Curved-rail-driven excavator bucket capable of adjusting earth excavating direction
A technology of arc-shaped rails and excavators, which is applied in the direction of mechanically driven excavators/dredgers, earth movers/shovels, construction, etc., which can solve the problem of dispersing the force of bucket digging and not being able to dig soil perpendicular to the ground And other issues
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
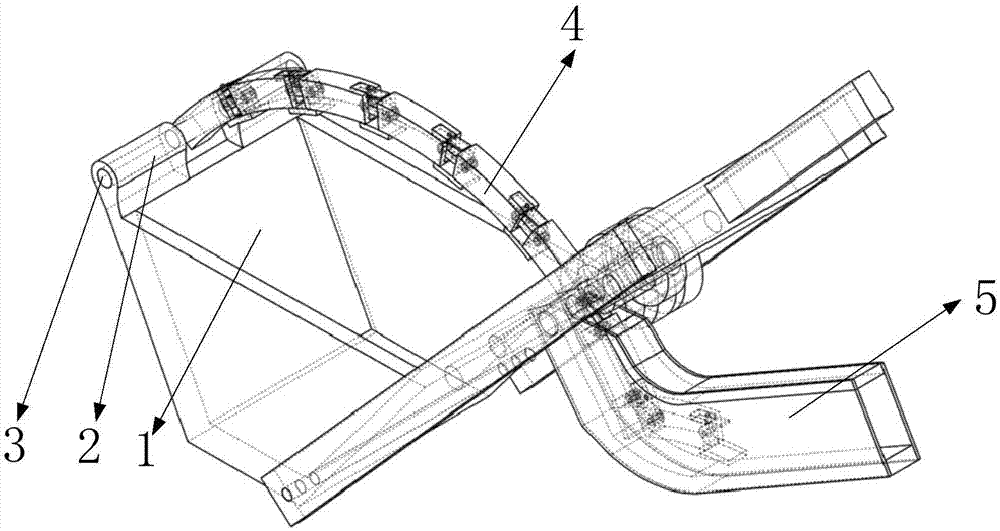
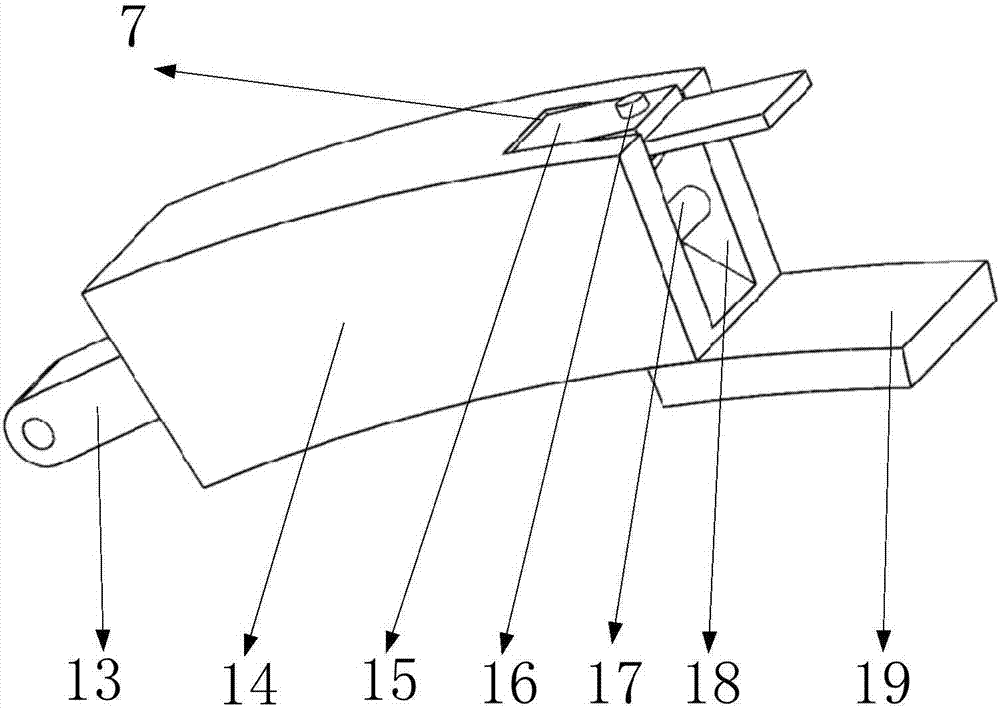
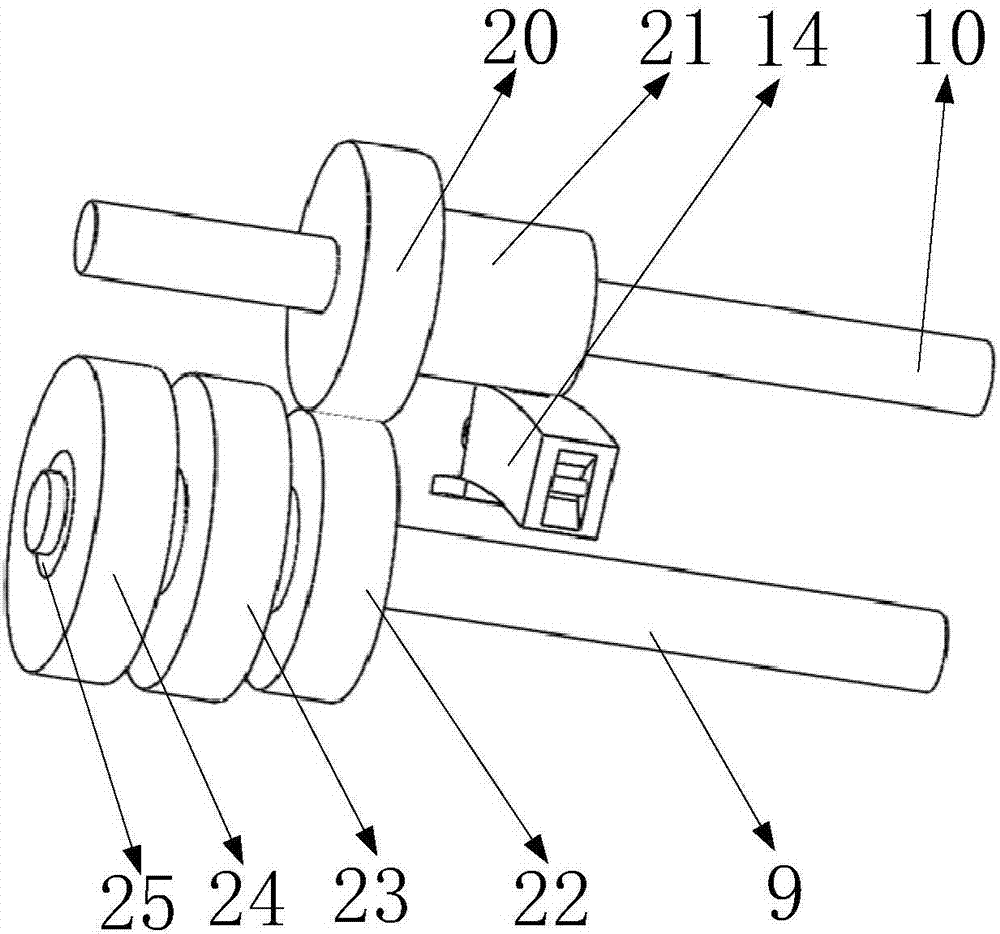
[0028] Such as Figure 5 , 6 As shown, it includes a bucket body 1, a bucket lug 2, a first one-way gear 62, a second one-way gear 63, a lug connecting pin 3, an arc rail 4, an arc rail bin 5, and a rotating hole 6. The first bucket arm 8, the first fixed column 9, the second fixed column 10, the bucket arm connecting plate 11, the second bucket arm 12, the first transmission gear 20, the second transmission gear 21, the third transmission Gear 22, hydraulic torque converter 23, hydraulic motor 24, transmission sleeve 25, rotating pin 26, shovel teeth 27, safety plate 28, strip groove 29, limit block 64, pressure plate 30, first gear 31, The first return spring 32, the second gear 33, the second retractable rack 34, the fourth rack 35, the moving bar 36, the third gear 37, the fixed shaft 38, the third rack 39, the second return spring 40, the second A telescopic rack 41, installation chamber 42, hydraulic oil storage chamber 43, connection block 44, first hydraulic cylinder...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com