Self-adaptive light-transfer single-shadow removal method based on block matching
A shadow removal and self-adaptive technology, applied in image data processing, instrumentation, computing, etc., can solve problems such as reflectivity changes, loss of texture details, algorithm failure, etc., to achieve natural shadow removal results, protect texture information, Consistent lighting effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
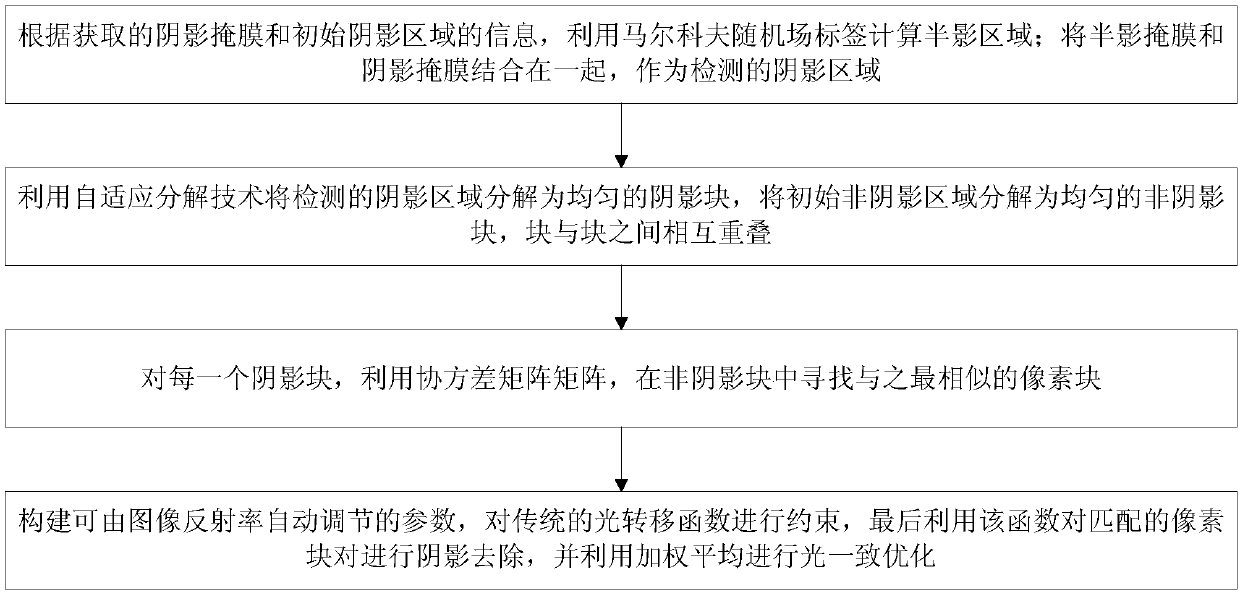
[0044] A single-frame shadow removal method based on block matching for adaptive light transfer, see figure 1 and figure 2 , the method includes the following steps:
[0045] 101: Provide the pixel coordinates of the initial seed point by the user in the initial shadow area and the initial non-shadow area by clicking the mouse, and use the RGB value in the coordinate field to perform support vector training, and divide the image pixels into shadow pixels and non-shadow pixels;
[0046] 102: Based on the pixel coordinates of the initial seed point, iterative region growth is performed, and shadow pixels are added to the initial shadow region to form a shadow mask;
[0047] 103: According to the acquired shadow mask and information of the initial shadow area, calculate the penumbra area by using the Markov random field label; combine the penumbra mask and the shadow mask together as the detected shadow area;
[0048] 104: Decompose the detected shadow area into uniform shadow...
Embodiment 2
[0053] The following is combined with specific calculation formulas, examples, figure 1 and figure 2 , the scheme in embodiment 1 is further introduced, see the following description for details:
[0054] 201: shadow detection;
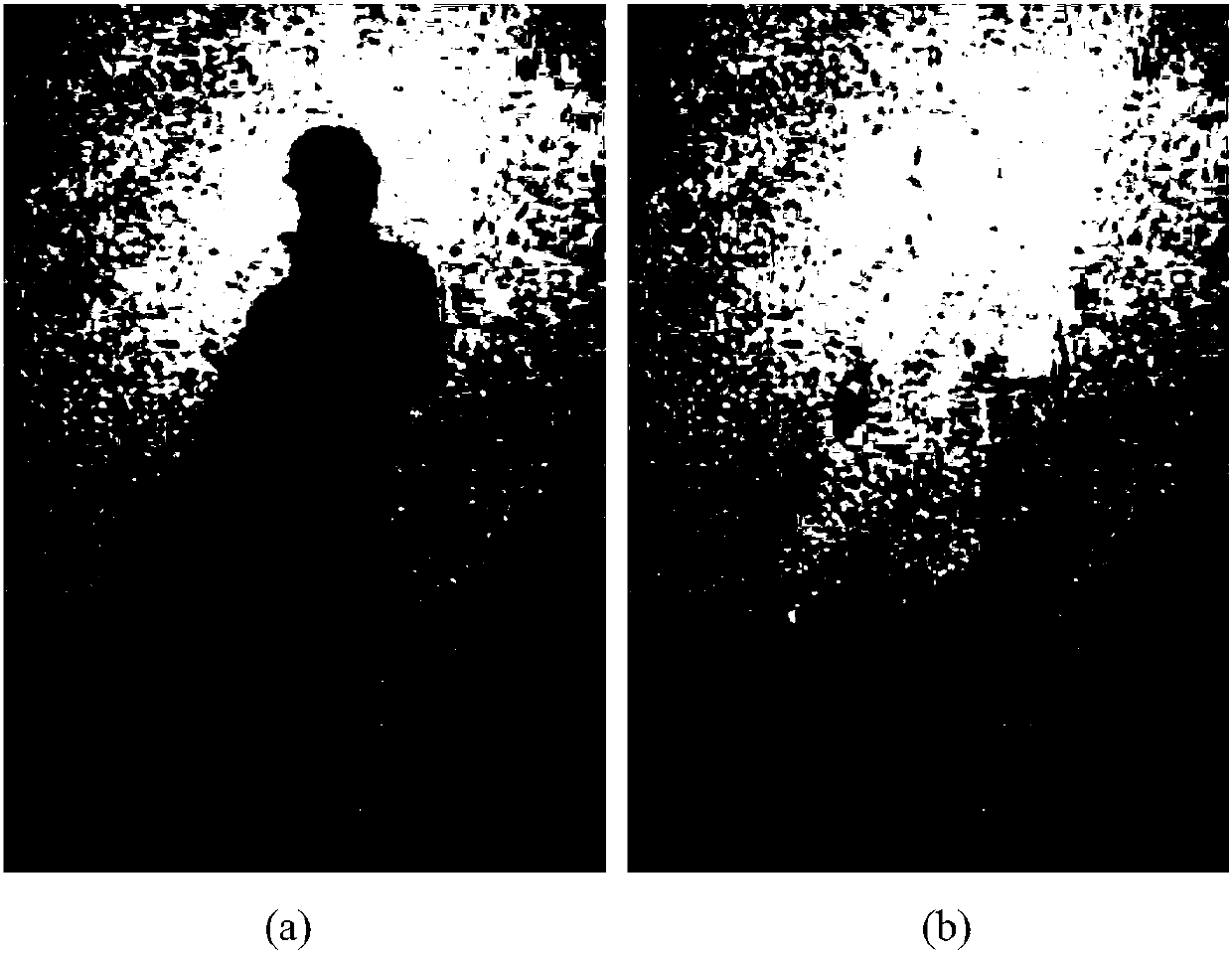
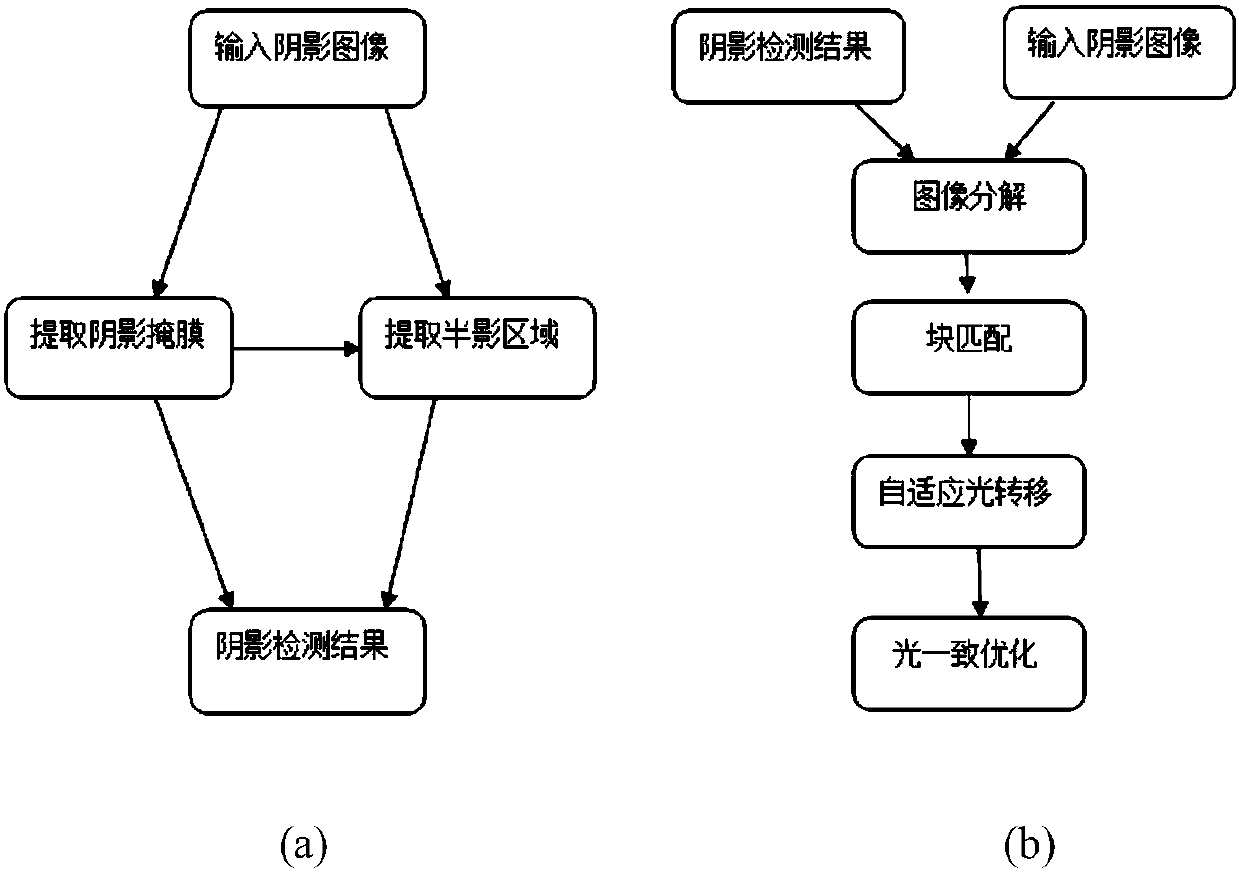
[0055] Shadow detection is the premise of shadow removal, and the quality of the detection effect directly affects the subsequent shadow removal effect. The embodiment of the present invention detects the shadow area based on a user-assisted method. The user clicks the mouse in the initial shadow area and the non-shade area to provide the initial seed point coordinates, and uses the RGB values in the coordinate field to perform support vector training and divide the image pixels. into shaded pixels and non-shaded pixels. Based on the initial seed point coordinates provided by the user, iterative region growing is performed to add shadow pixels to the initial shadow region to form a shadow mask.
[0056] see figure 2 (a), According to the ac...
Embodiment 3
[0115] Combined with the specific experimental data, Figure 3-Figure 7 Validation and robustness of the scheme in Examples 1 and 2 are verified, see the following description for details:
[0116] image 3 To deal with unevenly shaded images, image 3 There are obvious changes in the brightness of the shaded areas in (a), with darker areas at the bottom of the image. The embodiment of the present invention fully considers the brightness information at different positions by performing adaptive light transfer for each shadow block independently, which helps to remove uneven shadows, such as image 3 After the shadow is removed in (b), the illumination is consistent.
[0117] Figure 4 For handling shaded images containing highly structured textures, Figure 4 The image in (a) has a bumpy structure. The embodiment of the present invention improves the traditional light transfer function by using an adaptive parameter, which can be adjusted automatically with the reflectiv...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com