Method for Directed Induction and Differentiation of Human Embryonic Stem Cells into Corneal Endothelial Cells
A technology of human embryonic stem cells and inducing differentiation is applied in the field of directional induction and differentiation of human embryonic stem cells into corneal endothelial cells, which can solve the problems of difficulty in culturing and passage of corneal endothelial cells, and difficulty in realizing massive expansion of corneal endothelial cells in vitro.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0043] The following examples are used to illustrate the present invention, but are not intended to limit the scope of the present invention. Unless otherwise specified, the technical means used in the examples are conventional means well known to those skilled in the art, and the raw materials used are all commercially available products.
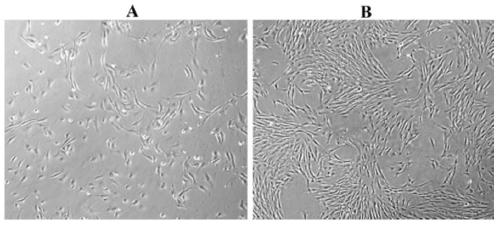
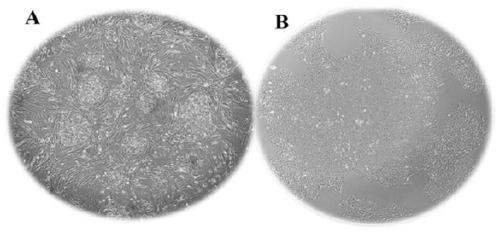
[0044] Embodiment The method for directional induction and differentiation of human embryonic stem cells into corneal endothelial cells
[0045] The method comprises the steps of:
[0046] S1. Human embryonic stem cells differentiated into human neural crest stem cells
[0047] S2. Human neural crest stem cells were induced to differentiate into human corneal endothelial cells
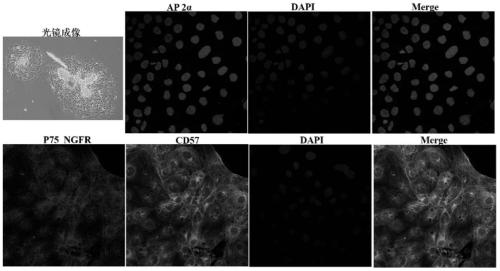
[0048] Preferably, after step S1, the method further includes the step of sorting induced differentiation cells by flow cytometry, and collecting cells showing positive expression of neural crest stem cell markers.
[0049] Step S1 is as follows: 37 ° C, 5% CO ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com