Decoding device and method
A decoding device and decoding technology, which are applied in the field of decoding devices and decoding, can solve the problems of synchronization code pseudo-synchronization and synchronization deviation, deviation, synchronization code false detection, false synchronization and synchronization, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
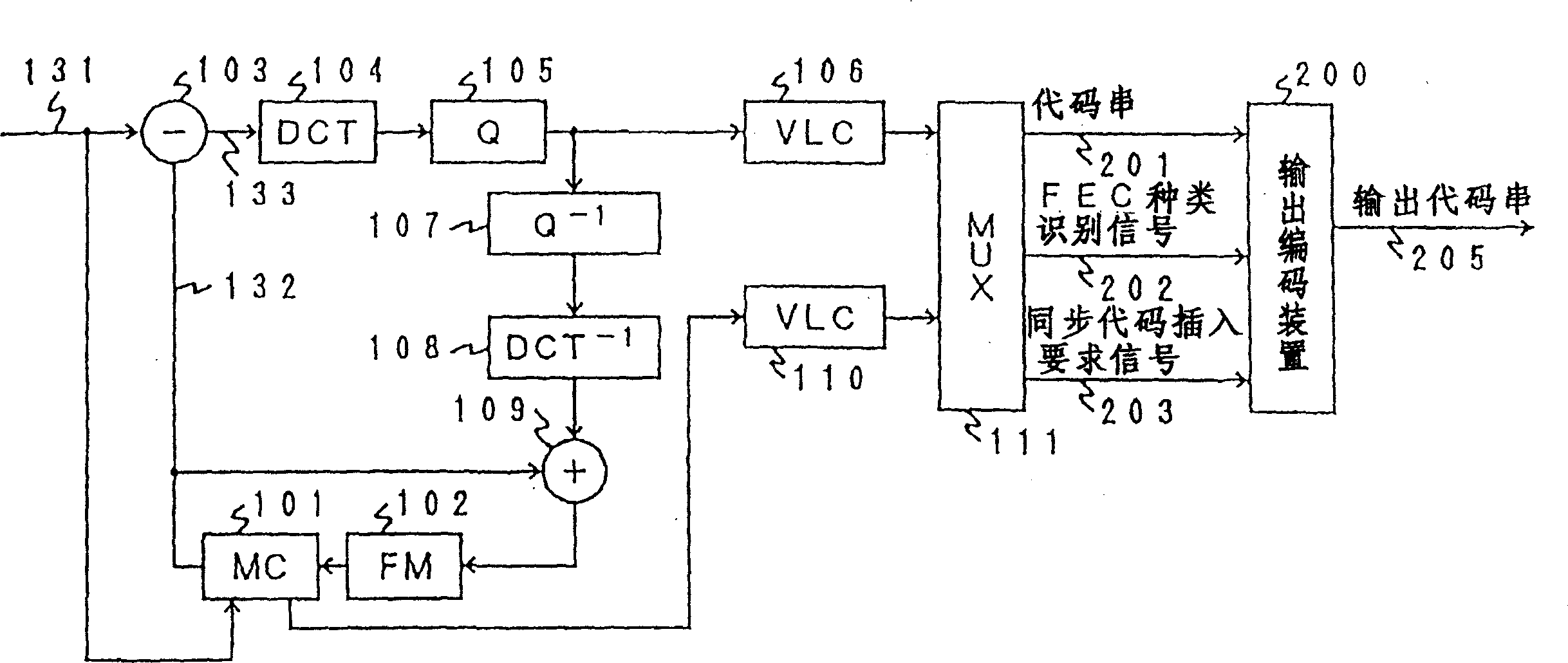
[0095] figure 1 It represents the moving image coding that combines the coding device having the error correction / detection code switching function of the present invention with a high-efficiency compression coding device that uses motion compensation adaptive prediction and orthogonal transform coding, that is, discrete cosine transform coding. Block diagram of Example 1 of the device. Regarding the encoding method combining adaptive prediction with motion compensation and discrete cosine transform encoding, for example, there are detailed descriptions in Document 1: Edited by Hiroshi Yasuda, "International Standards for Symbolization of Malchi Media", Maruzen, (June 2013), etc. Note, therefore, only an overview of the action is described here. In addition, the error correction / detection codes used in this embodiment are codes separated into information bits and check bits like BCH codes.
[0096] exist figure 1In this method, the input moving image signal 131 to be code...
Embodiment 2
[0171] Below, refer to Figure 12 to Figure 14 Example 2 of the present invention will be described. Even if the moving image encoding device and moving image decoding device of the present embodiment use a transmission path / storage medium in which a part of a bit sequence is eliminated to reduce the number of bits or add extra bits to increase the number of bits, the code sequence is transmitted / stored. , can also be reliably detected synchronously.
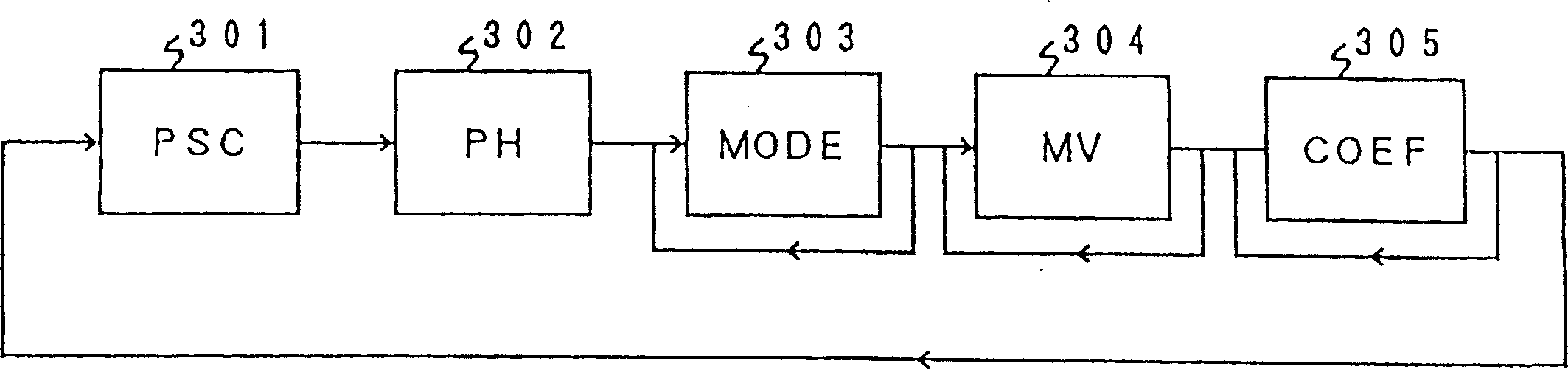
[0172] Figure 12 It is a block diagram showing the principle of the synchronization detection processing at the time of such bit addition / deletion. here, as Figure 12 As shown in (a), the correct synchronization code is composed of "0" of sync_0_len bit and "1" of 1 bit. Figure 12 The "×" in is a bit other than the synchronization code.
[0173] Figure 12 (b) to (e) show how the synchronization code changes due to bit addition / deletion. Here, the number of bits (Nid) to be added / disappeared is 1 bit at most. (b) is a...
Embodiment 3
[0221] Next, Embodiment 3 of the present invention will be described. The difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 and Embodiment 2 is that no error correction / detection code is used.
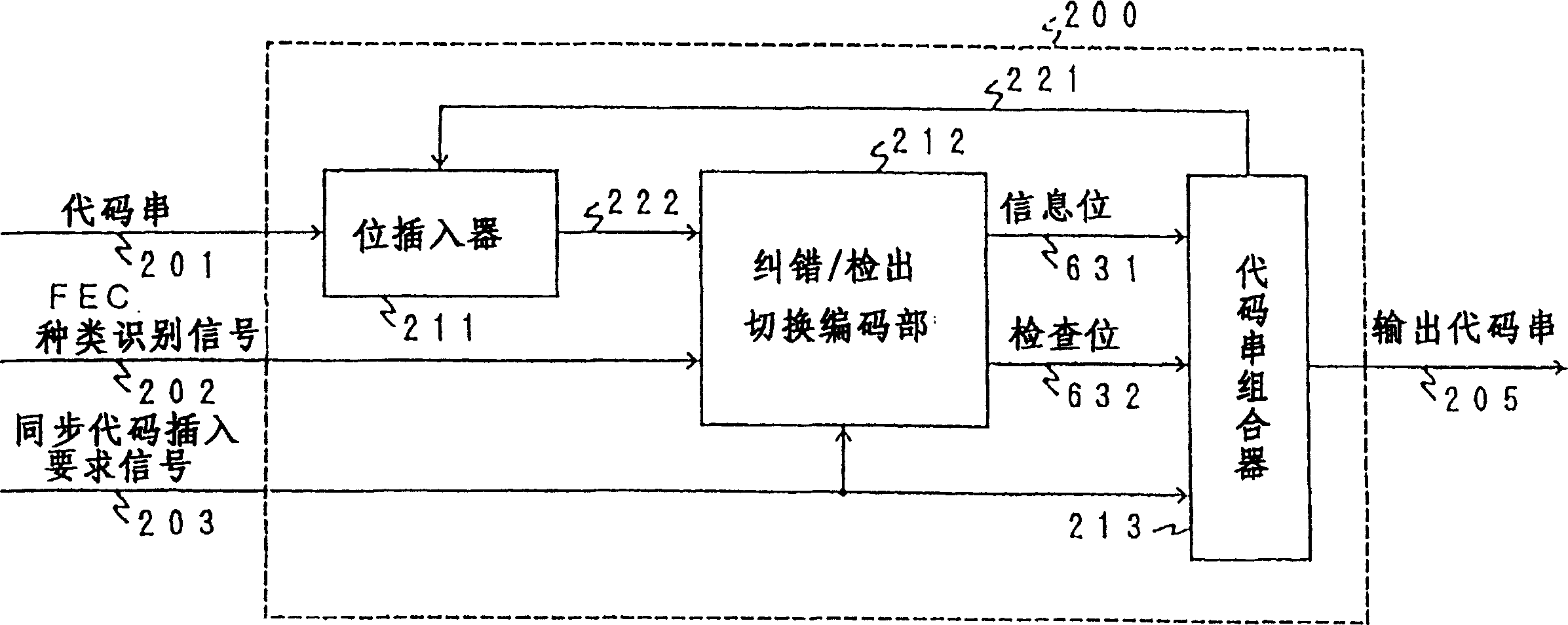
[0222] Figure 18 It is a block diagram of the video coding apparatus of this embodiment. right with figure 1 Corresponding parts are denoted by the same symbols and will be described focusing on differences from Embodiment 1. In this embodiment, the structure and operation of the output encoding device 200 are different. In addition, the basic actions of multiplexer 111 and figure 1 The multiplexer 111 is the same, however, as the error correction / detection code is not used, only the multiplexed code string 201 and the synchronous code insertion request signal 203 are output.
[0223] Figure 19 yes means Figure 18 A block diagram of the structure of the output encoding device 200 in FIG. The output encoding device 200 is composed of a counter 1701 for counting the number ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com