Pulse codec method and pulse codec
A pulse coding and pulse technology, used in instruments, code conversion, speech analysis, etc., can solve the problems of waste of coding bits, accumulation of coding index redundancy, and large computational complexity, and achieve the effect of saving coding bits.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
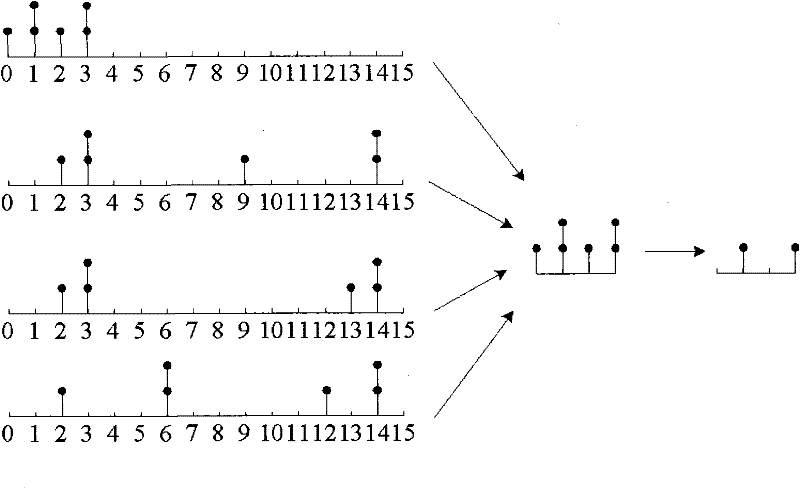
[0064] Embodiment 1. A pulse encoding method, such as figure 1 shown, including:
[0065] A1. Obtain pulses to be encoded on T tracks, where T is an integer greater than or equal to 2.
[0066] The total number of pulses that need to be encoded on each of the T tracks is usually determined according to the code rate. The more pulses that need to be encoded, the more bits are required for the encoding index and the higher the code rate. In this paper, pulse_num t Indicates the total number of pulses that need to be encoded on the t-th track, assuming The total number of pulses on each track jointly encoded can be the same or different.
[0067] A2. Count the pulses that need to be encoded on each track according to their positions, and obtain the number N of pulse positions on each track t , the distribution of pulsed positions on the track and the number of pulses at each pulsed position.
[0068] In this article:
[0069] to pos_num t Indicates the number of pulse po...
Embodiment 2
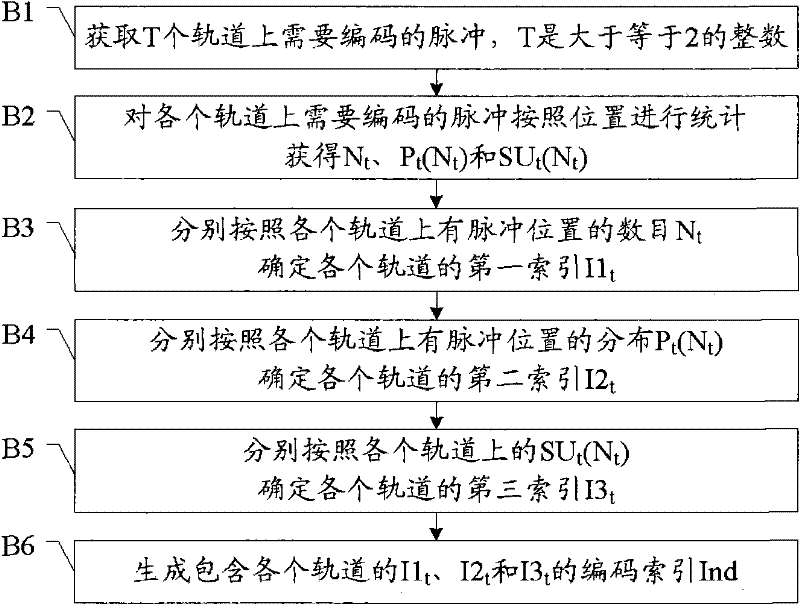
[0124] Embodiment 2. A pulse encoding method. In this embodiment, each track of the joint encoding is calculated for its respective index, and then combined into an encoding index, such as image 3 shown, including steps:
[0125] B1. Obtain pulses to be encoded on T tracks, where T is an integer greater than or equal to 2.
[0126] B2, count the pulses that need to be encoded on each track according to their positions, and obtain the number N of pulse positions on each track t , the distribution of pulsed positions on the track and the number of pulses at each pulsed position.
[0127] Steps B1 and B2 can be performed with reference to steps A1 and A2 of Embodiment 1.
[0128] B3. Determine the first index I1 of each track according to the number of pulse positions on each track respectively t , the first index I1 t Corresponding to the number of pulse positions it represents, all possible distributions of pulse positions on the track.
[0129] B4. Determine the second i...
Embodiment 3
[0139] Embodiment 3. A pulse coding method. This embodiment is based on Embodiment 1 or 2 and proposes a method for further saving coding bits.
[0140] The encoding index Ind generation process of the pulse encoding method in this embodiment can be performed with reference to the method in the first or second embodiment, and the following operations are performed after the encoding index Ind is generated, such as Figure 4 shown, including:
[0141] C1. Comparing the coding index Ind and adjusting the threshold value THR, wherein,
[0142] THR≤2 Bmax -I max (T),
[0143] I max (T) represents the upper limit of Ind, Bmax represents the upper limit of the number of bits used to encode the coding index, if Ind is less than THR, then go to step C2, otherwise go to step C3.
[0144] C2. Encode Ind by using the first number of encoding bits.
[0145] C3, using the second number of coded bit pairs plus an offset value THR 0 Ind is encoded, THR≤THR 0 ≤2 Bmax -I max (T), the...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com