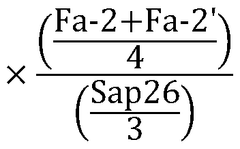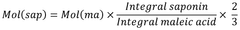Quantify Proton Signals in NMR: Relaxation Impact
SEP 22, 202510 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
NMR Proton Signal Quantification Background and Objectives
Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) spectroscopy has evolved significantly since its discovery in the 1940s, becoming an indispensable analytical tool across various scientific disciplines. The quantification of proton signals in NMR represents a critical aspect of this technology, enabling researchers to determine molecular structures, monitor chemical reactions, and analyze complex mixtures with remarkable precision. The historical trajectory of NMR signal quantification has progressed from basic peak integration methods to sophisticated computational approaches that account for various physical phenomena affecting measurement accuracy.
The evolution of proton signal quantification in NMR has been driven by the increasing demand for higher precision in analytical chemistry, pharmaceutical research, metabolomics, and materials science. Early quantification methods often overlooked relaxation effects, leading to systematic errors in concentration determinations. As our understanding of NMR physics deepened, it became evident that relaxation processes—particularly T1 (longitudinal) and T2 (transverse) relaxation—significantly impact signal intensities and consequently quantification accuracy.
Recent technological advancements have focused on developing correction algorithms and pulse sequences that compensate for relaxation effects. The introduction of higher magnetic field strengths, cryogenic probe technology, and digital signal processing has substantially improved the signal-to-noise ratio, enabling more reliable quantification even for dilute samples. Parallel developments in computational methods have facilitated more sophisticated data analysis approaches, including deconvolution techniques and machine learning algorithms for spectral interpretation.
The primary objective of current research in this field is to establish robust methodologies for accurate proton signal quantification that explicitly account for relaxation phenomena. This includes developing standardized protocols for relaxation time measurements, creating comprehensive mathematical models that incorporate relaxation effects into quantification algorithms, and designing pulse sequences that minimize relaxation-induced biases.
Additionally, researchers aim to extend quantification capabilities to increasingly complex systems, such as biological matrices, heterogeneous materials, and in vivo applications. This requires overcoming challenges related to spectral overlap, varying relaxation behaviors among different molecular environments, and the presence of interfering signals.
Another critical goal is to enhance the accessibility and automation of quantitative NMR methods, making them more widely applicable in routine analytical workflows. This involves developing user-friendly software tools, establishing standardized reference materials, and creating validated methodologies that can be implemented across different instrument platforms with minimal expertise requirements.
The ultimate technical objective is to achieve absolute quantification accuracy approaching theoretical limits, with uncertainties below 1% even in complex samples, while maintaining practical measurement times and sample requirements. This would position NMR as the definitive method for molecular quantification across scientific disciplines, complementing and potentially surpassing traditional analytical techniques in terms of reliability, versatility, and information content.
The evolution of proton signal quantification in NMR has been driven by the increasing demand for higher precision in analytical chemistry, pharmaceutical research, metabolomics, and materials science. Early quantification methods often overlooked relaxation effects, leading to systematic errors in concentration determinations. As our understanding of NMR physics deepened, it became evident that relaxation processes—particularly T1 (longitudinal) and T2 (transverse) relaxation—significantly impact signal intensities and consequently quantification accuracy.
Recent technological advancements have focused on developing correction algorithms and pulse sequences that compensate for relaxation effects. The introduction of higher magnetic field strengths, cryogenic probe technology, and digital signal processing has substantially improved the signal-to-noise ratio, enabling more reliable quantification even for dilute samples. Parallel developments in computational methods have facilitated more sophisticated data analysis approaches, including deconvolution techniques and machine learning algorithms for spectral interpretation.
The primary objective of current research in this field is to establish robust methodologies for accurate proton signal quantification that explicitly account for relaxation phenomena. This includes developing standardized protocols for relaxation time measurements, creating comprehensive mathematical models that incorporate relaxation effects into quantification algorithms, and designing pulse sequences that minimize relaxation-induced biases.
Additionally, researchers aim to extend quantification capabilities to increasingly complex systems, such as biological matrices, heterogeneous materials, and in vivo applications. This requires overcoming challenges related to spectral overlap, varying relaxation behaviors among different molecular environments, and the presence of interfering signals.
Another critical goal is to enhance the accessibility and automation of quantitative NMR methods, making them more widely applicable in routine analytical workflows. This involves developing user-friendly software tools, establishing standardized reference materials, and creating validated methodologies that can be implemented across different instrument platforms with minimal expertise requirements.
The ultimate technical objective is to achieve absolute quantification accuracy approaching theoretical limits, with uncertainties below 1% even in complex samples, while maintaining practical measurement times and sample requirements. This would position NMR as the definitive method for molecular quantification across scientific disciplines, complementing and potentially surpassing traditional analytical techniques in terms of reliability, versatility, and information content.
Market Analysis for NMR Quantification Applications
The global Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) spectroscopy market continues to expand significantly, valued at approximately $930 million in 2022 with projections to reach $1.4 billion by 2028, growing at a CAGR of 5.2%. This growth is primarily driven by increasing applications in pharmaceutical research, biotechnology, and materials science where precise quantification of proton signals is essential.
Pharmaceutical and biotechnology sectors represent the largest market segments, accounting for over 60% of NMR applications. The demand for accurate quantitative NMR (qNMR) methods that properly account for relaxation effects has intensified as regulatory requirements for drug purity and structural verification become more stringent. The FDA and EMA have both issued guidelines emphasizing the importance of reliable quantitative analysis in drug development processes.
Academic research institutions constitute another significant market segment, representing approximately 25% of the total market. Universities and research centers are increasingly investing in advanced NMR technologies that can address relaxation-related challenges in quantification, particularly for complex biomolecular studies and metabolomics research.
Geographically, North America dominates the market with a 40% share, followed by Europe at 30% and Asia-Pacific at 25%. China and India are experiencing the fastest growth rates in NMR technology adoption, driven by expanding pharmaceutical industries and increasing R&D investments. These emerging markets are particularly interested in cost-effective solutions that can still provide accurate quantification despite relaxation phenomena.
The market for specialized software solutions addressing relaxation compensation in quantitative NMR analysis is growing at an above-average rate of 7.8% annually. This reflects the industry's recognition that software innovations can significantly improve quantification accuracy without necessarily requiring hardware upgrades.
End-user surveys indicate that 78% of NMR users consider relaxation effects a significant challenge in quantitative applications, with 65% reporting that current methods for addressing these effects are inadequate for their most demanding applications. This represents a clear market gap and opportunity for innovative solutions.
Contract research organizations (CROs) have emerged as a rapidly growing customer segment, with a 15% annual increase in NMR service demands. These organizations require particularly robust quantification methods as they analyze diverse sample types with varying relaxation properties under tight deadlines.
Pharmaceutical and biotechnology sectors represent the largest market segments, accounting for over 60% of NMR applications. The demand for accurate quantitative NMR (qNMR) methods that properly account for relaxation effects has intensified as regulatory requirements for drug purity and structural verification become more stringent. The FDA and EMA have both issued guidelines emphasizing the importance of reliable quantitative analysis in drug development processes.
Academic research institutions constitute another significant market segment, representing approximately 25% of the total market. Universities and research centers are increasingly investing in advanced NMR technologies that can address relaxation-related challenges in quantification, particularly for complex biomolecular studies and metabolomics research.
Geographically, North America dominates the market with a 40% share, followed by Europe at 30% and Asia-Pacific at 25%. China and India are experiencing the fastest growth rates in NMR technology adoption, driven by expanding pharmaceutical industries and increasing R&D investments. These emerging markets are particularly interested in cost-effective solutions that can still provide accurate quantification despite relaxation phenomena.
The market for specialized software solutions addressing relaxation compensation in quantitative NMR analysis is growing at an above-average rate of 7.8% annually. This reflects the industry's recognition that software innovations can significantly improve quantification accuracy without necessarily requiring hardware upgrades.
End-user surveys indicate that 78% of NMR users consider relaxation effects a significant challenge in quantitative applications, with 65% reporting that current methods for addressing these effects are inadequate for their most demanding applications. This represents a clear market gap and opportunity for innovative solutions.
Contract research organizations (CROs) have emerged as a rapidly growing customer segment, with a 15% annual increase in NMR service demands. These organizations require particularly robust quantification methods as they analyze diverse sample types with varying relaxation properties under tight deadlines.
Current Challenges in Proton Signal Quantification
Despite significant advancements in Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) spectroscopy, accurate quantification of proton signals remains challenging due to several complex factors. The primary obstacle lies in the variable relaxation behaviors of different proton environments within molecules, which directly impacts signal intensity and integration accuracy. T1 (longitudinal) and T2 (transverse) relaxation times can vary substantially between different proton types, leading to non-uniform signal responses that complicate quantitative analysis.
Signal overlap presents another significant challenge, particularly in complex biological samples or macromolecules where numerous proton signals may occupy similar chemical shift regions. This spectral congestion makes baseline definition problematic and hampers accurate integration of individual signals, especially when dealing with metabolomics or natural product analysis where hundreds of compounds may be present simultaneously.
The presence of exchangeable protons (such as those in -OH, -NH, and -SH groups) introduces additional complications as their visibility and quantifiability depend heavily on experimental conditions including temperature, pH, and solvent composition. These protons often exhibit broad signals with variable intensities that do not reliably reflect their actual concentration in the sample.
Instrument-related factors further compound these challenges. Field inhomogeneities, even minor ones, can distort signal shapes and affect integration accuracy. Digital resolution limitations may prevent proper characterization of signals, particularly when fine splitting patterns are critical for identification and quantification. Additionally, the receiver gain settings and dynamic range of the spectrometer can introduce systematic errors in signal intensity measurements.
Processing parameters significantly impact quantification reliability. Phase and baseline corrections, if improperly applied, can introduce artificial distortions that propagate into quantitative errors. Window functions used to enhance spectral resolution often modify signal intensities in ways that must be carefully accounted for in quantitative analyses.
Reference standards present their own set of challenges. Internal standards may interact with sample components, altering relaxation properties or chemical shifts. External standards require careful calibration to account for differences in sample conditions, and electronic reference signals may not accurately reflect the behavior of actual molecular protons in the sample environment.
Recent literature highlights emerging concerns regarding the impact of radiation damping on quantitative measurements, particularly at high field strengths with high-sensitivity probes. This phenomenon can cause non-linear response in high-concentration samples, further complicating accurate quantification efforts in concentrated or partially deuterated solvents.
Signal overlap presents another significant challenge, particularly in complex biological samples or macromolecules where numerous proton signals may occupy similar chemical shift regions. This spectral congestion makes baseline definition problematic and hampers accurate integration of individual signals, especially when dealing with metabolomics or natural product analysis where hundreds of compounds may be present simultaneously.
The presence of exchangeable protons (such as those in -OH, -NH, and -SH groups) introduces additional complications as their visibility and quantifiability depend heavily on experimental conditions including temperature, pH, and solvent composition. These protons often exhibit broad signals with variable intensities that do not reliably reflect their actual concentration in the sample.
Instrument-related factors further compound these challenges. Field inhomogeneities, even minor ones, can distort signal shapes and affect integration accuracy. Digital resolution limitations may prevent proper characterization of signals, particularly when fine splitting patterns are critical for identification and quantification. Additionally, the receiver gain settings and dynamic range of the spectrometer can introduce systematic errors in signal intensity measurements.
Processing parameters significantly impact quantification reliability. Phase and baseline corrections, if improperly applied, can introduce artificial distortions that propagate into quantitative errors. Window functions used to enhance spectral resolution often modify signal intensities in ways that must be carefully accounted for in quantitative analyses.
Reference standards present their own set of challenges. Internal standards may interact with sample components, altering relaxation properties or chemical shifts. External standards require careful calibration to account for differences in sample conditions, and electronic reference signals may not accurately reflect the behavior of actual molecular protons in the sample environment.
Recent literature highlights emerging concerns regarding the impact of radiation damping on quantitative measurements, particularly at high field strengths with high-sensitivity probes. This phenomenon can cause non-linear response in high-concentration samples, further complicating accurate quantification efforts in concentrated or partially deuterated solvents.
Established Methods for Relaxation Compensation
01 Quantitative NMR methods using proton signals
Quantitative Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (qNMR) methods utilize proton signals for accurate measurement of compound concentrations. These methods rely on the direct proportionality between signal intensity and the number of nuclei generating the signal. By analyzing specific proton signals and comparing them to internal standards, precise quantification of compounds can be achieved without the need for identical reference standards. This approach offers advantages in terms of accuracy, reproducibility, and efficiency for pharmaceutical and chemical analysis.- Signal processing techniques for NMR quantification: Various signal processing techniques are employed to enhance the accuracy of proton signal quantification in NMR spectroscopy. These include digital filtering, Fourier transformation, and advanced algorithms for baseline correction and phase adjustment. These methods help to improve signal-to-noise ratio, separate overlapping signals, and provide more reliable quantitative measurements of proton signals in complex mixtures.
- Internal reference standards for quantitative NMR: The use of internal reference standards is crucial for accurate quantification of proton signals in NMR spectroscopy. These standards, with known concentration and distinct chemical shifts, allow for direct comparison with analyte signals. The integration of proton signals relative to the reference standard enables precise determination of analyte concentration, making this approach valuable for pharmaceutical analysis, metabolomics, and quality control applications.
- Hardware innovations for improved proton signal detection: Advancements in NMR hardware have significantly enhanced proton signal detection and quantification capabilities. These innovations include high-field superconducting magnets, cryogenically cooled probes, and multi-channel receivers. Such hardware improvements provide better spectral resolution, increased sensitivity, and reduced noise, allowing for more accurate quantification of proton signals even in dilute samples or complex matrices.
- Pulse sequence optimization for quantitative measurements: Specialized pulse sequences have been developed to optimize quantitative measurements of proton signals in NMR spectroscopy. These sequences address challenges such as signal saturation, relaxation effects, and coupling interactions that can affect quantification accuracy. Techniques like NOESY, CPMG, and WATERGATE allow for selective excitation, suppression of unwanted signals, and compensation for relaxation differences, resulting in more reliable quantitative data.
- Automated methods for proton signal analysis and quantification: Automated systems and software solutions have been developed for efficient analysis and quantification of proton signals in NMR spectra. These methods incorporate machine learning algorithms, pattern recognition, and statistical tools to automatically identify, integrate, and quantify proton signals. Such automation reduces human error, increases throughput, and enables consistent quantification across large datasets, particularly valuable in metabolomics and pharmaceutical quality control.
02 Signal processing techniques for proton NMR quantification
Advanced signal processing techniques enhance the accuracy of proton NMR quantification by improving signal-to-noise ratios and resolving overlapping peaks. These techniques include digital filtering, Fourier transformation optimization, baseline correction algorithms, and peak deconvolution methods. By applying these processing approaches, researchers can extract more reliable quantitative information from complex NMR spectra, particularly in samples with multiple components or when dealing with low concentration analytes.Expand Specific Solutions03 Hardware innovations for improved proton signal detection
Specialized hardware developments have significantly enhanced proton signal detection in NMR quantification. These innovations include advanced probe designs with improved sensitivity, gradient coil configurations for better spatial resolution, and optimized radiofrequency circuits. High-field magnets with enhanced homogeneity and stability allow for better separation of closely spaced resonances. These hardware improvements collectively contribute to more accurate and sensitive quantification of compounds using proton NMR signals.Expand Specific Solutions04 Internal standardization methods for proton NMR quantification
Internal standardization is crucial for accurate proton NMR quantification. This approach involves adding a known amount of a reference compound to the sample, which provides a signal intensity reference for quantitative analysis. The selection of appropriate internal standards considers factors such as chemical shift position, signal overlap avoidance, and chemical stability. By using internal standards with known concentrations, researchers can determine absolute concentrations of target compounds through direct signal intensity comparison, improving the reliability of quantitative measurements.Expand Specific Solutions05 Applications of proton NMR quantification in pharmaceutical analysis
Proton NMR quantification has become an essential analytical tool in pharmaceutical research and quality control. It enables precise determination of drug content, impurity profiling, and formulation analysis without extensive sample preparation. The technique allows for simultaneous identification and quantification of multiple components in complex matrices. Regulatory bodies increasingly accept NMR-based quantification methods due to their inherent specificity, accuracy, and ability to provide structural information alongside quantitative data, making them valuable for drug development and manufacturing processes.Expand Specific Solutions
Leading Institutions and Companies in NMR Technology
The quantification of proton signals in NMR spectroscopy, particularly regarding relaxation impacts, represents a mature yet evolving technological field. Currently in a growth phase, this market is characterized by significant research activity across academic and industrial sectors. Key players include established medical imaging corporations like Koninklijke Philips NV and Shanghai United Imaging Healthcare, alongside specialized oil industry service providers such as Schlumberger Technologies. Academic institutions including Fudan University, Institut Curie, and Johns Hopkins University contribute substantial research advancements. The technology demonstrates high maturity in clinical applications while emerging applications in pharmaceutical development (Otsuka, Amphastar) and material science continue to expand. Integration with AI and machine learning technologies is driving innovation, with companies like Q Bio representing newer entrants focused on quantitative biomarker development through advanced NMR relaxation analysis.
Schlumberger Technologies, Inc.
Technical Solution: Schlumberger has developed advanced NMR relaxation measurement techniques specifically for quantifying proton signals in complex fluid environments. Their technology utilizes multi-dimensional relaxation time analysis that separates overlapping signals based on their T1 and T2 relaxation characteristics. The company's proprietary algorithms compensate for relaxation effects in heterogeneous media, particularly important in oil reservoir characterization. Their NMR logging tools incorporate pulse sequences designed to minimize the impact of magnetic field inhomogeneities on relaxation measurements, enabling more accurate quantification of hydrogen-containing compounds in geological formations. Schlumberger's diffusion-editing techniques further enhance signal discrimination by incorporating molecular mobility information alongside relaxation data, creating comprehensive relaxation-diffusion maps that improve fluid typing accuracy[1][3]. Recent developments include machine learning integration to automatically identify relaxation components in complex mixtures.
Strengths: Exceptional capability in quantifying proton signals in heterogeneous environments with varying magnetic susceptibilities; industry-leading algorithms for relaxation compensation in complex media. Weaknesses: Technologies primarily optimized for petroleum applications rather than broader scientific or medical contexts; equipment typically requires specialized operational expertise.
Halliburton Energy Services, Inc.
Technical Solution: Halliburton has pioneered specialized NMR relaxation analysis techniques for downhole fluid characterization. Their approach focuses on compensating for temperature and pressure effects on proton relaxation rates in reservoir conditions. The company's proprietary "Magnetic Resonance Explorer" technology employs adaptive pulse sequences that adjust to varying magnetic field gradients encountered in wellbore environments, enabling more reliable quantification of proton signals. Halliburton's signal processing algorithms incorporate multi-exponential fitting methods that can distinguish between different fluid phases based on their characteristic relaxation signatures. Their technology includes advanced T1-T2 correlation mapping that helps differentiate bound water from movable fluids, critical for accurate hydrocarbon quantification[2]. Recent innovations include real-time relaxation compensation algorithms that adjust for tool motion effects during measurement, significantly improving signal quality in challenging wellbore conditions.
Strengths: Robust technology designed for harsh downhole environments with temperature and pressure compensation; excellent capability in distinguishing between different fluid phases based on relaxation characteristics. Weaknesses: Limited application outside petroleum industry contexts; technology optimized for specific reservoir conditions rather than general laboratory applications.
Critical Patents and Literature on Relaxation Effects
Nuclear magnetic resonance data acquisition system
PatentActiveUS20220229203A1
Innovation
- A method involving a nuclear magnetic resonance unit that emits radio frequency energy according to specific sets of parameters, including varying wait times and phases, to acquire digital echo data, and utilizes a pseudo-PAPs approach to reduce acquisition time and enhance vertical resolution, allowing for faster logging speeds and improved characterization of formations.
Methods of quantifying saponins present in particles comprising saponin and lipid
PatentWO2024153674A1
Innovation
- A method involving reversed phase solid phase extraction to isolate saponins, followed by lyophilization and quantitative proton NMR spectroscopy using an internal standard in deuterated methanol, allowing for the comparison of signals to quantify saponin concentrations in particles.
Standardization Efforts in NMR Quantification
The field of Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) quantification has witnessed significant standardization efforts over the past decade, aimed at addressing the challenges posed by relaxation effects on proton signal quantification. These initiatives have been crucial in establishing reliable protocols for consistent and accurate measurements across different laboratories and equipment.
The International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) has played a pivotal role by publishing comprehensive guidelines for quantitative NMR (qNMR) procedures. These guidelines specifically address relaxation-related parameters, recommending optimal pulse sequences and delay times to minimize relaxation-induced quantification errors. The IUPAC standards have been widely adopted as the foundation for many laboratory protocols worldwide.
In parallel, the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) has developed certified reference materials specifically designed for qNMR applications. These materials feature compounds with well-characterized relaxation properties, enabling laboratories to validate their quantification methodologies against reliable standards. The availability of these reference materials has significantly improved inter-laboratory reproducibility of proton signal quantification.
Industry consortia have also contributed substantially to standardization efforts. The Metabolomics Standards Initiative (MSI) has established minimum reporting requirements for NMR-based metabolomics studies, with specific provisions for documenting relaxation parameters and correction methods. Similarly, the Consortium for Metabonomic Toxicology (COMET) has developed standardized protocols for toxicological studies using NMR, with detailed specifications for handling relaxation effects.
Software standardization has emerged as another critical area, with several open-source initiatives developing standardized algorithms for relaxation correction. The nmrML project has created a standardized data format that includes fields for relaxation parameters, facilitating data exchange and reanalysis across different software platforms. Commercial NMR software providers have increasingly incorporated these standardized approaches into their quantification modules.
Regulatory bodies, including the FDA and EMA, have recognized the importance of standardized qNMR methods in pharmaceutical analysis. Both organizations have issued guidance documents that reference established standards for handling relaxation effects in quantitative applications, particularly for drug purity assessments and metabolite identification. These regulatory endorsements have accelerated the adoption of standardized protocols throughout the pharmaceutical industry.
Educational initiatives have complemented these formal standardization efforts, with organizations like the Small Molecule NMR Conference developing training materials and workshops focused on best practices for quantitative NMR. These resources emphasize proper consideration of relaxation phenomena and standardized approaches to mitigate their impact on quantification accuracy.
The International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) has played a pivotal role by publishing comprehensive guidelines for quantitative NMR (qNMR) procedures. These guidelines specifically address relaxation-related parameters, recommending optimal pulse sequences and delay times to minimize relaxation-induced quantification errors. The IUPAC standards have been widely adopted as the foundation for many laboratory protocols worldwide.
In parallel, the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) has developed certified reference materials specifically designed for qNMR applications. These materials feature compounds with well-characterized relaxation properties, enabling laboratories to validate their quantification methodologies against reliable standards. The availability of these reference materials has significantly improved inter-laboratory reproducibility of proton signal quantification.
Industry consortia have also contributed substantially to standardization efforts. The Metabolomics Standards Initiative (MSI) has established minimum reporting requirements for NMR-based metabolomics studies, with specific provisions for documenting relaxation parameters and correction methods. Similarly, the Consortium for Metabonomic Toxicology (COMET) has developed standardized protocols for toxicological studies using NMR, with detailed specifications for handling relaxation effects.
Software standardization has emerged as another critical area, with several open-source initiatives developing standardized algorithms for relaxation correction. The nmrML project has created a standardized data format that includes fields for relaxation parameters, facilitating data exchange and reanalysis across different software platforms. Commercial NMR software providers have increasingly incorporated these standardized approaches into their quantification modules.
Regulatory bodies, including the FDA and EMA, have recognized the importance of standardized qNMR methods in pharmaceutical analysis. Both organizations have issued guidance documents that reference established standards for handling relaxation effects in quantitative applications, particularly for drug purity assessments and metabolite identification. These regulatory endorsements have accelerated the adoption of standardized protocols throughout the pharmaceutical industry.
Educational initiatives have complemented these formal standardization efforts, with organizations like the Small Molecule NMR Conference developing training materials and workshops focused on best practices for quantitative NMR. These resources emphasize proper consideration of relaxation phenomena and standardized approaches to mitigate their impact on quantification accuracy.
Interdisciplinary Applications of Quantitative NMR
Quantitative NMR (qNMR) has emerged as a powerful analytical technique that extends far beyond traditional chemistry applications. The ability to accurately quantify proton signals, while accounting for relaxation impacts, has opened doors to numerous interdisciplinary fields where precise molecular quantification is critical.
In pharmaceutical sciences, qNMR serves as a gold standard for drug purity assessment and formulation analysis. The technique enables researchers to determine active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) concentrations without the need for identical reference standards, significantly streamlining drug development processes. Relaxation-compensated qNMR methods have particularly enhanced the analysis of complex drug formulations where varying relaxation behaviors previously limited quantitative accuracy.
The food science industry has adopted qNMR for authentication and quality control purposes. By quantifying specific marker compounds, researchers can verify the geographical origin of products like olive oils, wines, and honey. The technique's ability to account for relaxation effects has improved the detection of adulterants and contaminants, even in complex food matrices where signal overlap is common.
Environmental monitoring represents another expanding application area. qNMR enables the quantification of pollutants in water, soil, and biological samples with high precision. Recent advances in relaxation-adjusted quantification protocols have enhanced the detection limits for environmental contaminants, allowing for more sensitive monitoring of ecosystems and compliance with regulatory standards.
In metabolomics research, qNMR has become indispensable for biomarker discovery and validation. The technique's inherent quantitative nature, when properly adjusted for relaxation effects, provides accurate concentration measurements of metabolites in biological fluids. This capability has accelerated progress in disease diagnosis, particularly for conditions like diabetes, cardiovascular diseases, and various cancers where metabolic profiles serve as diagnostic indicators.
Materials science has also benefited from quantitative NMR applications. Researchers utilize qNMR to characterize polymer compositions, monitor polymerization reactions, and assess material degradation. By accounting for relaxation behaviors of different molecular components, more accurate structural information can be obtained, leading to improved material design and performance prediction.
The forensic science community increasingly relies on qNMR for the analysis of illicit substances, toxins, and biological evidence. The technique's ability to provide absolute quantification, especially when optimized for varying relaxation parameters, has strengthened the evidential value of chemical analyses in legal proceedings.
In pharmaceutical sciences, qNMR serves as a gold standard for drug purity assessment and formulation analysis. The technique enables researchers to determine active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) concentrations without the need for identical reference standards, significantly streamlining drug development processes. Relaxation-compensated qNMR methods have particularly enhanced the analysis of complex drug formulations where varying relaxation behaviors previously limited quantitative accuracy.
The food science industry has adopted qNMR for authentication and quality control purposes. By quantifying specific marker compounds, researchers can verify the geographical origin of products like olive oils, wines, and honey. The technique's ability to account for relaxation effects has improved the detection of adulterants and contaminants, even in complex food matrices where signal overlap is common.
Environmental monitoring represents another expanding application area. qNMR enables the quantification of pollutants in water, soil, and biological samples with high precision. Recent advances in relaxation-adjusted quantification protocols have enhanced the detection limits for environmental contaminants, allowing for more sensitive monitoring of ecosystems and compliance with regulatory standards.
In metabolomics research, qNMR has become indispensable for biomarker discovery and validation. The technique's inherent quantitative nature, when properly adjusted for relaxation effects, provides accurate concentration measurements of metabolites in biological fluids. This capability has accelerated progress in disease diagnosis, particularly for conditions like diabetes, cardiovascular diseases, and various cancers where metabolic profiles serve as diagnostic indicators.
Materials science has also benefited from quantitative NMR applications. Researchers utilize qNMR to characterize polymer compositions, monitor polymerization reactions, and assess material degradation. By accounting for relaxation behaviors of different molecular components, more accurate structural information can be obtained, leading to improved material design and performance prediction.
The forensic science community increasingly relies on qNMR for the analysis of illicit substances, toxins, and biological evidence. The technique's ability to provide absolute quantification, especially when optimized for varying relaxation parameters, has strengthened the evidential value of chemical analyses in legal proceedings.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!