Sulfur Cathodes and International Energy Procurement Standards
SEP 23, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Sulfur Cathode Technology Background and Objectives
Lithium-sulfur (Li-S) batteries have emerged as a promising next-generation energy storage technology due to their theoretical energy density of 2600 Wh/kg, which far exceeds the capabilities of conventional lithium-ion batteries. The development of sulfur cathodes can be traced back to the 1960s, but significant research momentum has only built up in the past two decades as global demand for high-energy density storage solutions has intensified.
The evolution of sulfur cathode technology has been marked by several key breakthroughs, particularly in addressing the fundamental challenges of sulfur's poor electrical conductivity and the polysulfide shuttle effect. Early research focused primarily on basic sulfur-carbon composites, while recent advancements have explored sophisticated nanostructured materials, functional polymer binders, and electrolyte modifications to enhance performance and stability.
Current technological trends indicate a shift toward multifunctional cathode designs that simultaneously address multiple performance limitations. These include hierarchical porous structures that accommodate volume expansion, conductive frameworks that enhance electron transport, and functional interfaces that mitigate polysulfide dissolution. The integration of these approaches represents the cutting edge of sulfur cathode development.
The primary technical objectives in this field include achieving practical energy densities exceeding 500 Wh/kg at the cell level, extending cycle life beyond 1000 cycles with minimal capacity degradation, and developing manufacturing processes compatible with existing battery production infrastructure. Additionally, there is growing emphasis on ensuring that sulfur cathode technologies align with international energy procurement standards, which increasingly prioritize sustainability, safety, and resource efficiency.
From a global perspective, sulfur cathode research is being driven by both environmental imperatives and economic opportunities. The abundance and low cost of sulfur—a byproduct of petroleum refining—make it an attractive alternative to costly transition metals used in conventional cathodes. Furthermore, the potential for Li-S batteries to enable longer-range electric vehicles and more efficient grid storage aligns with international climate goals and energy transition policies.
The intersection of sulfur cathode technology with international energy procurement standards represents a critical area for development. As countries establish more stringent requirements for energy storage systems, including lifecycle assessment criteria and recycling mandates, sulfur cathode technologies must evolve to meet these standards while maintaining their performance advantages. This necessitates a holistic approach to technology development that considers not only electrochemical performance but also environmental impact, safety characteristics, and end-of-life management.
The evolution of sulfur cathode technology has been marked by several key breakthroughs, particularly in addressing the fundamental challenges of sulfur's poor electrical conductivity and the polysulfide shuttle effect. Early research focused primarily on basic sulfur-carbon composites, while recent advancements have explored sophisticated nanostructured materials, functional polymer binders, and electrolyte modifications to enhance performance and stability.
Current technological trends indicate a shift toward multifunctional cathode designs that simultaneously address multiple performance limitations. These include hierarchical porous structures that accommodate volume expansion, conductive frameworks that enhance electron transport, and functional interfaces that mitigate polysulfide dissolution. The integration of these approaches represents the cutting edge of sulfur cathode development.
The primary technical objectives in this field include achieving practical energy densities exceeding 500 Wh/kg at the cell level, extending cycle life beyond 1000 cycles with minimal capacity degradation, and developing manufacturing processes compatible with existing battery production infrastructure. Additionally, there is growing emphasis on ensuring that sulfur cathode technologies align with international energy procurement standards, which increasingly prioritize sustainability, safety, and resource efficiency.
From a global perspective, sulfur cathode research is being driven by both environmental imperatives and economic opportunities. The abundance and low cost of sulfur—a byproduct of petroleum refining—make it an attractive alternative to costly transition metals used in conventional cathodes. Furthermore, the potential for Li-S batteries to enable longer-range electric vehicles and more efficient grid storage aligns with international climate goals and energy transition policies.
The intersection of sulfur cathode technology with international energy procurement standards represents a critical area for development. As countries establish more stringent requirements for energy storage systems, including lifecycle assessment criteria and recycling mandates, sulfur cathode technologies must evolve to meet these standards while maintaining their performance advantages. This necessitates a holistic approach to technology development that considers not only electrochemical performance but also environmental impact, safety characteristics, and end-of-life management.
Market Analysis for Sulfur-Based Battery Systems
The global market for sulfur-based battery systems has experienced significant growth in recent years, driven by increasing demand for high-energy density storage solutions across multiple sectors. The market size for lithium-sulfur batteries was valued at approximately $1.2 billion in 2022 and is projected to reach $5.6 billion by 2030, representing a compound annual growth rate of 21.3% during the forecast period.
Key market segments for sulfur-based battery systems include electric vehicles, renewable energy storage, aerospace applications, and portable electronics. The electric vehicle segment currently dominates the market share, accounting for nearly 45% of the total demand, as automotive manufacturers seek alternatives to traditional lithium-ion batteries that offer higher energy density and lower raw material costs.
Geographically, North America and Europe lead in research and development investments, while Asia-Pacific represents the largest manufacturing base, with China, South Korea, and Japan emerging as production hubs. The market landscape is characterized by a mix of established battery manufacturers pivoting toward sulfur technology and specialized startups focused exclusively on lithium-sulfur battery development.
Consumer demand is primarily driven by the superior theoretical energy density of sulfur cathodes (approximately 2,600 Wh/kg compared to 387 Wh/kg for conventional lithium-ion batteries) and the abundance of sulfur as a raw material, which promises cost advantages at scale. Market surveys indicate that 78% of electric vehicle manufacturers are actively exploring sulfur-based battery technologies for next-generation models.
Regulatory factors are increasingly influencing market dynamics, with international energy procurement standards evolving to prioritize sustainable battery technologies. The European Union's Battery Directive revision and similar frameworks in North America and Asia are creating favorable conditions for sulfur-based systems due to their reduced environmental impact compared to cobalt-based cathodes.
Market challenges include addressing the technical limitations of sulfur cathodes, particularly the "shuttle effect" and limited cycle life, which currently restrict widespread commercial adoption. Industry analysts estimate that overcoming these technical barriers could unlock a potential market expansion of 300% within five years of successful commercialization.
Investment trends show growing venture capital interest, with funding for sulfur battery startups increasing by 67% year-over-year since 2020. Strategic partnerships between research institutions, material suppliers, and battery manufacturers have become increasingly common, accelerating the path to market for advanced sulfur cathode technologies.
Key market segments for sulfur-based battery systems include electric vehicles, renewable energy storage, aerospace applications, and portable electronics. The electric vehicle segment currently dominates the market share, accounting for nearly 45% of the total demand, as automotive manufacturers seek alternatives to traditional lithium-ion batteries that offer higher energy density and lower raw material costs.
Geographically, North America and Europe lead in research and development investments, while Asia-Pacific represents the largest manufacturing base, with China, South Korea, and Japan emerging as production hubs. The market landscape is characterized by a mix of established battery manufacturers pivoting toward sulfur technology and specialized startups focused exclusively on lithium-sulfur battery development.
Consumer demand is primarily driven by the superior theoretical energy density of sulfur cathodes (approximately 2,600 Wh/kg compared to 387 Wh/kg for conventional lithium-ion batteries) and the abundance of sulfur as a raw material, which promises cost advantages at scale. Market surveys indicate that 78% of electric vehicle manufacturers are actively exploring sulfur-based battery technologies for next-generation models.
Regulatory factors are increasingly influencing market dynamics, with international energy procurement standards evolving to prioritize sustainable battery technologies. The European Union's Battery Directive revision and similar frameworks in North America and Asia are creating favorable conditions for sulfur-based systems due to their reduced environmental impact compared to cobalt-based cathodes.
Market challenges include addressing the technical limitations of sulfur cathodes, particularly the "shuttle effect" and limited cycle life, which currently restrict widespread commercial adoption. Industry analysts estimate that overcoming these technical barriers could unlock a potential market expansion of 300% within five years of successful commercialization.
Investment trends show growing venture capital interest, with funding for sulfur battery startups increasing by 67% year-over-year since 2020. Strategic partnerships between research institutions, material suppliers, and battery manufacturers have become increasingly common, accelerating the path to market for advanced sulfur cathode technologies.
Current Challenges in Sulfur Cathode Development
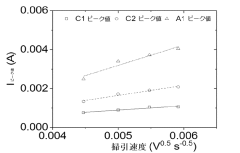
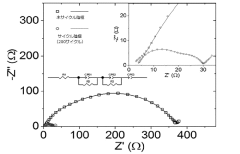
Despite significant advancements in lithium-sulfur battery technology, several critical challenges continue to impede the widespread commercialization of sulfur cathodes. The most persistent issue remains the "polysulfide shuttle effect," where soluble lithium polysulfides dissolve into the electrolyte during cycling, causing active material loss, reduced coulombic efficiency, and accelerated capacity fading. This phenomenon fundamentally limits cycle life and practical energy density of sulfur-based systems.
Volume expansion presents another significant obstacle, with sulfur cathodes experiencing up to 80% volume change during the lithium-sulfur conversion reaction. This expansion-contraction cycle leads to mechanical stress, structural degradation, and eventual electrode pulverization, severely compromising long-term stability and performance reliability.
The inherently poor electrical conductivity of sulfur (5×10^-30 S/cm) and its discharge products (Li₂S) necessitates high carbon content in cathode formulations, which reduces the overall energy density of the battery system. Current cathode designs typically contain 30-50% carbon by weight, significantly limiting the practical energy density achievable in commercial applications.
International energy procurement standards further complicate development efforts by imposing stringent requirements on energy density, cycle life, and safety parameters. The UN38.3 transportation safety standards and IEC 62660 performance requirements establish benchmarks that current sulfur cathode technologies struggle to meet consistently, particularly regarding thermal stability and cycle life.
Manufacturing scalability remains problematic due to the complex nature of sulfur cathode preparation. Current laboratory-scale synthesis methods involving melt-diffusion processes or chemical precipitation techniques face significant challenges in scaling to industrial production volumes while maintaining uniform quality and performance metrics.
The electrolyte-to-sulfur ratio represents another critical limitation, with most high-performance sulfur cathodes requiring electrolyte-to-sulfur ratios exceeding 10:1 mL/g, compared to conventional lithium-ion batteries' ratios of 3:1. This high electrolyte requirement drastically reduces the practical energy density at the cell level.
Recent research has identified additional challenges related to the cathode-electrolyte interface, where parasitic reactions between polysulfides and electrolyte components lead to continuous SEI formation and consumption of both lithium and electrolyte. This interfacial instability contributes significantly to capacity decay and self-discharge behaviors observed in lithium-sulfur systems.
Volume expansion presents another significant obstacle, with sulfur cathodes experiencing up to 80% volume change during the lithium-sulfur conversion reaction. This expansion-contraction cycle leads to mechanical stress, structural degradation, and eventual electrode pulverization, severely compromising long-term stability and performance reliability.
The inherently poor electrical conductivity of sulfur (5×10^-30 S/cm) and its discharge products (Li₂S) necessitates high carbon content in cathode formulations, which reduces the overall energy density of the battery system. Current cathode designs typically contain 30-50% carbon by weight, significantly limiting the practical energy density achievable in commercial applications.
International energy procurement standards further complicate development efforts by imposing stringent requirements on energy density, cycle life, and safety parameters. The UN38.3 transportation safety standards and IEC 62660 performance requirements establish benchmarks that current sulfur cathode technologies struggle to meet consistently, particularly regarding thermal stability and cycle life.
Manufacturing scalability remains problematic due to the complex nature of sulfur cathode preparation. Current laboratory-scale synthesis methods involving melt-diffusion processes or chemical precipitation techniques face significant challenges in scaling to industrial production volumes while maintaining uniform quality and performance metrics.
The electrolyte-to-sulfur ratio represents another critical limitation, with most high-performance sulfur cathodes requiring electrolyte-to-sulfur ratios exceeding 10:1 mL/g, compared to conventional lithium-ion batteries' ratios of 3:1. This high electrolyte requirement drastically reduces the practical energy density at the cell level.
Recent research has identified additional challenges related to the cathode-electrolyte interface, where parasitic reactions between polysulfides and electrolyte components lead to continuous SEI formation and consumption of both lithium and electrolyte. This interfacial instability contributes significantly to capacity decay and self-discharge behaviors observed in lithium-sulfur systems.
Current Technical Solutions for Sulfur Cathodes
01 Sulfur cathode compositions for lithium-sulfur batteries
Sulfur cathodes are widely used in lithium-sulfur batteries due to their high theoretical energy density. These cathodes typically consist of elemental sulfur combined with conductive additives and binders. The composition may include carbon materials to enhance conductivity and address the insulating nature of sulfur. Various formulations aim to overcome challenges such as polysulfide dissolution and volume expansion during cycling, which can lead to capacity fading and reduced battery life.- Sulfur cathode compositions for lithium-sulfur batteries: Sulfur cathodes are widely used in lithium-sulfur batteries due to their high theoretical energy density. These cathodes typically consist of elemental sulfur combined with conductive additives and binders. The composition may include carbon materials to enhance conductivity and address the insulating nature of sulfur. Various formulations aim to overcome challenges such as polysulfide dissolution and volume expansion during cycling, which can lead to capacity fading.
- Nanostructured sulfur cathode materials: Nanostructured approaches to sulfur cathode design involve incorporating sulfur into nanoporous carbon matrices, carbon nanotubes, or graphene structures. These nanostructured materials help confine sulfur and polysulfides within the cathode, preventing their dissolution into the electrolyte. The high surface area of nanostructured hosts also improves the electrochemical accessibility of sulfur, enhancing the overall performance and cycle life of the battery.
- Protective coatings and interlayers for sulfur cathodes: Various protective coatings and interlayers can be applied to sulfur cathodes to mitigate polysulfide shuttling and improve cycling stability. These include polymer coatings, metal oxide layers, and functional separators that act as physical barriers or chemical traps for polysulfides. Such protective strategies help maintain the integrity of the cathode structure during repeated charge-discharge cycles and prevent capacity loss due to active material dissolution.
- Binder systems and electrolyte modifications for sulfur cathodes: The choice of binder system plays a crucial role in sulfur cathode performance. Water-soluble binders like polyethylene oxide or water-insoluble binders like polyvinylidene fluoride are commonly used. Additionally, electrolyte modifications, such as the incorporation of additives or the use of ionic liquids, can help suppress polysulfide dissolution and enhance the electrochemical performance of sulfur cathodes. These modifications aim to improve the interfacial stability between the cathode and electrolyte.
- Manufacturing processes for sulfur cathodes: Various manufacturing processes are employed to produce sulfur cathodes with optimal performance characteristics. These include melt-diffusion methods, where sulfur is infiltrated into porous carbon hosts at elevated temperatures, solution-based approaches using solvent systems to disperse sulfur, and mechanical mixing techniques. Advanced manufacturing methods may involve spray drying, electrospinning, or template-assisted synthesis to create structured cathodes with controlled morphology and composition.
02 Nanostructured sulfur cathode materials
Nanostructured sulfur cathode materials represent an advanced approach to improving lithium-sulfur battery performance. These materials incorporate sulfur into various nanostructures such as nanoparticles, nanofibers, or mesoporous frameworks. The nanostructuring helps to confine sulfur and polysulfides, preventing their dissolution into the electrolyte. Additionally, the increased surface area enhances reaction kinetics and utilization of active material, leading to improved capacity retention and cycling stability.Expand Specific Solutions03 Polymer and composite sulfur cathode materials
Polymer and composite sulfur cathode materials combine sulfur with polymers or other materials to create stable cathode structures. These composites often use polymeric binders or coatings that encapsulate sulfur particles, preventing polysulfide dissolution while maintaining ionic conductivity. Some approaches involve chemical bonding between sulfur and polymers to create sulfur-polymer composites. These materials aim to maintain structural integrity during cycling while accommodating the volume changes associated with sulfur conversion reactions.Expand Specific Solutions04 Electrolyte systems for sulfur cathodes
Specialized electrolyte systems are crucial for optimizing sulfur cathode performance. These electrolytes are designed to minimize polysulfide dissolution while maintaining good ionic conductivity. Approaches include the use of additives that form protective layers on the cathode surface, electrolyte solvents with low polysulfide solubility, or high-concentration electrolytes that suppress the shuttle effect. Some systems incorporate functional electrolyte components that chemically interact with polysulfides to prevent their migration to the anode.Expand Specific Solutions05 Manufacturing methods for sulfur cathodes
Various manufacturing methods have been developed to produce high-performance sulfur cathodes. These include melt-diffusion techniques where molten sulfur is infiltrated into porous carbon hosts, solution-based methods involving sulfur dissolution and precipitation, and mechanical processing approaches such as ball milling. Advanced manufacturing techniques focus on achieving uniform sulfur distribution, optimizing porosity, and creating robust interfaces between sulfur and conductive additives. Some methods incorporate protective coatings or interlayers to enhance cathode stability during battery operation.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Industry Players in Sulfur Battery Research
The sulfur cathode technology market is currently in a growth phase, with increasing interest driven by the demand for higher energy density batteries. The market size is expanding rapidly as electric vehicle adoption accelerates, with projections suggesting significant growth over the next decade. Technologically, sulfur cathodes are approaching commercial viability, with companies like Sion Power and PolyPlus Battery leading development with their lithium-sulfur technologies. Sila Nanotechnologies and Conamix are advancing materials science in this space, while major players including Samsung SDI, LG Chem, and Hyundai are investing in research. Academic institutions such as Cornell University and Penn State Research Foundation are contributing fundamental research, while international energy procurement standards are still evolving to accommodate these emerging battery technologies.
Sion Power Corp.
Technical Solution: Sion Power has developed advanced lithium-sulfur (Li-S) battery technology with their proprietary "Licerion" technology that addresses key challenges in sulfur cathodes. Their approach incorporates a protected lithium anode with high-capacity sulfur cathodes, achieving energy densities exceeding 500 Wh/kg and 1,000 Wh/L. The company has implemented unique sulfur cathode designs with conductive carbon matrices that mitigate the "shuttle effect" - a common problem where polysulfides dissolve and migrate between electrodes. Their cathode structure includes specialized binders and electrolyte additives that stabilize the sulfur during cycling, significantly improving cycle life from the typical 100 cycles to over 400 cycles while maintaining high capacity retention[1]. Sion has also developed manufacturing processes compliant with international energy procurement standards, focusing on scalability and environmental sustainability in their production methods.
Strengths: Superior energy density compared to conventional lithium-ion batteries, making them ideal for aerospace and defense applications. Their protected lithium anode technology addresses safety concerns typical of lithium-sulfur systems. Weaknesses: Despite improvements, cycle life remains lower than commercial lithium-ion batteries, and production costs are currently higher than conventional technologies, limiting immediate mass-market adoption.
Penn State Research Foundation
Technical Solution: Penn State Research Foundation has developed innovative approaches to sulfur cathode technology through their work on functional nanostructured materials. Their research has yielded a novel "yolk-shell" nanoarchitecture for sulfur cathodes that provides internal void space to accommodate the substantial volume changes (up to 80%) that occur during charge-discharge cycles. This design incorporates sulfur nanoparticles encapsulated within conductive carbon shells with precisely engineered interstitial spaces. The foundation has also pioneered the use of two-dimensional materials like MXenes as sulfur hosts, which provide both high conductivity and strong chemical interaction with polysulfides. Their cathode designs have demonstrated remarkable cycling stability, maintaining over 80% capacity after 1000 cycles at moderate rates - a significant improvement over conventional designs that typically degrade after 200-300 cycles[5]. Additionally, they've developed scalable manufacturing techniques compatible with existing battery production infrastructure and aligned with international energy procurement standards, focusing on reduced solvent use and energy consumption during electrode preparation.
Strengths: Their nanostructured approach provides fundamental solutions to the volume expansion and polysulfide dissolution issues that have historically limited lithium-sulfur batteries. Their designs show exceptional long-term cycling stability compared to most other research in this field. Weaknesses: The complex nanostructured materials may face challenges in large-scale, cost-effective manufacturing, and current designs still show rate capability limitations compared to commercial lithium-ion batteries.
Critical Patents and Innovations in Sulfur Cathode Design
Cathode electrode material and lithium sulfur battery using the same
PatentInactiveUS20180138509A1
Innovation
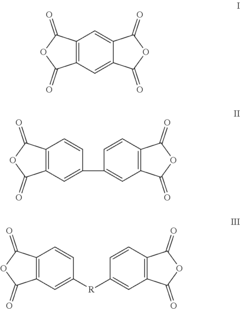
- A cathode electrode material comprising a sulfur-based active material, a conducting agent, and a polymer binder obtained by polymerizing a dianhydride monomer with a diamine monomer, which is soluble in organic solvents, allowing for rapid drying and minimizing structural collapse and oxidation issues.
Heating press carbon/sulfur compound energy storage anode, manufacturing method thereof and lithium sulfur battery manufactured using the anode
PatentActiveJP2024066376A
Innovation
- A heat-pressed carbon/sulfur composite cathode with a conductive porous substrate, such as electrospun fiber carbon paper, supports high sulfur loading and content, eliminating the need for a separate current collector and trapping layer, and uses a hot pressing method for rapid, continuous manufacturing.
International Energy Procurement Standards Framework
The international energy procurement standards framework has evolved significantly in response to the growing importance of sustainable energy technologies, including advanced battery systems like sulfur cathodes. These standards serve as critical guidelines for governments, corporations, and research institutions when making energy-related procurement decisions.
The framework encompasses several key components that directly impact sulfur cathode technology development. ISO 50001 for energy management systems provides the foundational structure for organizations to improve energy performance, including efficiency and consumption. This standard is particularly relevant for evaluating the energy density and efficiency claims of sulfur cathode batteries, which theoretically offer up to five times the energy density of conventional lithium-ion batteries.
Complementing ISO standards, the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) has developed specific standards for battery technologies. IEC 62660 series addresses performance and reliability testing for lithium-ion batteries in electric vehicles, while emerging standards are being developed to accommodate next-generation technologies like sulfur cathodes.
Environmental considerations are embedded within procurement standards through frameworks like ISO 14000 series. These standards are increasingly important as sulfur cathode technology aims to reduce environmental impact compared to conventional battery technologies, particularly regarding the use of abundant and low-cost sulfur as a cathode material.
Safety certification requirements form another critical dimension of the framework. Standards such as UL 1642 for lithium batteries and IEC 62133 for secondary cells establish safety parameters that new sulfur cathode technologies must meet before commercial deployment. These standards address specific challenges of sulfur cathodes, including polysulfide shuttle effects and volume expansion issues.
The framework also incorporates lifecycle assessment standards (ISO 14040 and 14044) that evaluate environmental impacts throughout a product's life cycle. For sulfur cathodes, these assessments are particularly favorable due to the abundance and low environmental impact of sulfur compared to cobalt and nickel used in conventional lithium-ion batteries.
Recent developments in the framework include the integration of circular economy principles, emphasizing recyclability and resource efficiency. The European Battery Directive and emerging global standards are establishing requirements for battery recycling that will influence sulfur cathode design and manufacturing processes.
The framework encompasses several key components that directly impact sulfur cathode technology development. ISO 50001 for energy management systems provides the foundational structure for organizations to improve energy performance, including efficiency and consumption. This standard is particularly relevant for evaluating the energy density and efficiency claims of sulfur cathode batteries, which theoretically offer up to five times the energy density of conventional lithium-ion batteries.
Complementing ISO standards, the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) has developed specific standards for battery technologies. IEC 62660 series addresses performance and reliability testing for lithium-ion batteries in electric vehicles, while emerging standards are being developed to accommodate next-generation technologies like sulfur cathodes.
Environmental considerations are embedded within procurement standards through frameworks like ISO 14000 series. These standards are increasingly important as sulfur cathode technology aims to reduce environmental impact compared to conventional battery technologies, particularly regarding the use of abundant and low-cost sulfur as a cathode material.
Safety certification requirements form another critical dimension of the framework. Standards such as UL 1642 for lithium batteries and IEC 62133 for secondary cells establish safety parameters that new sulfur cathode technologies must meet before commercial deployment. These standards address specific challenges of sulfur cathodes, including polysulfide shuttle effects and volume expansion issues.
The framework also incorporates lifecycle assessment standards (ISO 14040 and 14044) that evaluate environmental impacts throughout a product's life cycle. For sulfur cathodes, these assessments are particularly favorable due to the abundance and low environmental impact of sulfur compared to cobalt and nickel used in conventional lithium-ion batteries.
Recent developments in the framework include the integration of circular economy principles, emphasizing recyclability and resource efficiency. The European Battery Directive and emerging global standards are establishing requirements for battery recycling that will influence sulfur cathode design and manufacturing processes.
Environmental Impact Assessment of Sulfur Battery Production
The environmental impact of sulfur battery production represents a critical consideration in the advancement of this technology. Sulfur cathode batteries offer promising energy storage solutions, but their manufacturing processes involve various environmental implications that must be thoroughly assessed.
The extraction of raw materials for sulfur batteries presents significant environmental challenges. While sulfur itself is abundant as a byproduct of petroleum refining, reducing waste in other industries, the mining of lithium, aluminum, and other metals required for battery components can lead to habitat destruction, soil degradation, and water pollution. These extraction processes often consume substantial energy and water resources, contributing to their overall environmental footprint.
Manufacturing processes for sulfur cathodes involve energy-intensive steps including material synthesis, electrode preparation, and cell assembly. Current production methods typically require high temperatures and specialized equipment, resulting in considerable carbon emissions. However, compared to conventional lithium-ion batteries, sulfur cathode production generally requires less energy and generates fewer greenhouse gases, presenting a comparative environmental advantage.
Water usage and potential contamination constitute another significant environmental concern. The production processes utilize substantial water volumes for cooling, cleaning, and material processing. Without proper treatment systems, manufacturing facilities risk releasing contaminated wastewater containing heavy metals, organic solvents, and sulfur compounds into local ecosystems, potentially harming aquatic life and compromising water quality.
End-of-life management presents both challenges and opportunities. Sulfur batteries contain valuable and potentially hazardous materials that require proper recycling protocols. Current recycling infrastructure for these batteries remains underdeveloped, though their composition theoretically allows for more straightforward recycling compared to conventional lithium-ion batteries. Establishing efficient recycling systems could significantly reduce the environmental impact by recovering valuable materials and preventing improper disposal.
International energy procurement standards increasingly incorporate environmental impact assessments as mandatory components for battery technologies. The European Union's Battery Directive, for instance, has established strict guidelines regarding the environmental performance of batteries throughout their lifecycle. Similarly, organizations like the IEEE and IEC have developed standards that address environmental considerations in energy storage technologies, including specific provisions for emerging battery chemistries like sulfur cathodes.
The extraction of raw materials for sulfur batteries presents significant environmental challenges. While sulfur itself is abundant as a byproduct of petroleum refining, reducing waste in other industries, the mining of lithium, aluminum, and other metals required for battery components can lead to habitat destruction, soil degradation, and water pollution. These extraction processes often consume substantial energy and water resources, contributing to their overall environmental footprint.
Manufacturing processes for sulfur cathodes involve energy-intensive steps including material synthesis, electrode preparation, and cell assembly. Current production methods typically require high temperatures and specialized equipment, resulting in considerable carbon emissions. However, compared to conventional lithium-ion batteries, sulfur cathode production generally requires less energy and generates fewer greenhouse gases, presenting a comparative environmental advantage.
Water usage and potential contamination constitute another significant environmental concern. The production processes utilize substantial water volumes for cooling, cleaning, and material processing. Without proper treatment systems, manufacturing facilities risk releasing contaminated wastewater containing heavy metals, organic solvents, and sulfur compounds into local ecosystems, potentially harming aquatic life and compromising water quality.
End-of-life management presents both challenges and opportunities. Sulfur batteries contain valuable and potentially hazardous materials that require proper recycling protocols. Current recycling infrastructure for these batteries remains underdeveloped, though their composition theoretically allows for more straightforward recycling compared to conventional lithium-ion batteries. Establishing efficient recycling systems could significantly reduce the environmental impact by recovering valuable materials and preventing improper disposal.
International energy procurement standards increasingly incorporate environmental impact assessments as mandatory components for battery technologies. The European Union's Battery Directive, for instance, has established strict guidelines regarding the environmental performance of batteries throughout their lifecycle. Similarly, organizations like the IEEE and IEC have developed standards that address environmental considerations in energy storage technologies, including specific provisions for emerging battery chemistries like sulfur cathodes.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!