Butterfly orchid breeding method
A technique of Phalaenopsis and seedlings, which is applied in the breeding field of Phalaenopsis, can solve the problems such as the inability to guarantee the stability of seedlings, and achieve the effects of ensuring health and maturity, stable traits, and shortening the breeding period
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 2
[0050] The operation is basically the same as in Example 1, the difference is that in cross pollination: the female parent is JB2083; the male parent is JB2068
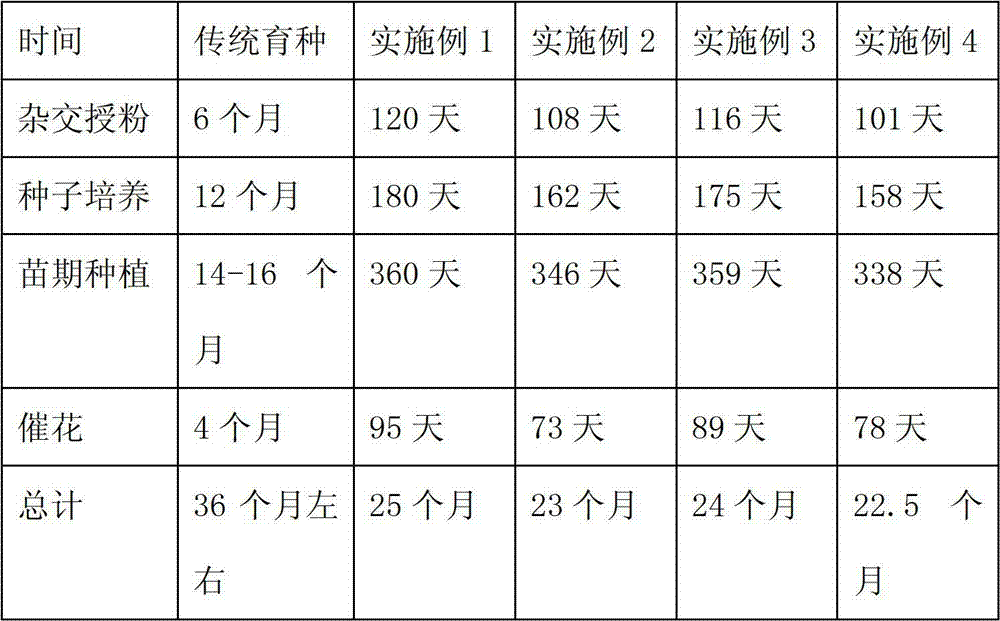
[0051] A. The first is the choice of time, choose to carry out pollination and hybridization between March and May every year, followed by the control of temperature and humidity, the temperature is controlled at 28±2°C, and the humidity is controlled at 60-80%. It takes about 4 months from pollination to fruit pod maturity.
[0052] B, the cultivation of seeds: Utilize aseptic sowing technique to sow mature fruit pods, what first implanted is Phalaenopsis sowing medium (Table 1), when 35 days after sowing, move into the medium (Table 2) that promotes the growth of protosphere ), to increase the growth space and promote growth; after 41 days of cultivation, replace it with a medium that promotes the growth of seedlings (Table 3); after 45 days of cultivation, the seedlings can be removed from the bottle for planting.
...
Embodiment 3
[0059] The operation is basically the same as in Example 1, the difference is that in cross pollination: the female parent is JB2191; the male parent is JB2088
[0060] A. Cross-pollination: Firstly, the choice of time, choose to carry out pollination and hybridization between March and May every year, followed by the control of temperature and humidity, the temperature is controlled at 28±2°C, and the humidity is controlled at 60-80%. Pollination to pod maturity is controlled within 4 months.
[0061] B, the cultivation of seeds: Utilize aseptic sowing technique to sow mature fruit pods, what first implanted is Phalaenopsis sowing medium (table 1), when 35-45 days after sowing, move into the medium that promotes the growth of protosphere ( Table 2), to increase the growth space and promote growth; after 35-45 days of cultivation, replace it with a medium that promotes the growth of seedlings (Table 3); after 45-60 days of cultivation, the seedlings can be removed from the bot...
Embodiment 4
[0069] The operation is basically the same as in Example 1, the difference is that in cross pollination: the female parent is JB2088; the male parent is JB2094
[0070] A. Cross-pollination: Firstly, the choice of time, choose to carry out pollination and hybridization between March and May every year, followed by the control of temperature and humidity, the temperature is controlled at 28±2°C, and the humidity is controlled at 60-80%. Pollination to pod maturity is controlled within 4 months.
[0071] B, the cultivation of seeds: Utilize aseptic sowing technique to sow mature fruit pods, what first implanted is Phalaenopsis sowing medium (table 1), when 35-45 days after sowing, move into the medium that promotes the growth of protosphere ( Table 2), to increase the growth space and promote growth; after 35-45 days of cultivation, replace it with a medium that promotes the growth of seedlings (Table 3); after 45-60 days of cultivation, the seedlings can be removed from the bot...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com