Control system and control method for short message value-added service
A service control and value-added service technology, applied in the direction of message/mailbox/notification, electrical components, radio/inductive link selection and arrangement, etc., can solve the problem that the short message center or short message gateway is not suitable for one-time transformation, so as to avoid continuous Change, flexible processing, and achieve the effect of control processing
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
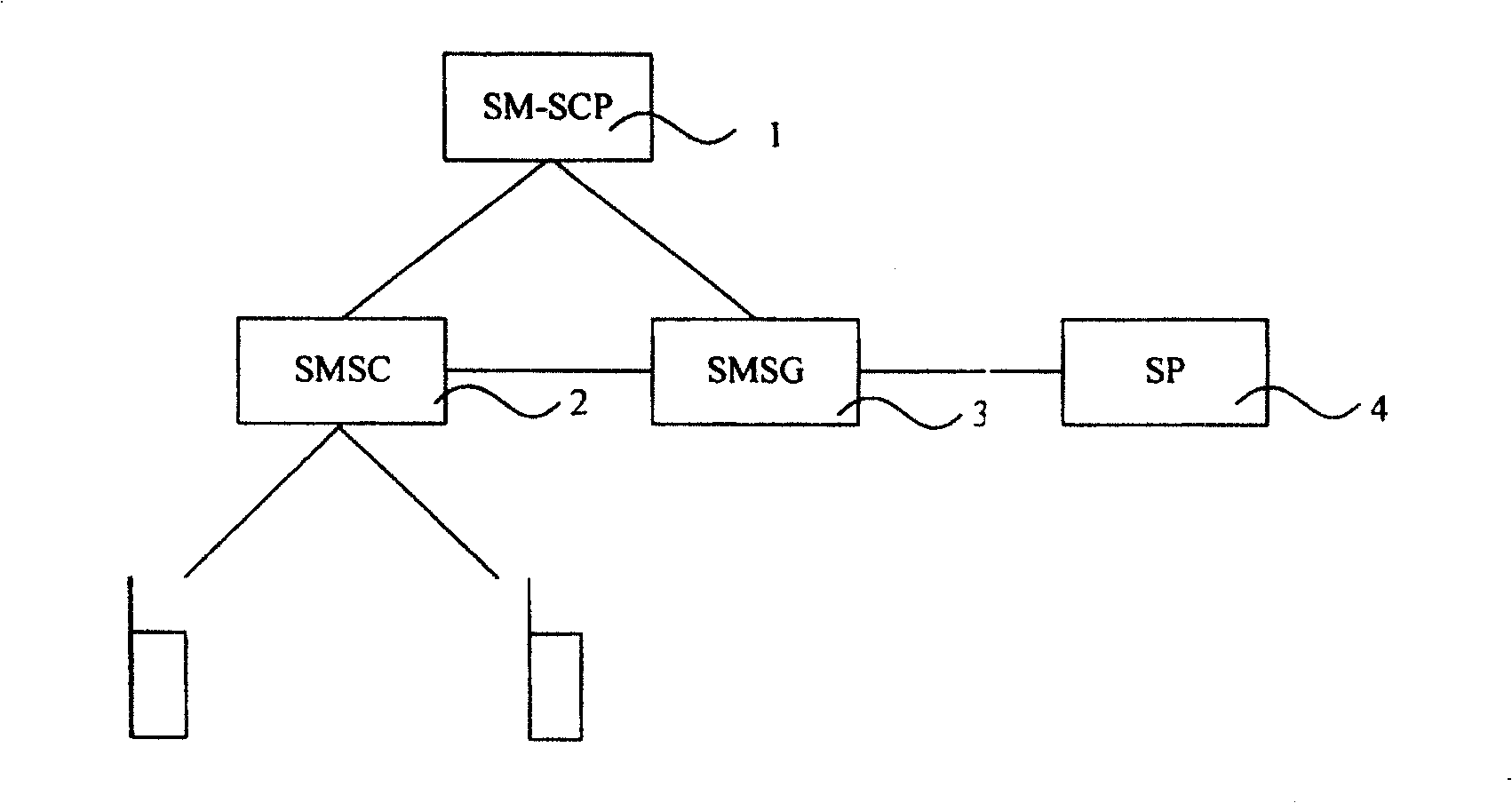
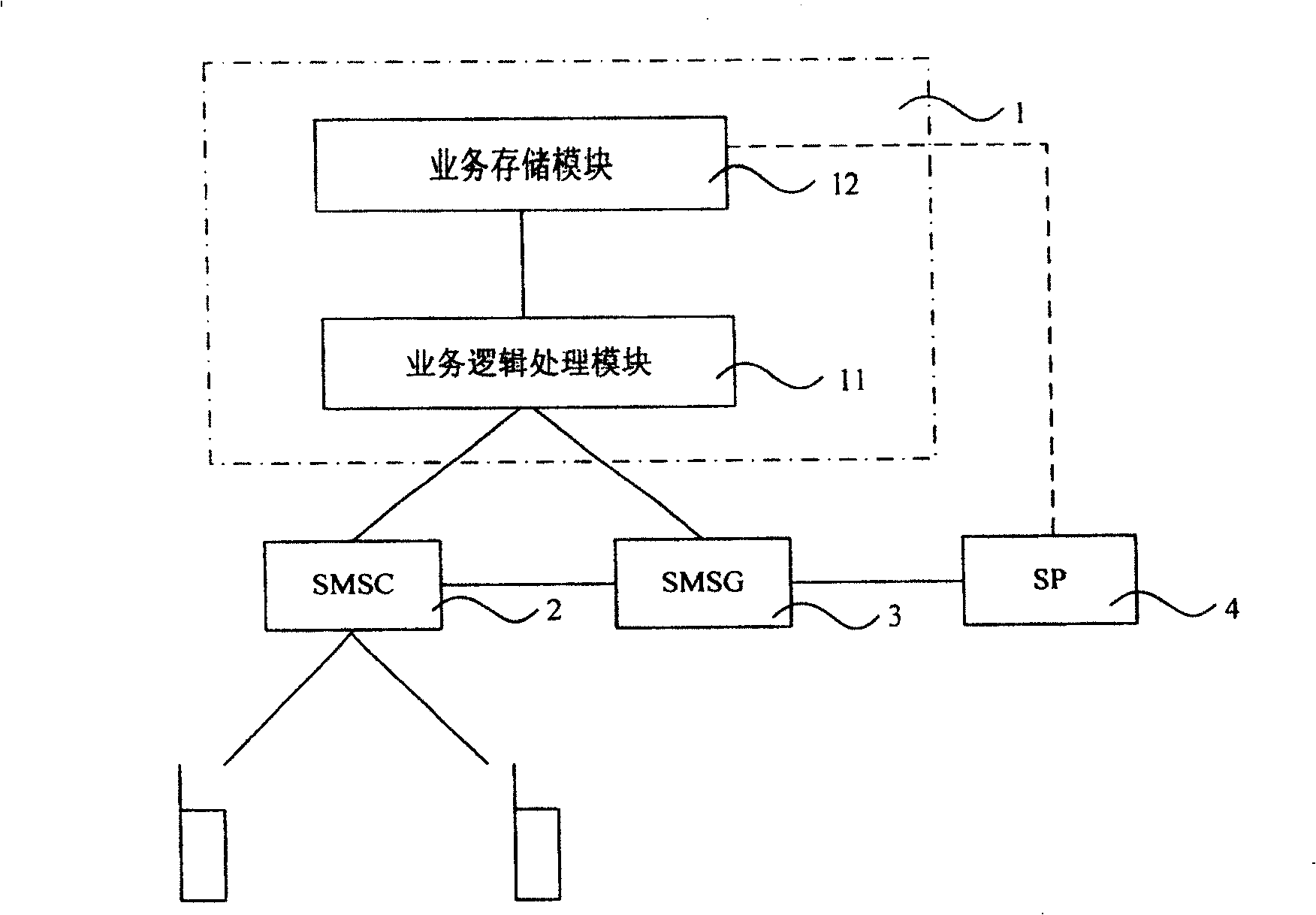
[0097] This embodiment is a process of sending a short message to the user terminal B by the user terminal A customized with the colorful processing function of the short message, including the following steps:
[0098] Step 101: SP1 actively synchronizes user terminal A and its service logic to SM-SCP;
[0099] Step 102: User terminal A sends a common short message to the SMSC, with the destination address being user terminal B;
[0100] Step 103: Upon receiving the short message, the SMSC realizes the control trigger condition: the MO short message is received;
[0101] Step 104: The SMSC sends the short message service to the SM-SCP device;
[0102] Step 105: The SM-SCP device invokes the logic of the sender user, namely user terminal A, and finds that the business modification logic is colorful processing, then modifies the content of the short message, and converts the black and white text short message into a colorful text short message;
[0103] Step 106: The SM-SCP device ...
Embodiment 2
[0108] This embodiment is a process for user terminal B that has customized short message forwarding to receive short messages, including the following steps:
[0109] Step 201, SM-SCP actively queries SP2, and synchronizes user terminal B and its business logic "forward to terminal C" and "holiday short message", and SP2's "receipt of called party";
[0110] Step 202: SP2 sends a holiday short message to SMSG, with the target address being user terminal B;
[0111] Step 203: When SMSG receives the short message, the control trigger condition is realized: the AO short message is received;
[0112] Step 204: The SMSG sends the short message service to the SM-SCP device;
[0113] Step 205: The SM-SCP device invokes the sender user, that is, the SP2 logic, and finds that there is a "callee receipt", it enters the sending status report processing, and inserts the status report identifier into the short message content;
[0114] Step 206: The SM-SCP device invokes the logic of the reci...
Embodiment 3
[0126] This embodiment is a process of sending failed point-to-point short messages for multiple times, including the following steps:
[0127] Step 301: The user terminal A sends a short message to the SMSC, and the destination is the user terminal B;
[0128] Step 302: After the SMSC has directly issued three failures, the trigger control condition is reached;
[0129] Step 303: The SMSC sends the short message to the SM-SCP;
[0130] Step 304: The SM-SCP returns a termination instruction according to the default parameters of the system;
[0131] Step 305: The SMSC ends the short message sending.
[0132] It can be seen from this embodiment that this method is also applicable to point-to-point short message services, and the realized processing operation is: abandon the short message and suspend the current short message processing flow.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com