Sulfur Cathodes Applications in Large-Scale Grid Deployments
SEP 23, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Sulfur Cathode Technology Background and Objectives
Sulfur cathode technology has evolved significantly over the past three decades, emerging as a promising solution for large-scale energy storage systems. Initially developed in the 1990s as a theoretical concept, lithium-sulfur (Li-S) battery technology has progressed from laboratory curiosity to a serious contender in grid-scale applications. The fundamental attraction lies in sulfur's exceptional theoretical specific capacity of 1,675 mAh/g, which far exceeds traditional lithium-ion cathode materials that typically deliver 140-200 mAh/g.
The evolution of sulfur cathodes has been marked by several technological breakthroughs, particularly in addressing the "polysulfide shuttle effect" - a phenomenon that historically limited cycle life and efficiency. Recent advancements in nanostructured carbon hosts, functional interlayers, and electrolyte engineering have significantly mitigated these challenges, pushing practical energy densities beyond 400 Wh/kg at the cell level.
Current technological trajectories indicate a convergence toward hybrid approaches that combine sulfur's high capacity with structural stabilizers to enhance longevity. The incorporation of conductive polymers and advanced carbon architectures has enabled more stable cycling performance, with some laboratory prototypes demonstrating over 1,000 cycles with minimal capacity degradation.
The primary technical objective for sulfur cathodes in grid applications centers on achieving cost-effective, long-duration energy storage with minimal environmental impact. With raw sulfur being an abundant by-product of petroleum refining (priced at approximately $100/ton), the material cost advantage over conventional lithium-ion batteries is substantial, potentially reducing energy storage costs below $100/kWh at scale.
Secondary objectives include improving operational safety profiles, as sulfur cathodes operate at lower voltages and present reduced thermal runaway risks compared to oxide-based cathodes. This characteristic makes them particularly suitable for large-scale stationary applications where safety concerns are paramount.
The technology aims to address the intermittency challenges of renewable energy integration by providing 6-10 hour duration storage capabilities at grid scale. Current research focuses on optimizing sulfur utilization rates, which typically hover around 60-70% in practical cells, with the goal of approaching the theoretical maximum.
Environmental sustainability represents another critical objective, as sulfur cathode technology offers a pathway to reduce dependence on critical minerals like cobalt and nickel. The circular economy potential is significant, with end-of-life sulfur cathodes being more readily recyclable than complex transition metal oxide alternatives.
The evolution of sulfur cathodes has been marked by several technological breakthroughs, particularly in addressing the "polysulfide shuttle effect" - a phenomenon that historically limited cycle life and efficiency. Recent advancements in nanostructured carbon hosts, functional interlayers, and electrolyte engineering have significantly mitigated these challenges, pushing practical energy densities beyond 400 Wh/kg at the cell level.
Current technological trajectories indicate a convergence toward hybrid approaches that combine sulfur's high capacity with structural stabilizers to enhance longevity. The incorporation of conductive polymers and advanced carbon architectures has enabled more stable cycling performance, with some laboratory prototypes demonstrating over 1,000 cycles with minimal capacity degradation.
The primary technical objective for sulfur cathodes in grid applications centers on achieving cost-effective, long-duration energy storage with minimal environmental impact. With raw sulfur being an abundant by-product of petroleum refining (priced at approximately $100/ton), the material cost advantage over conventional lithium-ion batteries is substantial, potentially reducing energy storage costs below $100/kWh at scale.
Secondary objectives include improving operational safety profiles, as sulfur cathodes operate at lower voltages and present reduced thermal runaway risks compared to oxide-based cathodes. This characteristic makes them particularly suitable for large-scale stationary applications where safety concerns are paramount.
The technology aims to address the intermittency challenges of renewable energy integration by providing 6-10 hour duration storage capabilities at grid scale. Current research focuses on optimizing sulfur utilization rates, which typically hover around 60-70% in practical cells, with the goal of approaching the theoretical maximum.
Environmental sustainability represents another critical objective, as sulfur cathode technology offers a pathway to reduce dependence on critical minerals like cobalt and nickel. The circular economy potential is significant, with end-of-life sulfur cathodes being more readily recyclable than complex transition metal oxide alternatives.
Grid-Scale Energy Storage Market Analysis
The global grid-scale energy storage market is experiencing unprecedented growth, driven by the increasing integration of renewable energy sources and the need for grid stability. As of 2023, the market valuation stands at approximately $8.5 billion, with projections indicating a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 28% through 2030, potentially reaching $45 billion by the end of the decade. This remarkable expansion reflects the critical role that large-scale energy storage systems play in modern electrical infrastructure.
Lithium-ion batteries currently dominate the market with roughly 70% market share, but their limitations in terms of cost, resource constraints, and safety concerns have created significant opportunities for alternative technologies. Sulfur-based cathode technologies are emerging as particularly promising contenders in this landscape, offering theoretical energy densities up to five times higher than conventional lithium-ion systems at potentially one-third the cost.
Demand drivers for grid-scale storage solutions include renewable energy integration, peak shaving capabilities, frequency regulation, and grid resilience enhancement. Particularly in regions with high renewable penetration such as California, Germany, and Australia, the need for long-duration storage solutions exceeding 8 hours is growing at 40% annually. Sulfur cathode technologies, with their potential for 10+ hour duration capabilities, are well-positioned to address this specific market segment.
Regional analysis reveals varying adoption patterns, with Asia-Pacific leading deployment volume (38% of global installations), followed by North America (32%) and Europe (24%). However, North America demonstrates the highest growth rate at 34% annually, driven by favorable regulatory frameworks and substantial infrastructure investment. The Inflation Reduction Act in the United States has allocated over $60 billion specifically for clean energy manufacturing and grid modernization, creating a conducive environment for sulfur cathode technology commercialization.
Customer segmentation within the market shows utilities as the primary adopters (58%), followed by independent power producers (22%), commercial/industrial users (15%), and microgrids/remote applications (5%). Each segment presents distinct requirements regarding discharge duration, cycle life, and cost parameters that influence technology selection criteria.
Competitive analysis indicates that while established players like Tesla, Fluence, and LG Energy Solution control 65% of current deployments, specialized technology developers focusing on novel chemistries are attracting significant venture capital investment, with sulfur cathode startups securing over $450 million in funding during 2022-2023 alone. This investment pattern signals strong market confidence in the potential of sulfur-based solutions to address the limitations of current technologies in grid-scale applications.
Lithium-ion batteries currently dominate the market with roughly 70% market share, but their limitations in terms of cost, resource constraints, and safety concerns have created significant opportunities for alternative technologies. Sulfur-based cathode technologies are emerging as particularly promising contenders in this landscape, offering theoretical energy densities up to five times higher than conventional lithium-ion systems at potentially one-third the cost.
Demand drivers for grid-scale storage solutions include renewable energy integration, peak shaving capabilities, frequency regulation, and grid resilience enhancement. Particularly in regions with high renewable penetration such as California, Germany, and Australia, the need for long-duration storage solutions exceeding 8 hours is growing at 40% annually. Sulfur cathode technologies, with their potential for 10+ hour duration capabilities, are well-positioned to address this specific market segment.
Regional analysis reveals varying adoption patterns, with Asia-Pacific leading deployment volume (38% of global installations), followed by North America (32%) and Europe (24%). However, North America demonstrates the highest growth rate at 34% annually, driven by favorable regulatory frameworks and substantial infrastructure investment. The Inflation Reduction Act in the United States has allocated over $60 billion specifically for clean energy manufacturing and grid modernization, creating a conducive environment for sulfur cathode technology commercialization.
Customer segmentation within the market shows utilities as the primary adopters (58%), followed by independent power producers (22%), commercial/industrial users (15%), and microgrids/remote applications (5%). Each segment presents distinct requirements regarding discharge duration, cycle life, and cost parameters that influence technology selection criteria.
Competitive analysis indicates that while established players like Tesla, Fluence, and LG Energy Solution control 65% of current deployments, specialized technology developers focusing on novel chemistries are attracting significant venture capital investment, with sulfur cathode startups securing over $450 million in funding during 2022-2023 alone. This investment pattern signals strong market confidence in the potential of sulfur-based solutions to address the limitations of current technologies in grid-scale applications.
Current Challenges in Sulfur Cathode Development
Despite the promising theoretical energy density of lithium-sulfur (Li-S) batteries, their application in large-scale grid deployments faces several significant challenges. The primary obstacle remains the "shuttle effect," where soluble polysulfide intermediates migrate between electrodes during cycling, causing rapid capacity fading and shortened battery lifespan. This phenomenon becomes particularly problematic in grid-scale applications where long cycle life is essential for economic viability.
Material stability presents another critical challenge. Sulfur cathodes undergo substantial volume expansion (up to 80%) during lithiation, leading to mechanical stress that can cause electrode pulverization and delamination. In large-scale deployments, this mechanical degradation accelerates capacity loss and increases safety risks, particularly when scaled to the megawatt-hour capacities required for grid applications.
The low electrical conductivity of sulfur (5×10^-30 S/cm) significantly impedes electron transport within the cathode, resulting in poor rate capability and reduced power performance. Grid applications often require rapid response to fluctuating energy demands, making this limitation particularly problematic for frequency regulation and peak shaving applications.
Self-discharge issues also plague sulfur cathode technology. The dissolution of lithium polysulfides leads to parasitic reactions that cause capacity loss even during idle periods. For grid storage applications requiring seasonal storage or infrequent discharge cycles, this self-discharge behavior severely compromises energy retention and system reliability.
Manufacturing scalability remains underdeveloped for sulfur cathodes. Current laboratory-scale production methods have not been successfully translated to industrial-scale manufacturing processes that maintain consistent quality and performance. The lack of standardized production techniques creates barriers to cost-effective mass production necessary for grid-scale deployment.
The operating temperature range of Li-S batteries is currently limited, with performance degrading significantly at temperature extremes. Grid installations often face diverse environmental conditions, from desert heat to arctic cold, requiring robust thermal stability that current sulfur cathode formulations cannot provide.
Safety concerns persist due to the formation of hydrogen sulfide gas under certain failure conditions. While manageable in small-scale applications, these risks become more significant when scaled to grid-level deployments where thermal runaway events could affect megawatt-hour systems.
Cost-performance optimization remains elusive, as current designs that mitigate technical issues often rely on expensive materials or complex architectures that undermine the inherent cost advantage of sulfur as a cathode material. Finding the optimal balance between performance, durability, and cost continues to challenge researchers and engineers working toward grid-scale implementation.
Material stability presents another critical challenge. Sulfur cathodes undergo substantial volume expansion (up to 80%) during lithiation, leading to mechanical stress that can cause electrode pulverization and delamination. In large-scale deployments, this mechanical degradation accelerates capacity loss and increases safety risks, particularly when scaled to the megawatt-hour capacities required for grid applications.
The low electrical conductivity of sulfur (5×10^-30 S/cm) significantly impedes electron transport within the cathode, resulting in poor rate capability and reduced power performance. Grid applications often require rapid response to fluctuating energy demands, making this limitation particularly problematic for frequency regulation and peak shaving applications.
Self-discharge issues also plague sulfur cathode technology. The dissolution of lithium polysulfides leads to parasitic reactions that cause capacity loss even during idle periods. For grid storage applications requiring seasonal storage or infrequent discharge cycles, this self-discharge behavior severely compromises energy retention and system reliability.
Manufacturing scalability remains underdeveloped for sulfur cathodes. Current laboratory-scale production methods have not been successfully translated to industrial-scale manufacturing processes that maintain consistent quality and performance. The lack of standardized production techniques creates barriers to cost-effective mass production necessary for grid-scale deployment.
The operating temperature range of Li-S batteries is currently limited, with performance degrading significantly at temperature extremes. Grid installations often face diverse environmental conditions, from desert heat to arctic cold, requiring robust thermal stability that current sulfur cathode formulations cannot provide.
Safety concerns persist due to the formation of hydrogen sulfide gas under certain failure conditions. While manageable in small-scale applications, these risks become more significant when scaled to grid-level deployments where thermal runaway events could affect megawatt-hour systems.
Cost-performance optimization remains elusive, as current designs that mitigate technical issues often rely on expensive materials or complex architectures that undermine the inherent cost advantage of sulfur as a cathode material. Finding the optimal balance between performance, durability, and cost continues to challenge researchers and engineers working toward grid-scale implementation.
Current Implementation Solutions for Grid Applications
01 Sulfur cathode compositions for lithium-sulfur batteries
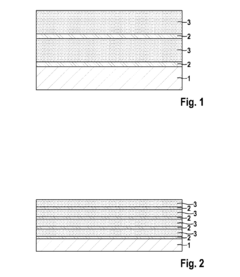
Various compositions for sulfur cathodes in lithium-sulfur batteries have been developed to improve energy density and cycle life. These compositions typically include elemental sulfur combined with conductive materials such as carbon and polymeric binders. The cathode compositions are designed to address challenges like polysulfide dissolution and volume expansion during cycling, which are common issues in sulfur-based battery systems.- Sulfur cathode compositions for lithium-sulfur batteries: Various compositions for sulfur cathodes in lithium-sulfur batteries have been developed to improve energy density and cycle life. These compositions typically include elemental sulfur combined with conductive additives, binders, and other materials to enhance electrochemical performance. The cathode compositions are designed to address challenges such as the insulating nature of sulfur and the polysulfide shuttle effect, which can lead to capacity fading during cycling.
- Protective coatings and encapsulation for sulfur cathodes: Protective coatings and encapsulation techniques are applied to sulfur cathodes to mitigate polysulfide dissolution and shuttle effect. These approaches involve encapsulating sulfur particles within conductive or polymeric shells, or applying protective layers to the cathode surface. Such strategies help contain sulfur and its discharge products within the cathode structure, preventing their migration to the anode and improving battery cycle life and stability.
- Carbon-sulfur composite cathode materials: Carbon-sulfur composites represent an important class of cathode materials for lithium-sulfur batteries. These composites typically incorporate sulfur into various carbon structures such as porous carbon, carbon nanotubes, or graphene. The carbon framework provides electrical conductivity and physical confinement for sulfur, while also offering pathways for lithium ion transport. This design approach helps overcome the insulating nature of sulfur and mitigates polysulfide dissolution.
- Electrolyte modifications for sulfur cathodes: Specialized electrolyte formulations are developed to enhance the performance of sulfur cathodes. These electrolytes may contain additives that form protective films on electrodes, suppress polysulfide dissolution, or improve ionic conductivity. Some approaches involve using high-concentration electrolytes, ionic liquids, or solid-state electrolytes that are less prone to polysulfide shuttling. These electrolyte modifications aim to improve the cycling stability and coulombic efficiency of lithium-sulfur batteries.
- Interlayers and separators for lithium-sulfur batteries: Functional interlayers and modified separators are employed between the sulfur cathode and lithium anode to block polysulfide migration. These components typically consist of conductive materials with polysulfide-trapping capabilities or selective ion-transport properties. By physically blocking or chemically binding polysulfides, these interlayers prevent their migration to the anode side, reducing capacity fading and improving the overall performance of lithium-sulfur batteries.
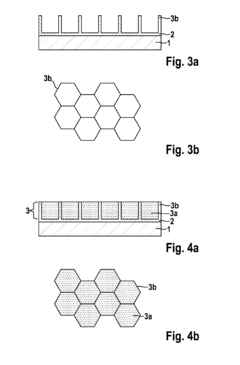
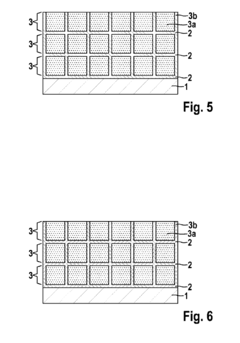
02 Nanostructured sulfur cathode materials
Nanostructured approaches to sulfur cathode design involve incorporating sulfur into nanoscale architectures such as nanoparticles, nanotubes, or mesoporous structures. These designs aim to confine sulfur within nanospaces to limit polysulfide shuttling and improve electronic conductivity. By controlling the sulfur distribution at the nanoscale, these cathodes can achieve higher utilization of active material and better cycling stability.Expand Specific Solutions03 Protective coatings and interlayers for sulfur cathodes
Various protective coatings and interlayers have been developed to enhance the performance of sulfur cathodes. These include polymer coatings, metal oxide layers, and functional separators that help contain polysulfides within the cathode region. Such protective strategies prevent the migration of dissolved polysulfides to the anode, thereby reducing capacity fade and extending battery life.Expand Specific Solutions04 Sulfur cathodes with conductive additives
Conductive additives are incorporated into sulfur cathodes to address the inherent poor conductivity of elemental sulfur. These additives include various forms of carbon (graphene, carbon nanotubes, carbon black), conductive polymers, and metal compounds. The addition of these materials creates conductive networks within the cathode structure, facilitating electron transport and improving the electrochemical performance of the battery.Expand Specific Solutions05 Manufacturing processes for sulfur cathodes
Various manufacturing techniques have been developed for producing high-performance sulfur cathodes. These include melt-diffusion methods, solution-based processes, and advanced deposition techniques. The manufacturing processes focus on achieving uniform sulfur distribution, optimal porosity, and strong adhesion between components. Proper control of these manufacturing parameters is crucial for producing cathodes with high sulfur loading and good mechanical stability.Expand Specific Solutions
Leading Companies and Research Institutions in Sulfur Cathode Field
The sulfur cathode market for grid-scale energy storage is currently in an early growth phase, with increasing commercial interest driven by the need for cost-effective, long-duration storage solutions. Market size is projected to expand significantly as renewable integration accelerates, with analysts forecasting substantial growth through 2030. Technologically, sulfur cathodes remain in the development-to-early commercialization stage, with companies at varying maturity levels. Leading players include PolyPlus Battery and Sion Power with advanced lithium-sulfur technologies, Form Energy developing iron-air batteries incorporating sulfur components, and Conamix working on low-cost sulfur-based materials. Academic institutions like USC, Drexel, and Rice University are advancing fundamental research, while established manufacturers like Bosch and Nissan are exploring integration into larger energy systems.
PolyPlus Battery Co., Inc.
Technical Solution: PolyPlus Battery has developed advanced lithium-sulfur battery technology specifically optimized for large-scale grid storage applications. Their proprietary Protected Lithium Electrode (PLE) technology creates a stable interface between lithium metal anodes and sulfur cathodes, addressing one of the fundamental challenges in lithium-sulfur battery commercialization. For grid applications, PolyPlus has engineered their sulfur cathodes with a hierarchical carbon structure that provides both macro and micropores to accommodate sulfur and its expansion during cycling while maintaining electrical connectivity. Their cathode design incorporates specialized binders and electrolyte additives that mitigate polysulfide dissolution and shuttle effects, extending cycle life to over 1,000 cycles at moderate depths of discharge. The company has demonstrated 100kWh modules designed for grid applications with energy densities exceeding 350 Wh/kg and simplified thermal management requirements compared to conventional lithium-ion systems. PolyPlus has focused on scalable manufacturing processes, utilizing water-based cathode production methods that reduce environmental impact and production costs.
Strengths: Protected electrode technology solves key degradation mechanisms in lithium-sulfur chemistry; Higher energy density than conventional grid storage solutions reduces installation footprint; Lower material costs through use of abundant sulfur rather than costly transition metals. Weaknesses: Still requires further scale-up to reach gigawatt-hour deployment levels; Performance in extreme temperature conditions needs optimization for certain grid environments; Current designs have moderate power capability, limiting applications requiring rapid response.
Vorbeck Materials Corp.
Technical Solution: Vorbeck Materials has developed an innovative approach to sulfur cathodes for grid-scale energy storage by integrating their proprietary Vor-x® graphene technology with high-capacity sulfur materials. Their cathode design utilizes a three-dimensional graphene network that provides exceptional electrical conductivity while accommodating the substantial volume changes that occur during sulfur's lithiation/delithiation processes. For grid applications, Vorbeck has engineered modular battery systems with capacities ranging from 250kWh to 2MWh that incorporate advanced thermal management and battery monitoring systems specifically calibrated for sulfur chemistry. Their cathode manufacturing process employs a scalable, solvent-free technique that reduces production costs and environmental impact. The company has demonstrated successful integration of their sulfur-graphene composite cathodes with various electrolyte systems, including conventional liquid electrolytes and emerging solid-state formulations, achieving energy densities above 400 Wh/kg at the cell level. Vorbeck's grid storage solutions feature proprietary electrolyte additives that suppress polysulfide shuttling, extending cycle life to approximately 2,000 cycles at moderate depths of discharge.
Strengths: Graphene-enhanced conductivity network addresses key performance limitations of traditional sulfur cathodes; Modular design allows flexible deployment across various grid applications; Manufacturing process is environmentally friendly and scalable. Weaknesses: Higher production costs compared to some competing technologies due to graphene component; Current designs still face challenges with high-rate performance; Technology requires further demonstration at utility scale.
Key Patents and Breakthroughs in Sulfur Cathode Technology
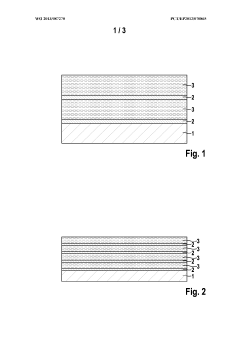
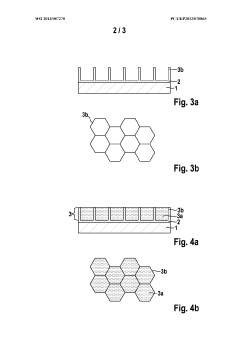
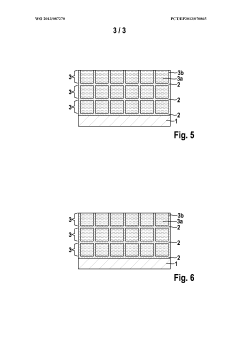
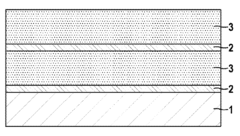
Lithium-sulphur cell cathode with a layer system
PatentWO2013087270A1
Innovation
- A multi-layer cathode system is introduced, comprising conductive layers and sulfur-containing layers applied to a current collector, where the conductive layers ensure targeted electrical contact and mechanical stability, potentially eliminating the need for a binder, and structured sulfur layers enhance sulfur utilization and ion transport.
Lithium-sulphur cell cathode with a layer system
PatentInactiveUS20140342227A1
Innovation
- A multilayered cathode structure with alternating conductive and sulfur-containing layers, optimized for electrical contact and mechanical stability, reduces internal resistance and prevents sulfur loss by creating targeted pathways and ion channels, enhancing energy density and cycle stability.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability Assessment
The environmental impact of sulfur cathode technology in large-scale grid deployments represents a critical consideration for sustainable energy storage solutions. Lithium-sulfur (Li-S) batteries offer significant environmental advantages compared to conventional lithium-ion technologies, primarily due to the abundance and low toxicity of sulfur as a cathode material. Sulfur is an industrial byproduct of petroleum refining processes, meaning its utilization in battery technology effectively repurposes a waste material, creating a circular economy benefit that reduces environmental burden.
Life cycle assessments indicate that sulfur cathode production generates substantially lower carbon emissions compared to traditional cobalt or nickel-based cathodes. Quantitative analyses demonstrate a potential reduction of 60-75% in greenhouse gas emissions during manufacturing processes, contributing significantly to climate change mitigation efforts when implemented at grid scale. Furthermore, the elimination of environmentally problematic materials such as cobalt reduces concerns regarding habitat destruction and water pollution associated with mining operations.
Water usage metrics for sulfur cathode production show approximately 40% lower requirements compared to conventional lithium-ion manufacturing processes. This water conservation aspect becomes particularly valuable when considering deployment in water-stressed regions where large-scale energy storage solutions are increasingly necessary for renewable energy integration.
End-of-life management presents both challenges and opportunities for sulfur cathode technologies. The inherent chemical stability of sulfur compounds facilitates more straightforward recycling processes, with laboratory studies demonstrating recovery rates exceeding 90% for sulfur materials. However, current recycling infrastructure requires adaptation to efficiently process these novel battery chemistries at scale.
Land use impact assessments for grid-scale deployments reveal that sulfur cathode storage systems can achieve 30-40% higher energy density by weight compared to conventional technologies, potentially reducing the physical footprint required for equivalent storage capacity. This spatial efficiency becomes particularly valuable in densely populated areas where land availability for energy infrastructure remains limited.
The sustainability profile of sulfur cathodes extends to supply chain resilience, as sulfur resources are geographically distributed across multiple regions, reducing geopolitical vulnerabilities associated with critical materials like cobalt and nickel. This distribution pattern supports more equitable global access to advanced energy storage technologies, aligning with sustainable development goals for energy equity.
Life cycle assessments indicate that sulfur cathode production generates substantially lower carbon emissions compared to traditional cobalt or nickel-based cathodes. Quantitative analyses demonstrate a potential reduction of 60-75% in greenhouse gas emissions during manufacturing processes, contributing significantly to climate change mitigation efforts when implemented at grid scale. Furthermore, the elimination of environmentally problematic materials such as cobalt reduces concerns regarding habitat destruction and water pollution associated with mining operations.
Water usage metrics for sulfur cathode production show approximately 40% lower requirements compared to conventional lithium-ion manufacturing processes. This water conservation aspect becomes particularly valuable when considering deployment in water-stressed regions where large-scale energy storage solutions are increasingly necessary for renewable energy integration.
End-of-life management presents both challenges and opportunities for sulfur cathode technologies. The inherent chemical stability of sulfur compounds facilitates more straightforward recycling processes, with laboratory studies demonstrating recovery rates exceeding 90% for sulfur materials. However, current recycling infrastructure requires adaptation to efficiently process these novel battery chemistries at scale.
Land use impact assessments for grid-scale deployments reveal that sulfur cathode storage systems can achieve 30-40% higher energy density by weight compared to conventional technologies, potentially reducing the physical footprint required for equivalent storage capacity. This spatial efficiency becomes particularly valuable in densely populated areas where land availability for energy infrastructure remains limited.
The sustainability profile of sulfur cathodes extends to supply chain resilience, as sulfur resources are geographically distributed across multiple regions, reducing geopolitical vulnerabilities associated with critical materials like cobalt and nickel. This distribution pattern supports more equitable global access to advanced energy storage technologies, aligning with sustainable development goals for energy equity.
Regulatory Framework for Grid Energy Storage Systems
The regulatory landscape for grid energy storage systems utilizing sulfur cathode technology is complex and evolving rapidly across different jurisdictions. In the United States, the Federal Energy Regulatory Commission (FERC) has established Order 841, which requires regional transmission organizations to establish market rules that recognize the physical and operational characteristics of storage resources. This regulatory framework has created pathways for large-scale sulfur-based battery systems to participate in wholesale electricity markets, though specific safety standards for sulfur cathodes remain under development.
The European Union has implemented the Clean Energy Package, which includes provisions for energy storage integration into grid systems. The EU Battery Directive is currently being revised to address emerging technologies like lithium-sulfur batteries, with particular focus on safety protocols, recycling requirements, and carbon footprint declarations. These regulations will significantly impact the deployment timeline and cost structure for sulfur cathode technologies in grid applications.
Safety standards represent a critical regulatory consideration for sulfur cathode deployment. Organizations such as UL (Underwriters Laboratories) and IEC (International Electrotechnical Commission) are developing specific testing protocols to address the unique characteristics of sulfur-based energy storage systems, including thermal runaway prevention, containment of hydrogen sulfide emissions, and long-term stability verification requirements.
Environmental regulations also shape the deployment landscape. The Resource Conservation and Recovery Act (RCRA) in the US and similar frameworks internationally govern the handling, storage, and disposal of sulfur compounds. Grid-scale deployments must demonstrate compliance with these regulations throughout the battery lifecycle, from manufacturing to decommissioning and recycling.
Permitting processes for large-scale grid storage installations vary significantly by region. In many jurisdictions, sulfur cathode systems face additional scrutiny due to limited operational history at utility scale. Developers must navigate local zoning requirements, environmental impact assessments, and grid interconnection studies, which can extend project timelines by 12-36 months depending on location.
Financial incentives and carbon accounting frameworks further influence deployment economics. Several countries have implemented investment tax credits, capacity payments, or carbon pricing mechanisms that can improve the business case for sulfur cathode systems. However, the regulatory classification of these technologies often determines eligibility for such programs, highlighting the importance of technology-specific regulatory frameworks.
The European Union has implemented the Clean Energy Package, which includes provisions for energy storage integration into grid systems. The EU Battery Directive is currently being revised to address emerging technologies like lithium-sulfur batteries, with particular focus on safety protocols, recycling requirements, and carbon footprint declarations. These regulations will significantly impact the deployment timeline and cost structure for sulfur cathode technologies in grid applications.
Safety standards represent a critical regulatory consideration for sulfur cathode deployment. Organizations such as UL (Underwriters Laboratories) and IEC (International Electrotechnical Commission) are developing specific testing protocols to address the unique characteristics of sulfur-based energy storage systems, including thermal runaway prevention, containment of hydrogen sulfide emissions, and long-term stability verification requirements.
Environmental regulations also shape the deployment landscape. The Resource Conservation and Recovery Act (RCRA) in the US and similar frameworks internationally govern the handling, storage, and disposal of sulfur compounds. Grid-scale deployments must demonstrate compliance with these regulations throughout the battery lifecycle, from manufacturing to decommissioning and recycling.
Permitting processes for large-scale grid storage installations vary significantly by region. In many jurisdictions, sulfur cathode systems face additional scrutiny due to limited operational history at utility scale. Developers must navigate local zoning requirements, environmental impact assessments, and grid interconnection studies, which can extend project timelines by 12-36 months depending on location.
Financial incentives and carbon accounting frameworks further influence deployment economics. Several countries have implemented investment tax credits, capacity payments, or carbon pricing mechanisms that can improve the business case for sulfur cathode systems. However, the regulatory classification of these technologies often determines eligibility for such programs, highlighting the importance of technology-specific regulatory frameworks.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!