Arbitrary boundary optical element uniline non-intersected random machining path planning method
A technology for optical components and processing paths, which is applied in the field of random path planning for small tool processing, and can solve problems such as difficulty in adapting to arbitrary boundary optical components, intermediate frequency errors, and crossing paths.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0040] The present invention will be further described below in conjunction with the embodiments and accompanying drawings, but the protection scope of the present invention should not be limited thereto.
[0041] A method for generating a computer-controlled small tool processing path for an arbitrary boundary optical element, comprising the following steps:
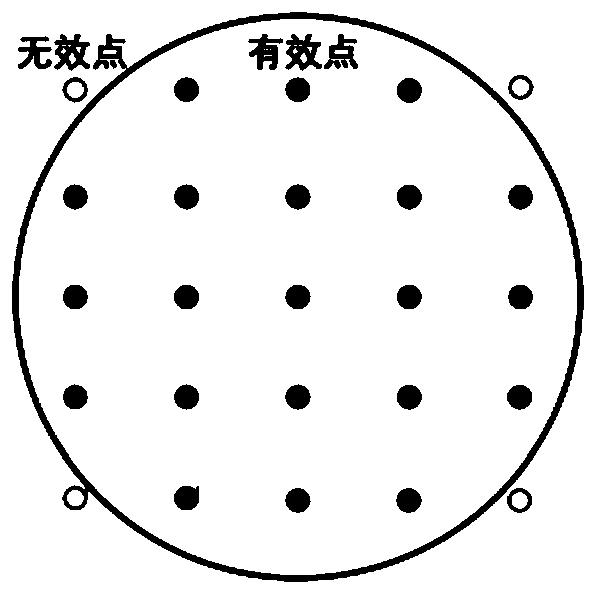
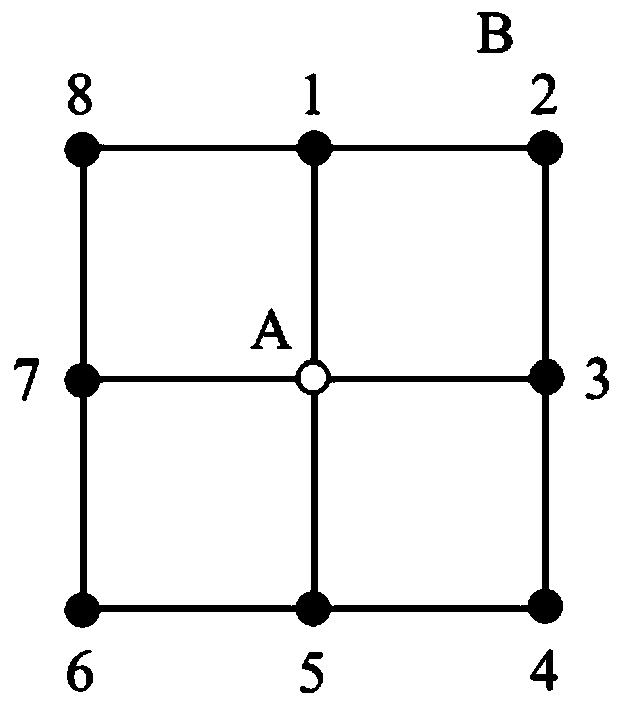
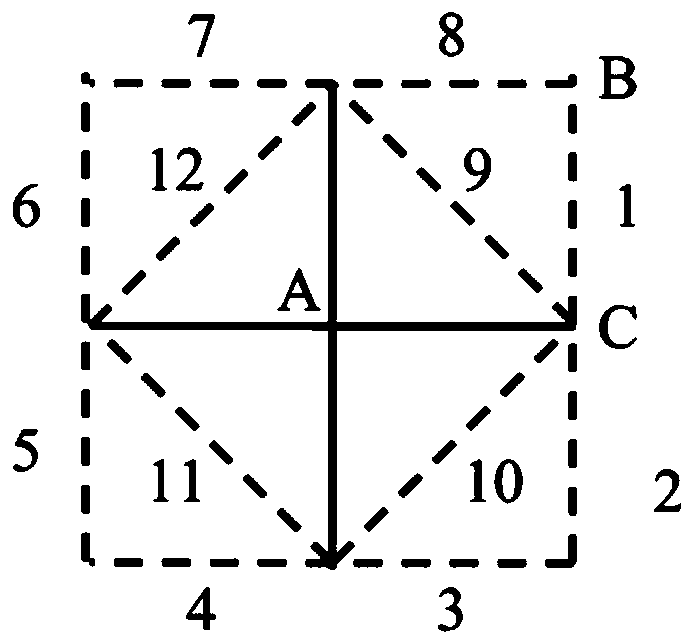
[0042] Step 1: Create three empty sets: a set of path points, a set of non-path points and a set of adjacent points. The elements in the three sets are the coordinate pairs corresponding to the points: (abscissa, ordinate). The set of waypoints is ordered, the set of non-waypoints and the set of adjacent points are unordered. figure 1Shown is a schematic diagram of the mesh division. The caliber of the component to be processed is divided into grids, and the grid spacing is equal to the grid spacing when calculating the dwell time. Select a full-caliber rectangular area that can cover the continuation distance as the ...
PUM
 Login to view more
Login to view more Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to view more
Login to view more - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap