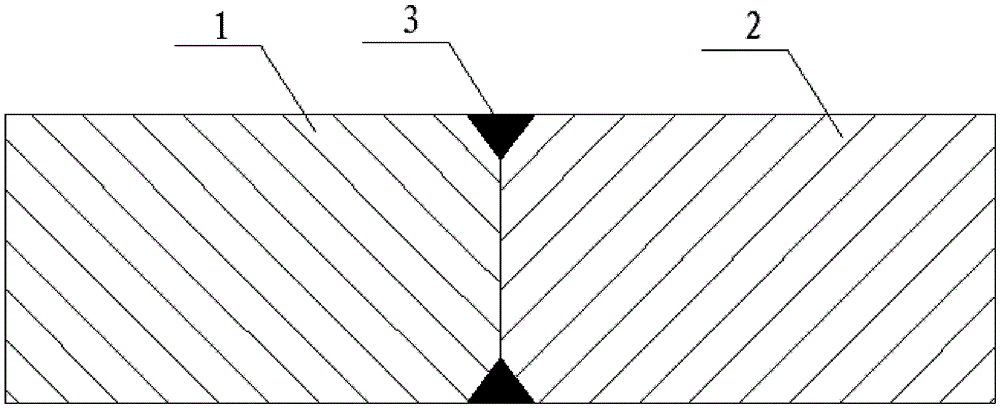
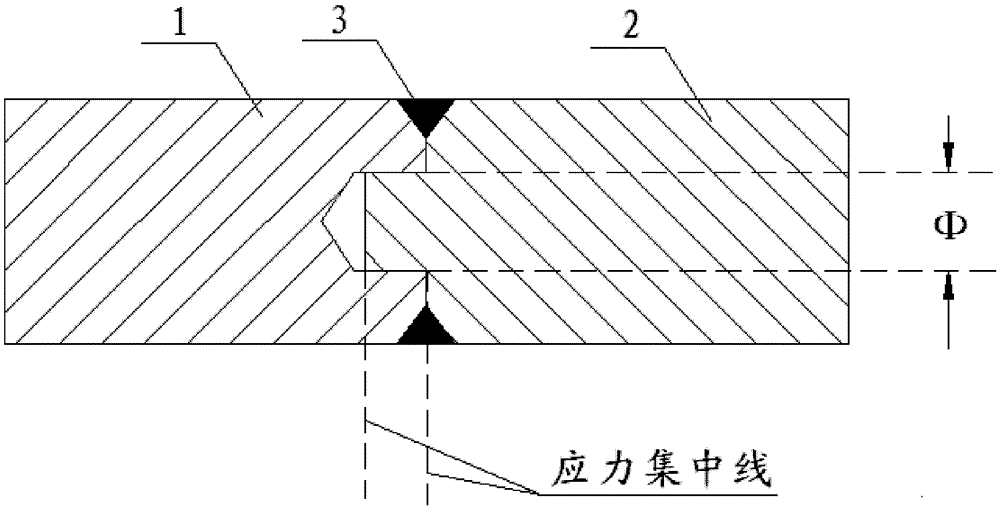
A Repairing Method for Broken Shaft
A repair method and technology for broken shafts, which are applied in the field of repairing broken shafts, can solve the problems of incomplete penetration, slag inclusion, and lack of fusion, so as to eliminate shear concentration stress parts, eliminate shear stress concentration and welding stress. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
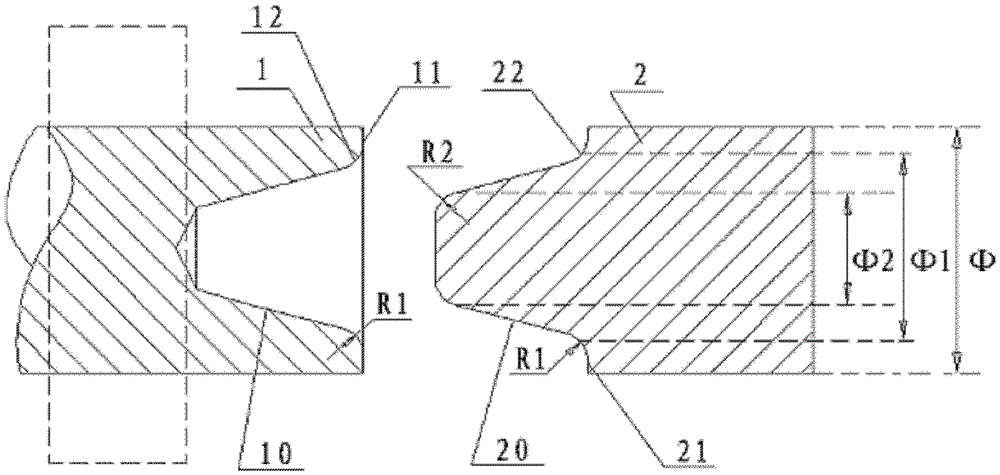
[0051] Example 1: Φ=150 mm, the material is 30 steel shaft shear fracture, and the main use section is reserved as the broken shaft section 1 . First, flatten the fracture surface 11 of the broken shaft section 1 and process the conical hole 10, the hole rounding R1=150, and then prepare the coupling shaft section 2 with a conical head 20 and coaxial diameter and rounding R1=150 And R2=300, the taper of the conical head 20 and the conical hole 10 is the same, and the taper is 10°~12°. Match the conical head 20 of the connecting shaft section 2 at room temperature to determine the distance of a, which is 15mm, and then process the spacer ring 3 with a height h of nine tenths of a, which is 13-14mm, and then insert the spacer ring 3 into the shaft connecting section 2 At the tail of the conical head 20, the gas flame heats the conical hole 10 of the broken shaft section 1 to 400°C within 5 minutes, and pushes the conical head 20 into the conical hole 10 to the root, and cools fr...
Embodiment 2
[0052] Example 2: Φ=100 mm, the gear shaft made of No. 45 steel is sheared and fractured, and the broken shaft at the gear end that has not been disassembled is kept as the broken shaft section 1 . First process the fracture surface 11 of the broken shaft section 1 to flatten and process the conical hole 10, the hole rounding angle R1=50, and then prepare the coupling shaft section 2 with the conical head 20 coaxial diameter and round the corner R1=50 and R2=100, the taper of the conical head 20 and the conical hole 10 is the same, and the taper is 10°~12°. The connecting shaft section 2 is selected from No. 35 or 40 steel, preferably No. 40 steel, and then the conical hole 10 of the broken shaft section 1 and the The conical head 20 of the connecting shaft section 2 is matched at room temperature to determine the distance of a, which is 10 mm, and the processing height h is nine tenths of a, which is 9 mm. , the gas flame heats the conical hole 10 of the broken shaft section ...
Embodiment 3
[0053] Example 3: Φ = 50mm, material 35 steel is sheared and fractured, and the broken shaft at the main use end is reserved as the broken shaft section 1 . First, the fracture surface 11 of the broken shaft section 1 is gold-processed and flattened, and the conical hole 10 is processed, and the hole is rounded R1=25. Next, prepare the connecting shaft section 2 with the conical head 20 and the coaxial diameter and fillet R1=25 and R2=50. The taper of the conical head 20 and the conical hole 10 is the same, and the taper is 10°~12°. The connecting shaft section 2 is selected. 25 or 30 steel, preferably 30 steel. Then match the conical hole 10 of the broken shaft section 1 with the conical head 20 of the connecting shaft section 2 at room temperature to determine the distance of a, which is 10 mm, and the processing height h is nine tenths of a, which is 4 mm spacer ring 3, and then set the spacer ring 3 sets Enter the tail of the conical head 20 of the connecting shaft sectio...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com