DMRS processing method and device
A processing method and technology of ID information, applied in the direction of transmission path sub-channel allocation, digital transmission system, electrical components, etc., can solve the problem that DMRS cannot be orthogonal, achieve the effect of overcoming the limitation of scheduling and improving transmission performance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
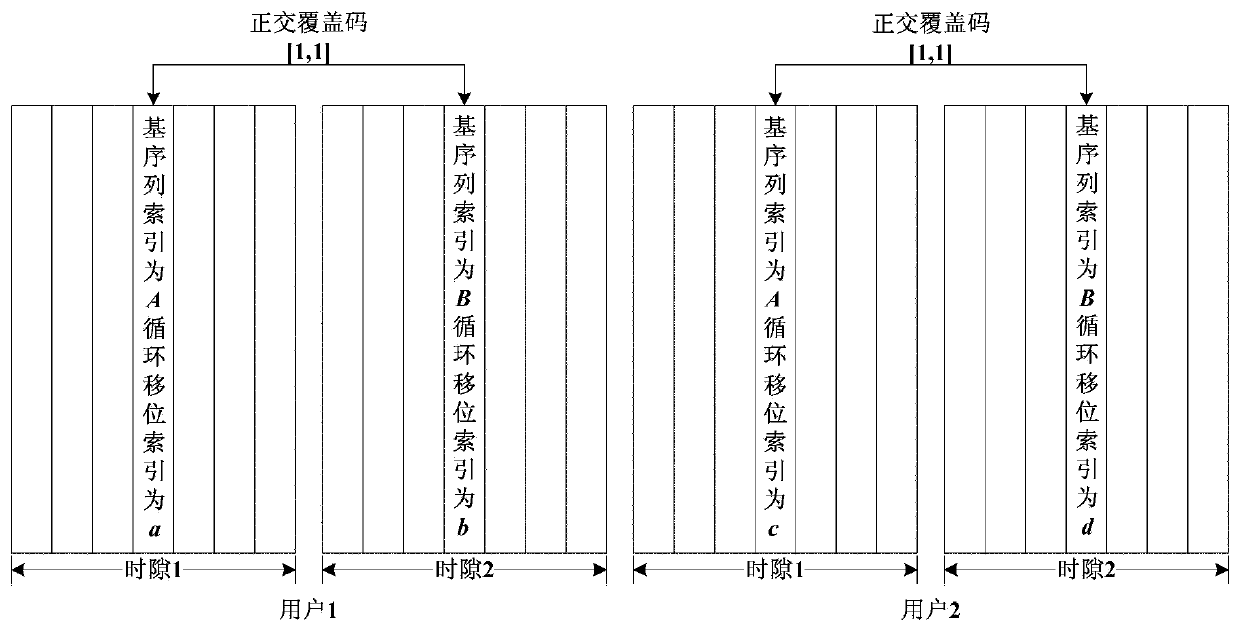
[0070] Assuming that the base station determines that the two terminals performing MU-MIMO paired transmission in the cell are UE1 and UE2 respectively, the base station determines the uplink transmission resources (that is, RB index) allocated to each UE, UE1 allocates resources as {RB1, RB2}, and UE2 allocates resources as {RB1, RB2, RB3}.
[0071] The base station sends the user-specific signaling for determining the DMRS of UE1 and UE2 to UE1 and UE2 respectively in two ways. Method 1, dynamic signaling notification: first, RRC configures N sets of UE-specific DMRS parameters, and uplink dynamic signaling (ULDCI) indicates which set of parameters UE1 and UE2 use. Mode 2, semi-static signaling notification: RRC directly configures semi-statically and notifies a set of UE-specific DMRS parameters to UE1 and UE2.
[0072] Such as Figure 11 As shown, UE1 performing MU-MIMO pairing transmission performs the following processing:
[0073] Step 1, UE1 receives the signaling s...
Embodiment 2
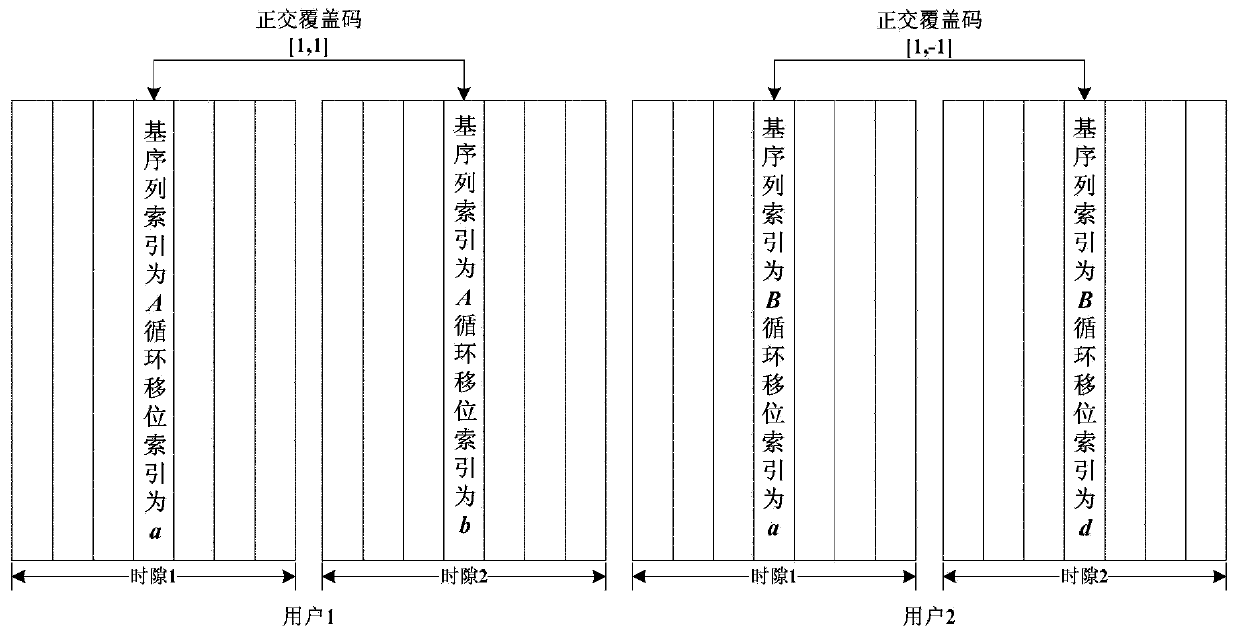
[0094] This embodiment differs from Embodiment 1 in step 3.
[0095] Step 3 of this embodiment is as follows: UE1 according to the virtual cell ID information And the resource allocation index indication information {RB1, RB2} determines the base sequence group index;
[0096] in slot n s The calculation method of the base sequence group index u in is as follows: u=f gh (n s )+f ss )mod30,
[0097] in,
[0098] function c(8n s +i) is a pseudo-random variable whose initial value is or or Wherein, RIV is the allocated RB index. For UE1, the RIV on RB1 is 1, and the RIV on RB2 is 2, which can be brought into the formula for calculation.
[0099] It is a dedicated virtual cell ID for UE1, which is notified by upper layer signaling or indicated by DCI;
[0100] According to the above method, the base station configures the same virtual cell ID information for UE1 and UE2 performing MU-MIMO pairing The same frequency hopping mode (enabled or disabled at the sa...
Embodiment 3
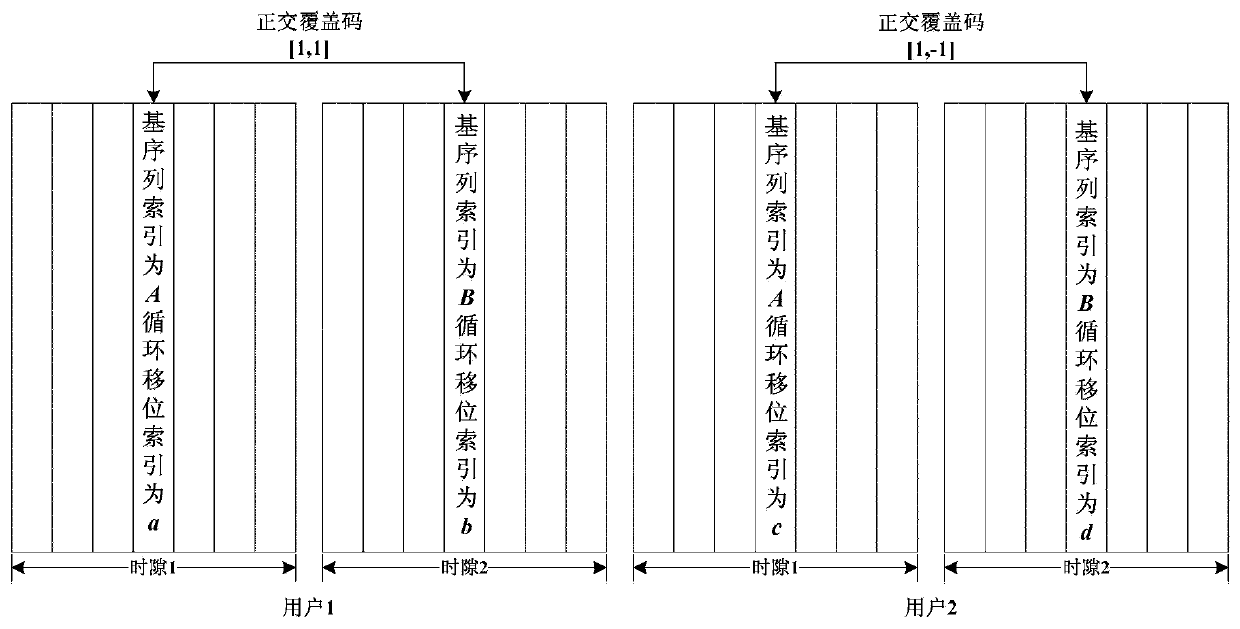
[0102] Assuming that the base station determines that the two terminals performing MU-MIMO paired transmission in the cell are UE1 and UE2 respectively, the base station determines the uplink transmission resources (that is, RB index) allocated to each UE, UE1 allocates resources as {RB1, RB2}, and UE2 allocates resources as {RB1, RB2, RB3}, the base station sends the user-specific signaling for determining the DMRS of UE1 and UE2 to UE1 and UE2 respectively in the following ways:
[0103] Method 1, dynamic signaling notification: first, RRC configures N sets of UE-specific DMRS parameters, and uplink dynamic signaling (UL DCI) indicates which set of parameters UE1 and UE2 use. The parameters include the cyclic shift of each user's transmission layer index alpha λ and the DMRS base sequence group index u.
[0104] Mode 2, semi-static signaling notification: RRC directly configures semi-statically and notifies a set of UE-specific DMRS parameters to UE1 and UE2. The parameters...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com