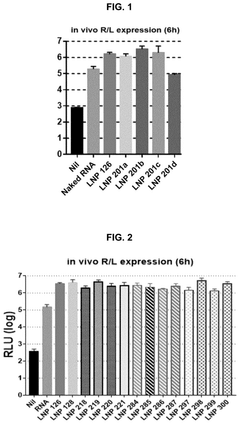
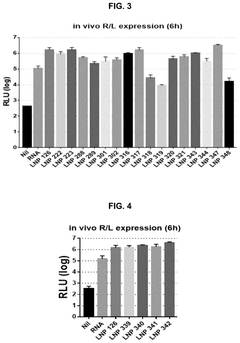
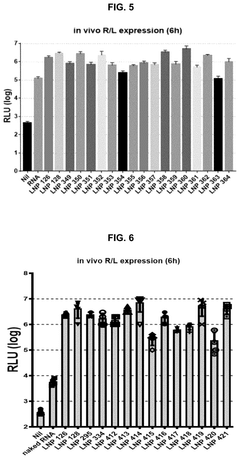
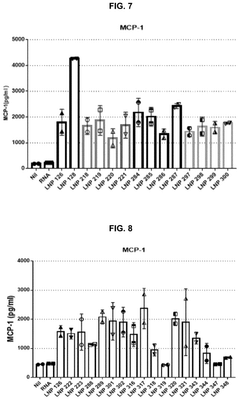
How Catalytic Properties Affect mRNA Lipid Nanoparticle Use
OCT 10, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
mRNA LNP Catalytic Properties Background and Objectives
Messenger RNA (mRNA) lipid nanoparticles (LNPs) have emerged as revolutionary delivery vehicles for genetic material, most notably showcased in the rapid development and deployment of COVID-19 vaccines. The catalytic properties of these nanostructures represent a critical yet underexplored dimension that significantly influences their efficacy, stability, and biocompatibility. This technological domain has evolved from basic liposomal research in the 1960s to the sophisticated, multi-component delivery systems we see today.
The catalytic properties of LNPs refer to their ability to facilitate chemical reactions or biological processes without being consumed themselves. These properties are primarily determined by the lipid composition, surface modifications, and structural arrangements within the nanoparticle. The ionizable lipids, in particular, play a dual role - they enable efficient encapsulation of mRNA through electrostatic interactions and catalyze endosomal escape through proton-sponge effects.
Recent technological advancements have focused on enhancing these catalytic properties through rational design of lipid components. The introduction of pH-responsive lipids, biodegradable linkers, and enzymatically cleavable moieties has expanded the functional repertoire of LNPs. These innovations have addressed historical limitations related to delivery efficiency, cellular uptake, and cytosolic release of the mRNA cargo.
The global research trajectory in this field demonstrates a clear shift from empirical formulation approaches to mechanism-based design strategies. Understanding the molecular interactions between LNP components and biological systems has become paramount for optimizing their performance. This includes elucidating how surface charge dynamics, lipid phase transitions, and membrane fusion capabilities influence the catalytic behavior of these nanostructures.
Our technical objectives in this investigation are multifaceted. First, we aim to comprehensively map the relationship between specific lipid structures and their resultant catalytic properties. Second, we seek to identify key molecular determinants that govern the efficiency of mRNA delivery across different tissue types. Third, we intend to establish predictive models that can accelerate the rational design of next-generation LNP formulations with enhanced catalytic capabilities.
The long-term technological goal is to develop a modular platform for customizing LNP catalytic properties according to specific therapeutic applications. This would enable precise control over biodistribution, cellular targeting, and release kinetics - ultimately expanding the therapeutic window of mRNA-based interventions. As this technology continues to mature, we anticipate its application beyond vaccines to encompass protein replacement therapies, gene editing, and immunomodulation.
The catalytic properties of LNPs refer to their ability to facilitate chemical reactions or biological processes without being consumed themselves. These properties are primarily determined by the lipid composition, surface modifications, and structural arrangements within the nanoparticle. The ionizable lipids, in particular, play a dual role - they enable efficient encapsulation of mRNA through electrostatic interactions and catalyze endosomal escape through proton-sponge effects.
Recent technological advancements have focused on enhancing these catalytic properties through rational design of lipid components. The introduction of pH-responsive lipids, biodegradable linkers, and enzymatically cleavable moieties has expanded the functional repertoire of LNPs. These innovations have addressed historical limitations related to delivery efficiency, cellular uptake, and cytosolic release of the mRNA cargo.
The global research trajectory in this field demonstrates a clear shift from empirical formulation approaches to mechanism-based design strategies. Understanding the molecular interactions between LNP components and biological systems has become paramount for optimizing their performance. This includes elucidating how surface charge dynamics, lipid phase transitions, and membrane fusion capabilities influence the catalytic behavior of these nanostructures.
Our technical objectives in this investigation are multifaceted. First, we aim to comprehensively map the relationship between specific lipid structures and their resultant catalytic properties. Second, we seek to identify key molecular determinants that govern the efficiency of mRNA delivery across different tissue types. Third, we intend to establish predictive models that can accelerate the rational design of next-generation LNP formulations with enhanced catalytic capabilities.
The long-term technological goal is to develop a modular platform for customizing LNP catalytic properties according to specific therapeutic applications. This would enable precise control over biodistribution, cellular targeting, and release kinetics - ultimately expanding the therapeutic window of mRNA-based interventions. As this technology continues to mature, we anticipate its application beyond vaccines to encompass protein replacement therapies, gene editing, and immunomodulation.
Market Analysis of mRNA LNP Therapeutics
The mRNA LNP therapeutics market has experienced unprecedented growth following the successful deployment of COVID-19 vaccines, with the global market value reaching $5.4 billion in 2022 and projected to expand at a CAGR of 10.2% through 2030. This remarkable trajectory is driven by the versatility of mRNA technology in addressing various therapeutic areas beyond infectious diseases, including oncology, rare genetic disorders, and autoimmune conditions.
Demand for mRNA LNP therapeutics is particularly strong in oncology, where personalized cancer vaccines represent a significant growth segment. The market for mRNA-based cancer therapeutics alone is expected to reach $2.8 billion by 2028, reflecting the increasing clinical validation of this approach. Additionally, rare disease applications are gaining traction, with over 40 clinical trials currently evaluating mRNA LNPs for conditions like cystic fibrosis and hemophilia.
Geographically, North America dominates the market with approximately 45% share, followed by Europe at 30% and Asia-Pacific at 20%. The Asia-Pacific region, particularly China and South Korea, is witnessing the fastest growth rate at 12.5% annually, driven by substantial government investments and expanding biotechnology infrastructure.
The catalytic properties of LNP components significantly influence market dynamics by directly impacting product efficacy, manufacturing costs, and regulatory approval timelines. Innovations in ionizable lipids with enhanced catalytic activity have created premium market segments commanding 30-40% higher prices due to improved delivery efficiency and reduced dosing requirements.
Reimbursement landscapes vary considerably across regions, with European markets demonstrating greater price sensitivity compared to the US. The average cost of mRNA LNP treatments ranges from $50,000 to $200,000 per patient annually for rare disease applications, while preventative vaccines are priced between $15 and $40 per dose in developed markets.
Key market barriers include cold chain requirements, manufacturing scalability challenges, and intellectual property constraints. The complex lipid formulations with specific catalytic properties are covered by approximately 350 active patents, creating significant entry barriers for new competitors. Manufacturing capacity remains concentrated among a handful of contract development and manufacturing organizations, with current global capacity estimated at 2 billion doses annually.
Consumer acceptance of mRNA therapeutics has improved substantially, with recent surveys indicating 72% of healthcare providers and 65% of patients expressing confidence in the technology's safety profile, representing a 25% increase from pre-pandemic levels.
Demand for mRNA LNP therapeutics is particularly strong in oncology, where personalized cancer vaccines represent a significant growth segment. The market for mRNA-based cancer therapeutics alone is expected to reach $2.8 billion by 2028, reflecting the increasing clinical validation of this approach. Additionally, rare disease applications are gaining traction, with over 40 clinical trials currently evaluating mRNA LNPs for conditions like cystic fibrosis and hemophilia.
Geographically, North America dominates the market with approximately 45% share, followed by Europe at 30% and Asia-Pacific at 20%. The Asia-Pacific region, particularly China and South Korea, is witnessing the fastest growth rate at 12.5% annually, driven by substantial government investments and expanding biotechnology infrastructure.
The catalytic properties of LNP components significantly influence market dynamics by directly impacting product efficacy, manufacturing costs, and regulatory approval timelines. Innovations in ionizable lipids with enhanced catalytic activity have created premium market segments commanding 30-40% higher prices due to improved delivery efficiency and reduced dosing requirements.
Reimbursement landscapes vary considerably across regions, with European markets demonstrating greater price sensitivity compared to the US. The average cost of mRNA LNP treatments ranges from $50,000 to $200,000 per patient annually for rare disease applications, while preventative vaccines are priced between $15 and $40 per dose in developed markets.
Key market barriers include cold chain requirements, manufacturing scalability challenges, and intellectual property constraints. The complex lipid formulations with specific catalytic properties are covered by approximately 350 active patents, creating significant entry barriers for new competitors. Manufacturing capacity remains concentrated among a handful of contract development and manufacturing organizations, with current global capacity estimated at 2 billion doses annually.
Consumer acceptance of mRNA therapeutics has improved substantially, with recent surveys indicating 72% of healthcare providers and 65% of patients expressing confidence in the technology's safety profile, representing a 25% increase from pre-pandemic levels.
Current Catalytic Challenges in mRNA LNP Development
The development of mRNA lipid nanoparticles (LNPs) faces several critical catalytic challenges that significantly impact their efficacy, stability, and scalability. One primary challenge involves the catalytic degradation of mRNA during the formulation process. The presence of metal ions, particularly transition metals like iron and copper, can catalyze oxidative reactions that damage the mRNA payload, reducing therapeutic efficacy. These catalytic reactions often occur at the lipid-water interface where mRNA molecules are most vulnerable.
Another significant challenge is the catalytic hydrolysis of lipid components within LNPs. The ionizable lipids that facilitate endosomal escape are particularly susceptible to base-catalyzed hydrolysis, which can compromise the structural integrity of the nanoparticle and lead to premature release of the mRNA cargo. This degradation pathway accelerates under physiological conditions, presenting a substantial hurdle for in vivo applications.
The catalytic activity at the LNP surface also affects protein corona formation—a phenomenon where serum proteins adsorb onto nanoparticles upon introduction to biological fluids. Surface catalytic properties can either promote or inhibit this process, directly influencing biodistribution, cellular uptake, and immune recognition of the LNPs. Controlling these catalytic interactions remains challenging but essential for optimizing therapeutic outcomes.
Manufacturing scalability presents additional catalytic challenges. The microfluidic mixing processes used in LNP production involve rapid pH changes and solvent exchanges that can trigger unwanted catalytic reactions. These reactions may alter lipid organization, affect particle size distribution, and compromise batch-to-batch consistency. Current production methods struggle to mitigate these catalytic effects during large-scale manufacturing.
Endosomal escape, a critical step for mRNA delivery to the cytosol, relies on pH-dependent catalytic processes. The ionizable lipids must undergo protonation in the acidic endosomal environment to disrupt the endosomal membrane. However, optimizing these catalytic properties without increasing cytotoxicity remains difficult. Too aggressive catalytic activity can damage cellular membranes beyond the endosome, while insufficient activity results in poor release efficiency.
Immunogenicity issues also stem from catalytic challenges. Oxidized nucleotides resulting from catalytic degradation can trigger innate immune responses through pattern recognition receptors. Similarly, lipid oxidation products generated through catalytic processes can act as damage-associated molecular patterns, potentially causing inflammatory responses that limit therapeutic windows and repeat dosing opportunities.
Another significant challenge is the catalytic hydrolysis of lipid components within LNPs. The ionizable lipids that facilitate endosomal escape are particularly susceptible to base-catalyzed hydrolysis, which can compromise the structural integrity of the nanoparticle and lead to premature release of the mRNA cargo. This degradation pathway accelerates under physiological conditions, presenting a substantial hurdle for in vivo applications.
The catalytic activity at the LNP surface also affects protein corona formation—a phenomenon where serum proteins adsorb onto nanoparticles upon introduction to biological fluids. Surface catalytic properties can either promote or inhibit this process, directly influencing biodistribution, cellular uptake, and immune recognition of the LNPs. Controlling these catalytic interactions remains challenging but essential for optimizing therapeutic outcomes.
Manufacturing scalability presents additional catalytic challenges. The microfluidic mixing processes used in LNP production involve rapid pH changes and solvent exchanges that can trigger unwanted catalytic reactions. These reactions may alter lipid organization, affect particle size distribution, and compromise batch-to-batch consistency. Current production methods struggle to mitigate these catalytic effects during large-scale manufacturing.
Endosomal escape, a critical step for mRNA delivery to the cytosol, relies on pH-dependent catalytic processes. The ionizable lipids must undergo protonation in the acidic endosomal environment to disrupt the endosomal membrane. However, optimizing these catalytic properties without increasing cytotoxicity remains difficult. Too aggressive catalytic activity can damage cellular membranes beyond the endosome, while insufficient activity results in poor release efficiency.
Immunogenicity issues also stem from catalytic challenges. Oxidized nucleotides resulting from catalytic degradation can trigger innate immune responses through pattern recognition receptors. Similarly, lipid oxidation products generated through catalytic processes can act as damage-associated molecular patterns, potentially causing inflammatory responses that limit therapeutic windows and repeat dosing opportunities.
Current Catalytic Enhancement Strategies for LNPs
01 Lipid nanoparticle composition for mRNA delivery
Specific lipid compositions can enhance the delivery efficiency of mRNA in lipid nanoparticles. These compositions typically include ionizable lipids, helper lipids, cholesterol, and PEG-lipids in optimized ratios. The careful selection and proportion of these components can improve the stability, cellular uptake, and transfection efficiency of the mRNA payload, leading to better therapeutic outcomes in various applications including vaccines and protein replacement therapies.- Lipid nanoparticle composition for mRNA delivery: Specific lipid compositions can enhance the delivery efficiency of mRNA in lipid nanoparticles. These compositions typically include ionizable lipids, helper lipids, cholesterol, and PEG-lipids in optimized ratios. The careful selection and proportion of these components can improve the stability, cellular uptake, and transfection efficiency of the mRNA payload, leading to better therapeutic outcomes in various applications including vaccines and protein replacement therapies.
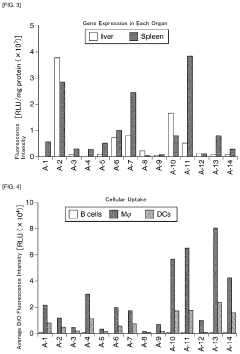
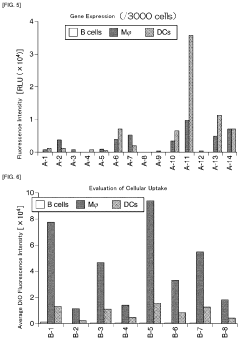
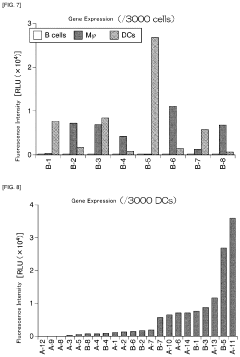
- Catalytic properties of lipid components in mRNA-LNPs: Certain lipid components in mRNA-loaded lipid nanoparticles exhibit catalytic properties that can enhance the efficiency of mRNA delivery and expression. These lipids can facilitate endosomal escape through pH-dependent conformational changes, promote membrane fusion, or catalyze the release of mRNA into the cytoplasm. The catalytic properties of these specialized lipids contribute significantly to the overall performance of mRNA therapeutics by improving intracellular delivery and subsequent protein expression.
- Surface modification of mRNA lipid nanoparticles: Surface modifications of mRNA lipid nanoparticles can enhance their targeting ability, stability, and catalytic properties. These modifications include the attachment of targeting ligands, antibodies, or specific polymers that can improve tissue-specific delivery or cellular uptake. Additionally, surface engineering can reduce immunogenicity, extend circulation time, and enhance the catalytic efficiency of the nanoparticles by creating favorable microenvironments for the encapsulated mRNA to function optimally.
- Metal ion incorporation for enhanced catalytic activity: Incorporation of specific metal ions into mRNA lipid nanoparticles can enhance their catalytic properties. These metal ions can act as cofactors that facilitate the structural integrity of the mRNA, promote enzymatic reactions, or catalyze the release of the mRNA payload at the target site. The strategic inclusion of metal ions can significantly improve the efficiency of mRNA delivery and expression, leading to enhanced therapeutic outcomes in various applications.
- Temperature-responsive catalytic behavior of mRNA-LNPs: mRNA lipid nanoparticles can be designed to exhibit temperature-responsive catalytic behavior, allowing for controlled release and enhanced activity at specific temperatures. These temperature-sensitive formulations undergo structural changes at predetermined temperatures, which can trigger the release of mRNA or enhance the catalytic efficiency of the delivery system. This property is particularly valuable for targeted delivery applications where local temperature differences can be exploited to improve therapeutic efficacy while minimizing off-target effects.
02 Catalytic properties of lipid components in mRNA-LNPs
Certain lipid components within mRNA lipid nanoparticles exhibit catalytic properties that can enhance the efficiency of mRNA delivery and expression. These catalytic lipids can facilitate endosomal escape, promote mRNA release into the cytoplasm, and protect the mRNA from degradation. The catalytic activity is often pH-dependent, allowing for controlled release of the mRNA payload in specific cellular compartments, which significantly improves the therapeutic efficacy of mRNA-based treatments.Expand Specific Solutions03 Surface modification of mRNA lipid nanoparticles
Surface modifications of mRNA lipid nanoparticles can enhance their targeting capabilities and catalytic properties. These modifications include the attachment of targeting ligands, antibodies, or peptides that can direct the nanoparticles to specific cell types or tissues. Additionally, surface engineering can improve the stability of the nanoparticles in circulation, reduce immunogenicity, and enhance cellular uptake, leading to more efficient mRNA delivery and expression in target cells.Expand Specific Solutions04 pH-responsive properties of mRNA lipid nanoparticles
mRNA lipid nanoparticles can be designed with pH-responsive properties that enhance their catalytic activity in specific cellular environments. These nanoparticles remain stable at physiological pH but undergo structural changes in the acidic environment of endosomes, facilitating endosomal escape and release of mRNA into the cytoplasm. The pH-responsive behavior is typically achieved through the incorporation of ionizable lipids that change their charge state depending on the environmental pH, which is crucial for efficient mRNA delivery and expression.Expand Specific Solutions05 Enzymatic interactions with mRNA lipid nanoparticles
mRNA lipid nanoparticles can interact with various enzymes in biological environments, which can affect their catalytic properties and delivery efficiency. These interactions can be designed to be beneficial, such as utilizing endogenous enzymes to trigger the release of mRNA, or they can be mitigated to prevent premature degradation of the nanoparticles. Understanding and controlling these enzymatic interactions is crucial for optimizing the stability, biodistribution, and therapeutic efficacy of mRNA lipid nanoparticle formulations.Expand Specific Solutions
Leading Companies in mRNA LNP Catalytic Research
The mRNA lipid nanoparticle (LNP) field is currently in a growth phase, with the market expected to reach significant expansion following COVID-19 vaccine successes. The competitive landscape features established players like Acuitas Therapeutics and CureVac alongside emerging companies such as Regis Biotechnology and Jiachen Xihai. Technical maturity varies across applications, with vaccine delivery systems more advanced than therapeutic applications. Academic institutions (University of British Columbia, Northwestern University) collaborate with industry leaders (AstraZeneca, GlaxoSmithKline) to overcome catalytic property challenges in LNP formulations. Research organizations like ITRI and KIST are advancing novel approaches to enhance LNP stability, targeting efficiency, and reduced immunogenicity, driving innovation in this rapidly evolving space.
Acuitas Therapeutics, Inc.
Technical Solution: Acuitas Therapeutics has developed proprietary lipid nanoparticle (LNP) delivery systems that enhance mRNA catalytic properties through optimized formulation chemistry. Their LNP technology incorporates ionizable lipids with pKa values specifically engineered to remain neutral at physiological pH but become positively charged in acidic endosomal environments, facilitating efficient endosomal escape of mRNA cargo. The company's LNPs feature a precise ratio of four lipid components: ionizable amino lipids, phospholipids, cholesterol, and PEG-lipids, each playing distinct roles in stability, cellular uptake, and release kinetics. Acuitas' technology was instrumental in the development of COVID-19 mRNA vaccines, where their LNP formulations demonstrated exceptional catalytic efficiency in delivering mRNA to ribosomes for protein translation, resulting in robust immune responses with relatively low mRNA doses.
Strengths: Superior endosomal escape efficiency leading to higher protein expression; established safety profile with regulatory approval in multiple vaccines; scalable manufacturing process. Weaknesses: Potential cold chain requirements for stability; limited tissue targeting beyond liver without additional modifications; proprietary formulations may limit broader research applications.
CureVac SE
Technical Solution: CureVac has developed a distinctive approach to enhancing the catalytic properties of mRNA-LNP formulations through their RNActive® technology platform. Their system focuses on sequence optimization and nucleotide modifications that significantly improve mRNA stability and translation efficiency. CureVac's LNP delivery system incorporates proprietary ionizable lipids with optimized pKa values (approximately 6.0-6.5) that enhance endosomal escape through pH-responsive conformational changes. A key innovation in their technology is the use of non-modified nucleotides combined with sequence optimization strategies that enhance ribosome loading while minimizing innate immune activation. Their LNP formulations feature precisely controlled particle sizes (typically 70-100 nm) and narrow size distributions that optimize biodistribution and cellular uptake kinetics. CureVac has demonstrated that their optimized mRNA-LNP formulations can achieve protein expression with significantly reduced mRNA doses compared to standard approaches, with some preclinical studies showing effective protein production at doses 2-3 times lower than conventional formulations.
Strengths: Proprietary sequence optimization technology that enhances translation efficiency; reduced production costs through non-modified nucleotides; established manufacturing infrastructure. Weaknesses: Potentially higher immunogenicity compared to modified mRNA approaches; more limited clinical validation in certain therapeutic areas; challenges in targeting specific tissues beyond liver and muscle.
Key Patents in Catalytic mRNA Delivery Systems
Lipid nanoparticles
PatentPendingUS20240238202A1
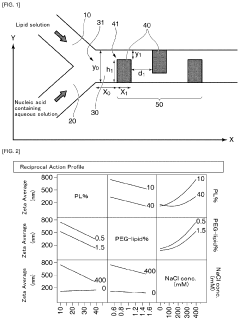
Innovation
- A lipid nanoparticle comprising a pH-sensitive cationic lipid and a polyalkylene glycol-modified lipid, with a number average particle diameter of 150 nm or greater, is used to enhance gene expression efficiency in splenic dendritic cells by optimizing the lipid composition and particle size.
Lipid nanoparticle composition comprising gallic acid derivative lipid and use thereof
PatentPendingUS20250213680A1
Innovation
- A lipid nanoparticle composition incorporating a gallic acid derivative lipid, which replaces a portion of the ionizable lipid, reducing toxicity and enhancing immune response efficiency.
Regulatory Considerations for Catalytic LNP Products
The regulatory landscape for catalytic lipid nanoparticles (LNPs) in mRNA therapeutics presents unique challenges due to their dual functionality as delivery vehicles and catalytic agents. Regulatory bodies such as the FDA, EMA, and NMPA have established frameworks for conventional LNPs, but catalytic LNPs require additional considerations due to their enhanced biological activity and potential for prolonged effects in vivo.
Primary regulatory concerns focus on the characterization of catalytic properties, including reaction kinetics, substrate specificity, and potential off-target catalytic activities. Regulatory agencies typically require comprehensive data demonstrating that catalytic functions remain stable and predictable throughout the product lifecycle, from manufacturing to administration and eventual clearance from the body.
Safety assessment protocols for catalytic LNPs must address both traditional nanoparticle toxicity parameters and the specific risks associated with catalytic activity. This includes evaluation of potential immunogenicity triggered by catalytic byproducts, metabolic interference, and long-term tissue accumulation profiles. The FDA's guidance on nanotechnology products emphasizes the need for specialized toxicological studies that account for these unique properties.
Manufacturing consistency represents another critical regulatory consideration. Catalytic LNPs must demonstrate batch-to-batch reproducibility not only in physical characteristics but also in catalytic performance metrics. Current Good Manufacturing Practice (cGMP) guidelines have been adapted to include specific controls for catalytic functionality, requiring manufacturers to implement robust analytical methods for quantifying catalytic activity throughout production.
Clinical trial designs for catalytic LNP products require modified endpoints that capture both the therapeutic effect of the delivered mRNA and any consequences of the catalytic activity. Regulatory agencies increasingly request pharmacokinetic models that incorporate catalytic reaction parameters alongside traditional distribution and clearance data.
Post-market surveillance requirements are typically more stringent for catalytic LNPs compared to conventional delivery systems. Long-term monitoring protocols must track potential delayed effects resulting from catalytic activity persisting beyond the therapeutic window of the mRNA payload.
International harmonization efforts are underway to standardize regulatory approaches to catalytic nanomedicines, with the International Council for Harmonisation (ICH) developing specific guidance documents addressing the unique regulatory challenges these advanced therapeutic products present. Companies developing catalytic LNP technologies must engage early and frequently with regulatory authorities through mechanisms such as the FDA's INTERACT program to establish appropriate development pathways.
Primary regulatory concerns focus on the characterization of catalytic properties, including reaction kinetics, substrate specificity, and potential off-target catalytic activities. Regulatory agencies typically require comprehensive data demonstrating that catalytic functions remain stable and predictable throughout the product lifecycle, from manufacturing to administration and eventual clearance from the body.
Safety assessment protocols for catalytic LNPs must address both traditional nanoparticle toxicity parameters and the specific risks associated with catalytic activity. This includes evaluation of potential immunogenicity triggered by catalytic byproducts, metabolic interference, and long-term tissue accumulation profiles. The FDA's guidance on nanotechnology products emphasizes the need for specialized toxicological studies that account for these unique properties.
Manufacturing consistency represents another critical regulatory consideration. Catalytic LNPs must demonstrate batch-to-batch reproducibility not only in physical characteristics but also in catalytic performance metrics. Current Good Manufacturing Practice (cGMP) guidelines have been adapted to include specific controls for catalytic functionality, requiring manufacturers to implement robust analytical methods for quantifying catalytic activity throughout production.
Clinical trial designs for catalytic LNP products require modified endpoints that capture both the therapeutic effect of the delivered mRNA and any consequences of the catalytic activity. Regulatory agencies increasingly request pharmacokinetic models that incorporate catalytic reaction parameters alongside traditional distribution and clearance data.
Post-market surveillance requirements are typically more stringent for catalytic LNPs compared to conventional delivery systems. Long-term monitoring protocols must track potential delayed effects resulting from catalytic activity persisting beyond the therapeutic window of the mRNA payload.
International harmonization efforts are underway to standardize regulatory approaches to catalytic nanomedicines, with the International Council for Harmonisation (ICH) developing specific guidance documents addressing the unique regulatory challenges these advanced therapeutic products present. Companies developing catalytic LNP technologies must engage early and frequently with regulatory authorities through mechanisms such as the FDA's INTERACT program to establish appropriate development pathways.
Manufacturing Scalability of Catalytic LNP Technologies
The scalability of catalytic LNP technologies represents a critical factor in their commercial viability for mRNA delivery applications. Current manufacturing processes for standard LNPs involve microfluidic mixing devices that enable precise control over particle formation. However, catalytic LNPs introduce additional complexity due to their reactive components and catalytic properties that must be preserved throughout the manufacturing process.
Scale-up challenges for catalytic LNP technologies primarily stem from maintaining consistent catalytic activity across larger production volumes. Traditional batch-to-batch variations become more pronounced when catalytic properties must remain uniform. The sensitivity of catalytic components to processing conditions—including temperature fluctuations, shear forces, and exposure time to organic solvents—creates significant hurdles for industrial-scale production.
Continuous manufacturing approaches show particular promise for catalytic LNP production. These systems allow for consistent reaction conditions and reduced exposure time to potentially damaging process parameters. Several pharmaceutical companies have reported success with continuous flow reactors that maintain catalytic integrity while increasing throughput by 10-50 fold compared to laboratory-scale production.
Equipment modifications specifically designed for catalytic LNP manufacturing have emerged in recent years. These include specialized mixing chambers with controlled reaction kinetics, rapid quenching capabilities to halt catalytic reactions at precise endpoints, and in-line monitoring systems that track catalytic activity throughout the production process. Such technological adaptations have enabled production scales of up to 100 liters while maintaining catalytic performance within 5% of small-scale benchmarks.
Regulatory considerations present another dimension to manufacturing scalability. Catalytic LNPs require additional characterization and quality control measures to ensure consistent catalytic properties. The FDA and EMA have begun developing specific guidance for catalytic nanomedicines, recognizing their unique manufacturing challenges. Companies must demonstrate that scaled processes maintain not only physical characteristics but also the specific catalytic activities that drive therapeutic efficacy.
Cost implications of scaling catalytic LNP technologies remain significant. Current estimates suggest a 30-40% premium over conventional LNP manufacturing costs, primarily due to specialized equipment requirements and more complex quality control procedures. However, as manufacturing technologies mature and become standardized, this cost differential is expected to narrow to 15-20% within the next five years, potentially accelerating commercial adoption across multiple therapeutic areas.
Scale-up challenges for catalytic LNP technologies primarily stem from maintaining consistent catalytic activity across larger production volumes. Traditional batch-to-batch variations become more pronounced when catalytic properties must remain uniform. The sensitivity of catalytic components to processing conditions—including temperature fluctuations, shear forces, and exposure time to organic solvents—creates significant hurdles for industrial-scale production.
Continuous manufacturing approaches show particular promise for catalytic LNP production. These systems allow for consistent reaction conditions and reduced exposure time to potentially damaging process parameters. Several pharmaceutical companies have reported success with continuous flow reactors that maintain catalytic integrity while increasing throughput by 10-50 fold compared to laboratory-scale production.
Equipment modifications specifically designed for catalytic LNP manufacturing have emerged in recent years. These include specialized mixing chambers with controlled reaction kinetics, rapid quenching capabilities to halt catalytic reactions at precise endpoints, and in-line monitoring systems that track catalytic activity throughout the production process. Such technological adaptations have enabled production scales of up to 100 liters while maintaining catalytic performance within 5% of small-scale benchmarks.
Regulatory considerations present another dimension to manufacturing scalability. Catalytic LNPs require additional characterization and quality control measures to ensure consistent catalytic properties. The FDA and EMA have begun developing specific guidance for catalytic nanomedicines, recognizing their unique manufacturing challenges. Companies must demonstrate that scaled processes maintain not only physical characteristics but also the specific catalytic activities that drive therapeutic efficacy.
Cost implications of scaling catalytic LNP technologies remain significant. Current estimates suggest a 30-40% premium over conventional LNP manufacturing costs, primarily due to specialized equipment requirements and more complex quality control procedures. However, as manufacturing technologies mature and become standardized, this cost differential is expected to narrow to 15-20% within the next five years, potentially accelerating commercial adoption across multiple therapeutic areas.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!