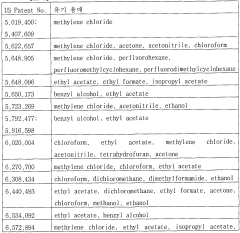
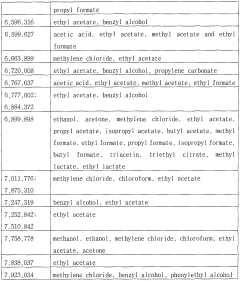
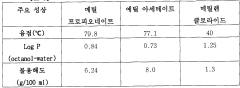
Ethyl Acetate as a Replacement for Harmful Solvents
JUN 27, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Ethyl Acetate Background and Objectives
Ethyl acetate, a versatile organic compound, has gained significant attention in recent years as a potential replacement for harmful solvents in various industrial applications. This colorless liquid, with its fruity odor, has been used in the production of perfumes, flavorings, and pharmaceuticals for decades. However, its potential as a safer alternative to traditional solvents has sparked renewed interest in its properties and applications.
The evolution of ethyl acetate as a solvent replacement is rooted in the growing concern over the environmental and health impacts of conventional solvents. Many commonly used solvents, such as methylene chloride and toluene, have been associated with serious health risks and environmental pollution. This has led to increased regulatory pressure and a shift towards more sustainable and less harmful alternatives in various industries.
Ethyl acetate's journey from a niche compound to a potential mainstream solvent replacement has been marked by significant technological advancements. Improvements in production methods have made it more economically viable, while research into its chemical properties has expanded its potential applications. The compound's low toxicity, biodegradability, and relatively low volatility make it an attractive option for industries seeking to reduce their environmental footprint and improve worker safety.
The primary objective of researching ethyl acetate as a replacement for harmful solvents is to develop safer, more sustainable industrial processes without compromising performance. This involves a comprehensive evaluation of ethyl acetate's physical and chemical properties, its behavior in various applications, and its overall impact on product quality and process efficiency. Additionally, researchers aim to identify and overcome any limitations or challenges associated with its use as a replacement solvent.
Another crucial goal is to assess the economic viability of transitioning to ethyl acetate-based processes. This includes analyzing production costs, potential modifications to existing equipment, and the long-term economic benefits of adopting a more environmentally friendly solvent. The research also seeks to explore innovative applications of ethyl acetate that could potentially open new markets or improve existing products.
Furthermore, the investigation into ethyl acetate as a solvent replacement aligns with broader industry trends towards green chemistry and sustainable manufacturing. By focusing on this compound, researchers hope to contribute to the development of cleaner production methods and more environmentally responsible industrial practices. This research has the potential to influence regulatory policies and industry standards, promoting a wider adoption of safer solvents across various sectors.
The evolution of ethyl acetate as a solvent replacement is rooted in the growing concern over the environmental and health impacts of conventional solvents. Many commonly used solvents, such as methylene chloride and toluene, have been associated with serious health risks and environmental pollution. This has led to increased regulatory pressure and a shift towards more sustainable and less harmful alternatives in various industries.
Ethyl acetate's journey from a niche compound to a potential mainstream solvent replacement has been marked by significant technological advancements. Improvements in production methods have made it more economically viable, while research into its chemical properties has expanded its potential applications. The compound's low toxicity, biodegradability, and relatively low volatility make it an attractive option for industries seeking to reduce their environmental footprint and improve worker safety.
The primary objective of researching ethyl acetate as a replacement for harmful solvents is to develop safer, more sustainable industrial processes without compromising performance. This involves a comprehensive evaluation of ethyl acetate's physical and chemical properties, its behavior in various applications, and its overall impact on product quality and process efficiency. Additionally, researchers aim to identify and overcome any limitations or challenges associated with its use as a replacement solvent.
Another crucial goal is to assess the economic viability of transitioning to ethyl acetate-based processes. This includes analyzing production costs, potential modifications to existing equipment, and the long-term economic benefits of adopting a more environmentally friendly solvent. The research also seeks to explore innovative applications of ethyl acetate that could potentially open new markets or improve existing products.
Furthermore, the investigation into ethyl acetate as a solvent replacement aligns with broader industry trends towards green chemistry and sustainable manufacturing. By focusing on this compound, researchers hope to contribute to the development of cleaner production methods and more environmentally responsible industrial practices. This research has the potential to influence regulatory policies and industry standards, promoting a wider adoption of safer solvents across various sectors.
Market Demand Analysis for Green Solvents
The global market for green solvents has been experiencing significant growth in recent years, driven by increasing environmental concerns and stringent regulations on volatile organic compounds (VOCs) emissions. This trend has created a substantial demand for eco-friendly alternatives to traditional harmful solvents, with ethyl acetate emerging as a promising candidate.
The market size for green solvents is projected to expand rapidly, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) exceeding 5% over the next five years. This growth is primarily attributed to the rising adoption of sustainable practices across various industries, including paints and coatings, pharmaceuticals, cosmetics, and electronics.
Ethyl acetate, in particular, has garnered attention as a potential replacement for harmful solvents due to its relatively low toxicity, biodegradability, and favorable environmental profile. The demand for ethyl acetate in the green solvents market is expected to grow at a faster rate than the overall market, with some estimates suggesting a CAGR of over 7% in the coming years.
Key factors driving the market demand for ethyl acetate as a green solvent include its versatility in applications, cost-effectiveness compared to some other eco-friendly alternatives, and its ability to meet regulatory requirements in various regions. Industries such as paints and coatings are increasingly turning to ethyl acetate as a replacement for more harmful solvents like toluene and xylene, contributing significantly to market growth.
The pharmaceutical sector is another major driver of demand for ethyl acetate as a green solvent. With the increasing focus on sustainable manufacturing practices in the pharmaceutical industry, ethyl acetate is being adopted in various processes, including drug formulation and extraction.
Geographically, North America and Europe are currently the largest markets for green solvents, including ethyl acetate, due to strict environmental regulations and high awareness of sustainability issues. However, the Asia-Pacific region is expected to witness the fastest growth in demand, driven by rapid industrialization, increasing environmental concerns, and government initiatives promoting sustainable practices.
Despite the positive outlook, challenges remain in the widespread adoption of ethyl acetate as a replacement for harmful solvents. These include the need for process modifications in some applications, potential performance trade-offs in certain use cases, and competition from other emerging green solvents. However, ongoing research and development efforts are focused on addressing these challenges and expanding the applicability of ethyl acetate across various industries.
The market size for green solvents is projected to expand rapidly, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) exceeding 5% over the next five years. This growth is primarily attributed to the rising adoption of sustainable practices across various industries, including paints and coatings, pharmaceuticals, cosmetics, and electronics.
Ethyl acetate, in particular, has garnered attention as a potential replacement for harmful solvents due to its relatively low toxicity, biodegradability, and favorable environmental profile. The demand for ethyl acetate in the green solvents market is expected to grow at a faster rate than the overall market, with some estimates suggesting a CAGR of over 7% in the coming years.
Key factors driving the market demand for ethyl acetate as a green solvent include its versatility in applications, cost-effectiveness compared to some other eco-friendly alternatives, and its ability to meet regulatory requirements in various regions. Industries such as paints and coatings are increasingly turning to ethyl acetate as a replacement for more harmful solvents like toluene and xylene, contributing significantly to market growth.
The pharmaceutical sector is another major driver of demand for ethyl acetate as a green solvent. With the increasing focus on sustainable manufacturing practices in the pharmaceutical industry, ethyl acetate is being adopted in various processes, including drug formulation and extraction.
Geographically, North America and Europe are currently the largest markets for green solvents, including ethyl acetate, due to strict environmental regulations and high awareness of sustainability issues. However, the Asia-Pacific region is expected to witness the fastest growth in demand, driven by rapid industrialization, increasing environmental concerns, and government initiatives promoting sustainable practices.
Despite the positive outlook, challenges remain in the widespread adoption of ethyl acetate as a replacement for harmful solvents. These include the need for process modifications in some applications, potential performance trade-offs in certain use cases, and competition from other emerging green solvents. However, ongoing research and development efforts are focused on addressing these challenges and expanding the applicability of ethyl acetate across various industries.
Current Status and Challenges of Ethyl Acetate
Ethyl acetate has gained significant attention as a potential replacement for harmful solvents in various industries. Currently, it is widely used in the production of paints, coatings, adhesives, and pharmaceuticals. The global ethyl acetate market is experiencing steady growth, driven by increasing demand for eco-friendly solvents and stringent environmental regulations.
The production of ethyl acetate has seen advancements in recent years, with improved catalytic processes and more efficient synthesis methods. However, challenges remain in scaling up production to meet growing demand while maintaining cost-effectiveness. The current annual global production capacity is estimated to be around 3.5 million tons, with Asia-Pacific region leading in both production and consumption.
One of the main challenges facing ethyl acetate adoption is its relatively higher cost compared to some traditional solvents. This price difference, although narrowing, still presents a barrier to widespread adoption in cost-sensitive industries. Additionally, the volatility of raw material prices, particularly ethanol and acetic acid, can impact the stability of ethyl acetate production and pricing.
From a technical standpoint, ethyl acetate faces challenges in certain applications due to its lower solvency power compared to some harmful solvents it aims to replace. This limitation requires reformulation of existing products and processes, which can be time-consuming and costly for manufacturers. Furthermore, its high volatility can lead to increased emissions during use, necessitating proper handling and ventilation systems.
Safety concerns, while less severe than those associated with many harmful solvents, still exist for ethyl acetate. Its flammability and potential for forming explosive mixtures with air require careful handling and storage. Occupational exposure limits have been established, but long-term health effects of prolonged exposure are still being studied.
Environmental challenges also persist. Although ethyl acetate is biodegradable and less toxic than many alternatives, its production still relies on petrochemical feedstocks. The industry is exploring bio-based production methods to address this issue, but these are not yet economically viable on a large scale.
Regulatory landscape for ethyl acetate is generally favorable, with many countries classifying it as a low-risk solvent. However, evolving regulations on volatile organic compounds (VOCs) emissions may pose challenges in certain applications and regions. Compliance with these regulations requires ongoing research and development efforts.
In conclusion, while ethyl acetate shows promise as a replacement for harmful solvents, it faces a complex landscape of technical, economic, and regulatory challenges. Overcoming these hurdles will require continued innovation in production methods, application technologies, and regulatory compliance strategies.
The production of ethyl acetate has seen advancements in recent years, with improved catalytic processes and more efficient synthesis methods. However, challenges remain in scaling up production to meet growing demand while maintaining cost-effectiveness. The current annual global production capacity is estimated to be around 3.5 million tons, with Asia-Pacific region leading in both production and consumption.
One of the main challenges facing ethyl acetate adoption is its relatively higher cost compared to some traditional solvents. This price difference, although narrowing, still presents a barrier to widespread adoption in cost-sensitive industries. Additionally, the volatility of raw material prices, particularly ethanol and acetic acid, can impact the stability of ethyl acetate production and pricing.
From a technical standpoint, ethyl acetate faces challenges in certain applications due to its lower solvency power compared to some harmful solvents it aims to replace. This limitation requires reformulation of existing products and processes, which can be time-consuming and costly for manufacturers. Furthermore, its high volatility can lead to increased emissions during use, necessitating proper handling and ventilation systems.
Safety concerns, while less severe than those associated with many harmful solvents, still exist for ethyl acetate. Its flammability and potential for forming explosive mixtures with air require careful handling and storage. Occupational exposure limits have been established, but long-term health effects of prolonged exposure are still being studied.
Environmental challenges also persist. Although ethyl acetate is biodegradable and less toxic than many alternatives, its production still relies on petrochemical feedstocks. The industry is exploring bio-based production methods to address this issue, but these are not yet economically viable on a large scale.
Regulatory landscape for ethyl acetate is generally favorable, with many countries classifying it as a low-risk solvent. However, evolving regulations on volatile organic compounds (VOCs) emissions may pose challenges in certain applications and regions. Compliance with these regulations requires ongoing research and development efforts.
In conclusion, while ethyl acetate shows promise as a replacement for harmful solvents, it faces a complex landscape of technical, economic, and regulatory challenges. Overcoming these hurdles will require continued innovation in production methods, application technologies, and regulatory compliance strategies.
Existing Ethyl Acetate Application Solutions
01 Production and purification of ethyl acetate
Various methods for producing and purifying ethyl acetate are described, including esterification processes, distillation techniques, and the use of catalysts. These processes aim to improve the yield and purity of ethyl acetate for industrial applications.- Production and purification of ethyl acetate: Various methods for producing and purifying ethyl acetate are described. These include esterification processes, distillation techniques, and the use of specific catalysts to improve yield and purity. The production methods aim to optimize the synthesis of ethyl acetate while minimizing byproducts and improving efficiency.
- Applications of ethyl acetate in chemical processes: Ethyl acetate is utilized in various chemical processes as a solvent, reagent, or intermediate. It finds applications in the production of pharmaceuticals, polymers, and other organic compounds. The versatility of ethyl acetate in different chemical reactions and industrial processes is highlighted.
- Ethyl acetate in extraction and separation processes: Ethyl acetate is employed in extraction and separation processes for various compounds. Its properties make it suitable for liquid-liquid extraction, azeotropic distillation, and other separation techniques. The use of ethyl acetate in these processes can improve efficiency and yield in the isolation of target compounds.
- Environmental and safety considerations for ethyl acetate: The environmental impact and safety aspects of ethyl acetate production and use are addressed. This includes methods for reducing emissions, improving handling safety, and developing more sustainable production processes. Techniques for the recovery and recycling of ethyl acetate in industrial applications are also considered.
- Novel formulations and compositions containing ethyl acetate: Innovative formulations and compositions incorporating ethyl acetate are developed for various applications. These may include adhesives, coatings, cleaning products, or specialized chemical mixtures. The unique properties of ethyl acetate are leveraged to enhance the performance or characteristics of these formulations.
02 Applications of ethyl acetate in chemical processes
Ethyl acetate is utilized in various chemical processes as a solvent, reactant, or intermediate. It finds applications in the production of pharmaceuticals, polymers, and other organic compounds. The versatility of ethyl acetate in different chemical reactions is highlighted.Expand Specific Solutions03 Ethyl acetate in extraction and separation processes
The use of ethyl acetate as an extraction solvent or in separation processes is discussed. Its properties make it suitable for extracting various compounds from mixtures or for use in liquid-liquid extraction techniques. Applications in the food, pharmaceutical, and chemical industries are mentioned.Expand Specific Solutions04 Environmental and safety considerations for ethyl acetate
Environmental and safety aspects related to the production, handling, and use of ethyl acetate are addressed. This includes methods for reducing emissions, improving workplace safety, and developing more sustainable production processes.Expand Specific Solutions05 Novel applications and formulations of ethyl acetate
Innovative uses and formulations of ethyl acetate are explored, including its incorporation into new products or processes. This may involve combining ethyl acetate with other compounds or developing novel applications in fields such as materials science, coatings, or energy storage.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Ethyl Acetate Production
The research on ethyl acetate as a replacement for harmful solvents is gaining traction in a maturing industry, driven by increasing environmental concerns and regulatory pressures. The market for eco-friendly solvents is expanding, with a projected global market size reaching billions of dollars in the coming years. Technologically, the field is advancing rapidly, with companies like Vertec Biosolvents and TBF Environmental Technology leading innovation in bio-based solvents. Established chemical giants such as Eastman Chemical, FUJIFILM, and Henkel are also investing in sustainable solvent solutions, indicating a shift towards greener alternatives. The involvement of diverse players, from specialized firms to multinational corporations, suggests a competitive landscape with significant potential for growth and technological breakthroughs.
Eastman Chemical Co.
Technical Solution: Eastman Chemical Co. has developed a novel approach to using ethyl acetate as a replacement for harmful solvents in various applications. Their research focuses on optimizing the production process of ethyl acetate through a more sustainable route, utilizing bioethanol as a feedstock[1]. This method reduces the carbon footprint of ethyl acetate production while maintaining its effectiveness as a solvent. Eastman has also engineered specialized formulations that enhance ethyl acetate's performance in specific applications, such as coatings and adhesives, where it can directly replace more harmful alternatives like methyl ethyl ketone (MEK) or toluene[2]. The company has implemented advanced purification techniques to produce high-purity ethyl acetate, ensuring its suitability for sensitive applications in the pharmaceutical and electronics industries[3].
Strengths: Sustainable production method, reduced carbon footprint, versatile applications across industries. Weaknesses: Potentially higher production costs compared to traditional methods, may require modifications to existing industrial processes for adoption.
Vertec Biosolvents, Inc.
Technical Solution: Vertec Biosolvents, Inc. has pioneered the development of ethyl acetate-based biosolvents as environmentally friendly alternatives to traditional harmful solvents. Their proprietary technology focuses on creating custom blends of ethyl acetate with other bio-based solvents to optimize performance for specific applications[1]. Vertec's research has resulted in a range of products that can replace acetone, MEK, and other volatile organic compounds (VOCs) in industries such as paint stripping, degreasing, and parts cleaning[2]. The company has also developed water-rinseable formulations of ethyl acetate-based solvents, addressing concerns about waste disposal and environmental impact[3]. Vertec's approach includes extensive testing and validation of their ethyl acetate blends to ensure they meet or exceed the performance of traditional solvents while significantly reducing toxicity and environmental hazards.
Strengths: Specialized in bio-based solvents, custom formulations for various applications, reduced environmental impact. Weaknesses: May have limited production capacity compared to larger chemical companies, potentially higher costs for specialized formulations.
Core Innovations in Ethyl Acetate Synthesis
Method for producing microspheres using methyl propionate
PatentWO2014104822A1
Innovation
- The use of methyl propionate as a dispersion solvent, which is a non-halogen organic solvent with improved solvation properties, allowing for the production of polymer microparticles with superior particle size, distribution, shape, drug content, and reduced residual organic solvent, thus overcoming the limitations of ethyl acetate and methylene chloride.
Hair spray and consumer sprays with reduced volatile organic compounds
PatentInactiveUS6752983B1
Innovation
- The use of alkyl acetates, particularly methyl acetate and t-butyl acetate, is proposed to replace part of the ethanol in hair spray formulations, combined with ethanol to mitigate odor issues and inhibit hydrolysis, thereby reducing VOC emissions and improving environmental acceptability.
Environmental Impact Assessment
The environmental impact assessment of ethyl acetate as a replacement for harmful solvents reveals several key advantages. Ethyl acetate is considered a more environmentally friendly alternative due to its lower toxicity and reduced persistence in the environment compared to many traditional solvents. It biodegrades relatively quickly and does not contribute significantly to the formation of ground-level ozone or smog.
When released into the atmosphere, ethyl acetate has a short half-life and breaks down rapidly through photochemical reactions. This characteristic minimizes its potential for long-term atmospheric pollution. In aquatic environments, ethyl acetate hydrolyzes quickly, further reducing its environmental persistence. The compound's low bioaccumulation potential in organisms also mitigates concerns about food chain contamination.
From a greenhouse gas perspective, ethyl acetate has a lower global warming potential compared to many chlorinated solvents and other volatile organic compounds (VOCs) commonly used in industrial processes. Its production can be achieved through sustainable methods, including the use of renewable resources like ethanol derived from biomass, which can further reduce its carbon footprint.
However, the environmental impact assessment also highlights some areas of concern. While less toxic than many alternatives, ethyl acetate is still classified as a VOC and can contribute to air pollution if released in large quantities. Proper handling, storage, and disposal practices are crucial to minimize environmental risks. Additionally, the production process of ethyl acetate should be carefully managed to prevent the release of precursor chemicals or by-products that may have their own environmental impacts.
In terms of workplace safety and human health, ethyl acetate presents a more favorable profile compared to many traditional solvents. Its lower toxicity and reduced inhalation risks contribute to improved occupational health outcomes. However, proper ventilation and personal protective equipment are still necessary when working with ethyl acetate, as it can cause eye and respiratory irritation in high concentrations.
The assessment also considers the lifecycle environmental impact of ethyl acetate, from production to disposal. While it offers advantages in terms of biodegradability and reduced persistence, the energy and resources required for its production and transportation must be factored into the overall environmental equation. Recycling and recovery systems for ethyl acetate can significantly improve its lifecycle environmental performance, making it an even more attractive alternative to harmful solvents.
When released into the atmosphere, ethyl acetate has a short half-life and breaks down rapidly through photochemical reactions. This characteristic minimizes its potential for long-term atmospheric pollution. In aquatic environments, ethyl acetate hydrolyzes quickly, further reducing its environmental persistence. The compound's low bioaccumulation potential in organisms also mitigates concerns about food chain contamination.
From a greenhouse gas perspective, ethyl acetate has a lower global warming potential compared to many chlorinated solvents and other volatile organic compounds (VOCs) commonly used in industrial processes. Its production can be achieved through sustainable methods, including the use of renewable resources like ethanol derived from biomass, which can further reduce its carbon footprint.
However, the environmental impact assessment also highlights some areas of concern. While less toxic than many alternatives, ethyl acetate is still classified as a VOC and can contribute to air pollution if released in large quantities. Proper handling, storage, and disposal practices are crucial to minimize environmental risks. Additionally, the production process of ethyl acetate should be carefully managed to prevent the release of precursor chemicals or by-products that may have their own environmental impacts.
In terms of workplace safety and human health, ethyl acetate presents a more favorable profile compared to many traditional solvents. Its lower toxicity and reduced inhalation risks contribute to improved occupational health outcomes. However, proper ventilation and personal protective equipment are still necessary when working with ethyl acetate, as it can cause eye and respiratory irritation in high concentrations.
The assessment also considers the lifecycle environmental impact of ethyl acetate, from production to disposal. While it offers advantages in terms of biodegradability and reduced persistence, the energy and resources required for its production and transportation must be factored into the overall environmental equation. Recycling and recovery systems for ethyl acetate can significantly improve its lifecycle environmental performance, making it an even more attractive alternative to harmful solvents.
Regulatory Framework for Solvent Substitution
The regulatory framework for solvent substitution plays a crucial role in driving the adoption of safer alternatives like ethyl acetate in place of harmful solvents. At the international level, the United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) has established guidelines for the phase-out of ozone-depleting substances, which has indirectly promoted the use of less harmful solvents. The European Union's REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals) regulation is another significant driver, requiring companies to assess and manage the risks associated with chemicals they manufacture or import.
In the United States, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) has implemented the Significant New Alternatives Policy (SNAP) program, which evaluates and regulates substitutes for ozone-depleting substances. The Toxic Substances Control Act (TSCA) also provides a framework for assessing and managing the risks of chemicals, including solvents. Additionally, the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) sets permissible exposure limits for various solvents in the workplace, encouraging the use of safer alternatives.
Many countries have introduced their own regulations to limit the use of harmful solvents. For instance, China's Volatile Organic Compounds (VOC) regulations aim to reduce emissions from industrial processes, including solvent use. Japan's Chemical Substances Control Law (CSCL) regulates the manufacture, import, and use of chemical substances, including solvents.
Industry-specific regulations also play a significant role in solvent substitution. For example, in the pharmaceutical industry, the International Conference on Harmonisation (ICH) guidelines provide recommendations on residual solvents in drug products, encouraging the use of less toxic solvents where possible.
The regulatory landscape is continuously evolving, with a growing emphasis on green chemistry and sustainable practices. Many jurisdictions are adopting more stringent environmental regulations, which are likely to further accelerate the transition to safer solvents like ethyl acetate. However, the regulatory framework also presents challenges, as companies must navigate complex and sometimes conflicting regulations across different regions and industries.
To facilitate compliance and promote innovation, some regulatory bodies are adopting more flexible approaches. For instance, the EPA's Safer Choice program recognizes products that use safer chemical ingredients, including solvents. Such initiatives provide incentives for companies to invest in the development and adoption of safer alternatives.
As the regulatory landscape continues to evolve, it is crucial for companies to stay informed about current and upcoming regulations related to solvent use. This proactive approach can help businesses anticipate regulatory changes, minimize compliance risks, and capitalize on opportunities presented by the shift towards safer solvents like ethyl acetate.
In the United States, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) has implemented the Significant New Alternatives Policy (SNAP) program, which evaluates and regulates substitutes for ozone-depleting substances. The Toxic Substances Control Act (TSCA) also provides a framework for assessing and managing the risks of chemicals, including solvents. Additionally, the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) sets permissible exposure limits for various solvents in the workplace, encouraging the use of safer alternatives.
Many countries have introduced their own regulations to limit the use of harmful solvents. For instance, China's Volatile Organic Compounds (VOC) regulations aim to reduce emissions from industrial processes, including solvent use. Japan's Chemical Substances Control Law (CSCL) regulates the manufacture, import, and use of chemical substances, including solvents.
Industry-specific regulations also play a significant role in solvent substitution. For example, in the pharmaceutical industry, the International Conference on Harmonisation (ICH) guidelines provide recommendations on residual solvents in drug products, encouraging the use of less toxic solvents where possible.
The regulatory landscape is continuously evolving, with a growing emphasis on green chemistry and sustainable practices. Many jurisdictions are adopting more stringent environmental regulations, which are likely to further accelerate the transition to safer solvents like ethyl acetate. However, the regulatory framework also presents challenges, as companies must navigate complex and sometimes conflicting regulations across different regions and industries.
To facilitate compliance and promote innovation, some regulatory bodies are adopting more flexible approaches. For instance, the EPA's Safer Choice program recognizes products that use safer chemical ingredients, including solvents. Such initiatives provide incentives for companies to invest in the development and adoption of safer alternatives.
As the regulatory landscape continues to evolve, it is crucial for companies to stay informed about current and upcoming regulations related to solvent use. This proactive approach can help businesses anticipate regulatory changes, minimize compliance risks, and capitalize on opportunities presented by the shift towards safer solvents like ethyl acetate.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!