Linear ion trap analyzer
A technology for ion traps and analyzers, applied to mass spectrometers, etc., which can solve problems such as increased instrument costs, field adjustment electrode settings, and voltage application difficulties
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 example
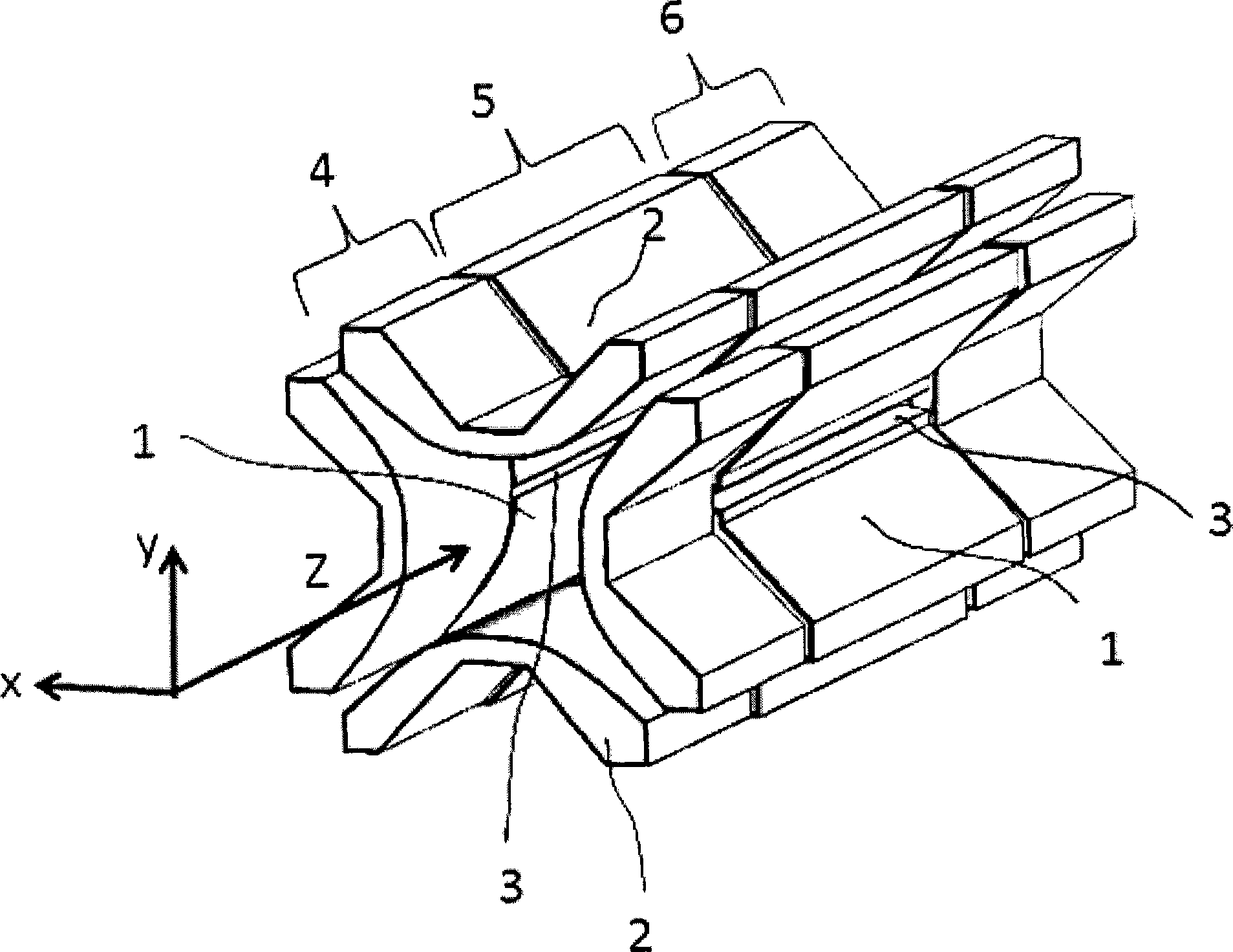
[0037] still refer to figure 1 An embodiment of the present invention will be described. The two-dimensional linear ion trap is structurally divided into a front section 4, a middle section 5 and a rear section 6. The front and rear sections 4 and 6 are applied with relatively high potentials to produce axial confinement of ions (for positive ions, for negative ions, it is relatively high. Low potential, the same below). Each segment has two pairs of main electrodes 1, 2 in the X and Y directions, on which driving high-frequency voltages of opposite phases are applied to form a radial trapping electric field. In an alternative embodiment, the front section 4 and the rear section 6 can also be replaced by front and rear end cap electrodes to generate a DC or AC trapping electric field in the axial direction. Ions are usually introduced from one end along the Z axis and are trapped in a linear region between two pairs of electrodes on the X and Y axes. If a dipole excitation ...
no. 2 example
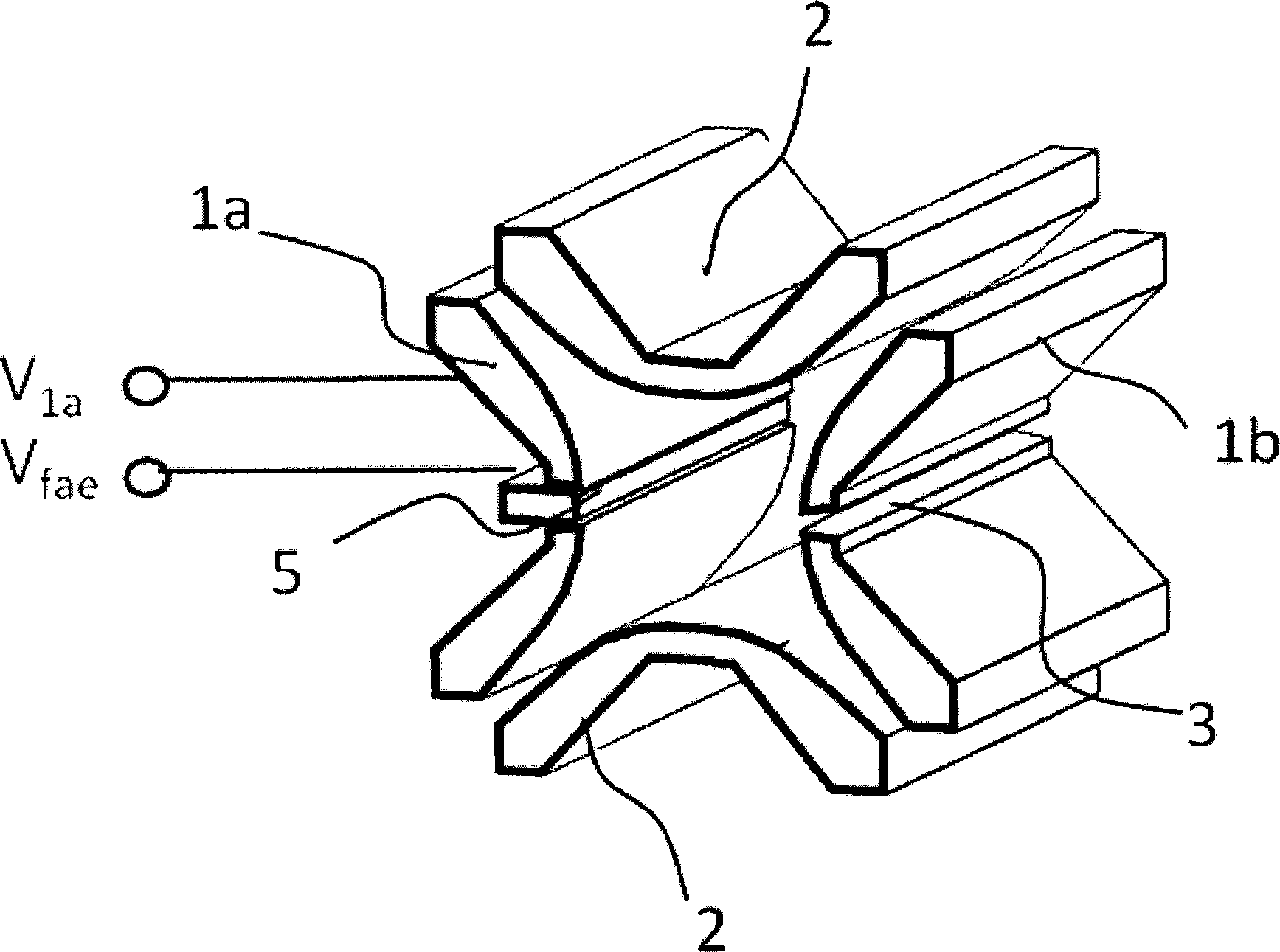
[0044] As mentioned above, planar electrodes, as a special case of cylindrical electrodes, can also be used to form linear ion traps. image 3 A schematic diagram of a rectangular linear ion trap constructed with four planar electrodes according to the second embodiment of the present invention is given. For clarity and brevity, image 3 Only the middle section is shown, and the front and rear sections or front and rear end caps are omitted. refer to image 3 As shown, two pairs of main electrodes 11 and 12 in the X and Y directions respectively apply driving high-frequency voltages of opposite phases to each other to form a radial trapping electric field. In the middle of the X electrode 11a opposite to the extraction groove 13, a field adjustment electrode 15 is provided. Similar to the first embodiment, the voltage on the field adjustment electrode is set to be the high frequency voltage V on the adjacent X electrode 11a 1a at least a portion of and a DC voltage V DC s...
no. 3 example
[0049] In this embodiment, in order to obtain a better quadrupole field shape for the rectangular linear ion trap built with planar electrodes, each electrode plane can be formed by several sub-electrodes, and each sub-electrode is added with a certain proportion of high-frequency voltage, forming a field shape similar to the electric field generated by the hyperbolic cylinder. The specific details of this type of ion trap can be found in Chinese patent CN1585081.
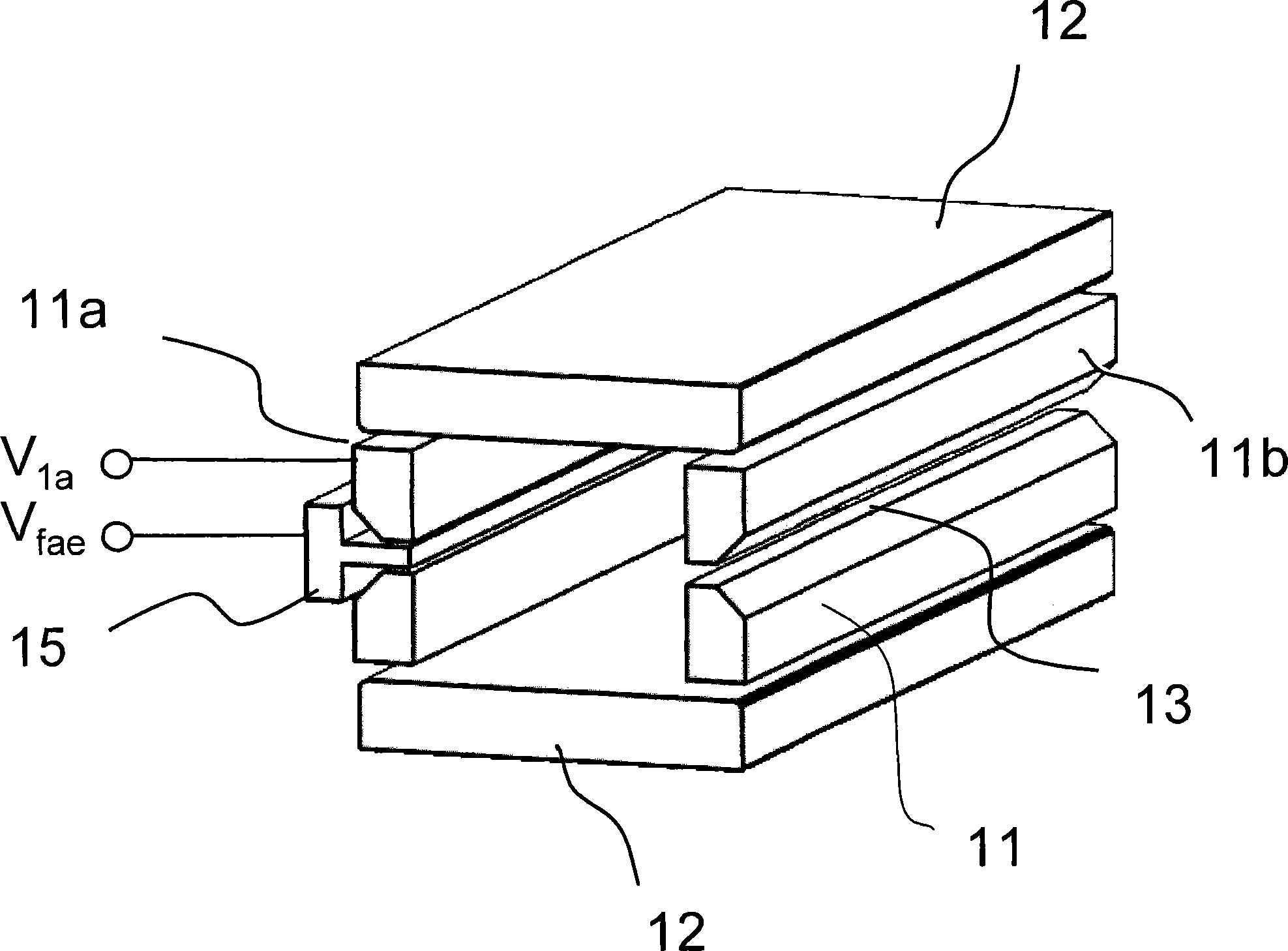
[0050] Figure 4 A planar printed circuit (PCB) type linear ion trap cross-sectional structure according to the present embodiment is shown. In the present embodiment, a flat strip-shaped printed circuit 26 is provided on at least a part of the electrode plate, and a field adjustment electrode 25 is provided in the middle of the X electrode plate 21 opposite to the lead-out groove 23 . Therein, the field adjusting electrode 25 of the trapezoidal cross-section can be retracted inside the adjacent X electrode plate...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com