Adaptive Zero Attraction Factor Blind Decision Feedback Equalization Algorithm with Sparse Constraint
A technology of decision feedback equalization and sparse constraints, which is applied to baseband system components, baseband systems, shaping networks in transmitters/receivers, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
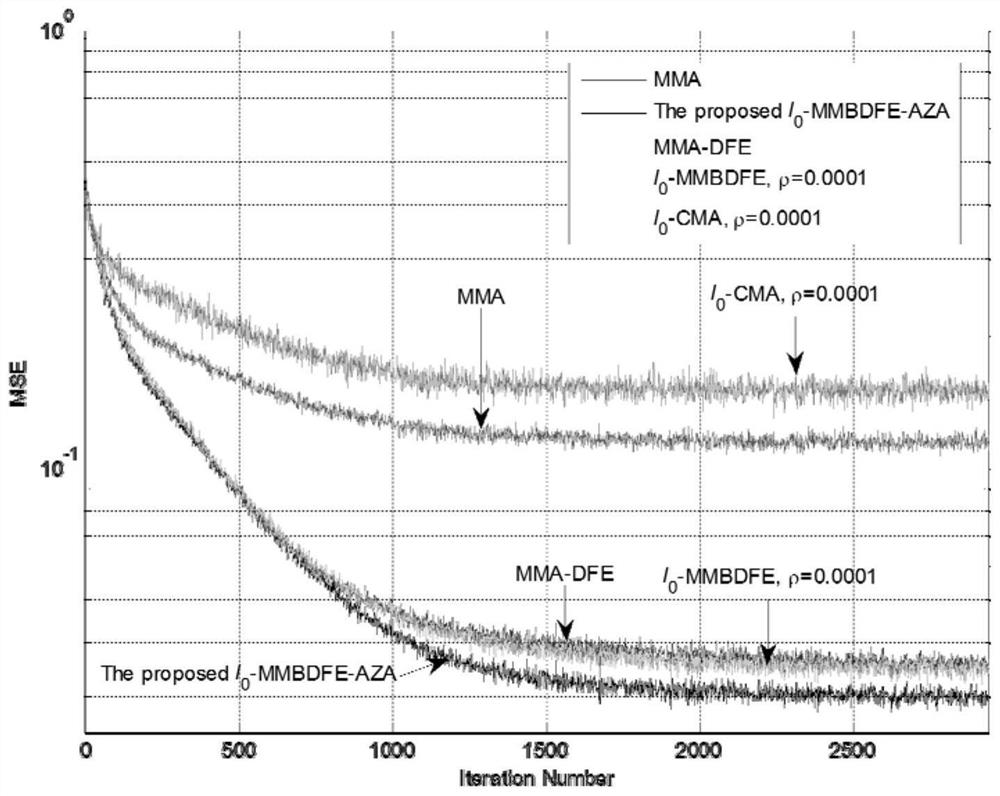
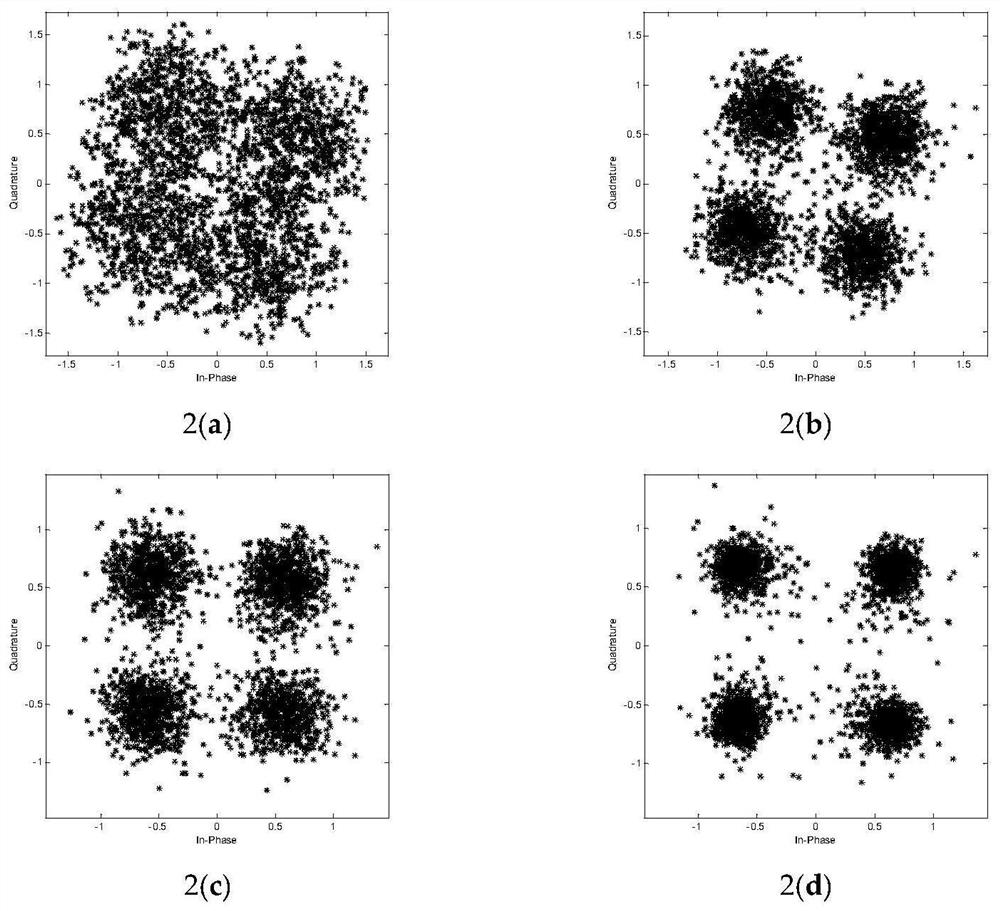
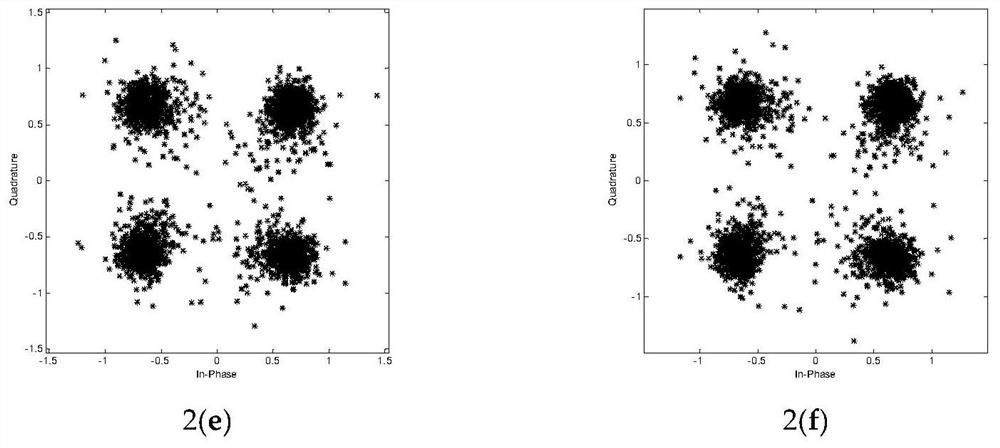
[0100] Compare 1 among the present invention below 0 - Performance of MMBDFE-AZA and existing methods. During the simulation, the underwater acoustic channel is generated using the Bellhop model, which is a ray acoustic model based on the Gaussian beam tracking method. In this model, the carrier frequency is 15khz, the distance between the transmitter and receiver is set to 1000m, the transmitter is located at a depth of 5m, the receiver is located at a depth of 10m, the sound velocity is set to 1540-1543, and the wave height is set to 0.2m. The modulation method adopts QPSK. In (22) and (23), μ f and μ b Both are set to 0.005. The symbol transmission rate is 4000 bits / second, the tap length of FFF is set to 59, and the tap length of FBF is set to 45. The tap coefficient vector of FFF initializes the center tap to be 1 and the other taps to zero, while the tap coefficient vector of FBF is initialized to all zero values. The variables used in the proposed algorithm are in...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com