Hybrid service scheduling method in LTE system
A scheduling method and technology for hybrid services, applied in electrical components, wireless communications, etc., can solve the problems of poor packet loss rate performance of QoS requirements of hybrid services, and difficulty in satisfying the scheduling algorithm, and achieve the effect of reasonable distribution.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
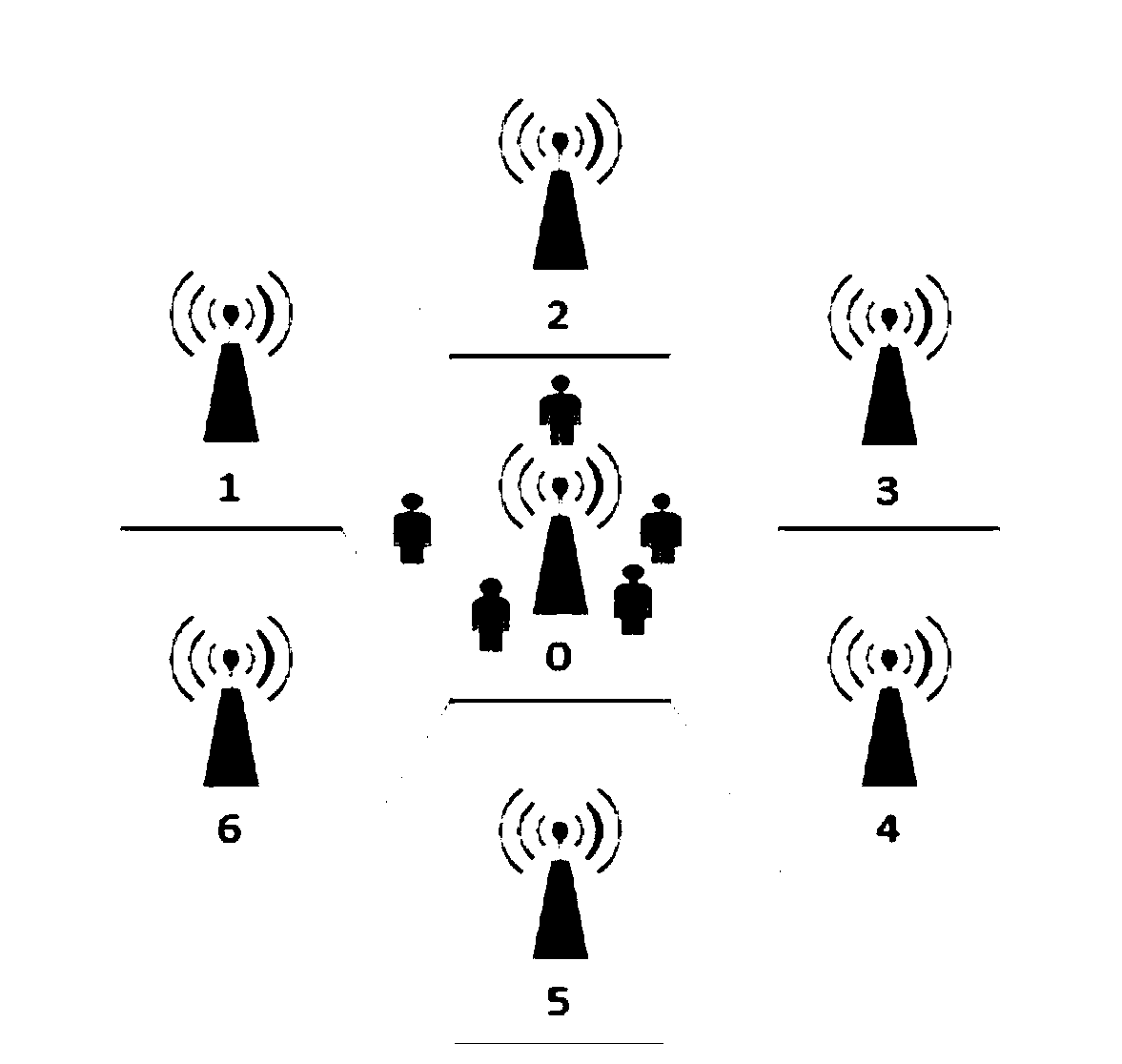
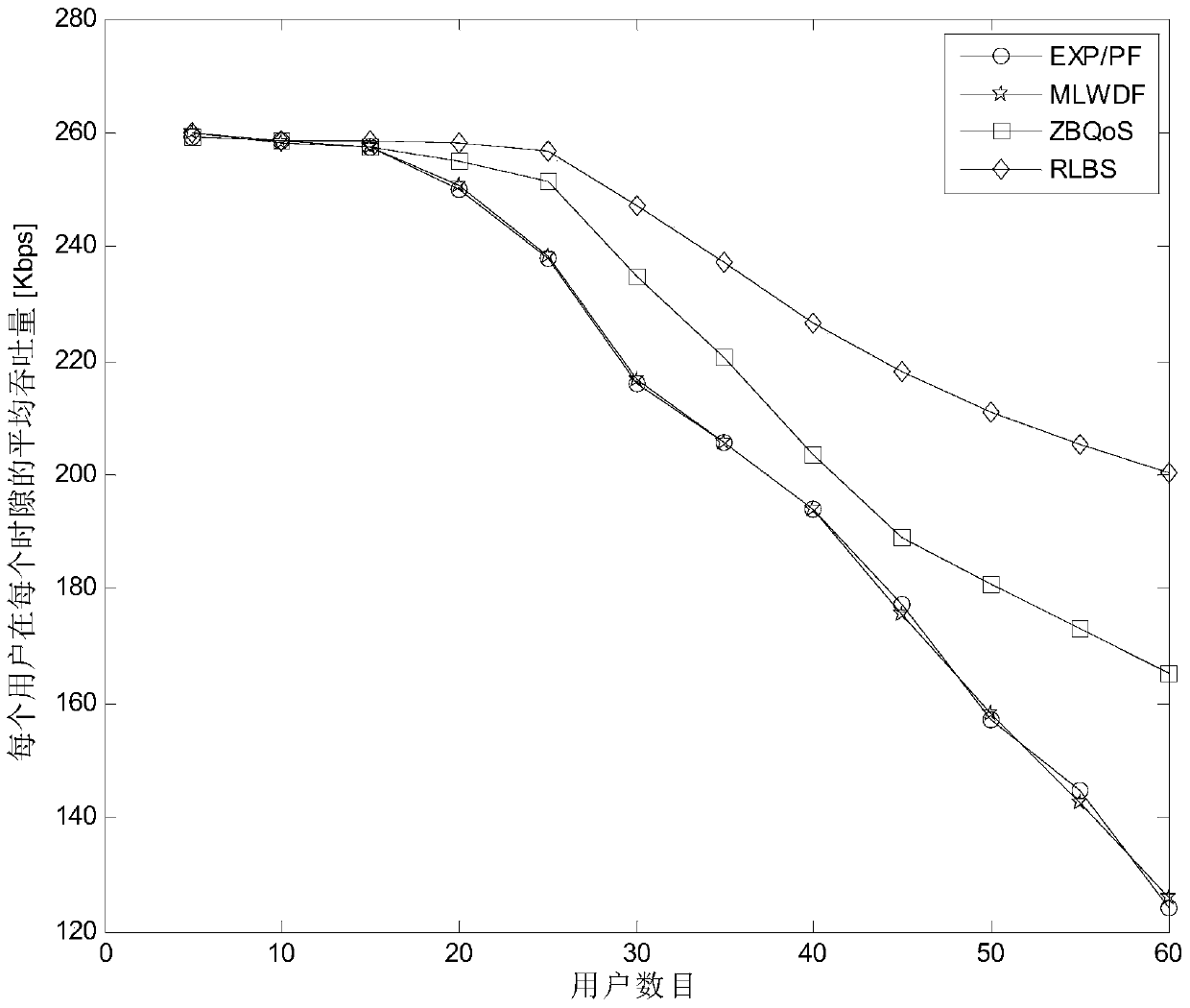
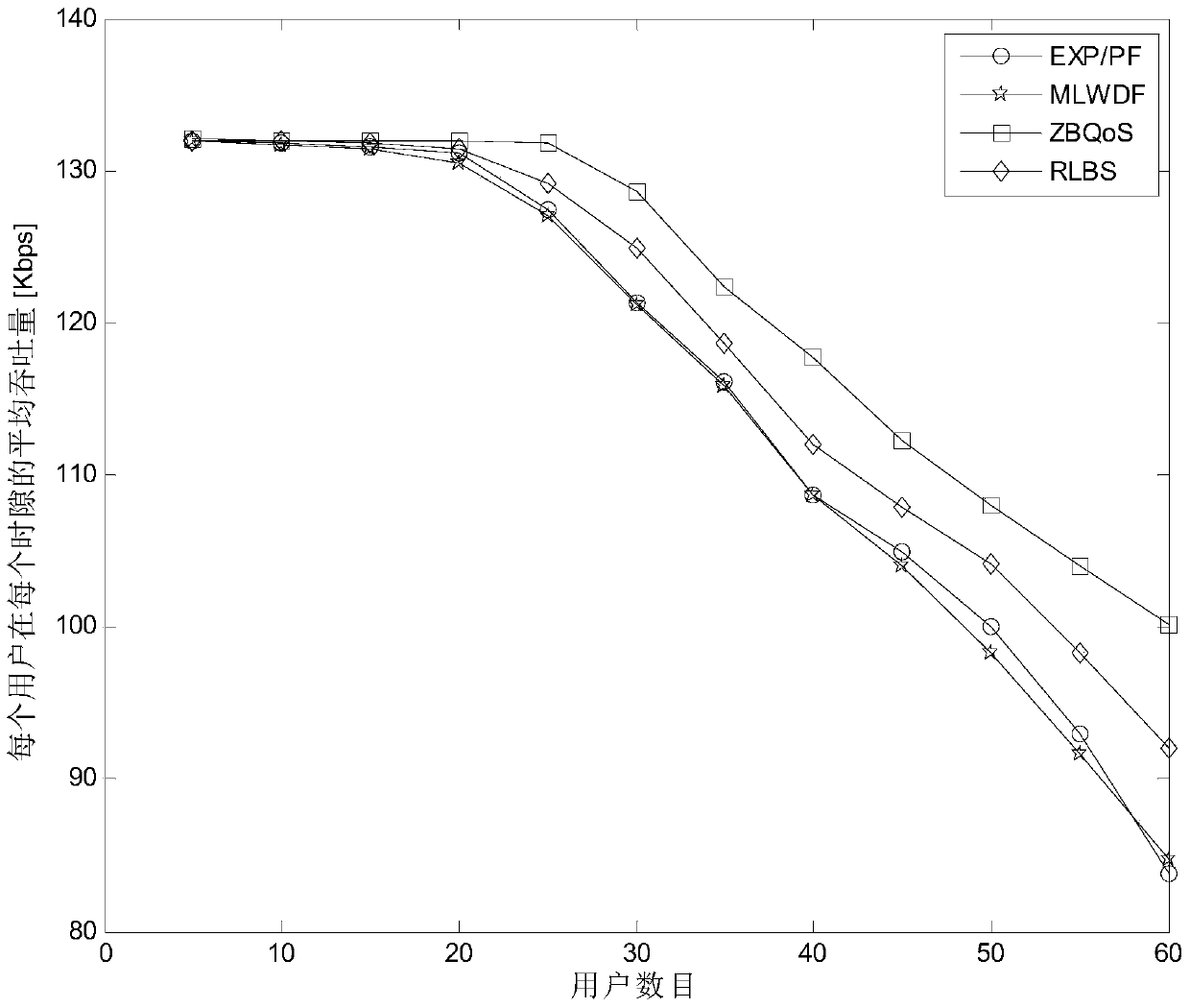
[0025] The hybrid service scheduling method in the LTE system of this embodiment, such as figure 1 As shown, in order to support the LTE system, that is, the mixed service resource scheduling in the long-term evolution system, improve the packet loss rate performance of the scheduling algorithm, and meet the service requirements, especially for services with high QoS requirements, based on the RLBS algorithm, that is, the mixed service resource scheduling Algorithm (Rate-Level-Based Scheduling) and proposed a hybrid traffic scheduling method in the LTE system. Considering that the GBR business, that is, the Guaranteed Bit Rate business (Guaranteed Bit Rate) has high requirements on data rate and packet delay, and GBR requires more resources to meet the business data rate requirements, so In the RLBS algorithm user priority formula, the information of the rate level determined by the service GBR value is introduced, so the service that requires a higher minimum transmission ra...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0033]The difference from Embodiment 1 is that in the method for scheduling mixed services in an LTE system according to this embodiment, in step 1, according to the channel quality indicator (CQI) value reported by the user in the service list, the current time slot for each user in each physical resource is calculated. The theoretical data rate process on the block is, according to the theoretical data rate calculation formula: Calculate the theoretical data rate of each user; where N represents the number of OFDM symbols on a subframe, M represents the number of subcarriers on a physical resource block, and Q k Indicates the number of bits that can be carried by one symbol of user k, which is determined by the modulation method; Indicates the coding rate of user k on physical resource block i mapped according to the SINR value of the user according to the provisions of the LTE protocol; where SINR is the ratio of signal to interference and noise.
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0034] The difference from Embodiment 1 or Embodiment 2 is that, in the hybrid service scheduling method in the LTE system of this embodiment, the process of calculating the priority value of each user in the current time slot according to the RLBS algorithm described in step 2 is to use the priority Numerical calculation formula: Calculate the priority value of the user in the current time slot; where,
[0035] W k () represents the queue head delay of real-time service user k, τ k Indicates the delay threshold of real-time service user k, Г k (t) represents the average spectral efficiency of user k on all physical resource blocks, In the formula, N PRB Indicates the number of physical resource blocks in the system, Indicates the spectral efficiency obtained by user k on the i-th physical resource block, the spectral efficiency It is determined by the channel quality indicator CQI value reported by the user, so Г k (t) represents the channel state of the user;
[...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com