Method for measuring flow parameter distribution in particle flow two-phase flow reactor
A technology of flow parameters and reactors, applied in fluid dynamics experiments, measuring devices, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of only paying attention to, not considering the influence of cross-scale correlation on mesoscopic structure, difficult selection of sample space, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
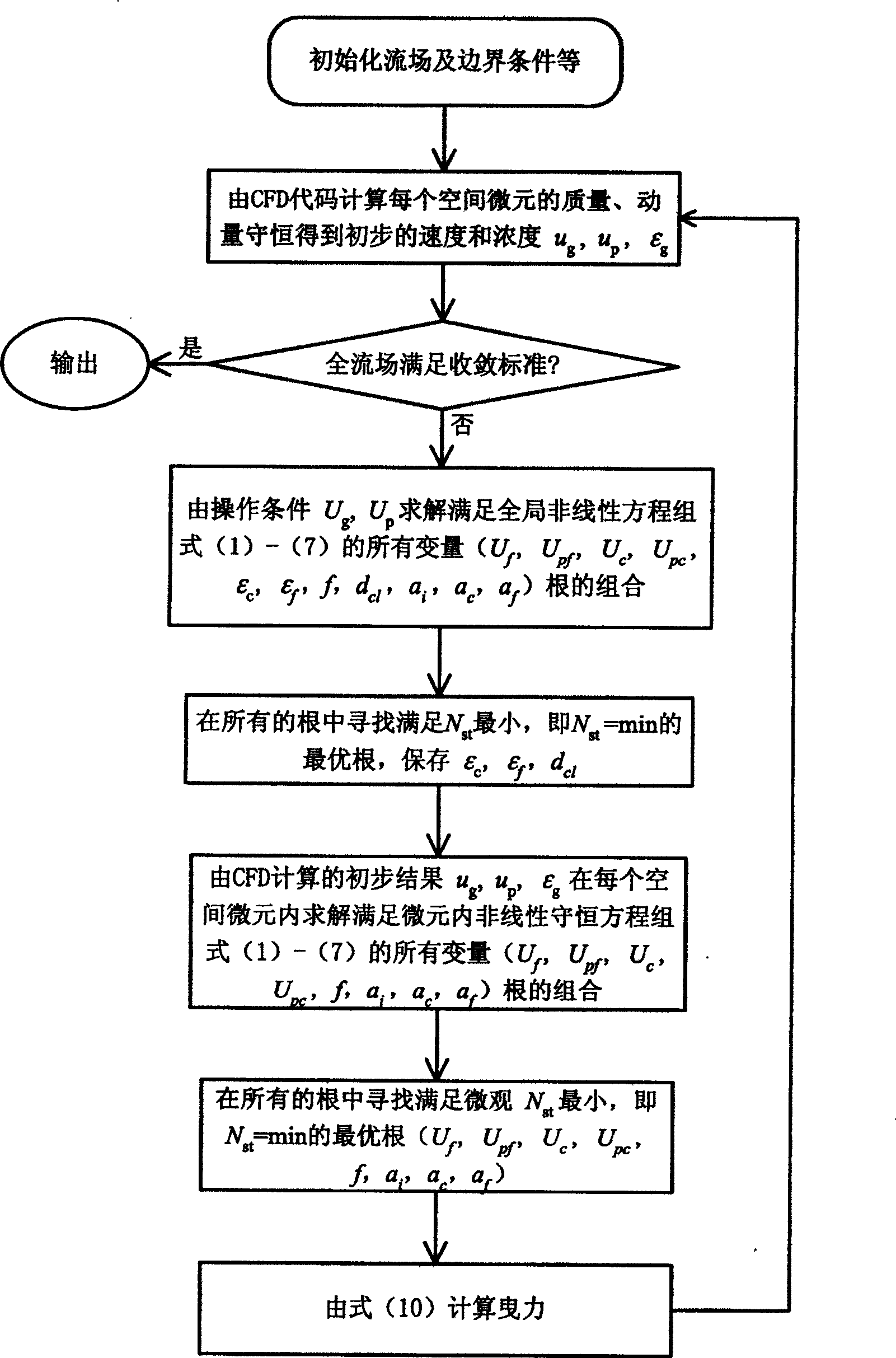
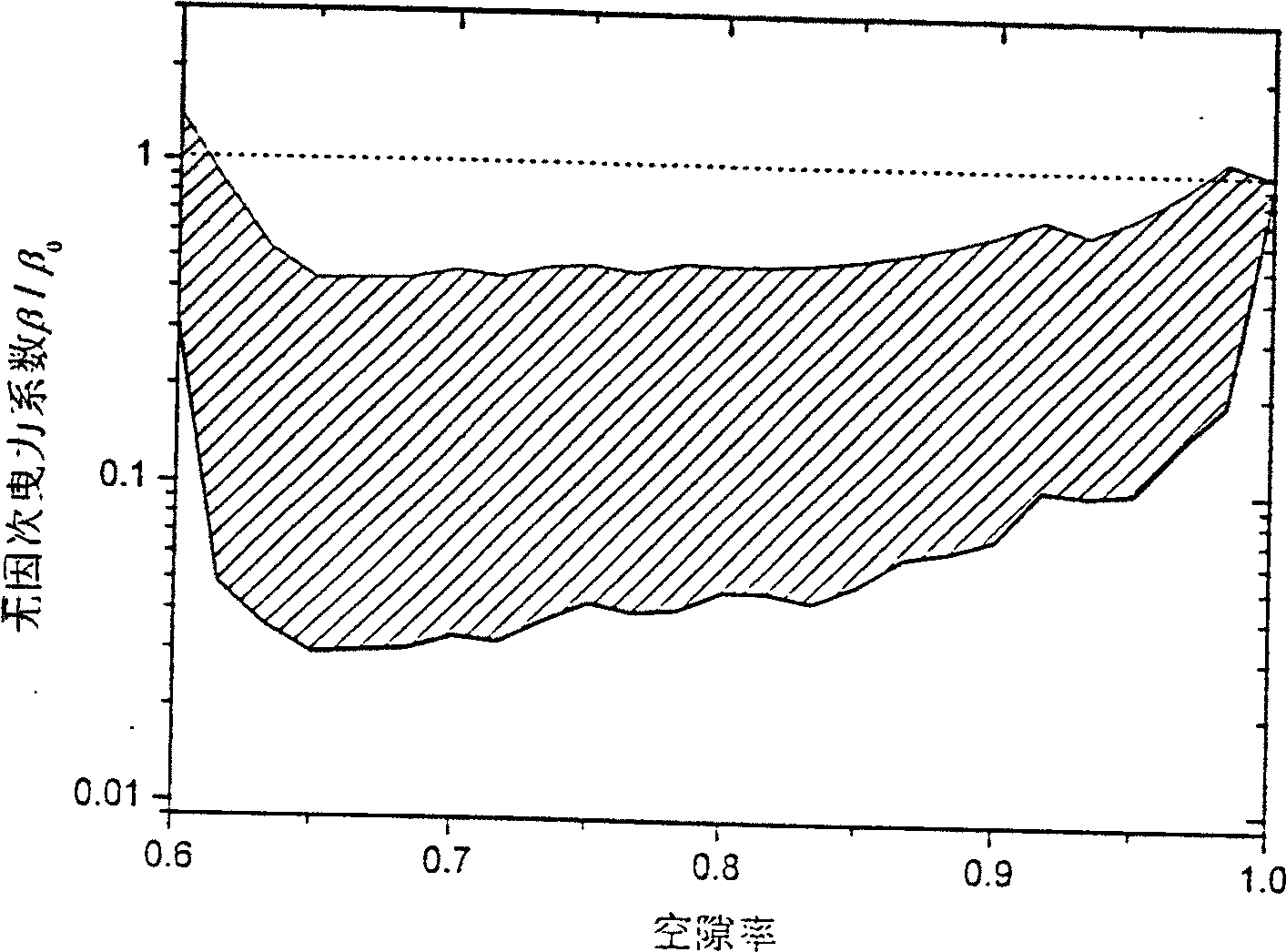
[0108] Example 1 The method of the present invention is applied to flow prediction in a fast fluidized calciner for coal-based kaolin with an annual output of 1,000 tons. The average particle size of raw material kaolin is 0.002mm, and the particle density is 800kg / m 3 , The inner diameter of the calcining furnace is 0.45m, and the height of the furnace is 10.5m. The furnace temperature is controlled at around 900℃. The main reaction is: C+O 2 →CO 2 , Al 2 O 3 ·2SiO 2 ·H 2 O→Al 2 O 3 ·2SiO 2 . When calculating, on a general platform provided by commercial CFD software, the drag coefficient calculated by the method of the present invention according to the calculation block diagram is compiled into an interface program to replace the method inside the software. First, perform a 1:1 geometric structure of the reaction device, select the calculation method to be a two-fluid model under double Euler coordinates; secondly, set the temperature and set the particle and gas properties acc...
Embodiment 2
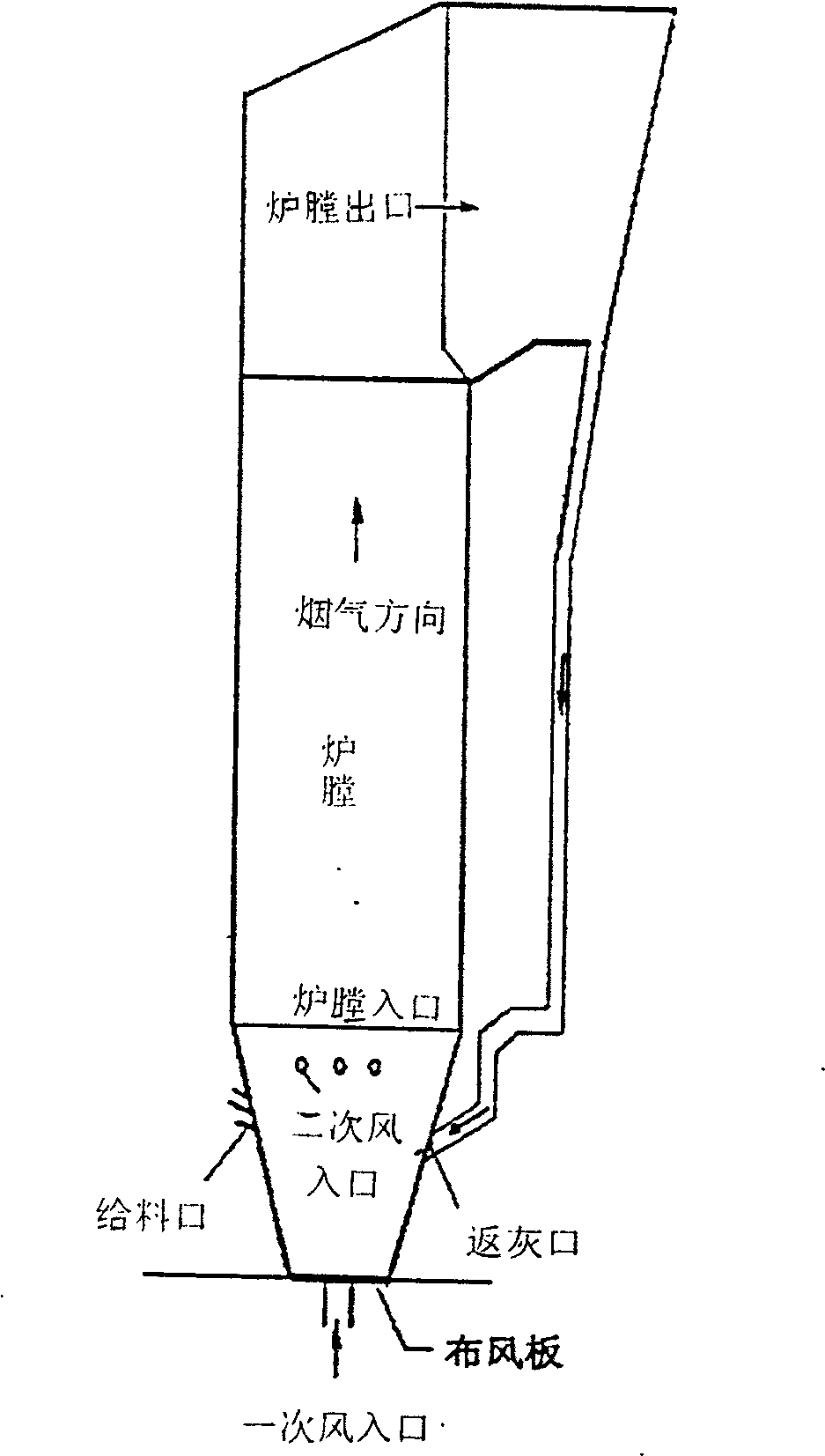
[0109] Example 2 The method of the present invention is applied to flow prediction in a circulating fluidized bed boiler of Wuhan Petrochemical Plant, which produces 75 tons of steam per hour, to assist in detecting faults. Such as image 3 As shown, the main section of the boiler furnace is 5.4×3.99m, the furnace height is about 22.5m, the average particle size of circulating ash particles in the furnace is 0.21mm, and the particle density is 2000kg / m. 3 , The furnace temperature is controlled at around 900℃, and the designed primary air volume is 49701Nm 3 / h, secondary air volume 33134Nm 3 / h. The main combustion reaction occurs in the furnace: C+O 2 →CO 2 . On the general platform provided by commercial CFD software, the drag coefficient calculated by the method of the present invention is written as an external interface program in a user-defined form to replace the method inside the software. When calculating, first perform a 1:1 geometric structure of the boiler furnace, an...
Embodiment 3
[0110] Example 3 The method of the present invention is applied to the prediction of flow field distribution in a new Sinopec oil refining multi-stage reactor to assist in optimization design. The diameter of the main section of the reactor is 3.4m, the inlet gas velocity is 15m / s, the inlet solid content is 1500t / h, the average particle size used is 0.075mm, and the particle density is 1300kg / m. 3 , The furnace operating temperature is about 400℃. The drag coefficient calculated by the method of the present invention is written as an external interface program to replace the internal method of the commercial software. When calculating, first perform a 1:1 geometric structure of the reactor, select the calculation method to be the two-fluid model under the double Euler coordinates; secondly set the temperature, and set the particle and gas properties according to the actual physical property system; the bottom surface gas The speed and solid speed are given according to the design...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com