RNAi-RELATED INHIBITION OF TNFalpha SIGNALING PATHWAY FOR TREATMENT OF OCULAR ANGIOGENESIS
a technology of tnfalpha signaling pathway and rnai, which is applied in the direction of drug compositions, genetic material ingredients, organic chemistry, etc., can solve the problems of tissue edema, impaired differentiation process, wet or exudative amd, and subsequent loss of cones and rods
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Interfering RNA for Specifically Silencing TNFR1 in GTM-3 Cells
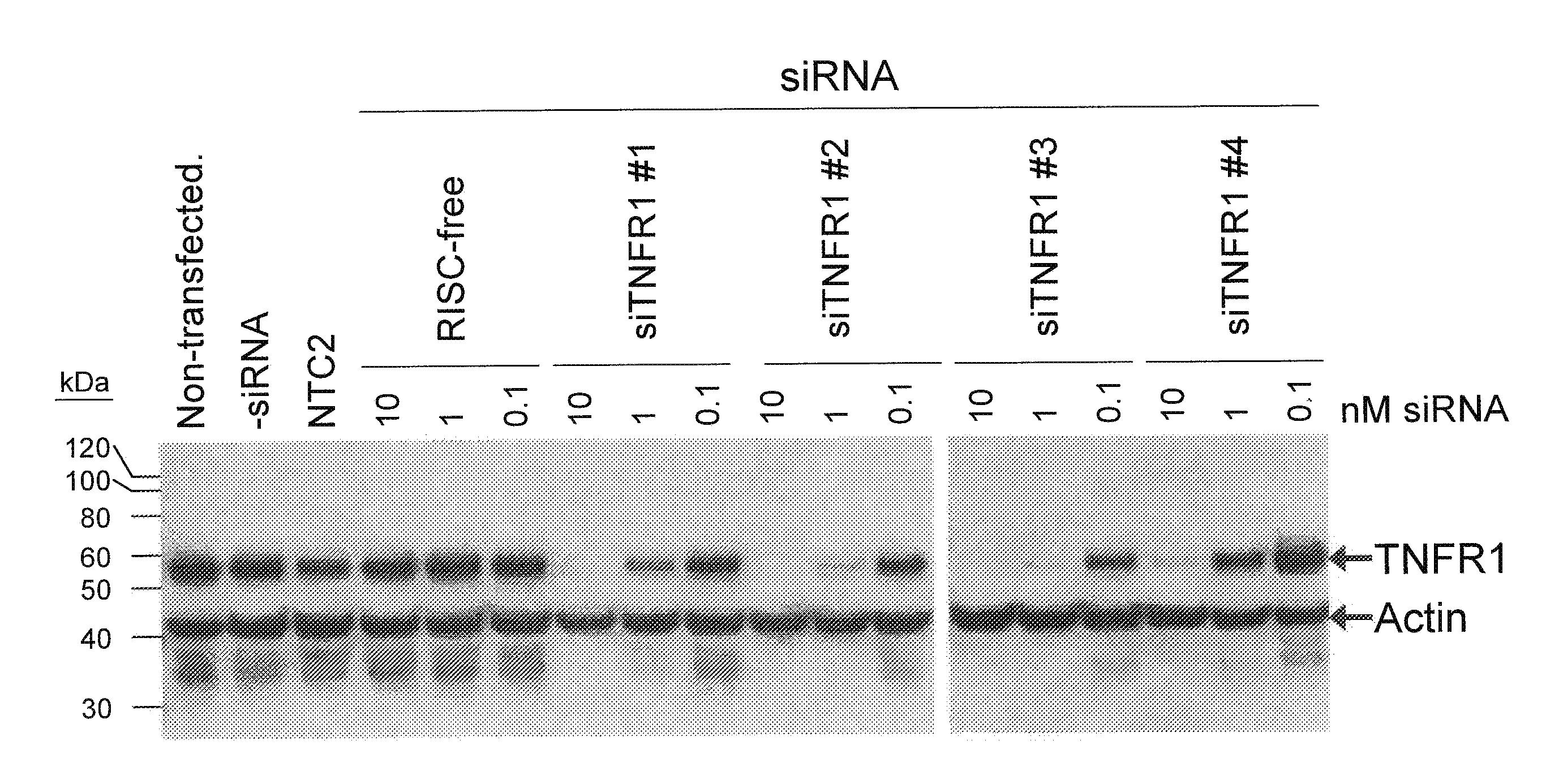
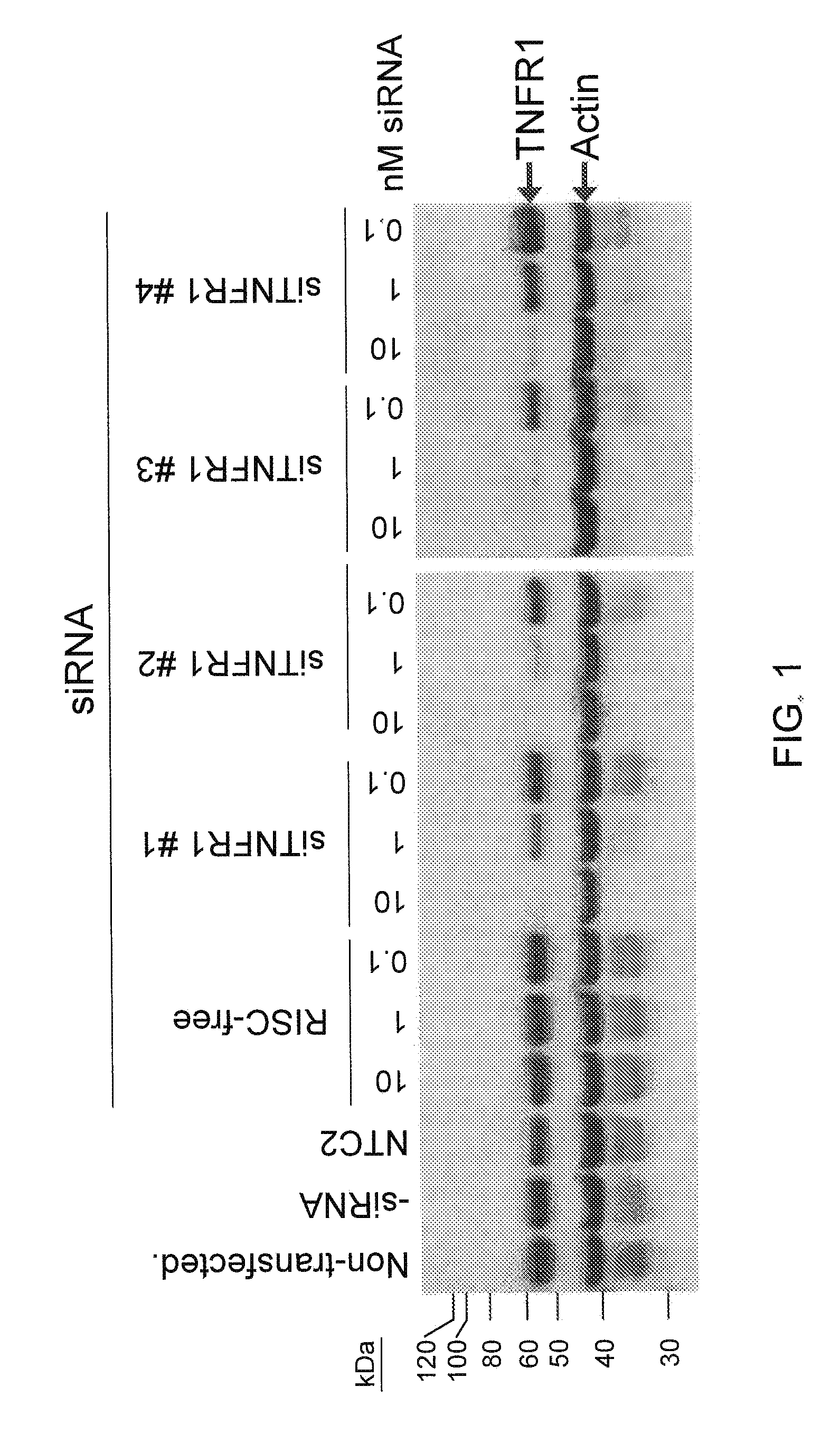
[0116]The present study examines the ability of TNFR1 interfering RNA to knock down the levels of endogenous TNFR1 protein expression in cultured GTM-3 cells.
[0117]Transfection of GTM-3 cells (Pang, I. H. et al., 1994. Curr. Eye Res. 13:51-63) was accomplished using standard in vitro concentrations (0.1-10 nM) of TNFR1 siRNAs, siCONTROL RISC-free siRNA, or siCONTROL Non-targeting siRNA #2 (NTC2) and DHARMAFECT® #1 transfection reagent (Dharmacon, Lafayette, Colo.). All siRNAs were dissolved in 1× siRNA buffer, an aqueous solution of 20 mM KCl, 6 mM HEPES (pH 7.5), 0.2 mM MgCl2. Control samples included a buffer control in which the volume of siRNA was replaced with an equal volume of 1× siRNA buffer (-siRNA). Western blots using an anti-TNFR1 antibody (Santa Cruz Biotechnology, Santa Cruz, Calif.) were performed to assess TNFR1 protein expression. The TNFR1 siRNAs are double-stranded interfering RNAs having specificity f...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com