HBM4 TSV Engineering: Resistance, Capacitance And Signal Quality
SEP 12, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
HBM4 TSV Technology Background and Objectives
High-Bandwidth Memory (HBM) technology has evolved significantly since its introduction, with HBM4 representing the latest advancement in 3D stacked memory solutions. Through Silicon Via (TSV) technology serves as the backbone of HBM architecture, enabling vertical interconnections between stacked memory dies. The evolution from HBM1 to HBM4 has been characterized by continuous improvements in bandwidth, capacity, and energy efficiency to meet the escalating demands of data-intensive applications.
The historical trajectory of HBM technology began with HBM1 in 2013, progressing to HBM2 in 2016, HBM2E in 2018, HBM3 in 2021, and now advancing toward HBM4, expected to be commercially available by 2025. Each generation has significantly increased bandwidth capabilities, with HBM4 projected to deliver up to 8TB/s bandwidth, representing a substantial leap from previous generations.
TSV technology has been central to this evolution, with continuous refinements in diameter, pitch, aspect ratio, and electrical characteristics. Early TSVs in HBM1 had relatively large dimensions and limited density, while HBM4 implementations feature significantly reduced TSV dimensions, enabling higher integration density and improved signal integrity. This miniaturization trend presents new engineering challenges related to resistance, capacitance, and overall signal quality.
The primary technical objectives for HBM4 TSV engineering focus on optimizing electrical parameters to support the increased bandwidth requirements while maintaining signal integrity. Specifically, engineers aim to minimize TSV resistance to reduce power consumption and heat generation, control capacitance to limit signal distortion and crosstalk, and enhance overall signal quality to ensure reliable data transmission at higher frequencies.
Current industry trends indicate a push toward TSVs with diameters below 5μm, aspect ratios exceeding 10:1, and pitches under 40μm for HBM4 implementations. These dimensional targets necessitate innovations in materials science, fabrication processes, and design methodologies to overcome the inherent physical limitations of conventional TSV technologies.
The broader context driving HBM4 TSV development includes the exponential growth in AI and high-performance computing applications, which demand unprecedented memory bandwidth and capacity. The emergence of large language models, real-time data analytics, and advanced scientific simulations has created a technological imperative for memory solutions that can deliver massive parallel data access with minimal latency.
Looking forward, the technical trajectory for HBM4 TSV engineering will likely involve novel materials for TSV conductors and insulators, advanced fabrication techniques to achieve higher aspect ratios, and sophisticated signal integrity solutions to mitigate the electrical challenges associated with higher frequencies and denser integration.
The historical trajectory of HBM technology began with HBM1 in 2013, progressing to HBM2 in 2016, HBM2E in 2018, HBM3 in 2021, and now advancing toward HBM4, expected to be commercially available by 2025. Each generation has significantly increased bandwidth capabilities, with HBM4 projected to deliver up to 8TB/s bandwidth, representing a substantial leap from previous generations.
TSV technology has been central to this evolution, with continuous refinements in diameter, pitch, aspect ratio, and electrical characteristics. Early TSVs in HBM1 had relatively large dimensions and limited density, while HBM4 implementations feature significantly reduced TSV dimensions, enabling higher integration density and improved signal integrity. This miniaturization trend presents new engineering challenges related to resistance, capacitance, and overall signal quality.
The primary technical objectives for HBM4 TSV engineering focus on optimizing electrical parameters to support the increased bandwidth requirements while maintaining signal integrity. Specifically, engineers aim to minimize TSV resistance to reduce power consumption and heat generation, control capacitance to limit signal distortion and crosstalk, and enhance overall signal quality to ensure reliable data transmission at higher frequencies.
Current industry trends indicate a push toward TSVs with diameters below 5μm, aspect ratios exceeding 10:1, and pitches under 40μm for HBM4 implementations. These dimensional targets necessitate innovations in materials science, fabrication processes, and design methodologies to overcome the inherent physical limitations of conventional TSV technologies.
The broader context driving HBM4 TSV development includes the exponential growth in AI and high-performance computing applications, which demand unprecedented memory bandwidth and capacity. The emergence of large language models, real-time data analytics, and advanced scientific simulations has created a technological imperative for memory solutions that can deliver massive parallel data access with minimal latency.
Looking forward, the technical trajectory for HBM4 TSV engineering will likely involve novel materials for TSV conductors and insulators, advanced fabrication techniques to achieve higher aspect ratios, and sophisticated signal integrity solutions to mitigate the electrical challenges associated with higher frequencies and denser integration.
Market Demand Analysis for Advanced Memory Solutions
The demand for advanced memory solutions has been experiencing unprecedented growth, driven primarily by the rapid expansion of data-intensive applications across multiple sectors. High Bandwidth Memory (HBM), particularly the upcoming HBM4 standard, represents a critical technology addressing these escalating requirements. Market research indicates that the global HBM market is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate exceeding 30% through 2028, with particular acceleration in AI/ML applications.
Data centers and cloud service providers constitute the largest market segment for HBM technology, as they continuously seek higher memory bandwidth and capacity to support increasingly complex workloads. The explosive growth in artificial intelligence training models, which have grown from billions to trillions of parameters in recent years, has created an urgent need for memory solutions that can deliver substantially higher bandwidth while maintaining signal integrity.
The semiconductor industry's shift toward heterogeneous integration and chiplet-based architectures has further amplified demand for advanced TSV (Through-Silicon Via) engineering. As computing architectures evolve, memory subsystems must deliver not only raw capacity but also unprecedented levels of bandwidth with minimal latency and power consumption. This has placed HBM4's TSV engineering at the forefront of industry attention.
Resistance and capacitance characteristics of TSVs directly impact signal quality, which becomes increasingly critical as data rates climb toward 8+ Gbps per pin in HBM4 designs. Market surveys indicate that system designers are prioritizing memory solutions that can maintain signal integrity while pushing bandwidth boundaries, with over 85% of respondents citing signal quality as a "very important" or "critical" consideration.
The automotive and edge computing sectors represent emerging markets for advanced memory solutions, with requirements for both high performance and reliability under challenging environmental conditions. These applications demand TSV engineering that addresses not only electrical parameters but also thermal and mechanical reliability concerns.
Energy efficiency has emerged as another significant market driver, with data centers increasingly constrained by power and cooling limitations. The industry is demanding memory solutions that can deliver more bandwidth per watt, placing additional pressure on TSV engineering to minimize resistance while controlling capacitance to optimize both performance and power consumption.
Geographic analysis reveals that while North America leads in HBM adoption for AI applications, Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing market segment, driven by investments in supercomputing infrastructure and advanced semiconductor manufacturing capabilities. European markets show particular interest in HBM solutions optimized for automotive and industrial applications, where reliability metrics often outweigh pure performance considerations.
Data centers and cloud service providers constitute the largest market segment for HBM technology, as they continuously seek higher memory bandwidth and capacity to support increasingly complex workloads. The explosive growth in artificial intelligence training models, which have grown from billions to trillions of parameters in recent years, has created an urgent need for memory solutions that can deliver substantially higher bandwidth while maintaining signal integrity.
The semiconductor industry's shift toward heterogeneous integration and chiplet-based architectures has further amplified demand for advanced TSV (Through-Silicon Via) engineering. As computing architectures evolve, memory subsystems must deliver not only raw capacity but also unprecedented levels of bandwidth with minimal latency and power consumption. This has placed HBM4's TSV engineering at the forefront of industry attention.
Resistance and capacitance characteristics of TSVs directly impact signal quality, which becomes increasingly critical as data rates climb toward 8+ Gbps per pin in HBM4 designs. Market surveys indicate that system designers are prioritizing memory solutions that can maintain signal integrity while pushing bandwidth boundaries, with over 85% of respondents citing signal quality as a "very important" or "critical" consideration.
The automotive and edge computing sectors represent emerging markets for advanced memory solutions, with requirements for both high performance and reliability under challenging environmental conditions. These applications demand TSV engineering that addresses not only electrical parameters but also thermal and mechanical reliability concerns.
Energy efficiency has emerged as another significant market driver, with data centers increasingly constrained by power and cooling limitations. The industry is demanding memory solutions that can deliver more bandwidth per watt, placing additional pressure on TSV engineering to minimize resistance while controlling capacitance to optimize both performance and power consumption.
Geographic analysis reveals that while North America leads in HBM adoption for AI applications, Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing market segment, driven by investments in supercomputing infrastructure and advanced semiconductor manufacturing capabilities. European markets show particular interest in HBM solutions optimized for automotive and industrial applications, where reliability metrics often outweigh pure performance considerations.
Current TSV Engineering Challenges and Limitations
Through Silicon Via (TSV) technology represents a critical advancement in 3D integration for high-bandwidth memory, particularly for HBM4. However, current TSV engineering faces significant challenges that limit performance optimization and manufacturing yield. The primary electrical challenges revolve around resistance, capacitance, and signal integrity issues that become increasingly problematic as TSV dimensions continue to shrink for higher density integration.
Resistance in TSVs has become a major concern as the aspect ratio (depth to diameter ratio) increases in pursuit of smaller footprints. Current TSVs in HBM applications typically exhibit resistances ranging from 50-200 mΩ, but variations in metal filling processes can cause up to 30% deviation in resistance values across a single wafer. This inconsistency directly impacts signal timing and power distribution, creating performance bottlenecks in HBM4 designs where thousands of TSVs operate simultaneously.
Capacitance management presents another significant challenge. The proximity of TSVs to each other and to active silicon areas generates parasitic capacitances typically ranging from 20-100 fF. These parasitic elements create coupling effects that degrade signal integrity and increase power consumption. Current isolation techniques using thick oxide liners compromise the effective use of silicon real estate, creating a difficult trade-off between electrical performance and integration density.
Signal quality degradation manifests through increased crosstalk, reflections, and timing jitter. As HBM4 pushes data rates beyond 8 Gbps per pin, maintaining signal integrity through TSVs becomes exponentially more difficult. Current designs struggle to maintain acceptable bit error rates without significant power increases or complex equalization schemes that add latency and circuit complexity.
Manufacturing challenges compound these electrical issues. Current TSV formation processes face limitations in achieving consistent aspect ratios above 10:1, while void-free metal filling becomes increasingly difficult below 5μm diameters. The thermal expansion mismatch between copper TSVs and silicon substrate creates mechanical stress that can propagate to nearby active devices, causing parametric shifts in transistor performance by up to 10%.
Testing and quality assurance of TSVs remain problematic, with limited in-line monitoring capabilities. Current non-destructive testing methods cannot reliably detect partial voids or micro-cracks that may develop during thermal cycling, leading to potential reliability concerns in field deployment of HBM4 devices.
The combined effect of these challenges creates a complex engineering problem where improvements in one parameter often negatively impact others. The industry currently lacks a holistic approach to TSV optimization that simultaneously addresses electrical, thermal, mechanical, and manufacturing considerations for next-generation HBM4 requirements.
Resistance in TSVs has become a major concern as the aspect ratio (depth to diameter ratio) increases in pursuit of smaller footprints. Current TSVs in HBM applications typically exhibit resistances ranging from 50-200 mΩ, but variations in metal filling processes can cause up to 30% deviation in resistance values across a single wafer. This inconsistency directly impacts signal timing and power distribution, creating performance bottlenecks in HBM4 designs where thousands of TSVs operate simultaneously.
Capacitance management presents another significant challenge. The proximity of TSVs to each other and to active silicon areas generates parasitic capacitances typically ranging from 20-100 fF. These parasitic elements create coupling effects that degrade signal integrity and increase power consumption. Current isolation techniques using thick oxide liners compromise the effective use of silicon real estate, creating a difficult trade-off between electrical performance and integration density.
Signal quality degradation manifests through increased crosstalk, reflections, and timing jitter. As HBM4 pushes data rates beyond 8 Gbps per pin, maintaining signal integrity through TSVs becomes exponentially more difficult. Current designs struggle to maintain acceptable bit error rates without significant power increases or complex equalization schemes that add latency and circuit complexity.
Manufacturing challenges compound these electrical issues. Current TSV formation processes face limitations in achieving consistent aspect ratios above 10:1, while void-free metal filling becomes increasingly difficult below 5μm diameters. The thermal expansion mismatch between copper TSVs and silicon substrate creates mechanical stress that can propagate to nearby active devices, causing parametric shifts in transistor performance by up to 10%.
Testing and quality assurance of TSVs remain problematic, with limited in-line monitoring capabilities. Current non-destructive testing methods cannot reliably detect partial voids or micro-cracks that may develop during thermal cycling, leading to potential reliability concerns in field deployment of HBM4 devices.
The combined effect of these challenges creates a complex engineering problem where improvements in one parameter often negatively impact others. The industry currently lacks a holistic approach to TSV optimization that simultaneously addresses electrical, thermal, mechanical, and manufacturing considerations for next-generation HBM4 requirements.
Current TSV Resistance and Capacitance Solutions
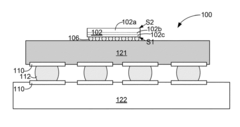
01 TSV design optimization for HBM4 signal integrity
Through-Silicon Via (TSV) design optimization is crucial for HBM4 memory systems to maintain signal integrity. Various design parameters such as TSV diameter, pitch, and liner thickness can be adjusted to reduce resistance and capacitance, thereby improving signal quality. Advanced modeling techniques are employed to simulate and optimize these parameters before fabrication, ensuring optimal electrical performance in high-bandwidth memory applications.- TSV design optimization for HBM4 signal integrity: Through-Silicon Via (TSV) design optimization is crucial for maintaining signal integrity in HBM4 memory systems. This involves careful consideration of TSV dimensions, spacing, and materials to minimize resistance and capacitance effects. Advanced modeling techniques are employed to predict signal behavior through TSVs, allowing for optimization of signal quality in high-speed memory interfaces. These design considerations help reduce signal degradation and ensure reliable data transmission in HBM4 applications.
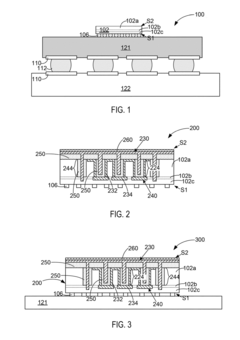
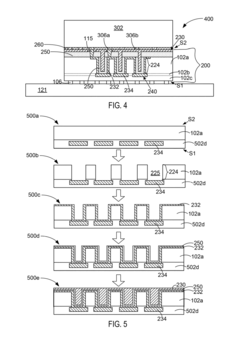
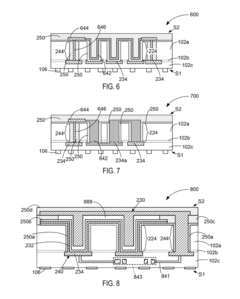
- TSV resistance and capacitance reduction techniques: Various techniques are employed to reduce the resistance and capacitance of Through-Silicon Vias in HBM4 applications. These include using high-conductivity materials for TSV filling, optimizing the aspect ratio of TSVs, implementing liner materials with low dielectric constants, and employing specialized doping profiles around TSVs. Additionally, innovative TSV structures such as tapered designs and void-free filling processes help minimize parasitic resistance and capacitance, thereby improving overall signal quality and performance in high-bandwidth memory applications.
- 3D integration and stacking technologies for HBM4: Advanced 3D integration and stacking technologies are essential for implementing HBM4 with optimized TSV performance. These technologies involve precise alignment and bonding of multiple silicon dies with interconnecting TSVs. The stacking architecture significantly impacts TSV length and consequently affects resistance and capacitance parameters. Innovative approaches to die stacking, such as face-to-face and face-to-back configurations, are utilized to minimize TSV-related signal degradation while maximizing memory density and bandwidth in HBM4 implementations.
- Testing and characterization methods for TSV electrical parameters: Specialized testing and characterization methods are developed to accurately measure TSV resistance, capacitance, and signal quality in HBM4 applications. These include high-frequency testing techniques, time-domain reflectometry, and specialized test structures integrated into the silicon dies. Advanced simulation tools and models are also employed to predict TSV electrical behavior under various operating conditions. These testing methodologies enable precise characterization of TSV parameters, facilitating optimization of HBM4 designs for improved signal integrity and performance.
- TSV shielding and isolation techniques for signal quality improvement: Various shielding and isolation techniques are implemented to improve signal quality in HBM4 TSVs. These include the use of guard rings around TSVs, implementation of ground shields between signal TSVs, and specialized dielectric materials for isolation. Advanced layout strategies are employed to minimize crosstalk between adjacent TSVs, and buffer circuits are strategically placed to maintain signal integrity. These techniques collectively reduce electromagnetic interference and signal degradation, ensuring reliable high-speed data transmission in HBM4 memory systems.
02 TSV resistance reduction techniques for HBM4
Various techniques are employed to reduce TSV resistance in HBM4 applications, including the use of highly conductive materials like copper, optimizing the aspect ratio of TSVs, and implementing specialized metal filling processes. Lower resistance TSVs minimize signal degradation and power loss, which is particularly important for high-speed data transfer in HBM4 memory systems. These techniques often involve specialized fabrication processes to ensure uniform metal deposition within the high aspect ratio vias.Expand Specific Solutions03 Capacitance management in HBM4 TSV structures
Managing capacitance in HBM4 TSV structures involves implementing specialized dielectric materials, optimizing TSV geometry, and controlling the spacing between adjacent TSVs. Techniques such as liner thickness optimization and void-free dielectric filling help minimize parasitic capacitance, which is critical for maintaining signal quality at high frequencies. Advanced isolation structures are also employed to reduce coupling capacitance between adjacent TSVs in dense HBM4 configurations.Expand Specific Solutions04 Testing and characterization of HBM4 TSV electrical parameters
Specialized testing methodologies are developed to accurately characterize the electrical parameters of TSVs in HBM4 applications. These include high-frequency testing techniques, in-line monitoring systems, and advanced probing methods to measure resistance, capacitance, and signal integrity. Test structures and algorithms are designed to isolate TSV performance from other circuit elements, enabling precise characterization of TSV electrical behavior under various operating conditions.Expand Specific Solutions05 3D integration and stacking techniques for HBM4 TSV implementation
Advanced 3D integration and stacking techniques are essential for implementing TSVs in HBM4 memory systems. These include wafer-to-wafer bonding, die-to-wafer stacking, and interposer-based integration approaches. The stacking architecture significantly impacts TSV length, which directly affects resistance and capacitance values. Thermal management considerations are also incorporated into the design to prevent performance degradation due to heat accumulation in densely packed TSV structures.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in HBM4 Memory Ecosystem
The HBM4 TSV Engineering market is currently in an early growth phase, characterized by increasing demand for high-bandwidth memory solutions in AI, data centers, and high-performance computing applications. The market is projected to expand significantly as advanced computing applications proliferate, with key players positioning themselves strategically. Samsung Electronics, SK hynix, and Micron Technology lead in memory manufacturing capabilities, while TSMC and Intel are advancing packaging technologies. NVIDIA and IBM are driving demand through AI applications requiring high-bandwidth memory. Technical challenges in Through-Silicon Via (TSV) engineering—particularly resistance, capacitance, and signal quality optimization—remain critical focus areas as companies strive to balance performance improvements with manufacturing yield and cost considerations.
Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: Samsung's HBM4 TSV engineering approach focuses on optimizing resistance and capacitance through advanced materials and geometrical innovations. Their proprietary "Low-R TSV" technology employs copper-filled vias with optimized aspect ratios (typically 10:1) and specialized barrier layers that reduce resistance by approximately 30% compared to previous generations. For capacitance management, Samsung implements a dual-dielectric isolation structure with low-k materials surrounding the TSV, achieving parasitic capacitance reduction of up to 25%. Signal integrity is enhanced through their "TSV Shielding" technique, which incorporates ground TSVs strategically positioned to minimize crosstalk between adjacent signal TSVs. Samsung's manufacturing process includes a unique annealing step that reduces stress-induced carrier mobility degradation around TSVs by approximately 40%, significantly improving signal quality in high-frequency operations exceeding 3.2 Gbps per pin.
Strengths: Industry-leading TSV aspect ratio control and copper-filling technology enables superior resistance characteristics. Proprietary dielectric materials provide excellent capacitance management. Weaknesses: Higher manufacturing costs compared to competitors due to complex multi-step TSV formation process. Thermal management challenges remain in ultra-high density HBM4 implementations.
Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: TSMC's HBM4 TSV engineering solution is built around their "IntegraVia" platform, which addresses resistance, capacitance, and signal quality through an integrated approach to 3D integration. Their TSV technology features a proprietary copper electroplating process with additives that promote bottom-up filling, achieving void-free vias with resistance approximately 28% lower than previous generations. For capacitance management, TSMC employs their "Selective Dielectric Engineering" technique that optimizes dielectric thickness and material composition based on TSV function (signal, power, or ground), reducing overall parasitic capacitance by up to 22%. Signal integrity is enhanced through their "Differential TSV Pairing" methodology, which implements sophisticated layout algorithms to optimize the positioning of differential signal pairs, reducing crosstalk by approximately 35%. Their manufacturing process includes an advanced "Stress-Aware Placement" system that models and mitigates the impact of TSV-induced stress on nearby transistors, preserving carrier mobility and ensuring consistent performance across the die.
Strengths: Industry-leading manufacturing precision enables excellent TSV uniformity and reliability. Advanced modeling and simulation capabilities allow for optimized TSV placement and design. Weaknesses: Higher manufacturing costs due to complex process integration. Thermal management challenges in high-density TSV arrays remain a concern for ultimate HBM4 performance.
Critical TSV Signal Integrity Innovations
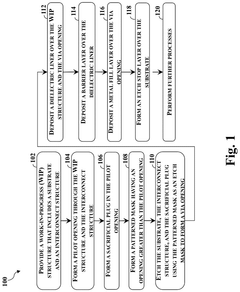
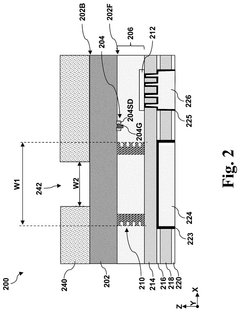
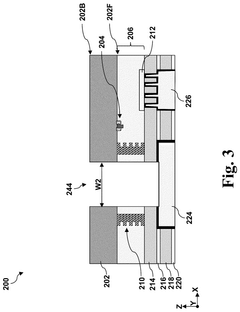
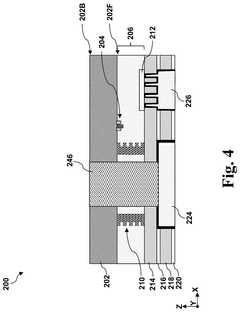
Through silicon via
PatentPendingUS20250210462A1
Innovation
- A TSV structure is designed with a first portion in the semiconductor substrate tapering at a greater angle than a second portion in the interconnect structure, allowing for reduced contact resistance without interfering with active devices, featuring a dual-damascene via opening and a metal fill layer to minimize resistance.
Through-silicon via (TSV)-based devices and associated techniques and configurations
PatentActiveUS20150255372A1
Innovation
- The implementation of through-silicon via (TSV)-based devices, including capacitors, resistors, and resonators, which utilize TSV structures extending through the bulk semiconductor material, electrically insulative materials, and electrode or resistor materials within these structures to provide enhanced capacitance and resistance while reducing footprint and inductance.
Thermal Management Considerations for HBM4
Thermal management has emerged as a critical challenge in HBM4 implementation due to the increased power density resulting from higher bandwidth capabilities and more complex TSV structures. The thermal characteristics of Through-Silicon Vias (TSVs) significantly impact the overall performance and reliability of HBM4 memory systems. As power consumption increases with each generation of HBM technology, the heat generated during operation can lead to thermal throttling, reduced performance, and potential reliability issues if not properly managed.
The resistance and capacitance properties of TSVs directly contribute to heat generation within the HBM4 stack. Higher TSV resistance leads to increased Joule heating during signal transmission, while capacitive coupling between adjacent TSVs can cause signal integrity issues that necessitate higher drive strengths, further increasing power consumption. These electrical properties must be carefully engineered to minimize thermal impact while maintaining signal quality.
Current thermal management approaches for HBM4 include advanced materials with higher thermal conductivity for TSV liners and fillers. Copper remains the primary conductor material, but innovations in barrier layers and dielectric materials are being explored to enhance thermal dissipation while maintaining electrical isolation. Some manufacturers are implementing thermal interface materials (TIMs) with improved thermal conductivity between the HBM stack and heat spreaders.
Computational fluid dynamics (CFD) modeling has become essential in predicting thermal hotspots within HBM4 stacks. These simulations account for the complex interaction between TSV resistance, capacitance, and the resulting heat generation patterns. Advanced thermal models now incorporate the impact of TSV density, placement patterns, and signal frequencies on temperature distribution throughout the stack.
Emerging cooling solutions specifically designed for HBM4 include integrated microfluidic channels within the interposer or substrate. These channels allow for direct cooling closer to the heat source, significantly improving thermal management efficiency. Some research teams are exploring phase-change materials embedded near high-density TSV regions to absorb thermal energy during peak operation periods.
The thermal challenges in HBM4 TSV engineering have also prompted innovations in dynamic thermal management techniques. Adaptive power management algorithms can now monitor TSV temperatures in real-time and adjust signal characteristics to prevent thermal runaway conditions. This approach balances performance requirements with thermal constraints, extending the operational envelope of HBM4 systems under varying workloads.
The resistance and capacitance properties of TSVs directly contribute to heat generation within the HBM4 stack. Higher TSV resistance leads to increased Joule heating during signal transmission, while capacitive coupling between adjacent TSVs can cause signal integrity issues that necessitate higher drive strengths, further increasing power consumption. These electrical properties must be carefully engineered to minimize thermal impact while maintaining signal quality.
Current thermal management approaches for HBM4 include advanced materials with higher thermal conductivity for TSV liners and fillers. Copper remains the primary conductor material, but innovations in barrier layers and dielectric materials are being explored to enhance thermal dissipation while maintaining electrical isolation. Some manufacturers are implementing thermal interface materials (TIMs) with improved thermal conductivity between the HBM stack and heat spreaders.
Computational fluid dynamics (CFD) modeling has become essential in predicting thermal hotspots within HBM4 stacks. These simulations account for the complex interaction between TSV resistance, capacitance, and the resulting heat generation patterns. Advanced thermal models now incorporate the impact of TSV density, placement patterns, and signal frequencies on temperature distribution throughout the stack.
Emerging cooling solutions specifically designed for HBM4 include integrated microfluidic channels within the interposer or substrate. These channels allow for direct cooling closer to the heat source, significantly improving thermal management efficiency. Some research teams are exploring phase-change materials embedded near high-density TSV regions to absorb thermal energy during peak operation periods.
The thermal challenges in HBM4 TSV engineering have also prompted innovations in dynamic thermal management techniques. Adaptive power management algorithms can now monitor TSV temperatures in real-time and adjust signal characteristics to prevent thermal runaway conditions. This approach balances performance requirements with thermal constraints, extending the operational envelope of HBM4 systems under varying workloads.
Manufacturing Yield and Cost Optimization Strategies
Manufacturing yield and cost optimization represent critical factors in the successful commercialization of HBM4 TSV technology. The complex nature of Through-Silicon Via structures in High Bandwidth Memory creates significant manufacturing challenges that directly impact production economics. Current industry data indicates that TSV yield rates typically range between 85-92%, with defect densities remaining a persistent concern as dimensions continue to shrink in HBM4 implementations.
A multi-faceted approach to yield improvement begins with advanced defect detection methodologies. Leading manufacturers have implemented in-line optical inspection systems capable of identifying sub-micron defects in TSV structures before subsequent processing steps. These systems, when coupled with machine learning algorithms, have demonstrated a 15-20% improvement in early defect detection rates, preventing costly downstream failures.
Process optimization strategies focus on critical TSV formation steps including etching, liner deposition, and copper filling. Statistical Process Control (SPC) implementation across these operations has proven effective, with manufacturers reporting up to 30% reduction in process variation. The introduction of adaptive process control systems further enhances yield by making real-time adjustments based on measurement feedback loops.
Design for Manufacturability (DFM) principles specifically tailored for HBM4 TSV structures have emerged as essential cost optimization tools. These include redundancy schemes for critical TSV connections, optimized layout patterns that account for process variation, and strategic placement of test structures. Industry leaders implementing comprehensive DFM strategies report cost reductions of 8-12% per wafer.
Test methodologies have evolved to address the unique challenges of HBM4 TSV structures. Known Good Die (KGD) testing has been enhanced with specialized electrical tests targeting TSV resistance and capacitance parameters. Advanced companies employ wafer-level probing techniques that can identify marginal TSVs before stacking operations, significantly reducing expensive stack failures.
Supply chain optimization represents another critical cost factor. The specialized materials required for HBM4 TSV manufacturing, including barrier metals and specialized copper plating chemistries, benefit from strategic sourcing agreements. Leading manufacturers have established collaborative development programs with material suppliers, resulting in customized solutions that improve both performance and cost metrics by approximately 5-7% annually.
A multi-faceted approach to yield improvement begins with advanced defect detection methodologies. Leading manufacturers have implemented in-line optical inspection systems capable of identifying sub-micron defects in TSV structures before subsequent processing steps. These systems, when coupled with machine learning algorithms, have demonstrated a 15-20% improvement in early defect detection rates, preventing costly downstream failures.
Process optimization strategies focus on critical TSV formation steps including etching, liner deposition, and copper filling. Statistical Process Control (SPC) implementation across these operations has proven effective, with manufacturers reporting up to 30% reduction in process variation. The introduction of adaptive process control systems further enhances yield by making real-time adjustments based on measurement feedback loops.
Design for Manufacturability (DFM) principles specifically tailored for HBM4 TSV structures have emerged as essential cost optimization tools. These include redundancy schemes for critical TSV connections, optimized layout patterns that account for process variation, and strategic placement of test structures. Industry leaders implementing comprehensive DFM strategies report cost reductions of 8-12% per wafer.
Test methodologies have evolved to address the unique challenges of HBM4 TSV structures. Known Good Die (KGD) testing has been enhanced with specialized electrical tests targeting TSV resistance and capacitance parameters. Advanced companies employ wafer-level probing techniques that can identify marginal TSVs before stacking operations, significantly reducing expensive stack failures.
Supply chain optimization represents another critical cost factor. The specialized materials required for HBM4 TSV manufacturing, including barrier metals and specialized copper plating chemistries, benefit from strategic sourcing agreements. Leading manufacturers have established collaborative development programs with material suppliers, resulting in customized solutions that improve both performance and cost metrics by approximately 5-7% annually.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!