Generation of failure models for embedded analytics and diagnostic/prognostic reasoning
A fault model, fault technology, applied in general control systems, control/regulation systems, electrical testing/monitoring, etc., to solve problems such as trouble, long-term hiding, damage, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
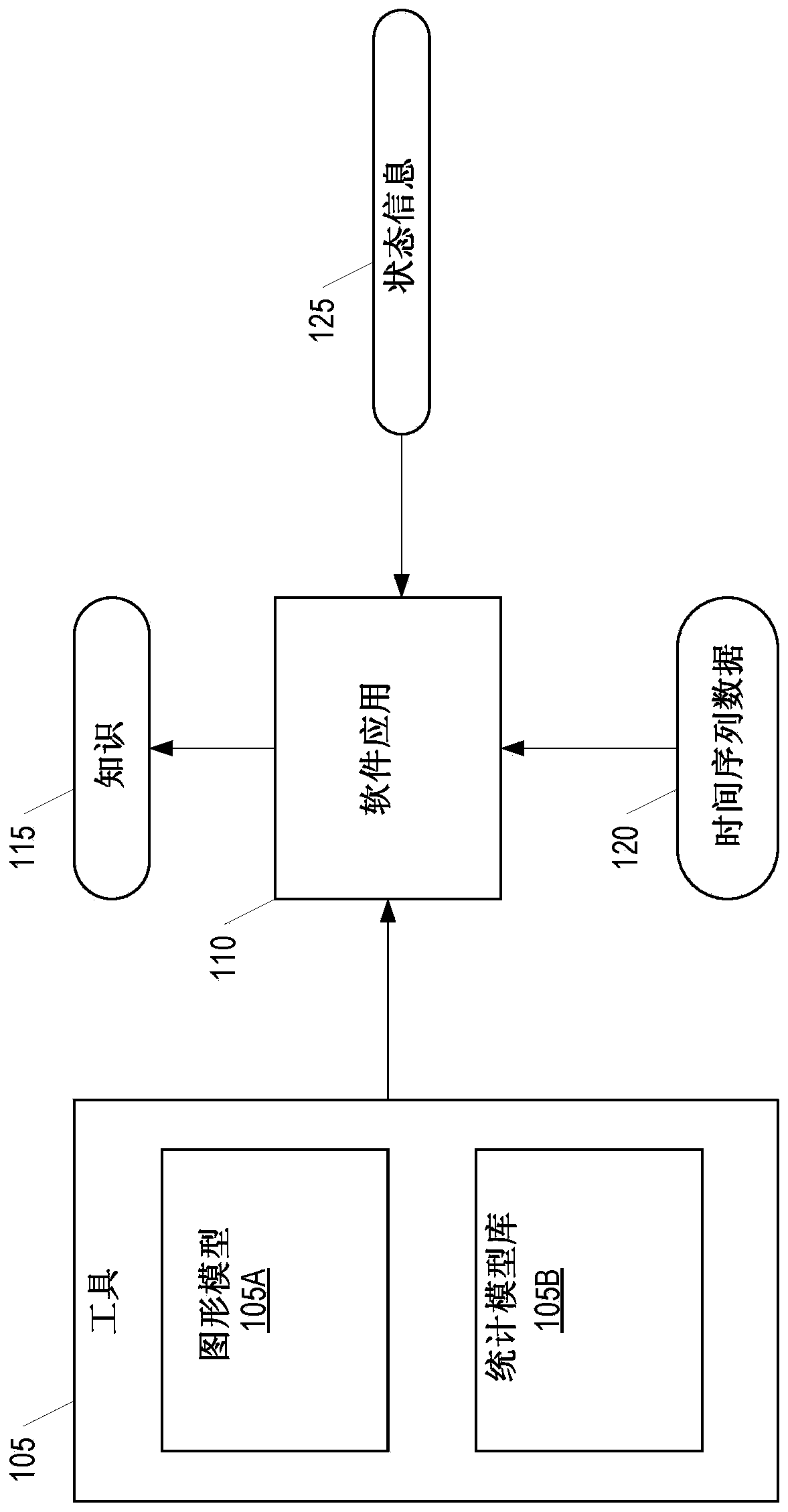
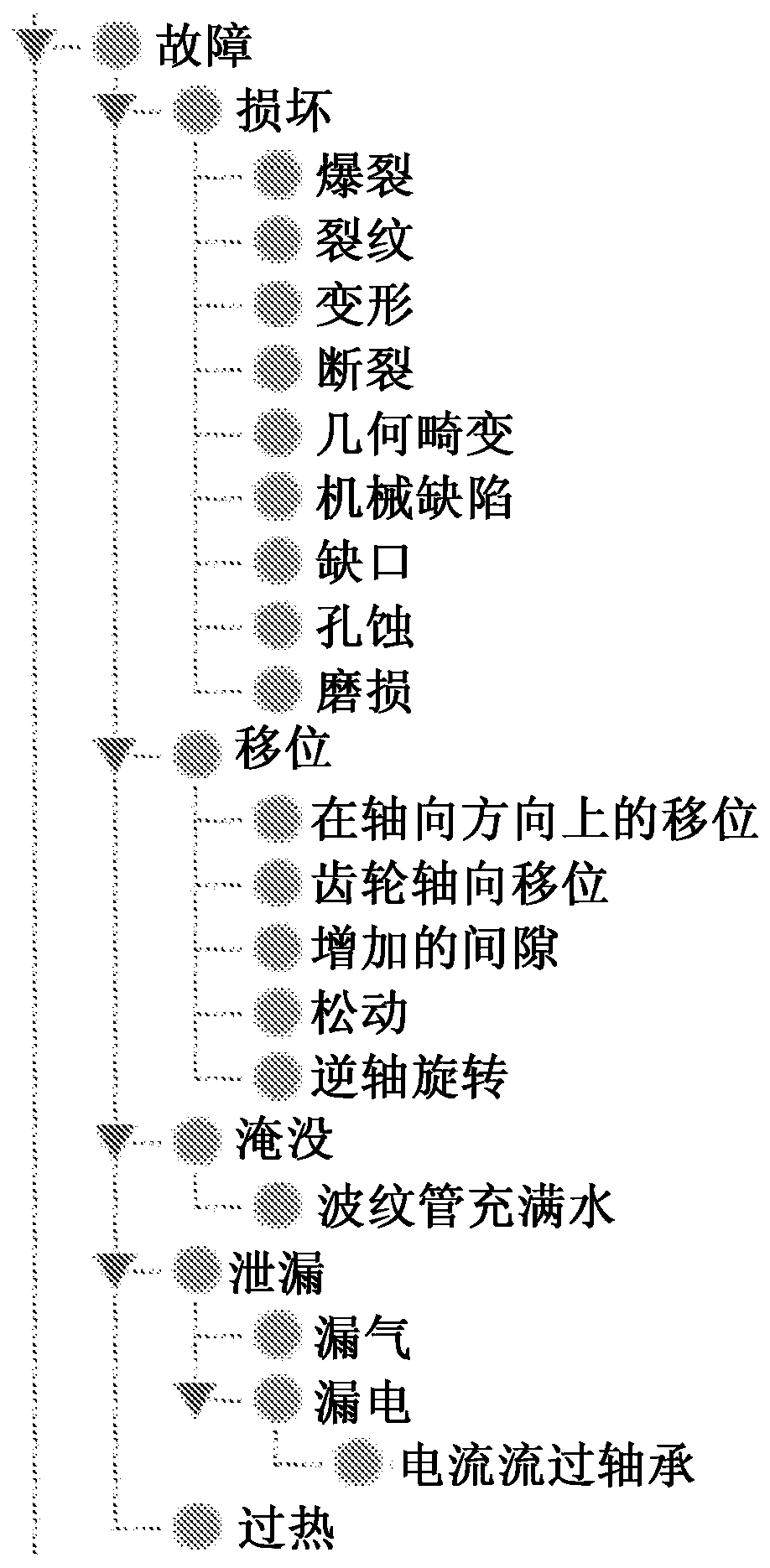
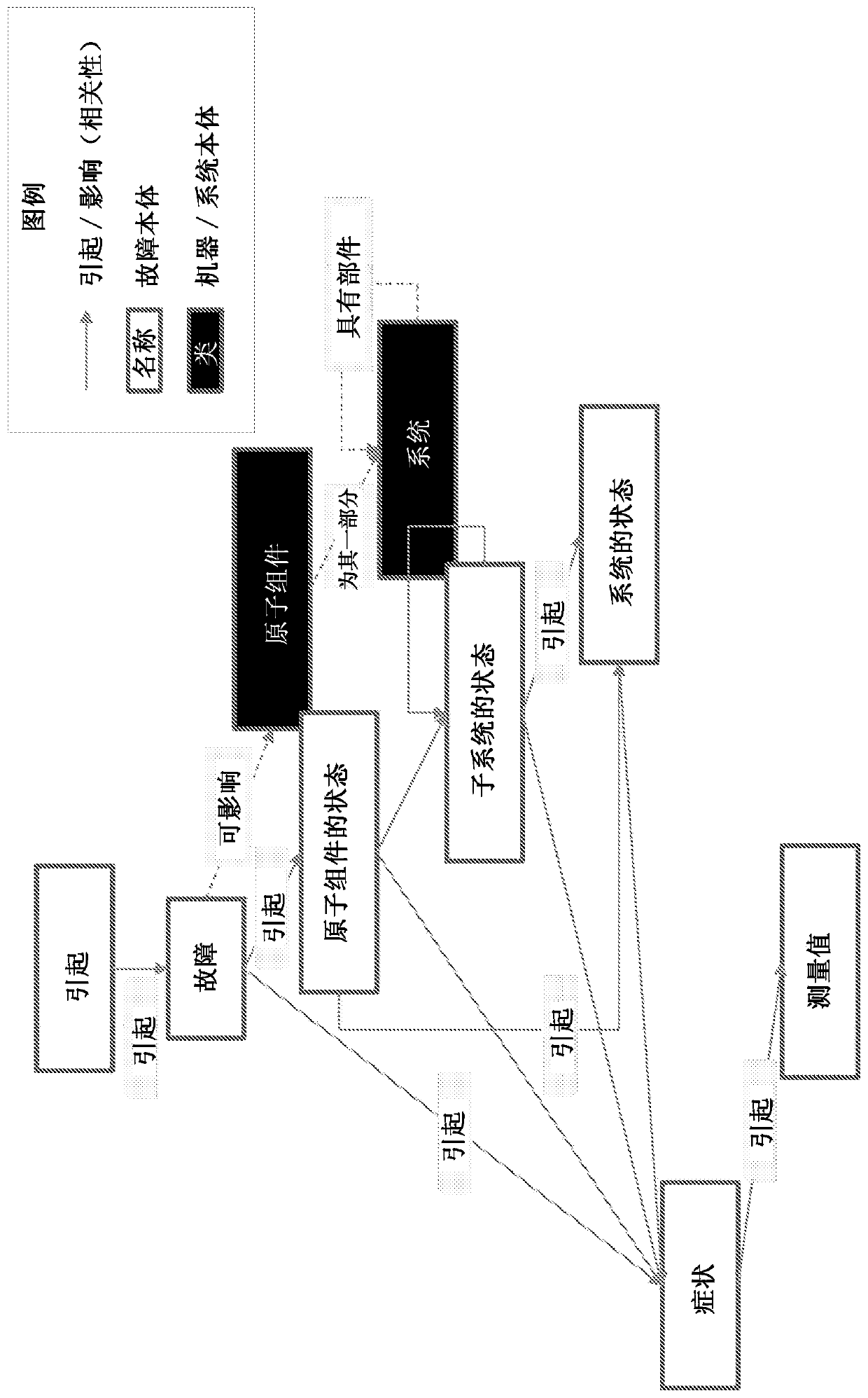
[0018] This document describes systems, methods, and apparatus that generally relate to building and using fault models for embedded analytics and diagnostic / predictive reasoning. The techniques described herein enable embedded devices with flexible embedded analytics capabilities to convert imprecise and incomplete data (from sensors, maintenance, etc.) its behavior. These techniques provide a systematic approach to defining fault knowledge, fault models, and the formalization of the basic architecture, concepts, and tasks required for fault modeling. Furthermore, fault models enable efficient reasoning with uncertain information at the device level and generate knowledge from data. Failure models also allow the utilization of numerical models that can be used to generate physically-based concrete data to generate parameters, thresholds, and even the raw (synthetic) data needed to learn the components used by the solution.
[0019] For complex systems, the actual data flow ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com