Resource allocation method and resource allocation system
A technology of resource allocation and correspondence table, applied in transmission systems, allocation standards, digital transmission systems, etc., can solve problems such as system performance degradation and improper cooperation, and achieve the effect of high theoretical spectral efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
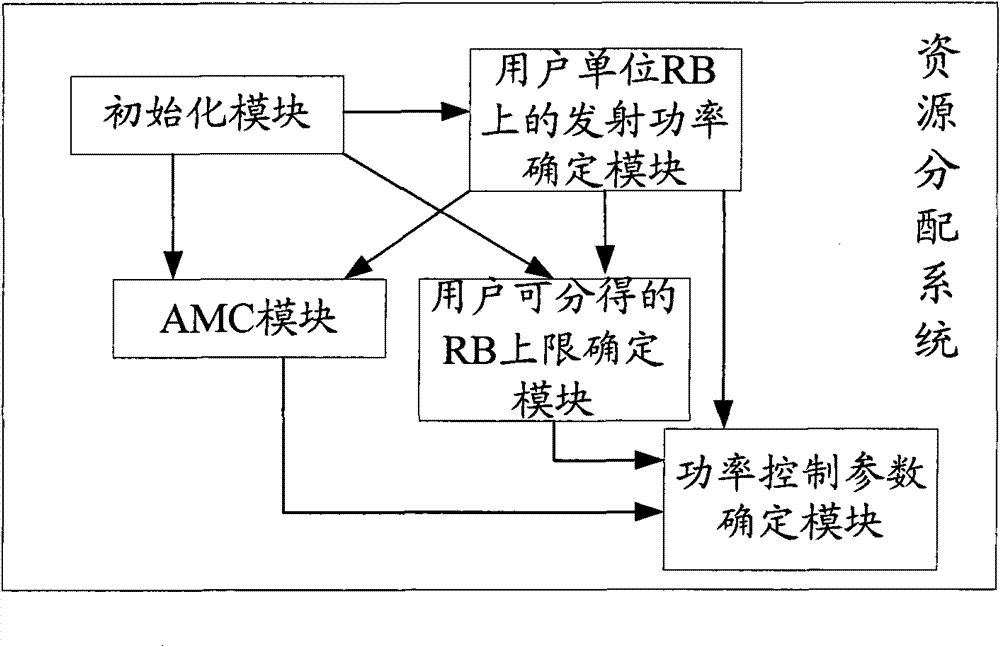
Image
Examples
example 1
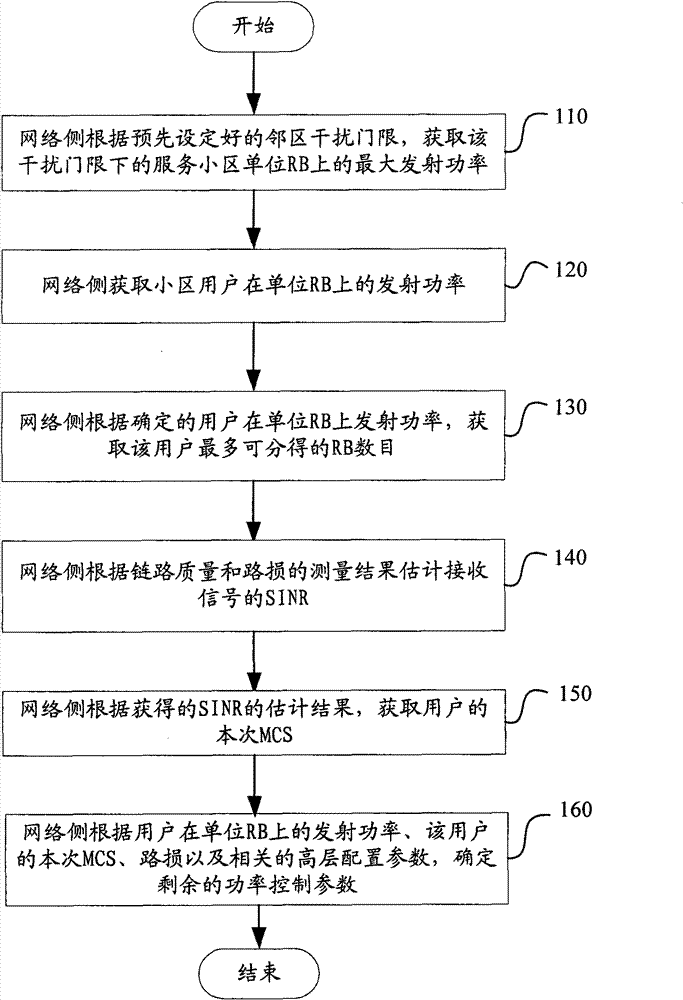
[0064] Example 1 provides a cooperative method of uplink RB allocation, AMC and power control, such as image 3 shown, including the following steps:
[0065] In step 301, the eNodeB acquires the maximum transmit power on the unit RB of the serving cell under the interference threshold according to the preset neighbor cell interference threshold, denoted as; P MAXfromInterference
[0066] Assumption: the user’s signal transmission power is P, the path loss to the serving cell is PL, the path loss to the neighbor cell eNodeBi is PLi′, and the neighbor cell eNodeBi interference threshold is set to Pi InterferenceTh , the number of adjacent eNodeBs i≤N Neighbor , then P-PLi′≤Pi InterferenceTh When i=1,...,N Neighbor , where N Neighbor Indicates the number of neighboring cells of the current serving cell;
[0067] so as to get P MAXfromInterfercnce =Min{Pi InterferenceTh +PLi'}, where i=1,...,N Neighbor
[0068] Step 302, the eNodeB obtains the transmit power of the user...
example 2
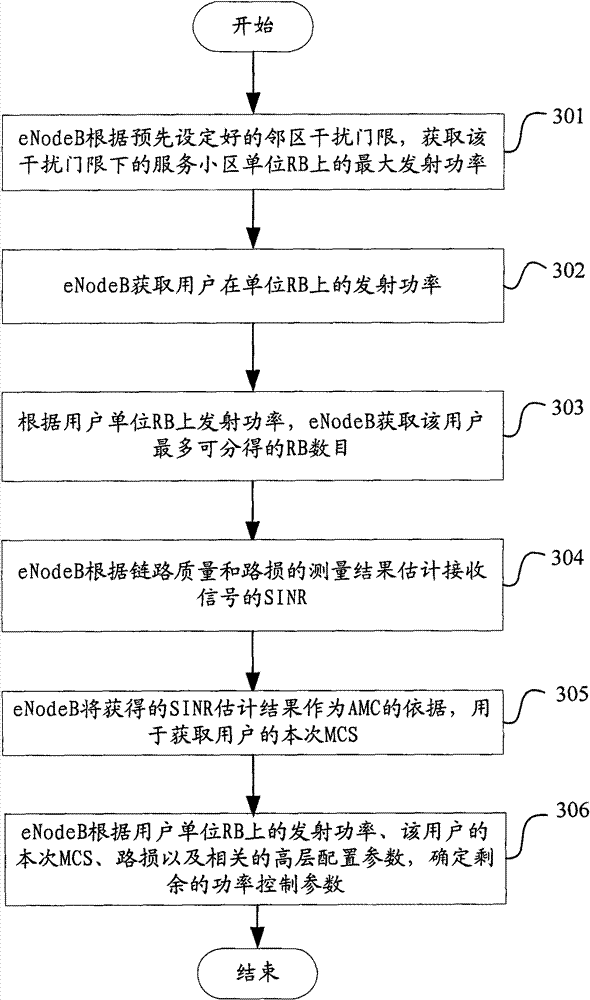
[0083] Example 2 provides a cooperative method of uplink RB allocation, AMC and power control, such as Figure 4 As shown, the method includes the following steps:
[0084] In step 401, the eNodeB obtains the maximum transmit power on the unit RB of the serving cell under the interference threshold according to the preset neighbor cell interference threshold, denoted as P MAXfromInterference ;
[0085] Such as Figure 5 As shown, the wireless network model with the number of neighboring cells as one is taken as an example; the signal transmission power of the serving cell is set to P, the path loss is PL, the path loss when reaching the neighboring cell eNodeB is PL′, and the neighboring cell interference threshold is set to P InterferenceTh , then P-PL′≤P InterferenceTh ;
[0086] so as to get P MAXfromInterfercnce =P InterferenceTh +PL'
[0087] Step 402, the eNodeB obtains the transmit power of the user on the unit RB;
[0088] The maximum transmit power of the desi...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com