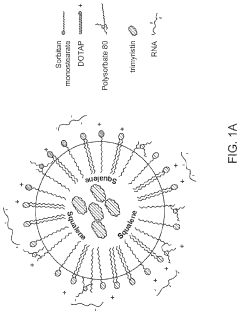
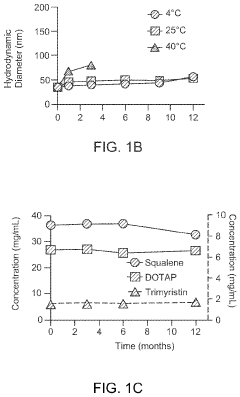
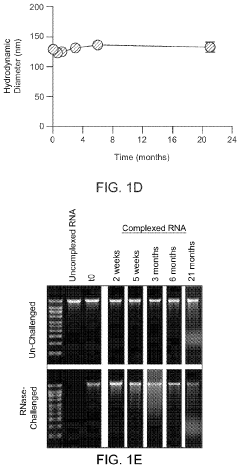
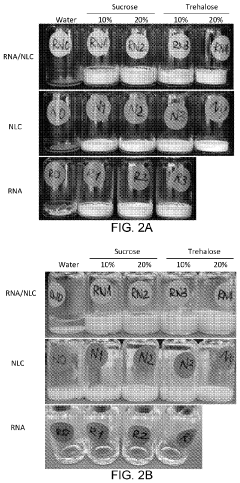
Research on mRNA Lipid Nanoparticle Thermal Stability
OCT 10, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
mRNA-LNP Thermal Stability Background and Objectives
Messenger RNA-Lipid Nanoparticle (mRNA-LNP) technology has emerged as a revolutionary platform in the biopharmaceutical industry, particularly highlighted by its pivotal role in COVID-19 vaccine development. The technology's evolution traces back to the early 2000s when researchers began exploring lipid-based delivery systems to overcome the inherent instability of naked mRNA in biological environments. The field has witnessed exponential growth over the past decade, transitioning from academic research to commercial applications.
Thermal stability represents one of the most critical challenges facing mRNA-LNP formulations. Current mRNA vaccines require ultra-cold chain storage conditions (-70°C to -20°C), significantly limiting global distribution and accessibility, particularly in resource-limited settings. This temperature sensitivity stems from the complex interplay between the mRNA molecule's structural integrity and the lipid nanoparticle's physical stability under varying thermal conditions.
The technological trajectory indicates a clear trend toward developing thermally stable formulations that can withstand higher temperatures without compromising efficacy. This evolution is driven by both scientific advancements in understanding RNA-lipid interactions and practical necessities for global healthcare deployment. Recent breakthroughs in lipid chemistry and nanoparticle engineering suggest potential pathways toward achieving room temperature stability.
The primary objective of this research is to comprehensively evaluate current approaches to enhancing mRNA-LNP thermal stability and identify promising directions for future development. Specifically, we aim to analyze how modifications in lipid composition, mRNA sequence engineering, and formulation processes impact thermal tolerance profiles.
Secondary objectives include mapping the relationship between thermal stability and other critical quality attributes such as transfection efficiency, immunogenicity, and manufacturing scalability. This multifactorial analysis will provide insights into potential trade-offs that must be considered when optimizing for thermal stability.
Additionally, this research seeks to establish standardized methodologies for assessing thermal stability across different mRNA-LNP platforms, enabling more consistent comparisons between competing technologies. Current literature reveals significant variability in stability testing protocols, complicating cross-study evaluations.
From a strategic perspective, achieving enhanced thermal stability would dramatically transform the mRNA therapeutic landscape by reducing cold chain requirements, extending shelf life, simplifying logistics, and ultimately expanding global access to these advanced therapies. The potential impact extends beyond vaccines to include mRNA-based treatments for cancer, genetic disorders, and regenerative medicine applications.
Thermal stability represents one of the most critical challenges facing mRNA-LNP formulations. Current mRNA vaccines require ultra-cold chain storage conditions (-70°C to -20°C), significantly limiting global distribution and accessibility, particularly in resource-limited settings. This temperature sensitivity stems from the complex interplay between the mRNA molecule's structural integrity and the lipid nanoparticle's physical stability under varying thermal conditions.
The technological trajectory indicates a clear trend toward developing thermally stable formulations that can withstand higher temperatures without compromising efficacy. This evolution is driven by both scientific advancements in understanding RNA-lipid interactions and practical necessities for global healthcare deployment. Recent breakthroughs in lipid chemistry and nanoparticle engineering suggest potential pathways toward achieving room temperature stability.
The primary objective of this research is to comprehensively evaluate current approaches to enhancing mRNA-LNP thermal stability and identify promising directions for future development. Specifically, we aim to analyze how modifications in lipid composition, mRNA sequence engineering, and formulation processes impact thermal tolerance profiles.
Secondary objectives include mapping the relationship between thermal stability and other critical quality attributes such as transfection efficiency, immunogenicity, and manufacturing scalability. This multifactorial analysis will provide insights into potential trade-offs that must be considered when optimizing for thermal stability.
Additionally, this research seeks to establish standardized methodologies for assessing thermal stability across different mRNA-LNP platforms, enabling more consistent comparisons between competing technologies. Current literature reveals significant variability in stability testing protocols, complicating cross-study evaluations.
From a strategic perspective, achieving enhanced thermal stability would dramatically transform the mRNA therapeutic landscape by reducing cold chain requirements, extending shelf life, simplifying logistics, and ultimately expanding global access to these advanced therapies. The potential impact extends beyond vaccines to include mRNA-based treatments for cancer, genetic disorders, and regenerative medicine applications.
Market Analysis for Thermally Stable mRNA Vaccines
The global mRNA vaccine market has experienced unprecedented growth following the COVID-19 pandemic, with thermal stability emerging as a critical factor influencing market adoption and expansion. Currently valued at approximately $29.7 billion in 2023, the mRNA therapeutics and vaccines market is projected to grow at a CAGR of 13.2% through 2030, with thermally stable formulations potentially capturing a significant portion of this expansion.
Market demand for thermally stable mRNA vaccines stems primarily from challenges in the cold chain infrastructure, particularly in low and middle-income countries (LMICs). The World Health Organization estimates that up to 50% of vaccines are wasted globally each year, with temperature excursions during storage and transportation being a major contributor. This represents not only a financial loss exceeding $1.5 billion annually but also a significant barrier to global immunization efforts.
The COVID-19 pandemic highlighted these challenges, as the first-generation mRNA vaccines required ultra-cold storage conditions (-70°C for Pfizer-BioNTech and -20°C for Moderna), creating substantial logistical hurdles. Healthcare facilities in many regions lack adequate ultra-cold storage capabilities, with only 28% of healthcare facilities in Africa having reliable electricity access, further complicating vaccine distribution.
Geographically, North America currently dominates the mRNA vaccine market with approximately 42% market share, followed by Europe at 31%. However, the Asia-Pacific region is expected to witness the fastest growth rate of 15.8% through 2030, driven by increasing healthcare expenditure and expanding vaccination programs. This regional growth presents significant opportunities for thermally stable formulations that can overcome infrastructure limitations.
Key market segments for thermally stable mRNA vaccines include infectious diseases (currently 78% of the market), oncology applications (15%), and rare genetic disorders (7%). The infectious disease segment is expected to maintain dominance due to the ongoing need for COVID-19 boosters and emerging applications for influenza, RSV, and other pathogens.
Consumer willingness to pay for improved vaccine technologies is evident, with surveys indicating that 67% of healthcare providers would prefer thermally stable vaccines even at a 15-20% price premium, citing reduced wastage and simplified logistics as primary benefits. Government procurement agencies similarly express strong interest, with potential volume commitments for formulations that can be stored at 2-8°C for extended periods.
Industry analysts project that achieving room temperature stability for mRNA vaccines could expand the addressable market by 35-40%, particularly in regions with limited cold chain infrastructure, representing an additional market opportunity of approximately $12 billion by 2030.
Market demand for thermally stable mRNA vaccines stems primarily from challenges in the cold chain infrastructure, particularly in low and middle-income countries (LMICs). The World Health Organization estimates that up to 50% of vaccines are wasted globally each year, with temperature excursions during storage and transportation being a major contributor. This represents not only a financial loss exceeding $1.5 billion annually but also a significant barrier to global immunization efforts.
The COVID-19 pandemic highlighted these challenges, as the first-generation mRNA vaccines required ultra-cold storage conditions (-70°C for Pfizer-BioNTech and -20°C for Moderna), creating substantial logistical hurdles. Healthcare facilities in many regions lack adequate ultra-cold storage capabilities, with only 28% of healthcare facilities in Africa having reliable electricity access, further complicating vaccine distribution.
Geographically, North America currently dominates the mRNA vaccine market with approximately 42% market share, followed by Europe at 31%. However, the Asia-Pacific region is expected to witness the fastest growth rate of 15.8% through 2030, driven by increasing healthcare expenditure and expanding vaccination programs. This regional growth presents significant opportunities for thermally stable formulations that can overcome infrastructure limitations.
Key market segments for thermally stable mRNA vaccines include infectious diseases (currently 78% of the market), oncology applications (15%), and rare genetic disorders (7%). The infectious disease segment is expected to maintain dominance due to the ongoing need for COVID-19 boosters and emerging applications for influenza, RSV, and other pathogens.
Consumer willingness to pay for improved vaccine technologies is evident, with surveys indicating that 67% of healthcare providers would prefer thermally stable vaccines even at a 15-20% price premium, citing reduced wastage and simplified logistics as primary benefits. Government procurement agencies similarly express strong interest, with potential volume commitments for formulations that can be stored at 2-8°C for extended periods.
Industry analysts project that achieving room temperature stability for mRNA vaccines could expand the addressable market by 35-40%, particularly in regions with limited cold chain infrastructure, representing an additional market opportunity of approximately $12 billion by 2030.
Current Challenges in mRNA-LNP Thermal Stability
The thermal stability of mRNA-LNP formulations represents one of the most significant hurdles in the widespread adoption of mRNA therapeutics and vaccines. Current mRNA-LNP formulations typically require ultra-cold chain storage conditions (-70°C to -20°C), which poses substantial logistical challenges, especially in resource-limited settings and developing regions. This stringent temperature requirement stems from the inherent instability of both the mRNA molecule and the lipid nanoparticle structure.
At the molecular level, mRNA is susceptible to hydrolysis, oxidation, and enzymatic degradation. The phosphodiester backbone of mRNA can undergo spontaneous hydrolysis at elevated temperatures, leading to strand breakage and loss of translational capacity. Additionally, the presence of reactive oxygen species can damage nucleobases, particularly guanine, further compromising mRNA integrity.
The lipid components of LNPs face their own stability challenges. Phospholipids and ionizable lipids are prone to oxidation and hydrolysis, which can alter the physical properties of the nanoparticle structure. Temperature fluctuations can induce phase transitions in the lipid bilayers, potentially leading to cargo leakage and particle aggregation. The PEGylated lipids, crucial for preventing opsonization and extending circulation time, may detach from the LNP surface during storage, reducing the formulation's efficacy.
Particle size stability represents another critical challenge. Temperature variations can trigger particle fusion or aggregation, resulting in increased polydispersity and altered biodistribution profiles. Even minor changes in particle size can significantly impact cellular uptake efficiency and the subsequent protein expression levels.
The interface between mRNA and lipid components introduces additional complexity. The electrostatic interactions between negatively charged mRNA and positively charged ionizable lipids are temperature-dependent. Thermal stress can disrupt these crucial interactions, potentially leading to incomplete encapsulation or premature release of the mRNA cargo.
Current stabilization approaches have shown limited success. Chemical modifications of mRNA, such as pseudouridine substitution and 5' cap analogs, improve thermal stability but often at the cost of reduced translation efficiency. Lyophilization (freeze-drying) has emerged as a promising approach but introduces challenges related to excipient selection and reconstitution protocols.
Regulatory hurdles compound these technical challenges. Demonstrating equivalent efficacy and safety profiles for thermally stabilized formulations compared to their cold-stored counterparts requires extensive comparative studies. Additionally, analytical methods for accurately assessing the integrity of mRNA-LNPs after thermal stress remain limited, complicating stability assessment and shelf-life determination.
At the molecular level, mRNA is susceptible to hydrolysis, oxidation, and enzymatic degradation. The phosphodiester backbone of mRNA can undergo spontaneous hydrolysis at elevated temperatures, leading to strand breakage and loss of translational capacity. Additionally, the presence of reactive oxygen species can damage nucleobases, particularly guanine, further compromising mRNA integrity.
The lipid components of LNPs face their own stability challenges. Phospholipids and ionizable lipids are prone to oxidation and hydrolysis, which can alter the physical properties of the nanoparticle structure. Temperature fluctuations can induce phase transitions in the lipid bilayers, potentially leading to cargo leakage and particle aggregation. The PEGylated lipids, crucial for preventing opsonization and extending circulation time, may detach from the LNP surface during storage, reducing the formulation's efficacy.
Particle size stability represents another critical challenge. Temperature variations can trigger particle fusion or aggregation, resulting in increased polydispersity and altered biodistribution profiles. Even minor changes in particle size can significantly impact cellular uptake efficiency and the subsequent protein expression levels.
The interface between mRNA and lipid components introduces additional complexity. The electrostatic interactions between negatively charged mRNA and positively charged ionizable lipids are temperature-dependent. Thermal stress can disrupt these crucial interactions, potentially leading to incomplete encapsulation or premature release of the mRNA cargo.
Current stabilization approaches have shown limited success. Chemical modifications of mRNA, such as pseudouridine substitution and 5' cap analogs, improve thermal stability but often at the cost of reduced translation efficiency. Lyophilization (freeze-drying) has emerged as a promising approach but introduces challenges related to excipient selection and reconstitution protocols.
Regulatory hurdles compound these technical challenges. Demonstrating equivalent efficacy and safety profiles for thermally stabilized formulations compared to their cold-stored counterparts requires extensive comparative studies. Additionally, analytical methods for accurately assessing the integrity of mRNA-LNPs after thermal stress remain limited, complicating stability assessment and shelf-life determination.
Current Approaches to Enhance mRNA-LNP Thermal Stability
01 Lipid composition optimization for thermal stability
Specific lipid compositions can be optimized to enhance the thermal stability of mRNA lipid nanoparticles. By carefully selecting lipid components with higher melting points or incorporating stabilizing lipids such as cholesterol derivatives, researchers can create formulations that maintain integrity at elevated temperatures. These optimized compositions prevent premature release of mRNA cargo and maintain particle size distribution during storage and transportation at various temperatures.- Lipid composition optimization for thermal stability: Specific lipid compositions can be formulated to enhance the thermal stability of mRNA lipid nanoparticles. By carefully selecting lipid components with higher melting points and optimizing the molar ratios of structural lipids, helper lipids, and ionizable lipids, the overall thermal stability of the nanoparticle structure can be improved. These optimized formulations maintain integrity during storage at elevated temperatures and prevent premature mRNA degradation.
- Cryoprotectants and lyophilization techniques: The incorporation of cryoprotectants and application of specialized lyophilization techniques significantly improves the thermal stability of mRNA lipid nanoparticles. Sugars such as trehalose and sucrose, along with amino acids and polymers, protect the nanoparticle structure during freeze-drying processes. These approaches allow for the production of thermally stable dry powder formulations that can withstand higher temperatures compared to liquid suspensions.
- Surface modification and PEGylation strategies: Surface modification of mRNA lipid nanoparticles, particularly through PEGylation, enhances thermal stability by creating a protective hydrophilic shell. The polyethylene glycol (PEG) coating prevents particle aggregation at elevated temperatures and shields the lipid bilayer from thermal stress. Various PEG chain lengths and densities can be optimized to provide maximum thermal protection while maintaining transfection efficiency.
- pH and buffer system optimization: The thermal stability of mRNA lipid nanoparticles can be enhanced through careful optimization of pH and buffer systems. Specific buffer compositions that maintain a stable pH environment under thermal stress conditions help preserve the structural integrity of the nanoparticles. Addition of antioxidants and chelating agents in the buffer system further protects against temperature-induced degradation by preventing oxidative damage and metal ion-catalyzed hydrolysis of the mRNA.
- Novel stabilizing excipients and additives: Incorporation of novel stabilizing excipients and additives improves the thermal stability of mRNA lipid nanoparticles. These include specialized polymers, amino acid derivatives, and natural compounds that interact with the lipid bilayer to maintain structural integrity at elevated temperatures. Some formulations utilize thermally responsive materials that provide additional protection specifically when exposed to temperature fluctuations, creating a dynamic protective mechanism.
02 Cryoprotectants and lyophilization techniques
The use of cryoprotectants and advanced lyophilization techniques significantly improves the thermal stability of mRNA lipid nanoparticles. Sugars like trehalose and sucrose, as well as amino acids and polymers, protect the nanoparticles during freeze-drying processes. These approaches allow for the production of thermally stable dry powder formulations that can be stored at room temperature or higher without degradation, eliminating the need for cold chain storage in some cases.Expand Specific Solutions03 Surface modification and PEGylation strategies
Surface modification of lipid nanoparticles, particularly through PEGylation, enhances thermal stability by creating a protective hydration layer around the particles. These modifications prevent aggregation at elevated temperatures and reduce interactions with proteins that could destabilize the formulation. Various PEG chain lengths and densities can be optimized to provide maximum thermal protection while maintaining the functional properties of the mRNA delivery system.Expand Specific Solutions04 pH and buffer system optimization
The thermal stability of mRNA lipid nanoparticles can be significantly improved through careful optimization of pH and buffer systems. Specific buffer compositions maintain the structural integrity of the nanoparticles across a range of temperatures by preventing hydrolysis of the lipid components and protecting the mRNA cargo. The addition of antioxidants and chelating agents further enhances stability by preventing oxidative degradation during thermal stress.Expand Specific Solutions05 Novel manufacturing and processing techniques
Advanced manufacturing and processing techniques have been developed to enhance the thermal stability of mRNA lipid nanoparticles. These include microfluidic mixing under controlled temperature conditions, rapid quenching processes, and specialized extrusion methods. Post-formation thermal cycling treatments can also induce structural rearrangements that result in more thermally stable configurations. These manufacturing innovations produce nanoparticles with improved resistance to temperature fluctuations during storage and transport.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Industry Players in mRNA-LNP Development
The mRNA Lipid Nanoparticle Thermal Stability landscape is currently in a growth phase, with the market expanding rapidly following COVID-19 vaccine breakthroughs. Major players like Moderna, BioNTech, and Translate Bio are leading innovation, while emerging companies such as SiSaf and Gennova are developing novel stabilization technologies. The competitive field includes pharmaceutical giants (Sanofi, GSK) and specialized biotech firms focusing on improving thermal stability—a critical challenge for mRNA therapeutics. Academic institutions, particularly Zhejiang University and Sun Yat-sen University, are contributing significant research. The technology remains in early maturity, with companies actively addressing cold chain requirements through innovations in lipid formulations, lyophilization techniques, and novel delivery systems to enhance stability at ambient temperatures.
Translate Bio, Inc.
Technical Solution: Translate Bio (now part of Sanofi) has developed the MRT platform (Messenger RNA Therapeutics) with specialized LNP formulations designed for enhanced thermal stability. Their approach centers on proprietary ionizable lipids with optimized tail structures that maintain phase transition properties across temperature ranges. The company's LNP formulation process employs T-cell microfluidics that creates uniform particles (70-100 nm) with consistent mRNA encapsulation efficiency exceeding 90%, contributing to stability. Their technology incorporates modified nucleosides (including 5-methoxyuridine) in the mRNA structure to reduce immunogenicity while enhancing stability. Translate Bio's formulations typically include proprietary ionizable lipids (e.g., DOTMA derivatives), helper phospholipids, cholesterol, and PEG-lipids in specific molar ratios (approximately 50:10:38.5:1.5) that have been optimized for thermal resilience. Recent innovations include the development of lyoprotectant systems using disaccharide combinations and amino acid buffers that maintain LNP integrity during lyophilization and subsequent storage at elevated temperatures. Their research has demonstrated maintenance of mRNA integrity in LNPs stored at 2-8°C for extended periods (>3 months) with minimal potency loss.
Strengths: Specialized expertise in designing LNPs for pulmonary delivery requiring enhanced stability; proprietary ionizable lipid chemistry optimized for thermal resistance; advanced manufacturing processes for consistent LNP production. Weaknesses: Less extensive clinical validation compared to some competitors; integration with Sanofi may have shifted research priorities; formulations may still require refrigeration for optimal long-term stability.
ModernaTX, Inc.
Technical Solution: Moderna has developed a proprietary lipid nanoparticle (LNP) delivery system for mRNA therapeutics with enhanced thermal stability. Their approach involves using ionizable lipids with optimized pKa values that facilitate efficient endosomal escape while maintaining structural integrity at varying temperatures. The company employs a specialized microfluidic mixing process that creates uniform LNPs with consistent size distribution (typically 80-100 nm), which contributes to stability. Moderna's formulation includes SM-102 (proprietary ionizable lipid), cholesterol, DSPC, and PEG2000-DMG in specific molar ratios that have been engineered to withstand temperature fluctuations. Their mRNA-1273 COVID-19 vaccine demonstrated stability at 2-8°C for up to 30 days and at room temperature for 12 hours, representing a significant advancement in LNP thermal stability. Recent innovations include lyophilization techniques that potentially extend shelf life at higher temperatures and the incorporation of trehalose and other disaccharides as cryoprotectants to prevent aggregation during freeze-thaw cycles.
Strengths: Industry-leading LNP formulation expertise with proven clinical success; proprietary ionizable lipids that enhance endosomal escape while maintaining thermal stability; advanced manufacturing capabilities for consistent LNP production. Weaknesses: Still requires cold chain infrastructure for long-term storage (-20°C); relatively high production costs compared to traditional vaccine platforms; formulation complexity may limit scalability in resource-limited settings.
Critical Patents and Innovations in mRNA-LNP Stabilization
Pharmaceutical compositions comprising particles and mRNA and methods of making and storing same
PatentPendingCN116669709A
Innovation
- By adjusting the pH of the formulation to be lower than the pKa of the cationic ionizable lipids, and excluding NaCl, KCl, citric acid anions and inorganic phosphate anions, a stable frozen or freeze-dried LNP formulation can be prepared, which can be stored at temperatures of about -25°C or higher.
Co-lyophilized RNA and nanostructured lipid carrier
PatentPendingUS20230310323A1
Innovation
- Development of a thermostable nanostructured lipid carrier (NLC) system that can be lyophilized with RNA, maintaining stability and bioactivity for extended periods at room and refrigerated temperatures, allowing for distribution without cold chain maintenance and effective immune response induction.
Cold Chain Infrastructure and Logistics Considerations
The successful deployment of mRNA vaccines and therapeutics critically depends on maintaining the thermal stability of lipid nanoparticles (LNPs) throughout the distribution chain. Current mRNA-LNP formulations require ultra-cold storage conditions (-70°C to -80°C), presenting significant logistical challenges that limit global accessibility, particularly in resource-limited regions.
Standard cold chain infrastructure for pharmaceuticals typically operates at 2-8°C, making the extreme temperature requirements of mRNA-LNPs exceptionally demanding. This necessitates specialized ultra-low temperature freezers, dry ice packaging systems, and temperature-controlled transportation vehicles, all of which substantially increase distribution costs and complexity. The energy consumption of maintaining such extreme temperatures also raises environmental sustainability concerns.
The "last mile" delivery presents particularly acute challenges, as temperature excursions during this phase can compromise product integrity. Remote and rural areas often lack reliable electricity for continuous cold storage, while temperature monitoring systems may be insufficient to detect critical deviations. These limitations have created significant disparities in access to mRNA therapeutics between high-income and low-income regions.
Economic analyses indicate that cold chain requirements can account for up to 30% of the total cost of mRNA vaccine deployment programs. This includes capital investments in specialized equipment, operational costs for temperature maintenance, and losses from product wastage due to cold chain failures. The COVID-19 pandemic highlighted these challenges, with estimates suggesting that 5-20% of vaccine doses were wasted globally due to cold chain breaches.
Technological innovations are emerging to address these challenges, including improved insulation materials, phase-change materials for passive cooling, and advanced real-time temperature monitoring systems using IoT sensors. Additionally, alternative distribution models such as hub-and-spoke systems with mobile vaccination units have shown promise in expanding reach while maintaining cold chain integrity.
Regulatory frameworks are evolving to accommodate the unique requirements of thermally sensitive biologics. The WHO's Vaccine Vial Monitor (VVM) system has been adapted for mRNA products, while international standards for temperature-controlled pharmaceutical distribution (such as EU GDP guidelines) continue to be refined to address the specific needs of these novel therapeutics.
Standard cold chain infrastructure for pharmaceuticals typically operates at 2-8°C, making the extreme temperature requirements of mRNA-LNPs exceptionally demanding. This necessitates specialized ultra-low temperature freezers, dry ice packaging systems, and temperature-controlled transportation vehicles, all of which substantially increase distribution costs and complexity. The energy consumption of maintaining such extreme temperatures also raises environmental sustainability concerns.
The "last mile" delivery presents particularly acute challenges, as temperature excursions during this phase can compromise product integrity. Remote and rural areas often lack reliable electricity for continuous cold storage, while temperature monitoring systems may be insufficient to detect critical deviations. These limitations have created significant disparities in access to mRNA therapeutics between high-income and low-income regions.
Economic analyses indicate that cold chain requirements can account for up to 30% of the total cost of mRNA vaccine deployment programs. This includes capital investments in specialized equipment, operational costs for temperature maintenance, and losses from product wastage due to cold chain failures. The COVID-19 pandemic highlighted these challenges, with estimates suggesting that 5-20% of vaccine doses were wasted globally due to cold chain breaches.
Technological innovations are emerging to address these challenges, including improved insulation materials, phase-change materials for passive cooling, and advanced real-time temperature monitoring systems using IoT sensors. Additionally, alternative distribution models such as hub-and-spoke systems with mobile vaccination units have shown promise in expanding reach while maintaining cold chain integrity.
Regulatory frameworks are evolving to accommodate the unique requirements of thermally sensitive biologics. The WHO's Vaccine Vial Monitor (VVM) system has been adapted for mRNA products, while international standards for temperature-controlled pharmaceutical distribution (such as EU GDP guidelines) continue to be refined to address the specific needs of these novel therapeutics.
Regulatory Pathways for Novel mRNA-LNP Formulations
The regulatory landscape for mRNA-LNP formulations presents a complex and evolving framework that developers must navigate carefully. Currently, the FDA and EMA classify mRNA-LNP products as biological products, requiring comprehensive stability data throughout the development process. Thermal stability considerations are particularly critical, as they directly impact product safety, efficacy, and shelf-life determinations.
For novel mRNA-LNP formulations with enhanced thermal stability profiles, regulatory agencies typically require extensive characterization studies demonstrating the relationship between thermal properties and product integrity. These include accelerated and real-time stability studies under various temperature conditions, freeze-thaw cycle testing, and stress testing to establish stability boundaries.
The regulatory pathway generally follows a stepwise approach beginning with pre-IND (Investigational New Drug) consultations where thermal stability data requirements are established. During IND submission, preliminary stability data must demonstrate product viability throughout the proposed clinical trial duration. As development progresses to Biologics License Application (BLA), comprehensive stability data packages become mandatory, including validation of analytical methods used to assess thermal stability.
International harmonization efforts through ICH guidelines (particularly ICH Q1A-Q1F for stability testing) provide standardized approaches, though specific requirements for mRNA-LNP products continue to evolve. The novel nature of thermally stable formulations may necessitate additional characterization beyond standard requirements, especially regarding lipid component interactions under thermal stress.
Regulatory agencies increasingly accept innovative approaches for stability assessment, including predictive modeling and accelerated stability protocols, provided they are scientifically justified. The FDA's Emerging Technology Program and EMA's Innovation Task Force offer pathways for early engagement on novel stability testing methodologies for advanced formulations.
Post-approval commitments typically include ongoing stability monitoring programs, with particular attention to thermal excursions during distribution. The regulatory framework also requires change management protocols for manufacturing modifications that might affect thermal stability profiles, with clearly defined thresholds for when additional regulatory review becomes necessary.
Companies developing thermally enhanced mRNA-LNP formulations should engage regulatory agencies early and frequently, as this technology space continues to evolve rapidly, with regulatory expectations adapting accordingly to ensure patient safety while enabling innovation.
For novel mRNA-LNP formulations with enhanced thermal stability profiles, regulatory agencies typically require extensive characterization studies demonstrating the relationship between thermal properties and product integrity. These include accelerated and real-time stability studies under various temperature conditions, freeze-thaw cycle testing, and stress testing to establish stability boundaries.
The regulatory pathway generally follows a stepwise approach beginning with pre-IND (Investigational New Drug) consultations where thermal stability data requirements are established. During IND submission, preliminary stability data must demonstrate product viability throughout the proposed clinical trial duration. As development progresses to Biologics License Application (BLA), comprehensive stability data packages become mandatory, including validation of analytical methods used to assess thermal stability.
International harmonization efforts through ICH guidelines (particularly ICH Q1A-Q1F for stability testing) provide standardized approaches, though specific requirements for mRNA-LNP products continue to evolve. The novel nature of thermally stable formulations may necessitate additional characterization beyond standard requirements, especially regarding lipid component interactions under thermal stress.
Regulatory agencies increasingly accept innovative approaches for stability assessment, including predictive modeling and accelerated stability protocols, provided they are scientifically justified. The FDA's Emerging Technology Program and EMA's Innovation Task Force offer pathways for early engagement on novel stability testing methodologies for advanced formulations.
Post-approval commitments typically include ongoing stability monitoring programs, with particular attention to thermal excursions during distribution. The regulatory framework also requires change management protocols for manufacturing modifications that might affect thermal stability profiles, with clearly defined thresholds for when additional regulatory review becomes necessary.
Companies developing thermally enhanced mRNA-LNP formulations should engage regulatory agencies early and frequently, as this technology space continues to evolve rapidly, with regulatory expectations adapting accordingly to ensure patient safety while enabling innovation.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!