A kind of nano-drug carrier and its combination medicine for the treatment of diabetes
A nanoparticle, gene recombination technology, applied in the intersection of bionics and biomedicine, in the field of nanobiology
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
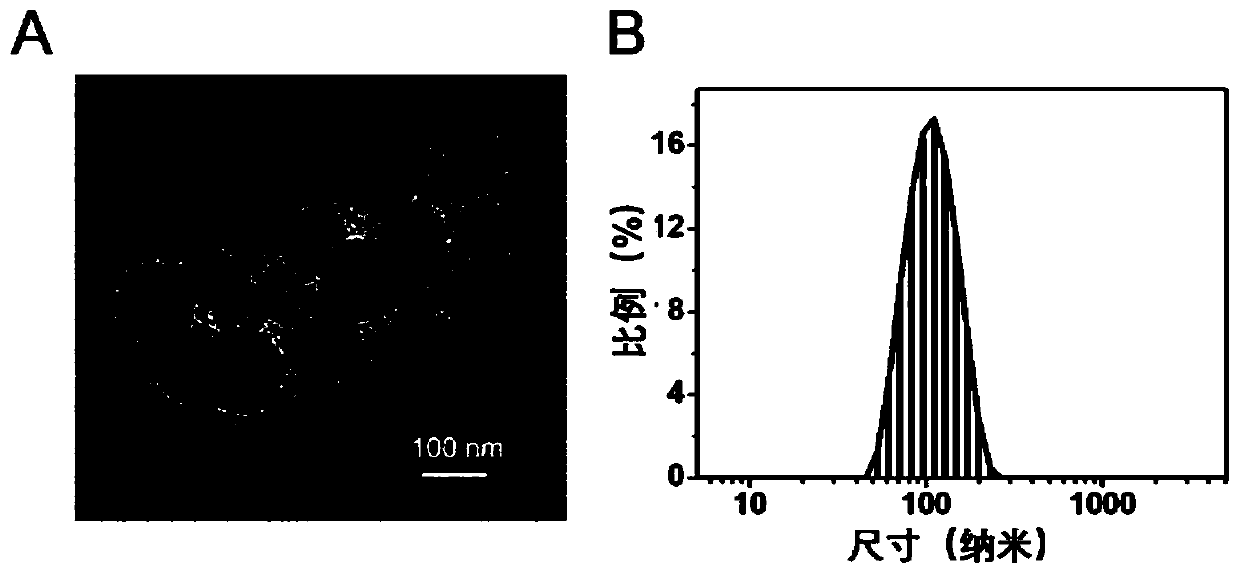
[0028] Example 1 After ferritin is mixed with insulin, stable insulin-ferritin nanoparticles can be formed
[0029] In order to study whether ferritin and insulin can interact with each other to form stable nanoparticles, recombinant human H-ferritin (prepared by the inventor, see invention patent ZL201110122433.0) and human recombinant insulin (91077c, Sigma) were selected for Research. In vitro, firstly, the present invention proves that ferritin and insulin are mixed in a certain ratio to form stable nanoparticles; and the insulin-ferritin nanoparticles are characterized.
[0030] The experimental method is as follows:
[0031] 1.1 Preparation of insulin-ferritin nanoparticles.
[0032] Ferritin and insulin were mixed in 0.2M concentration of PBS (137mM NaCl, 2.7mM KCl, 10mM NaCl at a molar ratio of 1:1 2 HPO4,2mM KH 2 PO4, pH 7.4) buffer and incubated at 4°C for 45 minutes. Then, by molecular exclusion, the Superdex 200 10 / 300GL molecular sieve purification method was...
Embodiment 2
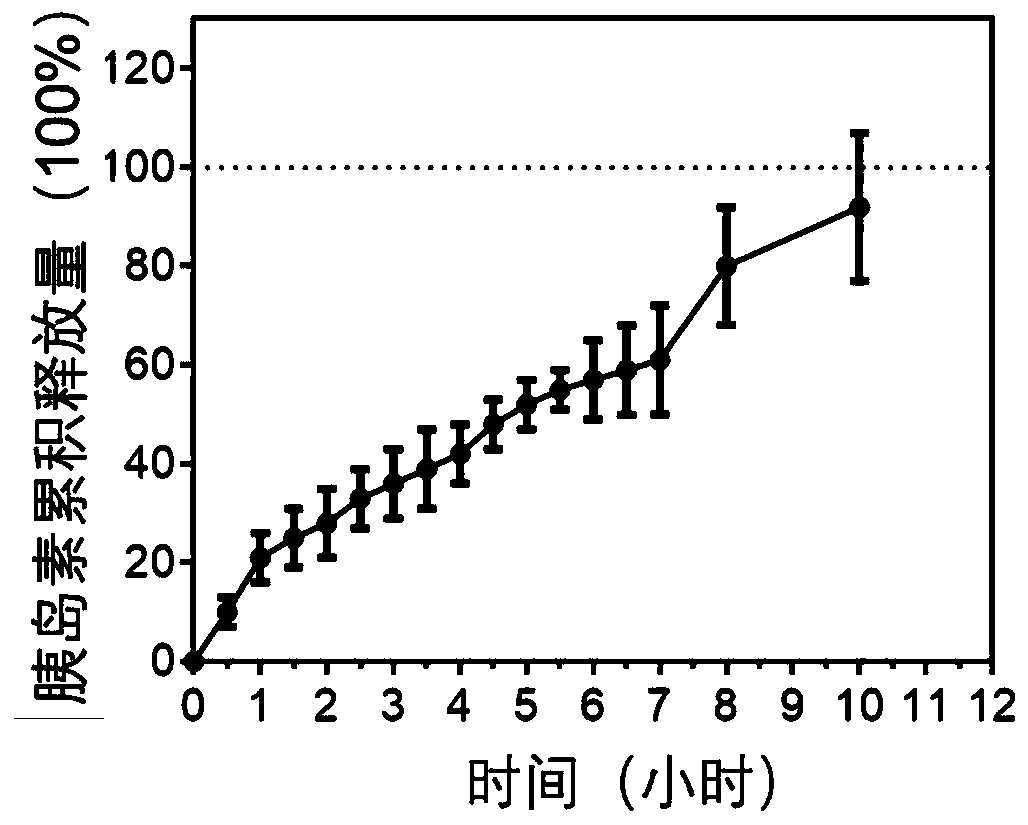
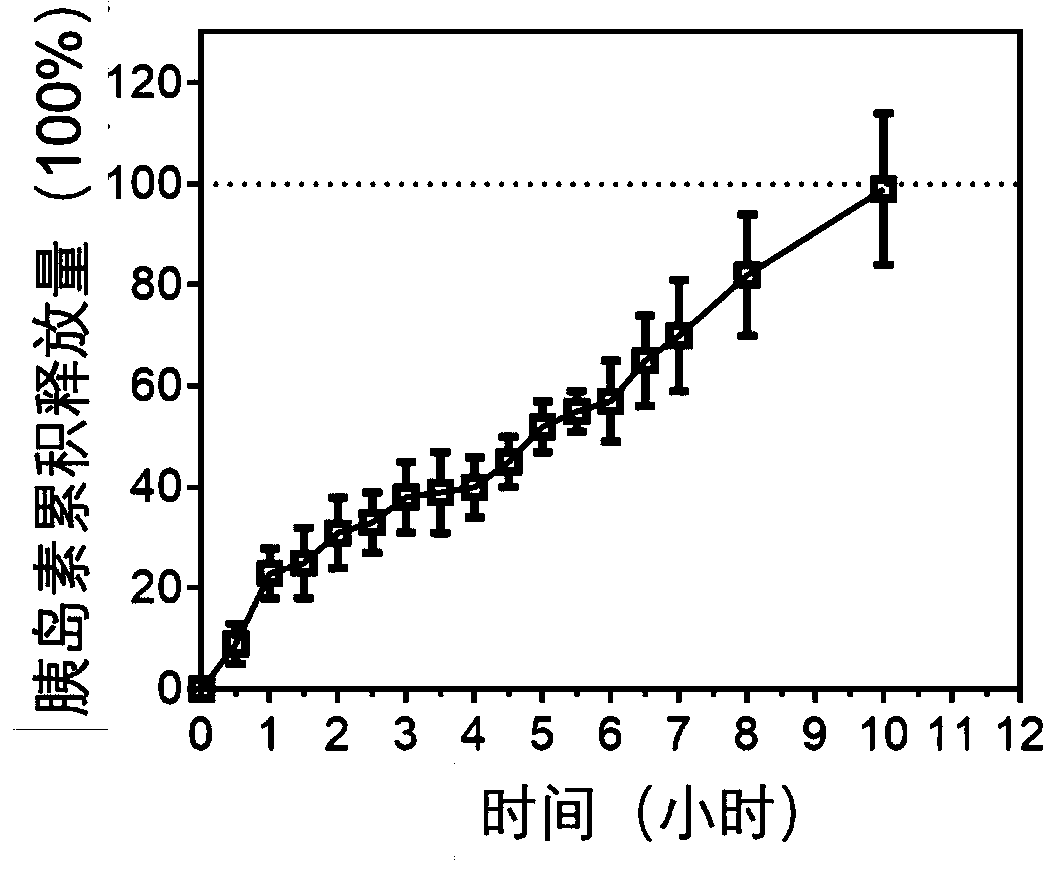
[0036] Example 2 Insulin-ferritin nanoparticles can realize the slow release of insulin
[0037] After insulin-ferritin self-organizes into stable particles, the first question that needs to be verified is whether the assembled insulin can be effectively released slowly and exert its activity. The invention proves for the first time that insulin and ferritin can be self-assembled into stable nanoparticles based on the hydrophilic-hydrophobic interaction of the surface residues of the two proteins, and can release insulin slowly. The released insulin remains highly biologically active.
[0038] The specific experimental method is as follows:
[0039] 2.1 Slow release curve of insulin-ferritin in PBS
[0040] To evaluate the ability of insulin-ferritin nanoparticles to release insulin slowly, the inventors performed an insulin release experiment. First, using known concentration of insulin, using HPLC technology, draw the A280 value of the peak at a specific position on the HPL...
Embodiment 3
[0046] Example 3 Insulin-ferritin sustained release system can effectively reduce blood sugar level
[0047] In order to directly evaluate the reduction of blood glucose level by insulin-ferritin nanoparticles, the inventors conducted a blood glucose reduction experiment at the animal level. The experimental animals were male Sprague-Dawley rats, weighing 200-250 g, purchased from Beijing Huafukang Biotechnology Co., Ltd. (China). The experimental animals were divided into 3 groups (6 animals in each group), and they were fasted for 12 hours before the experiment. Then, equimolar amounts of ferritin, insulin, and insulin-ferritin nanoparticles dissolved in PBS were injected subcutaneously into these rats. Tail blood samples were collected before dosing and at 5, 15, 30, 60 minutes after dosing, and every hour thereafter. The experiment lasted for 12 hours, and the One-touch blood glucose meter ( Perfoma) was used to measure the blood glucose concentration of samples.
[0...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com