Regulatory Standards for mRNA Lipid Nanoparticle Use
OCT 10, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
mRNA LNP Regulatory Background and Objectives
Messenger RNA (mRNA) technology has emerged as a revolutionary platform in the biopharmaceutical industry, particularly following the successful development of COVID-19 vaccines. The delivery system for mRNA therapeutics, primarily lipid nanoparticles (LNPs), represents a critical component that determines efficacy, safety, and stability. The regulatory landscape for mRNA LNPs has evolved rapidly, yet remains fragmented across different jurisdictions, creating challenges for global development and commercialization.
The history of LNP technology dates back to the 1960s with liposome research, but significant breakthroughs in mRNA delivery occurred only in the past decade. The 2018 FDA approval of Onpattro (patisiran), the first LNP-formulated siRNA therapeutic, established an initial regulatory framework. However, the accelerated development and emergency use authorizations for COVID-19 mRNA vaccines in 2020 dramatically altered the regulatory timeline and expectations for these technologies.
Current regulatory frameworks for mRNA LNPs span multiple domains including chemistry, manufacturing, and controls (CMC), nonclinical safety assessment, clinical evaluation, and post-market surveillance. Key regulatory bodies including the FDA, EMA, PMDA, and NMPA have developed varying approaches to address the unique characteristics of these complex delivery systems. The lack of harmonized standards presents significant challenges for developers navigating multiple regulatory pathways.
Technical evolution in the field continues at a rapid pace, with innovations in lipid chemistry, manufacturing processes, and analytical characterization methods. Regulatory science must evolve in parallel to address emerging questions about novel excipients, characterization requirements, stability assessments, and the potential for immunogenicity or toxicity related to LNP components.
The primary objective of this technical research report is to comprehensively analyze the current global regulatory landscape for mRNA LNP technologies, identify gaps and inconsistencies in existing frameworks, and propose potential pathways toward more harmonized standards. Additionally, we aim to evaluate how regulatory approaches may need to evolve as mRNA LNP applications expand beyond vaccines to therapeutics for rare diseases, cancer, and other chronic conditions.
This analysis will serve as a foundation for strategic decision-making in research and development, regulatory planning, and business development. By anticipating regulatory trends and requirements, organizations can optimize development pathways, reduce regulatory risks, and accelerate the translation of innovative mRNA LNP technologies from laboratory to patients.
The history of LNP technology dates back to the 1960s with liposome research, but significant breakthroughs in mRNA delivery occurred only in the past decade. The 2018 FDA approval of Onpattro (patisiran), the first LNP-formulated siRNA therapeutic, established an initial regulatory framework. However, the accelerated development and emergency use authorizations for COVID-19 mRNA vaccines in 2020 dramatically altered the regulatory timeline and expectations for these technologies.
Current regulatory frameworks for mRNA LNPs span multiple domains including chemistry, manufacturing, and controls (CMC), nonclinical safety assessment, clinical evaluation, and post-market surveillance. Key regulatory bodies including the FDA, EMA, PMDA, and NMPA have developed varying approaches to address the unique characteristics of these complex delivery systems. The lack of harmonized standards presents significant challenges for developers navigating multiple regulatory pathways.
Technical evolution in the field continues at a rapid pace, with innovations in lipid chemistry, manufacturing processes, and analytical characterization methods. Regulatory science must evolve in parallel to address emerging questions about novel excipients, characterization requirements, stability assessments, and the potential for immunogenicity or toxicity related to LNP components.
The primary objective of this technical research report is to comprehensively analyze the current global regulatory landscape for mRNA LNP technologies, identify gaps and inconsistencies in existing frameworks, and propose potential pathways toward more harmonized standards. Additionally, we aim to evaluate how regulatory approaches may need to evolve as mRNA LNP applications expand beyond vaccines to therapeutics for rare diseases, cancer, and other chronic conditions.
This analysis will serve as a foundation for strategic decision-making in research and development, regulatory planning, and business development. By anticipating regulatory trends and requirements, organizations can optimize development pathways, reduce regulatory risks, and accelerate the translation of innovative mRNA LNP technologies from laboratory to patients.
Market Analysis for mRNA LNP Therapeutics
The global mRNA therapeutics market, particularly those utilizing lipid nanoparticle (LNP) delivery systems, has experienced unprecedented growth following the successful deployment of COVID-19 vaccines. Current market valuations place the mRNA therapeutics sector at approximately $46.7 billion in 2023, with projections indicating a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 13.2% through 2030, potentially reaching $109.8 billion by the end of the decade.
Geographically, North America dominates the market with roughly 42% market share, followed by Europe at 31% and Asia-Pacific at 18%. The United States remains the epicenter of innovation and commercialization, hosting major players like Moderna, Pfizer-BioNTech, and numerous emerging biotech companies focused on mRNA technology.
Beyond vaccines, which currently represent approximately 68% of the market value, therapeutic applications are rapidly expanding. Oncology represents the fastest-growing segment with 17.5% CAGR, followed by rare genetic disorders at 15.8%. The versatility of mRNA LNP platforms has attracted significant investment, with venture capital funding exceeding $12.3 billion since 2020.
Regulatory considerations significantly impact market dynamics. Regions with streamlined regulatory pathways for mRNA therapeutics demonstrate accelerated market penetration. The FDA's establishment of specific guidance for LNP-based mRNA products has created a more predictable development environment in the US, while the European Medicines Agency has implemented similar frameworks, albeit with additional emphasis on long-term safety monitoring.
Healthcare payer systems represent another critical market factor. The high initial pricing of mRNA therapeutics (ranging from $50,000 to $2 million per treatment course for gene replacement therapies) creates reimbursement challenges. Several innovative payment models are emerging, including outcomes-based contracts and installment payment structures.
Manufacturing capacity remains a constraint on market growth. Current global capacity can support approximately 7-9 billion doses annually, primarily concentrated among contract manufacturing organizations and major pharmaceutical companies. Significant investments in manufacturing infrastructure are underway, with an estimated $8.4 billion allocated to new facilities between 2022-2025.
Supply chain vulnerabilities represent another market challenge. Critical raw materials for LNP production, particularly specialized lipids and nucleotide precursors, have experienced supply constraints. This has prompted vertical integration strategies among leading companies and diversification of supplier networks to ensure production continuity.
Geographically, North America dominates the market with roughly 42% market share, followed by Europe at 31% and Asia-Pacific at 18%. The United States remains the epicenter of innovation and commercialization, hosting major players like Moderna, Pfizer-BioNTech, and numerous emerging biotech companies focused on mRNA technology.
Beyond vaccines, which currently represent approximately 68% of the market value, therapeutic applications are rapidly expanding. Oncology represents the fastest-growing segment with 17.5% CAGR, followed by rare genetic disorders at 15.8%. The versatility of mRNA LNP platforms has attracted significant investment, with venture capital funding exceeding $12.3 billion since 2020.
Regulatory considerations significantly impact market dynamics. Regions with streamlined regulatory pathways for mRNA therapeutics demonstrate accelerated market penetration. The FDA's establishment of specific guidance for LNP-based mRNA products has created a more predictable development environment in the US, while the European Medicines Agency has implemented similar frameworks, albeit with additional emphasis on long-term safety monitoring.
Healthcare payer systems represent another critical market factor. The high initial pricing of mRNA therapeutics (ranging from $50,000 to $2 million per treatment course for gene replacement therapies) creates reimbursement challenges. Several innovative payment models are emerging, including outcomes-based contracts and installment payment structures.
Manufacturing capacity remains a constraint on market growth. Current global capacity can support approximately 7-9 billion doses annually, primarily concentrated among contract manufacturing organizations and major pharmaceutical companies. Significant investments in manufacturing infrastructure are underway, with an estimated $8.4 billion allocated to new facilities between 2022-2025.
Supply chain vulnerabilities represent another market challenge. Critical raw materials for LNP production, particularly specialized lipids and nucleotide precursors, have experienced supply constraints. This has prompted vertical integration strategies among leading companies and diversification of supplier networks to ensure production continuity.
Global Regulatory Landscape and Technical Challenges
The global regulatory landscape for mRNA lipid nanoparticle (LNP) technologies presents a complex and evolving framework. Currently, regulatory bodies including the FDA, EMA, and NMPA have not established comprehensive, dedicated guidelines specifically for mRNA-LNP products. Instead, these novel therapeutics are evaluated through existing regulatory pathways for biologics, gene therapies, or vaccines, creating significant challenges for developers navigating between jurisdictional differences.
In the United States, the FDA evaluates mRNA-LNP products primarily through the Center for Biologics Evaluation and Research (CBER), requiring extensive characterization of both the mRNA component and the lipid delivery system. The Emergency Use Authorization (EUA) pathway, utilized during the COVID-19 pandemic, provided valuable insights but differs substantially from standard approval processes, creating regulatory precedents that may not apply in non-emergency contexts.
The European Medicines Agency employs a centralized procedure for mRNA therapeutics, with particular emphasis on environmental risk assessments and manufacturing consistency. Their Advanced Therapy Medicinal Products (ATMP) framework partially addresses these technologies but leaves significant gaps regarding LNP-specific requirements and long-term safety monitoring protocols.
In Asia, regulatory approaches vary considerably. Japan's PMDA has implemented a conditional early approval system potentially beneficial for novel mRNA therapies, while China's NMPA has recently accelerated reforms to accommodate innovative biologics but lacks LNP-specific guidance.
Technical challenges intersecting with regulatory concerns include standardization of analytical methods for LNP characterization. Current techniques for measuring particle size distribution, encapsulation efficiency, and lipid composition lack harmonized protocols across regulatory jurisdictions, complicating multi-regional development programs and data submission packages.
Stability testing represents another critical challenge, as mRNA-LNP formulations often require ultra-cold storage conditions. Regulatory agencies differ in their requirements for demonstrating shelf-life, in-use stability, and the validation of cold chain management systems, creating compliance complexities for global distribution.
Manufacturing consistency and scale-up validation face particularly stringent oversight, with regulatory bodies requiring extensive comparability studies when production processes evolve from clinical to commercial scale. The lipid components present unique challenges due to their synthetic nature and potential batch-to-batch variability, requiring sophisticated analytical methods to demonstrate consistency.
Immunogenicity assessment frameworks remain underdeveloped for mRNA-LNP products, with regulatory agencies still determining appropriate pre-clinical models and clinical monitoring protocols to evaluate potential immune responses to both the mRNA payload and the lipid components.
In the United States, the FDA evaluates mRNA-LNP products primarily through the Center for Biologics Evaluation and Research (CBER), requiring extensive characterization of both the mRNA component and the lipid delivery system. The Emergency Use Authorization (EUA) pathway, utilized during the COVID-19 pandemic, provided valuable insights but differs substantially from standard approval processes, creating regulatory precedents that may not apply in non-emergency contexts.
The European Medicines Agency employs a centralized procedure for mRNA therapeutics, with particular emphasis on environmental risk assessments and manufacturing consistency. Their Advanced Therapy Medicinal Products (ATMP) framework partially addresses these technologies but leaves significant gaps regarding LNP-specific requirements and long-term safety monitoring protocols.
In Asia, regulatory approaches vary considerably. Japan's PMDA has implemented a conditional early approval system potentially beneficial for novel mRNA therapies, while China's NMPA has recently accelerated reforms to accommodate innovative biologics but lacks LNP-specific guidance.
Technical challenges intersecting with regulatory concerns include standardization of analytical methods for LNP characterization. Current techniques for measuring particle size distribution, encapsulation efficiency, and lipid composition lack harmonized protocols across regulatory jurisdictions, complicating multi-regional development programs and data submission packages.
Stability testing represents another critical challenge, as mRNA-LNP formulations often require ultra-cold storage conditions. Regulatory agencies differ in their requirements for demonstrating shelf-life, in-use stability, and the validation of cold chain management systems, creating compliance complexities for global distribution.
Manufacturing consistency and scale-up validation face particularly stringent oversight, with regulatory bodies requiring extensive comparability studies when production processes evolve from clinical to commercial scale. The lipid components present unique challenges due to their synthetic nature and potential batch-to-batch variability, requiring sophisticated analytical methods to demonstrate consistency.
Immunogenicity assessment frameworks remain underdeveloped for mRNA-LNP products, with regulatory agencies still determining appropriate pre-clinical models and clinical monitoring protocols to evaluate potential immune responses to both the mRNA payload and the lipid components.
Current Regulatory Approaches for mRNA LNP Products
01 Regulatory compliance for mRNA lipid nanoparticle formulations
Regulatory standards for mRNA lipid nanoparticles focus on ensuring safety, efficacy, and quality of these novel therapeutic delivery systems. These standards include requirements for characterization of physicochemical properties, stability testing, and manufacturing consistency. Regulatory bodies have established specific guidelines for submission of data related to lipid nanoparticle formulations used in mRNA vaccines and therapeutics, with particular emphasis on critical quality attributes that impact product performance.- Regulatory compliance for mRNA lipid nanoparticle formulations: Regulatory standards for mRNA lipid nanoparticles focus on ensuring safety, efficacy, and quality of these novel therapeutic delivery systems. These standards include requirements for characterization of physicochemical properties, stability testing, and manufacturing consistency. Regulatory bodies have established specific guidelines for submitting applications for mRNA-LNP products, including documentation of quality control measures and risk assessment protocols to ensure patient safety.
- Safety assessment protocols for lipid nanoparticle delivery systems: Safety assessment protocols for lipid nanoparticle delivery systems involve comprehensive toxicological evaluations, biodistribution studies, and immunogenicity testing. These protocols are designed to identify potential adverse effects and establish acceptable safety margins for clinical use. The standards include evaluation of acute and chronic toxicity, genotoxicity, reproductive toxicity, and local tolerance to ensure that mRNA-LNP formulations meet stringent safety requirements before human administration.
- Manufacturing standards and quality control for mRNA-LNP products: Manufacturing standards for mRNA-LNP products encompass Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP) requirements specific to these complex biologics. These standards address critical aspects such as aseptic processing, lipid quality specifications, particle size distribution control, and encapsulation efficiency. Quality control measures include validated analytical methods for characterizing lipid composition, mRNA integrity, and nanoparticle homogeneity to ensure batch-to-batch consistency and product stability throughout the shelf life.
- Clinical trial requirements for mRNA-LNP therapeutics: Clinical trial requirements for mRNA-LNP therapeutics include specialized protocols for evaluating pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics, and clinical efficacy. Regulatory standards mandate comprehensive assessment of biodistribution, cellular uptake, and protein expression levels in target tissues. These requirements also address the need for long-term follow-up studies to monitor potential delayed adverse effects and establish appropriate dosing regimens for different patient populations based on safety and efficacy profiles.
- International harmonization of regulatory standards for mRNA-LNP technologies: International harmonization efforts aim to establish consistent regulatory frameworks for mRNA-LNP technologies across different jurisdictions. These initiatives focus on developing standardized approaches for quality assessment, safety evaluation, and efficacy demonstration to facilitate global development and approval of these innovative therapeutics. Collaborative efforts between regulatory agencies work toward creating unified guidelines that address the unique characteristics of mRNA-LNP products while ensuring appropriate oversight throughout the product lifecycle.
02 Quality control standards for mRNA-LNP manufacturing
Quality control standards for manufacturing mRNA lipid nanoparticles involve rigorous testing protocols to ensure batch-to-batch consistency, purity, and potency. These standards include specifications for particle size distribution, encapsulation efficiency, lipid composition analysis, and mRNA integrity verification. Manufacturing processes must adhere to Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP) guidelines with validated analytical methods for in-process and release testing to ensure product quality and patient safety.Expand Specific Solutions03 Safety assessment requirements for mRNA-LNP products
Safety assessment requirements for mRNA lipid nanoparticle products encompass comprehensive toxicological evaluations, biodistribution studies, and immunogenicity assessments. Regulatory standards mandate thorough preclinical testing to identify potential adverse effects, including local and systemic reactions. These requirements include evaluation of the lipid components for cytotoxicity, genotoxicity, and potential immunostimulatory effects, as well as assessment of the degradation products and their safety profiles.Expand Specific Solutions04 Characterization standards for lipid nanoparticle components
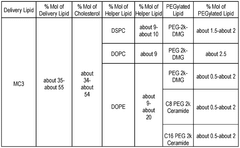
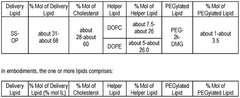
Characterization standards for lipid nanoparticle components require detailed analysis of the structural and functional properties of each lipid used in the formulation. These standards include specifications for ionizable lipids, helper lipids, cholesterol, and PEG-lipids, with emphasis on purity, identity, and consistency. Regulatory guidelines mandate comprehensive physicochemical characterization including lipid ratios, phase transition temperatures, surface charge, and morphological analysis to ensure consistent performance of the delivery system.Expand Specific Solutions05 Clinical trial requirements specific to mRNA-LNP therapeutics
Clinical trial requirements for mRNA lipid nanoparticle therapeutics include specialized protocols for evaluating safety, immunogenicity, and efficacy. Regulatory standards mandate phased clinical studies with particular attention to dose-finding, pharmacokinetics, and pharmacodynamics of these novel modalities. These requirements include monitoring for unique adverse events associated with lipid components, evaluation of immune responses to both the mRNA payload and delivery system, and long-term follow-up assessments to identify potential delayed effects.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Regulatory Bodies and Industry Stakeholders
The regulatory landscape for mRNA Lipid Nanoparticle (LNP) technology is evolving rapidly as the market transitions from early development to commercial maturity. Currently valued at approximately $5 billion, this sector is projected to grow significantly due to COVID-19 vaccine successes. The competitive environment features established leaders like Moderna and CureVac alongside emerging players such as Translate Bio and Abogen Biosciences. Technical maturity varies considerably across applications, with vaccine delivery systems more advanced than therapeutic applications. Key technical challenges include standardization of characterization methods, stability parameters, and manufacturing processes. Academic institutions (MIT, University of Pennsylvania) continue to drive innovation while pharmaceutical companies (Sanofi, Eli Lilly) focus on clinical translation and regulatory compliance, creating a dynamic ecosystem balancing innovation with increasing regulatory scrutiny.
ModernaTX, Inc.
Technical Solution: Moderna has developed a comprehensive regulatory framework for its mRNA lipid nanoparticle (LNP) technology, focusing on quality control and safety standards. Their approach includes rigorous characterization of LNP components, with specific attention to lipid purity, particle size distribution, and encapsulation efficiency. Moderna implements a Quality by Design (QbD) methodology that establishes critical quality attributes (CQAs) and process parameters for consistent manufacturing. Their regulatory strategy addresses FDA and EMA requirements through extensive toxicology studies, including genotoxicity, reproductive toxicity, and biodistribution analyses. Moderna has pioneered standardized analytical methods for LNP characterization, including dynamic light scattering for particle size measurement and HPLC techniques for lipid quantification. Their regulatory submissions include detailed CMC (Chemistry, Manufacturing, and Controls) documentation that has helped establish industry benchmarks for mRNA-LNP products.
Strengths: Extensive experience with regulatory agencies through COVID-19 vaccine approvals; established precedents for mRNA-LNP regulatory pathways; robust manufacturing infrastructure compliant with GMP standards. Weaknesses: Proprietary nature of some analytical methods limits industry standardization; regulatory framework primarily developed for vaccines, potentially requiring adaptation for other therapeutic applications.
Suzhou Abogen Biosciences Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: Abogen Biosciences has developed a regulatory approach for mRNA-LNP products that addresses both international standards and China's specific regulatory requirements. Their strategy incorporates ICH guidelines while navigating the unique aspects of China's National Medical Products Administration (NMPA) approval process. Abogen's technical platform includes proprietary LNP formulations optimized for stability in various temperature conditions, addressing a critical regulatory concern for global distribution. Their regulatory submissions feature comprehensive characterization of lipid components using orthogonal analytical methods, including HPLC and mass spectrometry techniques. Abogen has established detailed specifications for critical quality attributes, with particular emphasis on endotoxin testing and sterility assurance for parenteral administration. Their approach includes validation of analytical methods for detecting residual components from the manufacturing process, addressing regulatory concerns about process-related impurities. Abogen collaborates with Chinese regulatory authorities to establish appropriate standards for novel mRNA-LNP products in the rapidly evolving regulatory landscape.
Strengths: Strong understanding of Chinese regulatory requirements; experience navigating dual regulatory pathways (international and domestic); technical platform optimized for stability in challenging conditions. Weaknesses: Less extensive global regulatory experience compared to Western competitors; regulatory framework still evolving with the rapidly developing Chinese regulatory environment for advanced therapies.
Critical Regulatory Guidelines and Scientific Literature
Lipid nanoparticle (LNP) formulations
PatentWO2024226779A1
Innovation
- The development of lipid nanoparticle (LNP) formulations comprising specific lipids that associate with nucleic acid-based agents, including modified mRNA and plasmid DNA, to form aggregates or particles that can be delivered to the retina, utilizing a combination of cationic, anionic, and neutral lipids, along with PEGylated lipids to enhance stability and targeting.
Lipid nanoparticles containing polynucleotides encoding glucose-6-phosphatase and uses thereof
PatentWO2021247535A1
Innovation
- Ionizable lipid-based lipid nanoparticles are used to deliver messenger RNA encoding glucose-6-phosphatase, enabling intracellular synthesis of functional glucose-6-phosphatase protein to address the enzymatic deficiency.
Safety and Toxicity Assessment Standards
The assessment of safety and toxicity profiles for mRNA lipid nanoparticles (LNPs) requires comprehensive regulatory frameworks that continue to evolve as this technology advances. Current standards focus on multiple evaluation dimensions to ensure patient safety while enabling innovation in this promising therapeutic area.
Regulatory bodies including the FDA, EMA, and PMDA have established specific guidelines for evaluating the toxicological profiles of LNP components. These standards mandate acute, sub-chronic, and chronic toxicity studies across multiple species, with particular emphasis on hepatotoxicity assessment due to the liver-targeting nature of many LNP formulations. The ICH S6(R1) guideline provides the foundation for biotechnology-derived pharmaceuticals, though specific adaptations for mRNA-LNP complexes continue to develop.
Genotoxicity and carcinogenicity testing requirements for LNPs differ from traditional small molecules, with regulatory authorities increasingly accepting weight-of-evidence approaches rather than standard battery testing when scientifically justified. This reflects the unique characteristics of LNPs as delivery systems rather than traditional active pharmaceutical ingredients.
Immunogenicity assessment has emerged as a critical component of safety evaluation, with standards requiring characterization of both innate and adaptive immune responses. This includes cytokine release profiling, complement activation assessment, and anti-PEG antibody monitoring for PEGylated LNP formulations. The FDA's 2014 guidance on immunogenicity assessment for therapeutic proteins provides partial framework, though LNP-specific guidance continues to evolve.
Distribution and clearance studies represent another key regulatory focus, with standards requiring quantitative biodistribution analysis using advanced imaging techniques or bioanalytical methods. Particular attention is given to understanding accumulation in reproductive tissues, with reproductive toxicity studies mandated for most mRNA-LNP therapeutics intended for systemic administration.
Impurity profiling standards have become increasingly stringent, with regulatory expectations for characterization of residual components from manufacturing processes, including organic solvents, heavy metals, and process-related impurities. The ICH Q3 guidelines provide general framework, though specific acceptance criteria for novel LNP components remain under development.
Standardized in vitro models for preliminary toxicity screening continue to gain regulatory acceptance, with initiatives like the FDA's Predictive Toxicology Roadmap encouraging the development of alternative testing methods. These approaches aim to reduce animal testing while providing mechanistic insights into potential toxicity pathways specific to LNP formulations.
Regulatory bodies including the FDA, EMA, and PMDA have established specific guidelines for evaluating the toxicological profiles of LNP components. These standards mandate acute, sub-chronic, and chronic toxicity studies across multiple species, with particular emphasis on hepatotoxicity assessment due to the liver-targeting nature of many LNP formulations. The ICH S6(R1) guideline provides the foundation for biotechnology-derived pharmaceuticals, though specific adaptations for mRNA-LNP complexes continue to develop.
Genotoxicity and carcinogenicity testing requirements for LNPs differ from traditional small molecules, with regulatory authorities increasingly accepting weight-of-evidence approaches rather than standard battery testing when scientifically justified. This reflects the unique characteristics of LNPs as delivery systems rather than traditional active pharmaceutical ingredients.
Immunogenicity assessment has emerged as a critical component of safety evaluation, with standards requiring characterization of both innate and adaptive immune responses. This includes cytokine release profiling, complement activation assessment, and anti-PEG antibody monitoring for PEGylated LNP formulations. The FDA's 2014 guidance on immunogenicity assessment for therapeutic proteins provides partial framework, though LNP-specific guidance continues to evolve.
Distribution and clearance studies represent another key regulatory focus, with standards requiring quantitative biodistribution analysis using advanced imaging techniques or bioanalytical methods. Particular attention is given to understanding accumulation in reproductive tissues, with reproductive toxicity studies mandated for most mRNA-LNP therapeutics intended for systemic administration.
Impurity profiling standards have become increasingly stringent, with regulatory expectations for characterization of residual components from manufacturing processes, including organic solvents, heavy metals, and process-related impurities. The ICH Q3 guidelines provide general framework, though specific acceptance criteria for novel LNP components remain under development.
Standardized in vitro models for preliminary toxicity screening continue to gain regulatory acceptance, with initiatives like the FDA's Predictive Toxicology Roadmap encouraging the development of alternative testing methods. These approaches aim to reduce animal testing while providing mechanistic insights into potential toxicity pathways specific to LNP formulations.
International Harmonization Efforts
The global nature of pharmaceutical development and the rapid advancement of mRNA lipid nanoparticle (LNP) technologies necessitate coordinated international regulatory approaches. Currently, significant efforts are underway to harmonize regulatory standards for mRNA LNP products across major jurisdictions, with the International Council for Harmonisation of Technical Requirements for Pharmaceuticals for Human Use (ICH) playing a central role.
The ICH has established working groups specifically focused on novel delivery technologies, including LNPs, to develop consensus guidelines that can be adopted across member regions. These efforts aim to standardize quality control parameters, safety assessment protocols, and manufacturing requirements for mRNA LNP products, reducing regulatory divergence that could impede global development and access.
Parallel to ICH initiatives, bilateral agreements between regulatory authorities have emerged as pragmatic approaches to harmonization. The FDA-EMA mutual recognition agreement represents a significant step forward, allowing inspection results and certain testing data for mRNA LNP products to be shared between these major regulatory bodies, streamlining approval processes for manufacturers operating in both markets.
The World Health Organization has established an mRNA vaccine technology transfer hub to support standardization efforts in emerging markets. This initiative not only facilitates technology transfer but also promotes regulatory convergence by providing technical guidance aligned with international standards, particularly beneficial for regions with less established regulatory frameworks for advanced therapeutics.
Industry consortia have become instrumental in driving harmonization through pre-competitive collaboration. Organizations like the LNP Alliance and the International Pharmaceutical Aerosol Consortium on Regulation and Science (IPAC-RS) are developing standardized analytical methods and proposing common approaches to characterization and quality control of LNP formulations, which are subsequently presented to regulatory authorities for consideration.
Challenges to harmonization persist, including divergent regional priorities, varying risk tolerance levels among regulatory authorities, and the rapid pace of technological innovation outstripping regulatory adaptation. Cultural and legal differences in regulatory approaches—such as the precautionary principle emphasized in European regulations versus the risk-benefit approach more common in the US—create additional complexity in achieving true international alignment.
Recent progress includes the development of the first ICH reflection paper on lipid-based drug delivery systems, scheduled for public consultation in 2023, and the establishment of international reference standards for critical LNP components through collaborative efforts between the USP, Ph. Eur., and JP pharmacopeial organizations, marking significant steps toward global regulatory convergence in this rapidly evolving field.
The ICH has established working groups specifically focused on novel delivery technologies, including LNPs, to develop consensus guidelines that can be adopted across member regions. These efforts aim to standardize quality control parameters, safety assessment protocols, and manufacturing requirements for mRNA LNP products, reducing regulatory divergence that could impede global development and access.
Parallel to ICH initiatives, bilateral agreements between regulatory authorities have emerged as pragmatic approaches to harmonization. The FDA-EMA mutual recognition agreement represents a significant step forward, allowing inspection results and certain testing data for mRNA LNP products to be shared between these major regulatory bodies, streamlining approval processes for manufacturers operating in both markets.
The World Health Organization has established an mRNA vaccine technology transfer hub to support standardization efforts in emerging markets. This initiative not only facilitates technology transfer but also promotes regulatory convergence by providing technical guidance aligned with international standards, particularly beneficial for regions with less established regulatory frameworks for advanced therapeutics.
Industry consortia have become instrumental in driving harmonization through pre-competitive collaboration. Organizations like the LNP Alliance and the International Pharmaceutical Aerosol Consortium on Regulation and Science (IPAC-RS) are developing standardized analytical methods and proposing common approaches to characterization and quality control of LNP formulations, which are subsequently presented to regulatory authorities for consideration.
Challenges to harmonization persist, including divergent regional priorities, varying risk tolerance levels among regulatory authorities, and the rapid pace of technological innovation outstripping regulatory adaptation. Cultural and legal differences in regulatory approaches—such as the precautionary principle emphasized in European regulations versus the risk-benefit approach more common in the US—create additional complexity in achieving true international alignment.
Recent progress includes the development of the first ICH reflection paper on lipid-based drug delivery systems, scheduled for public consultation in 2023, and the establishment of international reference standards for critical LNP components through collaborative efforts between the USP, Ph. Eur., and JP pharmacopeial organizations, marking significant steps toward global regulatory convergence in this rapidly evolving field.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!