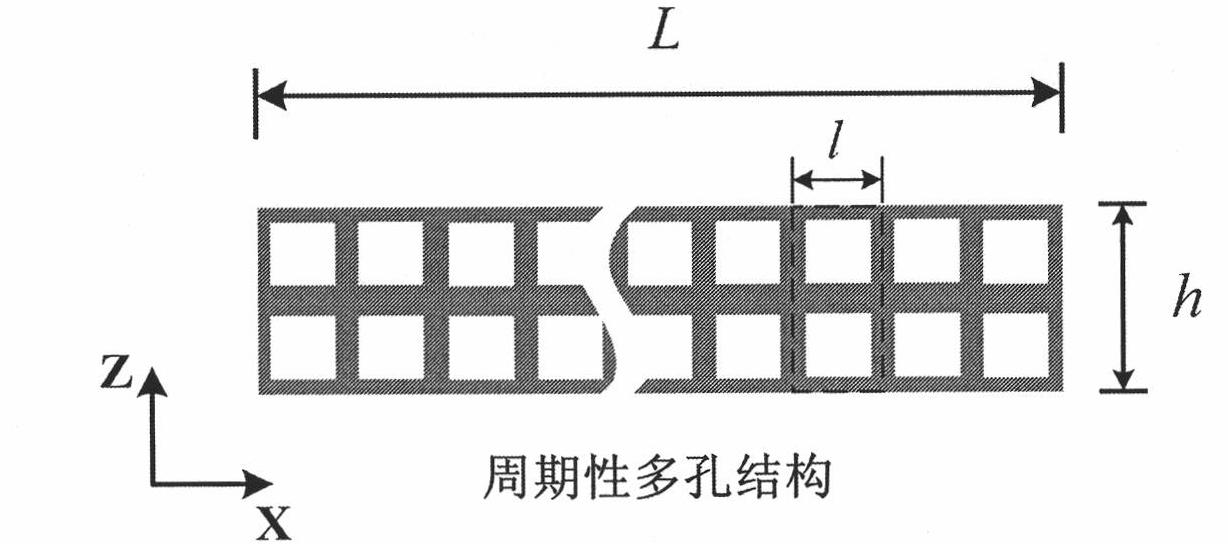
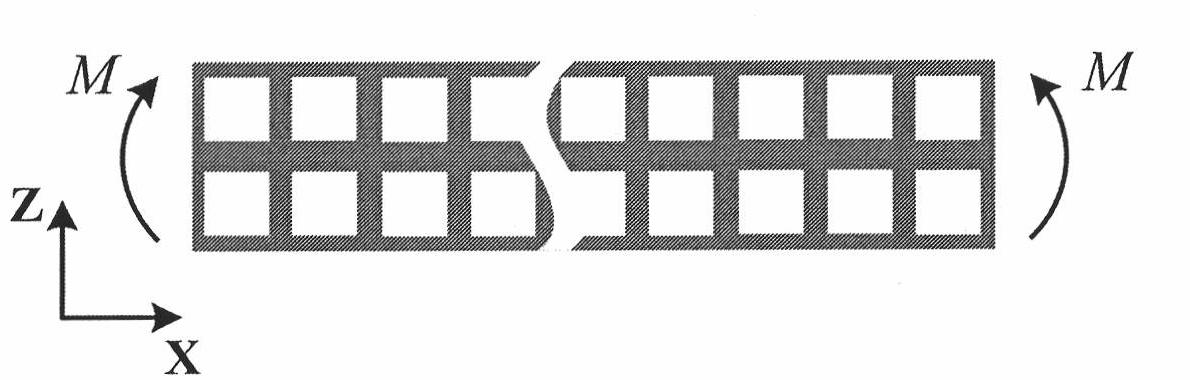
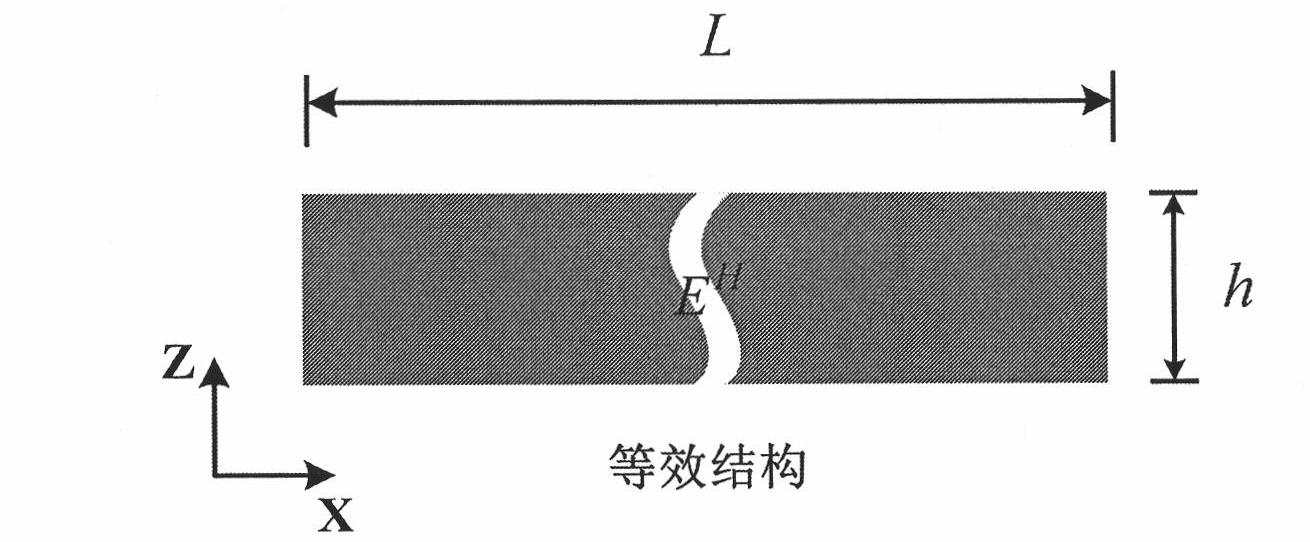
Method for predicating periodic porous material equivalent young's modulus
A technology of Young's modulus and porous materials, which is applied in the direction of testing the strength of materials by applying a stable bending force, and can solve the problem of predicting the equivalent Young's modulus of materials that cannot reflect changes in cell size
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0036] Example 1: Equivalent Young's modulus of a square hole unit cell.
[0037] 1) To establish a porous beam structure with periodic square holes, its parameters include the length of the beam L=60, the period length l=1 of the microstructure along the x direction, the thickness of the beam along the z direction h=2l, and the wall thickness of the square hole unit cell t=0.1; the properties of the solid material are: Young's modulus E=70e9, Poisson's ratio v=0.34, density ρ=2774; set the scaling factor n=1 at this time.
[0038] 2) Perform pure bending loading on the periodic square hole porous beam structure, according to the periodicity and symmetry of the structure along the x direction, the bending strain energy U on a single period l b for:
[0039] U b = M 2 2 ∫ 0 l 1 E ( ...
Embodiment 2
[0058] Example 2: Equivalent Young's modulus of equilateral triangular pore unit cell.
[0059] 1) To establish a porous beam structure with periodic equilateral triangular holes, its parameters include the length L=60 of the beam, the period length l=1 of the microstructure along the x direction, and the thickness of the beam along the z direction h = 3 2 l , The wall thickness of the equilateral triangular hole unit cell is t=0.1; the material properties of the entity are: Young's modulus E=70e9, Poisson's ratio v=0.34, and density ρ=2774; set the scale factor n=1 at this time.
[0060] 2) Perform pure bending loading on the porous beam structure with periodic equilateral triangular holes. According to the periodicity and symmetry of the structure along the x direction, the bending strain energy U on a single period lb for:
[0061] U b = ...
Embodiment 3
[0080] Example 3: Equivalent Young's modulus of regular hexagonal pore unit cells.
[0081] 1) To establish a porous beam structure with periodic regular hexagonal holes, its parameters include the length L=60 of the beam, the period length 3l=3 of the microstructure along the x direction, and the thickness of the beam along the z direction h = 3 l , The wall thickness of the regular hexagonal hole unit cell is t=0.1; the property of the solid material is:
[0082] Young's modulus E=70e9, Poisson's ratio v=0.34, density ρ=2774; set the scaling factor n=1 at this time.
[0083] 2) Perform pure bending loading on the porous beam structure with periodic regular hexagonal holes. According to the periodicity and symmetry of the structure along the x direction, the bending strain energy U on a single period l b for:
[0084] U b = M 2 ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Poisson's ratio | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com