfur within conductive carbon matrices, specifically using hollow carbon spheres and graphene oxide wrapping. This creates a physical barrier that prevents polysulfide dissolution while maintaining electrical conductivity. Samsung's research has demonstrated energy densities exceeding 400 Wh/kg at the cell level, significantly higher than conventional lithium-ion batteries. Their proprietary binder systems enhance the mechanical stability of sulfur cathodes during cycling, addressing the volume expansion issues (up to 80%) that typically occur during lithium-sulfur battery operation. Samsung has also pioneered the use of functional electrolyte additives that form protective films on lithium anodes, further suppressing the shuttle effect and extending cycle life to over 500 cycles with capacity retention above 80%.
Strengths: Superior energy density (400+ Wh/kg) compared to conventional lithium-ion batteries; innovative carbon encapsulation techniques effectively mitigate polysulfide shuttling; proprietary binder systems accommodate large volume changes. Weaknesses: Still faces challenges with long-term cycling stability beyond 500 cycles; production costs remain higher than conventional cathode materials; rate capability limitations at high discharge rates.
LG Energy Solution Ltd.
Technical Solution: LG Energy Solution has developed a multi-faceted approach to sulfur cathode technology, focusing on practical implementation in commercial cells. Their strategy involves creating a carbon-sulfur composite where sulfur is infiltrated into mesoporous carbon structures with precisely controlled pore size distribution (primarily 2-5 nm pores) to physically confine polysulfides. LG's proprietary cathode formulation includes functional polymeric binders with strong affinity for polysulfides, creating chemical bonds that prevent their dissolution into the electrolyte. Their research has demonstrated cells with energy densities of 350-450 Wh/kg while achieving over 600 cycles with 80% capacity retention. LG has also pioneered a gradient cathode structure where sulfur concentration varies throughout the electrode thickness, optimizing both energy density and ion transport properties. Additionally, they've developed specialized electrolyte systems containing lithium bis(fluorosulfonyl)imide (LiFSI) salt and ether-based solvents that form stable interfaces on both electrodes, significantly improving cycling performance.
Strengths: Practical approach focused on commercial viability; superior cycle life (600+ cycles) compared to many competitors; innovative gradient cathode structure optimizes both energy density and ion transport. Weaknesses: Slightly lower energy density than some research-focused competitors; complex manufacturing process increases production costs; performance degradation at high discharge rates remains a challenge.
Key Innovations in Sulfur Cathode Electrochemistry
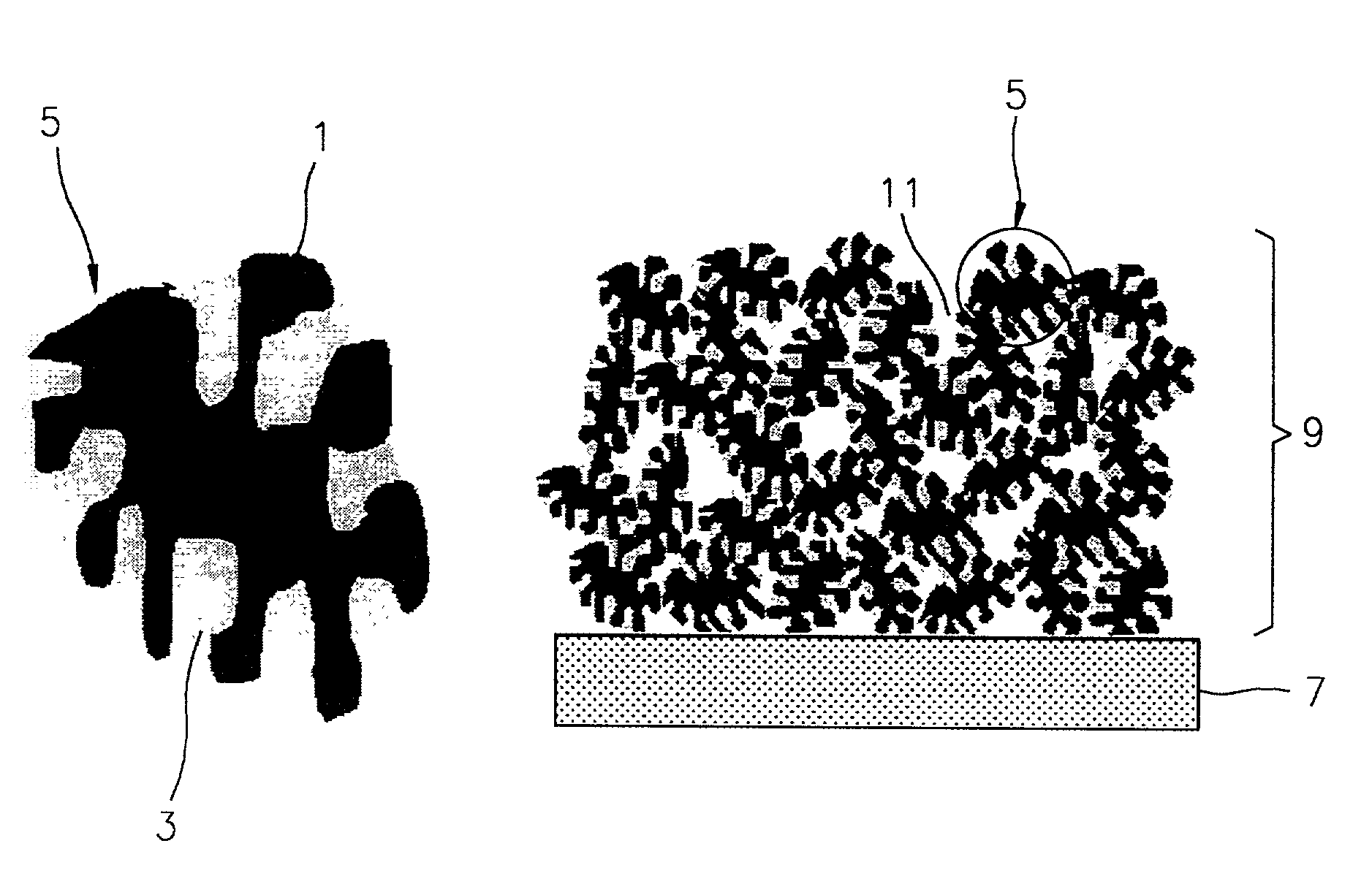
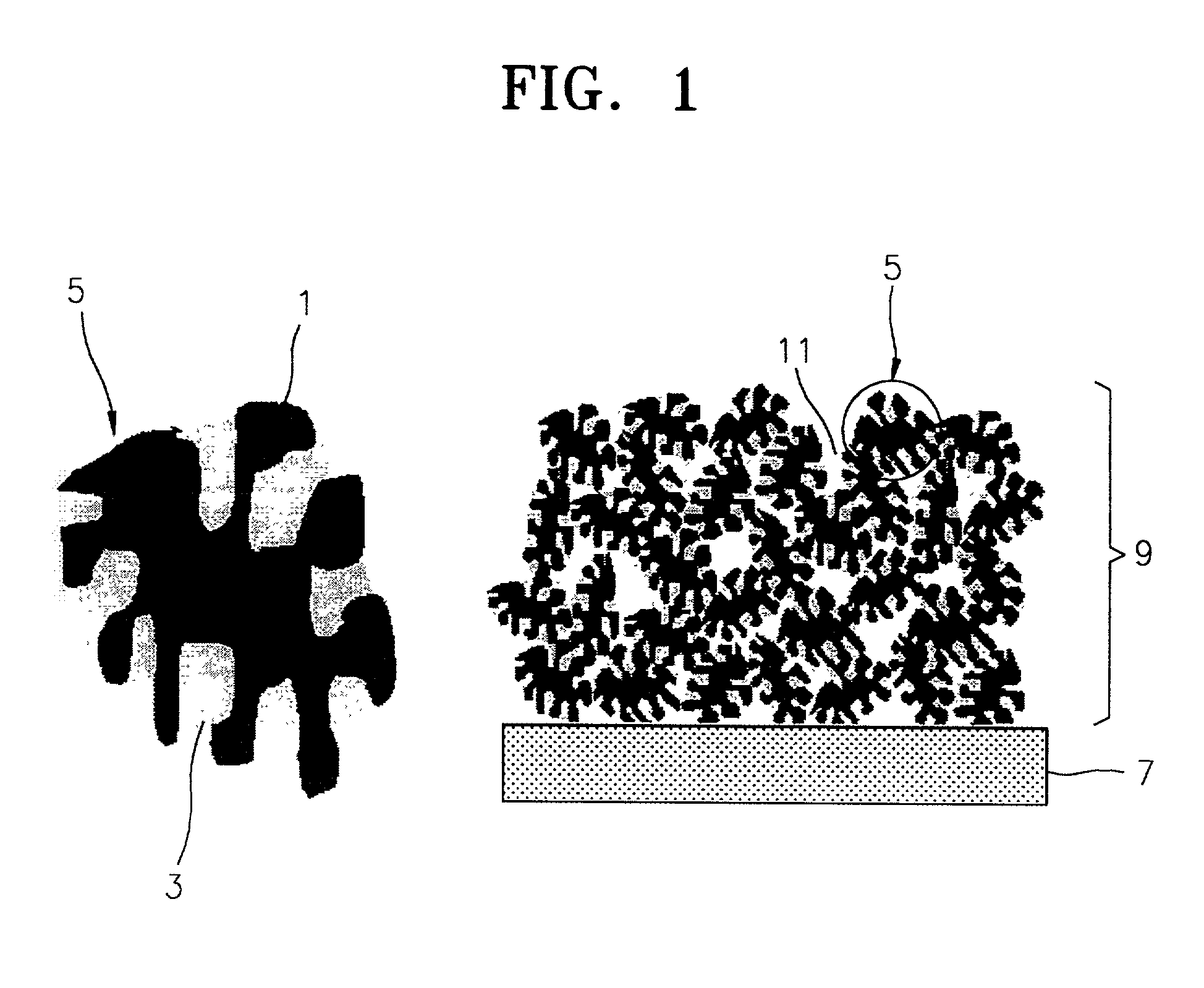
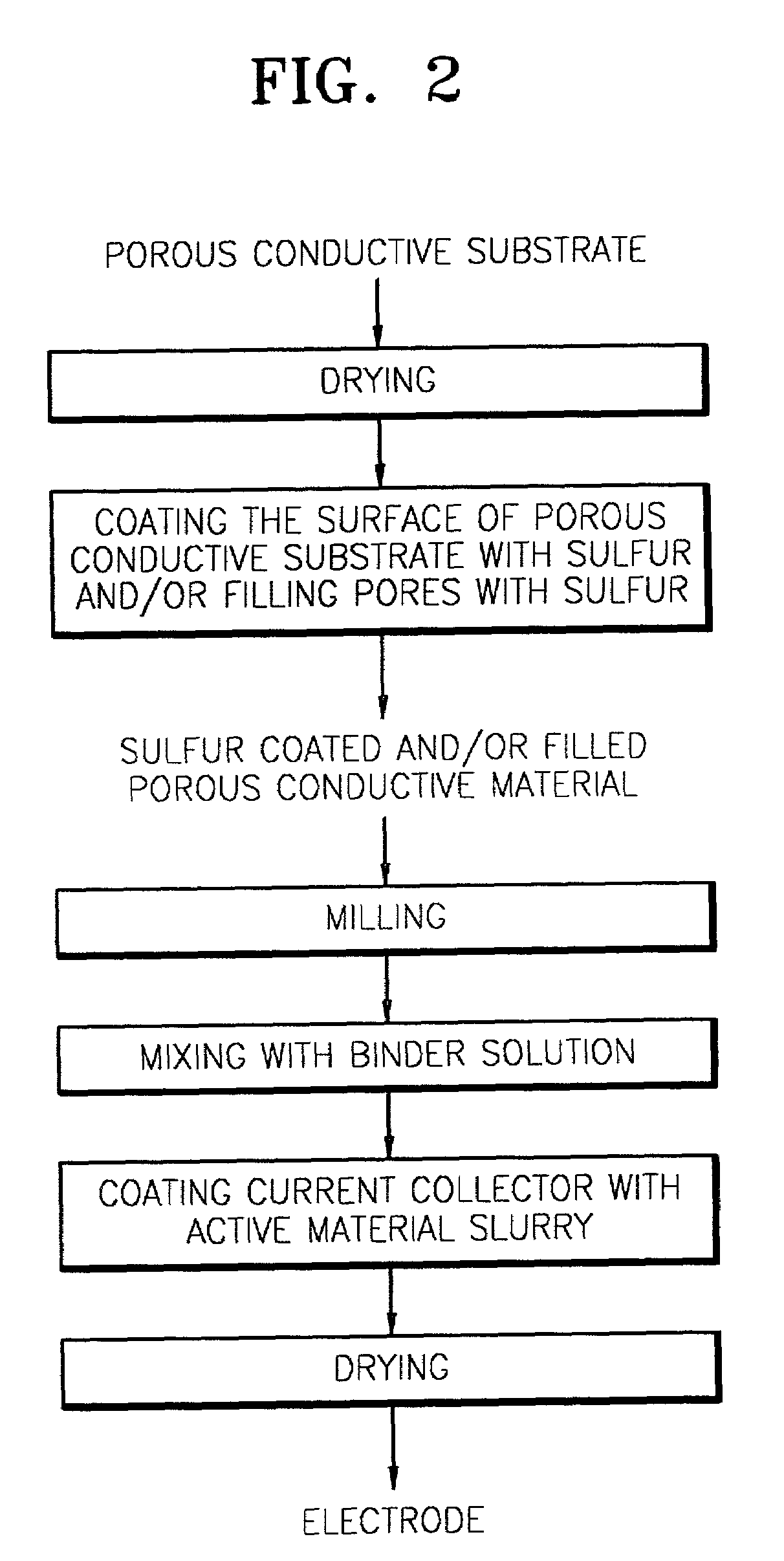
Cathode electrode including a porous conductive material coated and/or filled with sulfur and/or a sulfur-containing organic compound and lithium battery containing the same
PatentInactiveUS7361431B2
Innovation
- A cathode electrode with a porous conductive material whose surface is coated or pores are filled with sulfur, maintaining the structure during phase transitions, utilizing a specific surface area and pore size range to ensure electrochemical connectivity and sufficient reaction sites.
Cathode electrode, method for manufacturing the same and lithium battery containing the same
PatentInactiveEP1324409A3
Innovation
- A cathode electrode with a porous conductive material that is either filled with sulfur or coated with sulfur, maintaining structural integrity during phase transitions, using a specific surface area of 300 m2/g or higher and pore diameters between 0.05 nm to 1 µm, and bound with a binder to ensure electrochemical connectivity.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability of Sulfur Cathodes
The environmental impact of lithium-sulfur (Li-S) batteries represents a significant advantage over conventional lithium-ion technologies. Sulfur cathodes utilize elemental sulfur, an abundant by-product of petroleum refining that is currently considered industrial waste. This repurposing of waste material creates a circular economy opportunity while reducing environmental burden associated with sulfur disposal.
When comparing carbon footprints, Li-S batteries demonstrate approximately 20% lower greenhouse gas emissions during manufacturing than traditional lithium-ion batteries. This reduction stems primarily from the simplified cathode production process and the elimination of cobalt and nickel mining, which are associated with significant environmental degradation and social concerns in many regions.
The end-of-life management of sulfur cathodes presents both challenges and opportunities. Unlike conventional batteries containing toxic heavy metals, sulfur-based cathodes pose fewer environmental hazards during disposal. Research indicates that sulfur can be recovered from spent batteries at rates exceeding 85%, creating potential for closed-loop recycling systems that further enhance sustainability credentials.
Water consumption represents another critical environmental metric. Manufacturing processes for sulfur cathodes require approximately 35% less water than conventional cathode production, primarily due to simplified processing requirements and reduced need for water-intensive purification steps.
Energy density improvements in Li-S batteries also contribute to sustainability through system-level efficiencies. The theoretical energy density of sulfur cathodes (2,600 Wh/kg) far exceeds that of conventional cathodes, potentially reducing material requirements for equivalent energy storage capacity. This translates to resource conservation across battery production supply chains.
Land use impacts associated with sulfur sourcing are minimal compared to traditional cathode materials, as sulfur extraction typically occurs as a secondary process within existing industrial operations rather than requiring dedicated mining activities. This avoids additional habitat disruption and biodiversity impacts associated with expanding mining operations.
Recent life cycle assessment studies indicate that widespread adoption of sulfur cathodes could reduce the battery industry's overall ecological footprint by 15-25% when accounting for raw material extraction, manufacturing, use phase, and end-of-life management. However, these benefits are partially contingent upon developing effective recycling infrastructure specifically designed for sulfur recovery from spent batteries.
When comparing carbon footprints, Li-S batteries demonstrate approximately 20% lower greenhouse gas emissions during manufacturing than traditional lithium-ion batteries. This reduction stems primarily from the simplified cathode production process and the elimination of cobalt and nickel mining, which are associated with significant environmental degradation and social concerns in many regions.
The end-of-life management of sulfur cathodes presents both challenges and opportunities. Unlike conventional batteries containing toxic heavy metals, sulfur-based cathodes pose fewer environmental hazards during disposal. Research indicates that sulfur can be recovered from spent batteries at rates exceeding 85%, creating potential for closed-loop recycling systems that further enhance sustainability credentials.
Water consumption represents another critical environmental metric. Manufacturing processes for sulfur cathodes require approximately 35% less water than conventional cathode production, primarily due to simplified processing requirements and reduced need for water-intensive purification steps.
Energy density improvements in Li-S batteries also contribute to sustainability through system-level efficiencies. The theoretical energy density of sulfur cathodes (2,600 Wh/kg) far exceeds that of conventional cathodes, potentially reducing material requirements for equivalent energy storage capacity. This translates to resource conservation across battery production supply chains.
Land use impacts associated with sulfur sourcing are minimal compared to traditional cathode materials, as sulfur extraction typically occurs as a secondary process within existing industrial operations rather than requiring dedicated mining activities. This avoids additional habitat disruption and biodiversity impacts associated with expanding mining operations.
Recent life cycle assessment studies indicate that widespread adoption of sulfur cathodes could reduce the battery industry's overall ecological footprint by 15-25% when accounting for raw material extraction, manufacturing, use phase, and end-of-life management. However, these benefits are partially contingent upon developing effective recycling infrastructure specifically designed for sulfur recovery from spent batteries.
Manufacturing Scalability and Cost Analysis
The scalability of sulfur cathode manufacturing represents a critical factor in the widespread adoption of lithium-sulfur (Li-S) batteries. Current production methods for conventional lithium-ion batteries benefit from decades of optimization, whereas sulfur cathode manufacturing processes remain relatively immature. The transition from laboratory-scale production to industrial-scale manufacturing faces several significant challenges that directly impact cost structures and market viability.
Material handling presents a primary obstacle in scaling sulfur cathode production. Elemental sulfur's poor electrical conductivity necessitates the incorporation of conductive additives and careful control of particle morphology. Industrial-scale mixing and dispersion processes must be developed to ensure homogeneous distribution of sulfur within the carbon matrix while maintaining the delicate nanostructures that enable optimal electrochemical performance.
Coating technologies represent another critical aspect of manufacturing scalability. Traditional slurry-based coating methods used for conventional lithium-ion batteries require significant adaptation for sulfur cathodes due to different rheological properties and solvent compatibility issues. High-precision coating equipment capable of handling the unique characteristics of sulfur-carbon composites at high throughput rates remains under development.
From a cost perspective, raw material economics strongly favor sulfur cathodes. Elemental sulfur, being an abundant byproduct of petroleum refining, costs approximately $0.10-0.20 per kilogram—orders of magnitude less expensive than conventional cathode materials like nickel-manganese-cobalt (NMC) compounds at $15-40 per kilogram. However, this inherent material cost advantage is currently offset by higher processing costs and additional components required to mitigate polysulfide shuttling.
Equipment investment represents a significant barrier to commercialization. Purpose-built manufacturing lines for sulfur cathodes require specialized equipment for handling, mixing, coating, and post-processing that differs from conventional battery production lines. Industry estimates suggest capital expenditure requirements of $50-80 million for a modest production facility (500 MWh/year), with economies of scale improving at higher production volumes.
Energy consumption during manufacturing also impacts overall cost structures. Current laboratory and pilot-scale processes for sulfur cathode production typically involve energy-intensive steps such as high-temperature carbon treatment, solvent removal, and specialized drying protocols. Optimization of these processes for energy efficiency represents a critical path toward cost reduction and environmental sustainability.
The development of standardized quality control protocols and in-line monitoring systems specific to sulfur cathode manufacturing remains in early stages. Without robust quality assurance mechanisms, production yields may suffer, further impacting economic viability. Industry consortia and research institutions are actively developing specialized analytical techniques and process control methodologies to address this gap.
Material handling presents a primary obstacle in scaling sulfur cathode production. Elemental sulfur's poor electrical conductivity necessitates the incorporation of conductive additives and careful control of particle morphology. Industrial-scale mixing and dispersion processes must be developed to ensure homogeneous distribution of sulfur within the carbon matrix while maintaining the delicate nanostructures that enable optimal electrochemical performance.
Coating technologies represent another critical aspect of manufacturing scalability. Traditional slurry-based coating methods used for conventional lithium-ion batteries require significant adaptation for sulfur cathodes due to different rheological properties and solvent compatibility issues. High-precision coating equipment capable of handling the unique characteristics of sulfur-carbon composites at high throughput rates remains under development.
From a cost perspective, raw material economics strongly favor sulfur cathodes. Elemental sulfur, being an abundant byproduct of petroleum refining, costs approximately $0.10-0.20 per kilogram—orders of magnitude less expensive than conventional cathode materials like nickel-manganese-cobalt (NMC) compounds at $15-40 per kilogram. However, this inherent material cost advantage is currently offset by higher processing costs and additional components required to mitigate polysulfide shuttling.
Equipment investment represents a significant barrier to commercialization. Purpose-built manufacturing lines for sulfur cathodes require specialized equipment for handling, mixing, coating, and post-processing that differs from conventional battery production lines. Industry estimates suggest capital expenditure requirements of $50-80 million for a modest production facility (500 MWh/year), with economies of scale improving at higher production volumes.
Energy consumption during manufacturing also impacts overall cost structures. Current laboratory and pilot-scale processes for sulfur cathode production typically involve energy-intensive steps such as high-temperature carbon treatment, solvent removal, and specialized drying protocols. Optimization of these processes for energy efficiency represents a critical path toward cost reduction and environmental sustainability.
The development of standardized quality control protocols and in-line monitoring systems specific to sulfur cathode manufacturing remains in early stages. Without robust quality assurance mechanisms, production yields may suffer, further impacting economic viability. Industry consortia and research institutions are actively developing specialized analytical techniques and process control methodologies to address this gap.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!