What Ensures Stability in mRNA Lipid Nanoparticle Systems
OCT 10, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
mRNA-LNP Stability Background and Objectives
Messenger RNA-lipid nanoparticle (mRNA-LNP) technology has emerged as a revolutionary platform in the fields of therapeutics and vaccines, most notably demonstrated by the rapid development and deployment of COVID-19 vaccines. The technology's roots trace back to the 1990s when researchers began exploring lipid-based delivery systems for nucleic acids. However, significant breakthroughs in mRNA stabilization and delivery efficiency only materialized in the past decade, catalyzing the current acceleration in mRNA-LNP applications.
The evolution of this technology has been marked by progressive improvements in lipid chemistry, formulation techniques, and manufacturing processes. Early challenges included rapid degradation of mRNA in biological environments, inefficient cellular uptake, and immunogenicity concerns. These obstacles have been gradually overcome through innovations in modified nucleosides, optimized lipid compositions, and advanced production methods.
Current technological trends indicate a shift toward more sophisticated LNP designs with enhanced stability profiles, targeted delivery capabilities, and reduced side effects. The field is witnessing increasing integration of computational modeling and high-throughput screening approaches to optimize formulation parameters that directly impact stability.
The stability of mRNA-LNP systems represents a multifaceted challenge involving physical stability (prevention of aggregation and particle size maintenance), chemical stability (protection against hydrolysis and oxidation), and biological stability (resistance to enzymatic degradation and immune recognition). These stability aspects are critical determinants of shelf life, in vivo efficacy, and safety profiles.
The primary technical objectives of this investigation are to comprehensively analyze the factors governing mRNA-LNP stability across various dimensions. This includes examining the role of lipid composition, particularly the impact of ionizable lipids, helper phospholipids, cholesterol, and PEGylated lipids on the structural integrity of nanoparticles. Additionally, we aim to evaluate how formulation parameters such as N/P ratio, particle size distribution, and surface charge influence stability profiles.
Further objectives include assessing the effectiveness of various stabilization strategies, including lyophilization techniques, cryoprotectants, and buffer optimization. We will also explore emerging technologies for stability enhancement, such as novel lipid designs, alternative particle architectures, and innovative manufacturing approaches that may extend product shelf life and maintain efficacy under challenging storage conditions.
This analysis seeks to establish a framework for predicting stability profiles based on formulation characteristics and to identify critical quality attributes that correlate with enhanced stability. The ultimate goal is to provide actionable insights for developing next-generation mRNA-LNP systems with superior stability properties that can withstand diverse environmental conditions while maintaining therapeutic potency.
The evolution of this technology has been marked by progressive improvements in lipid chemistry, formulation techniques, and manufacturing processes. Early challenges included rapid degradation of mRNA in biological environments, inefficient cellular uptake, and immunogenicity concerns. These obstacles have been gradually overcome through innovations in modified nucleosides, optimized lipid compositions, and advanced production methods.
Current technological trends indicate a shift toward more sophisticated LNP designs with enhanced stability profiles, targeted delivery capabilities, and reduced side effects. The field is witnessing increasing integration of computational modeling and high-throughput screening approaches to optimize formulation parameters that directly impact stability.
The stability of mRNA-LNP systems represents a multifaceted challenge involving physical stability (prevention of aggregation and particle size maintenance), chemical stability (protection against hydrolysis and oxidation), and biological stability (resistance to enzymatic degradation and immune recognition). These stability aspects are critical determinants of shelf life, in vivo efficacy, and safety profiles.
The primary technical objectives of this investigation are to comprehensively analyze the factors governing mRNA-LNP stability across various dimensions. This includes examining the role of lipid composition, particularly the impact of ionizable lipids, helper phospholipids, cholesterol, and PEGylated lipids on the structural integrity of nanoparticles. Additionally, we aim to evaluate how formulation parameters such as N/P ratio, particle size distribution, and surface charge influence stability profiles.
Further objectives include assessing the effectiveness of various stabilization strategies, including lyophilization techniques, cryoprotectants, and buffer optimization. We will also explore emerging technologies for stability enhancement, such as novel lipid designs, alternative particle architectures, and innovative manufacturing approaches that may extend product shelf life and maintain efficacy under challenging storage conditions.
This analysis seeks to establish a framework for predicting stability profiles based on formulation characteristics and to identify critical quality attributes that correlate with enhanced stability. The ultimate goal is to provide actionable insights for developing next-generation mRNA-LNP systems with superior stability properties that can withstand diverse environmental conditions while maintaining therapeutic potency.
Market Analysis for Stable mRNA-LNP Therapeutics
The mRNA-LNP therapeutics market has experienced unprecedented growth following the successful deployment of COVID-19 vaccines, with the global market value reaching $5.4 billion in 2022. Projections indicate a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 28.4% through 2030, potentially reaching $37.8 billion. This remarkable expansion is driven by increasing investment in mRNA technology platforms and growing recognition of their potential beyond vaccines.
Oncology represents the largest application segment, accounting for approximately 32% of the current market share. The ability to deliver personalized cancer vaccines and immunotherapies positions mRNA-LNPs as revolutionary tools in precision medicine. Infectious disease applications follow closely at 29% market share, bolstered by the pandemic response and ongoing development of vaccines for influenza, RSV, and emerging pathogens.
Pharmaceutical giants including Moderna, BioNTech/Pfizer, and CureVac currently dominate the market landscape, collectively holding over 65% of market share. However, specialized biotech firms focusing exclusively on LNP delivery systems, such as Acuitas Therapeutics and Arbutus Biopharma, are gaining significant traction as technology providers.
Regional analysis reveals North America leading with 48% of the global market, followed by Europe at 31% and Asia-Pacific at 17%. China and India are emerging as high-growth regions with annual growth rates exceeding 35%, driven by substantial government investments in biotechnology infrastructure and favorable regulatory frameworks.
The market demonstrates strong demand for stability innovations, with approximately 22% of industry R&D expenditure directed toward enhancing LNP formulation stability. End-users consistently identify storage requirements and shelf-life as critical factors influencing adoption decisions, with 78% of healthcare providers citing stability concerns as a significant barrier to widespread implementation.
Pricing analysis indicates premium valuation for products with enhanced stability profiles. Products demonstrating room temperature stability command price premiums of 15-20% compared to conventional cold-chain dependent formulations. This pricing differential underscores the substantial market value of stability innovations.
Market forecasts suggest specialized stability-enhancing technologies could develop into a distinct sub-segment worth $3.2 billion by 2028. Investors have recognized this potential, with venture capital funding for startups focused on mRNA-LNP stability solutions increasing by 145% between 2020 and 2022, reaching $1.8 billion in cumulative investment.
Oncology represents the largest application segment, accounting for approximately 32% of the current market share. The ability to deliver personalized cancer vaccines and immunotherapies positions mRNA-LNPs as revolutionary tools in precision medicine. Infectious disease applications follow closely at 29% market share, bolstered by the pandemic response and ongoing development of vaccines for influenza, RSV, and emerging pathogens.
Pharmaceutical giants including Moderna, BioNTech/Pfizer, and CureVac currently dominate the market landscape, collectively holding over 65% of market share. However, specialized biotech firms focusing exclusively on LNP delivery systems, such as Acuitas Therapeutics and Arbutus Biopharma, are gaining significant traction as technology providers.
Regional analysis reveals North America leading with 48% of the global market, followed by Europe at 31% and Asia-Pacific at 17%. China and India are emerging as high-growth regions with annual growth rates exceeding 35%, driven by substantial government investments in biotechnology infrastructure and favorable regulatory frameworks.
The market demonstrates strong demand for stability innovations, with approximately 22% of industry R&D expenditure directed toward enhancing LNP formulation stability. End-users consistently identify storage requirements and shelf-life as critical factors influencing adoption decisions, with 78% of healthcare providers citing stability concerns as a significant barrier to widespread implementation.
Pricing analysis indicates premium valuation for products with enhanced stability profiles. Products demonstrating room temperature stability command price premiums of 15-20% compared to conventional cold-chain dependent formulations. This pricing differential underscores the substantial market value of stability innovations.
Market forecasts suggest specialized stability-enhancing technologies could develop into a distinct sub-segment worth $3.2 billion by 2028. Investors have recognized this potential, with venture capital funding for startups focused on mRNA-LNP stability solutions increasing by 145% between 2020 and 2022, reaching $1.8 billion in cumulative investment.
Current Challenges in mRNA-LNP Stability
Despite significant advancements in mRNA-LNP technology, several critical stability challenges persist that impede broader clinical applications and commercial viability. The primary challenge lies in the inherent instability of mRNA molecules, which are highly susceptible to enzymatic degradation by ubiquitous ribonucleases. This vulnerability necessitates stringent handling protocols and cold chain requirements, significantly increasing production costs and limiting global distribution capabilities.
Temperature sensitivity represents another major hurdle, as current mRNA-LNP formulations typically require ultra-cold storage conditions (-70°C to -20°C) to maintain efficacy. This requirement creates substantial logistical barriers, particularly in resource-limited settings lacking reliable cold chain infrastructure, thereby restricting equitable access to mRNA-based therapeutics and vaccines.
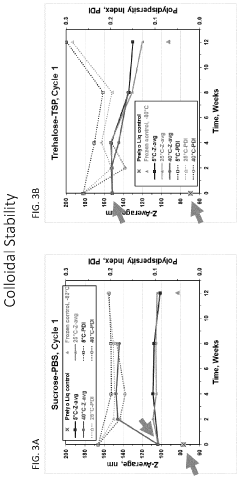
The colloidal stability of LNPs presents additional complications, as these nanoparticles tend to aggregate over time, leading to reduced efficacy and potential safety concerns. Particle size distribution changes during storage can alter biodistribution profiles and cellular uptake efficiency, ultimately compromising therapeutic outcomes. Furthermore, the lipid components themselves are prone to oxidation and hydrolysis, which can generate toxic byproducts and trigger inflammatory responses.
Encapsulation efficiency and cargo retention represent persistent technical challenges. Current formulations often struggle to maintain consistent mRNA encapsulation during storage, resulting in premature release and degradation before reaching target tissues. This issue is particularly pronounced with larger mRNA constructs, which are increasingly important for complex therapeutic applications.
The interface between mRNA and lipid components introduces additional stability concerns. Electrostatic interactions between negatively charged mRNA and cationic lipids, while essential for complex formation, can be disrupted by environmental factors such as pH changes and ionic strength fluctuations. These disruptions can lead to structural reorganization of the LNPs and compromise their functional integrity.
Scalable manufacturing processes that maintain product stability present significant technical barriers. Current production methods often introduce variability in critical quality attributes that affect stability profiles. The lack of standardized analytical methods for characterizing LNP stability further complicates quality control efforts and regulatory compliance.
Immunogenicity concerns also impact stability considerations, as lipid oxidation products and mRNA degradation fragments can trigger undesired immune responses. These reactions not only affect safety profiles but can also reduce therapeutic efficacy through accelerated clearance mechanisms and neutralizing responses against the delivery system itself.
Temperature sensitivity represents another major hurdle, as current mRNA-LNP formulations typically require ultra-cold storage conditions (-70°C to -20°C) to maintain efficacy. This requirement creates substantial logistical barriers, particularly in resource-limited settings lacking reliable cold chain infrastructure, thereby restricting equitable access to mRNA-based therapeutics and vaccines.
The colloidal stability of LNPs presents additional complications, as these nanoparticles tend to aggregate over time, leading to reduced efficacy and potential safety concerns. Particle size distribution changes during storage can alter biodistribution profiles and cellular uptake efficiency, ultimately compromising therapeutic outcomes. Furthermore, the lipid components themselves are prone to oxidation and hydrolysis, which can generate toxic byproducts and trigger inflammatory responses.
Encapsulation efficiency and cargo retention represent persistent technical challenges. Current formulations often struggle to maintain consistent mRNA encapsulation during storage, resulting in premature release and degradation before reaching target tissues. This issue is particularly pronounced with larger mRNA constructs, which are increasingly important for complex therapeutic applications.
The interface between mRNA and lipid components introduces additional stability concerns. Electrostatic interactions between negatively charged mRNA and cationic lipids, while essential for complex formation, can be disrupted by environmental factors such as pH changes and ionic strength fluctuations. These disruptions can lead to structural reorganization of the LNPs and compromise their functional integrity.
Scalable manufacturing processes that maintain product stability present significant technical barriers. Current production methods often introduce variability in critical quality attributes that affect stability profiles. The lack of standardized analytical methods for characterizing LNP stability further complicates quality control efforts and regulatory compliance.
Immunogenicity concerns also impact stability considerations, as lipid oxidation products and mRNA degradation fragments can trigger undesired immune responses. These reactions not only affect safety profiles but can also reduce therapeutic efficacy through accelerated clearance mechanisms and neutralizing responses against the delivery system itself.
Current Stabilization Strategies for mRNA-LNP Systems
01 Lipid composition optimization for mRNA stability
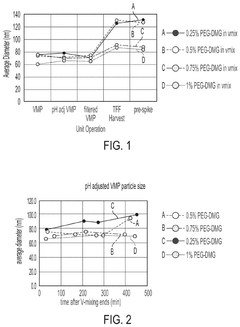
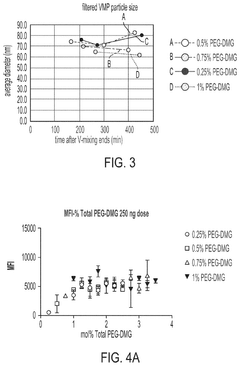
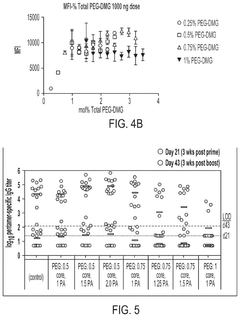
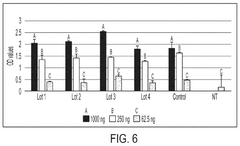
The stability of mRNA lipid nanoparticle systems can be enhanced through optimization of lipid compositions. This includes the selection of specific ionizable lipids, helper lipids, cholesterol, and PEG-lipids in precise ratios. These optimized formulations can protect the mRNA from degradation, improve encapsulation efficiency, and extend shelf-life of the nanoparticle system. The lipid composition directly affects the phase transition temperature, membrane fluidity, and overall structural integrity of the nanoparticles.- Lipid composition optimization for mRNA stability: The stability of mRNA lipid nanoparticle systems can be enhanced through optimization of lipid compositions. This includes the selection of specific ionizable lipids, helper lipids, cholesterol, and PEG-lipids in precise ratios. The lipid composition affects the encapsulation efficiency, particle size, and overall stability of the mRNA cargo. Optimized formulations can protect the mRNA from degradation and improve shelf-life while maintaining therapeutic efficacy.
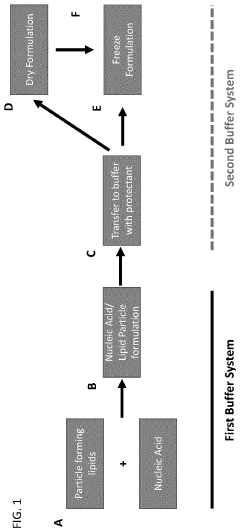
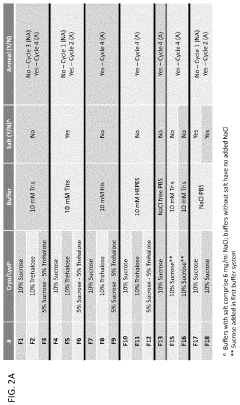
- Freeze-drying and lyophilization techniques: Freeze-drying and lyophilization techniques are employed to enhance the long-term stability of mRNA lipid nanoparticle systems. These processes involve the removal of water from the formulation under controlled temperature and pressure conditions, resulting in a dry powder form that is less susceptible to degradation. The addition of cryoprotectants and lyoprotectants, such as sugars and amino acids, helps maintain the structural integrity of the nanoparticles during the freeze-drying process and subsequent storage.
- pH and buffer system optimization: The stability of mRNA lipid nanoparticle systems is significantly influenced by pH and buffer composition. Optimizing the buffer system can prevent hydrolysis of the mRNA and maintain the structural integrity of the lipid components. Specific buffers, such as citrate, phosphate, or acetate buffers, at controlled pH ranges (typically between 5.5 and 7.5) can enhance the stability of the formulation. The buffer system also affects the ionization state of the lipids, which impacts particle formation and mRNA encapsulation efficiency.
- Temperature control and storage conditions: Temperature control and appropriate storage conditions are critical for maintaining the stability of mRNA lipid nanoparticle systems. Ultra-low temperature storage (typically -70°C to -80°C) is often required to prevent mRNA degradation and maintain lipid nanoparticle integrity. Innovations in formulation design have enabled the development of thermostable variants that can withstand higher temperatures, facilitating easier distribution and storage. Controlled temperature cycling studies help determine the impact of temperature fluctuations on stability and establish appropriate handling protocols.
- Surface modification and stabilizing agents: Surface modification of lipid nanoparticles and the incorporation of stabilizing agents can significantly enhance the stability of mRNA delivery systems. PEGylation of the nanoparticle surface provides steric stabilization, preventing aggregation and improving colloidal stability. Additional stabilizing agents such as antioxidants, metal chelators, and specific polymers can protect against oxidative damage and degradation. These modifications not only improve physical stability but also enhance biological stability by reducing interactions with serum proteins and extending circulation time in vivo.
02 Freeze-drying and lyophilization techniques
Freeze-drying and lyophilization techniques are employed to enhance the long-term stability of mRNA lipid nanoparticle systems. These processes involve the removal of water from the formulation under controlled temperature and pressure conditions, resulting in a dry powder form that is less susceptible to hydrolysis and oxidation. The addition of cryoprotectants and lyoprotectants, such as sugars and amino acids, helps maintain the structural integrity of the nanoparticles during the freeze-drying process and subsequent storage.Expand Specific Solutions03 pH and buffer system optimization
The stability of mRNA lipid nanoparticle systems is significantly influenced by the pH and buffer composition of the formulation. Optimizing these parameters can prevent degradation of the mRNA and maintain the structural integrity of the lipid nanoparticles. Buffer systems that maintain a slightly acidic to neutral pH range help protect the mRNA from hydrolysis while preserving the electrostatic interactions between the mRNA and ionizable lipids. Additionally, the inclusion of specific buffer components can minimize aggregation and fusion of nanoparticles during storage.Expand Specific Solutions04 Surface modification and PEGylation strategies
Surface modification of lipid nanoparticles, particularly through PEGylation, can significantly enhance the stability of mRNA delivery systems. The incorporation of polyethylene glycol (PEG) on the nanoparticle surface creates a hydrophilic shield that prevents aggregation, reduces opsonization, and increases colloidal stability. Various PEG-lipid conjugates with different chain lengths and densities can be utilized to optimize the stability profile. Additionally, alternative surface modification approaches using polymers or targeting ligands can provide both stability and functional benefits.Expand Specific Solutions05 Antioxidant and stabilizing agent incorporation
The incorporation of antioxidants and stabilizing agents into mRNA lipid nanoparticle formulations can significantly enhance their stability. These additives protect against oxidative damage, prevent lipid peroxidation, and maintain the integrity of both the lipid components and the mRNA payload. Common antioxidants include tocopherols, ascorbic acid derivatives, and butylated hydroxytoluene. Additionally, specific stabilizing agents such as sucrose, trehalose, and certain amino acids can prevent aggregation and maintain the colloidal stability of the nanoparticle system during storage and administration.Expand Specific Solutions
Leading Companies in mRNA-LNP Development
The mRNA lipid nanoparticle (LNP) stability landscape is currently in a growth phase, with the market expanding rapidly following COVID-19 vaccine successes. Key players include established pharmaceutical companies like BioNTech, Moderna, and AstraZeneca alongside specialized firms such as Arbutus Biopharma and SiSaf. The technology is approaching commercial maturity but still faces challenges in stability optimization. Leading research institutions (University of Pennsylvania, CNRS, INSERM) collaborate with industry to address critical stability factors including lipid composition, RNA modifications, and manufacturing processes. Companies like Translate Bio and GreenLight Biosciences are advancing proprietary stabilization technologies, while newer entrants like Quantoom Biosciences and NanoVation Therapeutics focus on next-generation delivery systems with enhanced stability profiles.
Translate Bio, Inc.
Technical Solution: Translate Bio has developed a proprietary mRNA Therapeutic (MRT) platform that addresses stability challenges in lipid nanoparticle delivery systems through multiple innovative approaches. Their technology employs custom-designed ionizable lipids with optimized pKa values (typically between 6.2-6.8) that remain neutral at physiological pH but become positively charged in the acidic endosomal environment, facilitating both stable encapsulation and efficient endosomal escape. Translate Bio's LNP formulations incorporate a precise ratio of four key components: their proprietary ionizable lipids, helper phospholipids (typically DOPE or DSPC), cholesterol, and PEG-lipids, with the exact composition tailored to specific tissue targets and mRNA cargo characteristics. Their manufacturing process utilizes controlled rapid mixing techniques that produce uniformly sized particles (typically 70-100 nm) with high encapsulation efficiency (>90%). To enhance stability during storage, Translate Bio employs lyophilization techniques with specialized cryoprotectants that prevent aggregation and protect the mRNA structure during freeze-thaw cycles. Additionally, they have developed proprietary mRNA sequence modifications and purification methods that enhance inherent stability of the mRNA cargo itself, complementing the protective effects of the LNP system.
Strengths: Translate Bio's technology demonstrates excellent stability profiles at refrigerated temperatures (2-8°C) for extended periods, reducing cold chain demands. Their platform shows versatility across multiple tissue targets, particularly in pulmonary applications where they've achieved efficient delivery to lung epithelial cells. Weaknesses: Their system may show variable transfection efficiency across different cell types, potentially limiting applications in certain tissues, and some of their proprietary lipid components may present manufacturing scalability challenges for large-scale production.
ModernaTX, Inc.
Technical Solution: Moderna has developed a proprietary lipid nanoparticle (LNP) delivery system that ensures mRNA stability through several key mechanisms. Their LNPs utilize ionizable lipids that change charge depending on pH, allowing efficient encapsulation during formulation and enhanced cellular uptake in the acidic endosomal environment. The company employs specific lipid compositions including SM-102 (an ionizable lipid), cholesterol, DSPC (distearoylphosphatidylcholine), and PEG-lipids in precise ratios to create a protective shell around the mRNA. This formulation prevents enzymatic degradation while facilitating endosomal escape after cellular uptake. Moderna's LNPs also incorporate polyethylene glycol (PEG) modifications that extend circulation time by reducing clearance and preventing aggregation. Their manufacturing process involves rapid mixing techniques that produce consistently sized particles (approximately 80-100 nm), which is critical for stability, biodistribution, and cellular uptake efficiency.
Strengths: Moderna's LNP technology demonstrates exceptional stability at refrigerated temperatures (2-8°C) for extended periods and has proven efficacy in clinical applications with their COVID-19 vaccine. Their proprietary ionizable lipids show reduced toxicity compared to earlier generations. Weaknesses: The system still requires cold chain storage (-20°C for long-term), limiting distribution in resource-limited settings, and the PEG components may trigger allergic reactions in some individuals.
Critical Patents and Innovations in LNP Formulation
Compositions and methods for stabilization of lipid nanoparticle mRNA vaccines
PatentPendingUS20240041785A1
Innovation
- Development of LNP formulations comprising specific lipid components like ((4-hydroxybutyl)azanediyl)bis(hexane-6,1-diyl)bis(2-hexyldecanoate), 2-[(polyethylene glycol)-2000]-N,N-ditetradecylacetamide, distearoylphosphatidylcholine, and cholesterol, with sucrose or trehalose, and Tris buffer, enabling stability and handling at temperatures up to 25°C or room temperature, and allowing for dry or frozen formulations.
Lipid nanoparticle formulations and methods of synthesis thereof
PatentPendingUS20250281418A1
Innovation
- A method of producing lipid nanoparticles (LNPs) with improved biophysical properties and stability by incorporating specific concentrations of PEG-lipids during different stages of the manufacturing process, including the nanoprecipitation step and excipient addition, to enhance long-term stability and preserve mRNA functionality.
Regulatory Considerations for mRNA-LNP Products
The regulatory landscape for mRNA-LNP products represents a complex and evolving framework that developers must navigate carefully. Regulatory agencies worldwide, including the FDA, EMA, and PMDA, have established specific guidelines addressing the unique characteristics of these advanced therapeutic products. These guidelines focus particularly on stability parameters as critical quality attributes that directly impact safety and efficacy profiles.
Manufacturing consistency requirements for mRNA-LNP systems are especially stringent, with regulatory bodies demanding robust stability data across multiple time points and storage conditions. Developers must demonstrate that their formulations maintain integrity throughout the product lifecycle, from production to administration. This includes comprehensive characterization of particle size distribution, encapsulation efficiency, and lipid oxidation rates under various environmental stresses.
Stability-indicating analytical methods require validation according to ICH guidelines, with particular emphasis on methods that can detect subtle changes in LNP structure and mRNA integrity. Regulatory submissions typically require accelerated and real-time stability studies, with agencies increasingly requesting forced degradation studies to identify potential breakdown products and establish safety margins.
The cold chain requirements for mRNA-LNP products present unique regulatory challenges, with authorities requiring evidence-based justification for storage conditions and shelf-life claims. Temperature excursion studies have become standard expectations in regulatory submissions, with data demonstrating product stability during simulated distribution conditions.
Batch release specifications must include stability-related parameters with scientifically justified acceptance criteria. These specifications often evolve during clinical development as more stability data becomes available, requiring ongoing dialogue with regulatory agencies. Post-approval stability commitments typically include continued monitoring of commercial batches under real-time and accelerated conditions.
Global regulatory harmonization efforts are underway to standardize stability requirements for mRNA-LNP products, though significant regional differences persist. The FDA typically requires more extensive characterization of lipid components and their degradation pathways, while the EMA places greater emphasis on environmental impact assessments of novel lipid excipients. Emerging markets often reference ICH guidelines but may impose additional local requirements based on infrastructure limitations.
Regulatory agencies are increasingly focusing on the relationship between stability parameters and clinical outcomes, requiring sponsors to establish clinically relevant specifications. This trend reflects the maturing regulatory framework for these innovative therapeutic modalities, with stability considerations becoming increasingly integrated into benefit-risk assessments.
Manufacturing consistency requirements for mRNA-LNP systems are especially stringent, with regulatory bodies demanding robust stability data across multiple time points and storage conditions. Developers must demonstrate that their formulations maintain integrity throughout the product lifecycle, from production to administration. This includes comprehensive characterization of particle size distribution, encapsulation efficiency, and lipid oxidation rates under various environmental stresses.
Stability-indicating analytical methods require validation according to ICH guidelines, with particular emphasis on methods that can detect subtle changes in LNP structure and mRNA integrity. Regulatory submissions typically require accelerated and real-time stability studies, with agencies increasingly requesting forced degradation studies to identify potential breakdown products and establish safety margins.
The cold chain requirements for mRNA-LNP products present unique regulatory challenges, with authorities requiring evidence-based justification for storage conditions and shelf-life claims. Temperature excursion studies have become standard expectations in regulatory submissions, with data demonstrating product stability during simulated distribution conditions.
Batch release specifications must include stability-related parameters with scientifically justified acceptance criteria. These specifications often evolve during clinical development as more stability data becomes available, requiring ongoing dialogue with regulatory agencies. Post-approval stability commitments typically include continued monitoring of commercial batches under real-time and accelerated conditions.
Global regulatory harmonization efforts are underway to standardize stability requirements for mRNA-LNP products, though significant regional differences persist. The FDA typically requires more extensive characterization of lipid components and their degradation pathways, while the EMA places greater emphasis on environmental impact assessments of novel lipid excipients. Emerging markets often reference ICH guidelines but may impose additional local requirements based on infrastructure limitations.
Regulatory agencies are increasingly focusing on the relationship between stability parameters and clinical outcomes, requiring sponsors to establish clinically relevant specifications. This trend reflects the maturing regulatory framework for these innovative therapeutic modalities, with stability considerations becoming increasingly integrated into benefit-risk assessments.
Manufacturing Challenges and Scale-up Solutions
The manufacturing of mRNA lipid nanoparticle (LNP) systems presents significant challenges when transitioning from laboratory-scale production to industrial manufacturing. One primary challenge is maintaining consistent particle size distribution during scale-up, as even minor variations can dramatically affect biodistribution, cellular uptake, and ultimately therapeutic efficacy. Traditional microfluidic mixing devices that work effectively at small scales often encounter flow rate limitations and potential clogging issues when production volumes increase.
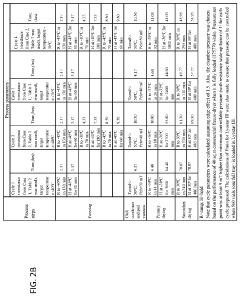
Temperature control represents another critical manufacturing challenge. The lipid-ethanol and mRNA-aqueous phases must be maintained at precise temperatures throughout the mixing process to ensure proper LNP formation. As batch sizes increase, maintaining uniform temperature becomes increasingly difficult, potentially leading to heterogeneous particle populations and reduced stability.
Sterility assurance during large-scale production poses additional complications. Unlike small-scale laboratory environments, industrial manufacturing requires closed systems with rigorous contamination controls. The implementation of aseptic processing techniques while maintaining the delicate balance of LNP formation parameters demands sophisticated engineering solutions and validated cleaning protocols.
Scale-up solutions have emerged to address these manufacturing hurdles. Advanced microfluidic platforms with parallelized mixing channels allow for increased throughput while maintaining the critical parameters that ensure LNP stability. These systems can process larger volumes while preserving the rapid mixing kinetics essential for consistent nanoparticle formation.
Continuous manufacturing approaches represent a paradigm shift from traditional batch processing. These systems enable consistent production of LNPs with improved homogeneity by maintaining identical mixing conditions throughout the manufacturing run. Integrated process analytical technology (PAT) allows real-time monitoring of critical quality attributes, enabling immediate adjustments to preserve stability parameters.
Cryoprotectant optimization has proven essential for maintaining LNP integrity during freeze-thaw cycles in large-scale production. Systematic studies have identified optimal combinations of sugars, amino acids, and other excipients that prevent aggregation and lipid bilayer disruption during freezing and subsequent storage.
Automated formulation systems with precise control over mixing ratios, flow rates, and environmental conditions have significantly improved manufacturing reproducibility. These systems minimize human intervention, reducing variability while enabling the production of consistent LNP batches with predictable stability profiles across multiple manufacturing sites.
Temperature control represents another critical manufacturing challenge. The lipid-ethanol and mRNA-aqueous phases must be maintained at precise temperatures throughout the mixing process to ensure proper LNP formation. As batch sizes increase, maintaining uniform temperature becomes increasingly difficult, potentially leading to heterogeneous particle populations and reduced stability.
Sterility assurance during large-scale production poses additional complications. Unlike small-scale laboratory environments, industrial manufacturing requires closed systems with rigorous contamination controls. The implementation of aseptic processing techniques while maintaining the delicate balance of LNP formation parameters demands sophisticated engineering solutions and validated cleaning protocols.
Scale-up solutions have emerged to address these manufacturing hurdles. Advanced microfluidic platforms with parallelized mixing channels allow for increased throughput while maintaining the critical parameters that ensure LNP stability. These systems can process larger volumes while preserving the rapid mixing kinetics essential for consistent nanoparticle formation.
Continuous manufacturing approaches represent a paradigm shift from traditional batch processing. These systems enable consistent production of LNPs with improved homogeneity by maintaining identical mixing conditions throughout the manufacturing run. Integrated process analytical technology (PAT) allows real-time monitoring of critical quality attributes, enabling immediate adjustments to preserve stability parameters.
Cryoprotectant optimization has proven essential for maintaining LNP integrity during freeze-thaw cycles in large-scale production. Systematic studies have identified optimal combinations of sugars, amino acids, and other excipients that prevent aggregation and lipid bilayer disruption during freezing and subsequent storage.
Automated formulation systems with precise control over mixing ratios, flow rates, and environmental conditions have significantly improved manufacturing reproducibility. These systems minimize human intervention, reducing variability while enabling the production of consistent LNP batches with predictable stability profiles across multiple manufacturing sites.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!