Virtual world internet web site using common and user-specific metrics
a virtual world and web site technology, applied in the internet field, can solve the problems of taking a long time for a site to be contacted, stressful rather than relaxing experience, and none of which, however, presents a real-life encounter experience, and achieves the effect of improving a user's experien
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
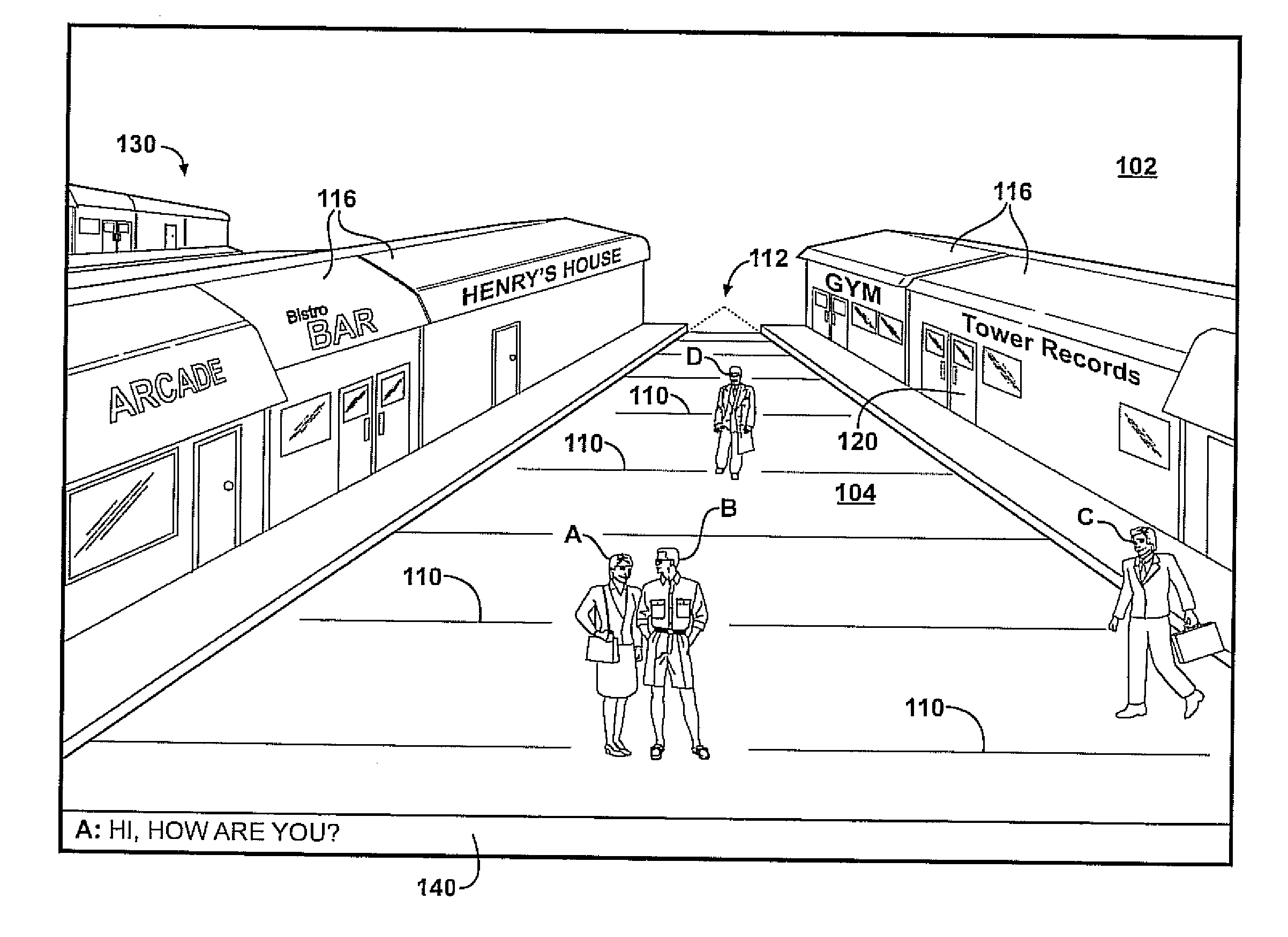
[0012] This invention addresses problem areas or needs associated with the Web to make surfing more satisfying or pleasurable. Broadly, the goal is a Web site which simulates a “Virtual World” so as to graphically and functionally restore the sense of proximity, or distance, while surfing on the Web. In accordance with the invention, a visitor to the Virtual World will be presented with a two- or three-dimensional depiction of a geographic terrain, and a means of virtual locomotion. For example, if the person wants to have a leisurely “stroll,” the user can “walk,” whereas, if a person wants to have a quick tour of what is available, he or she can “drive,” ride a bicycle or an airliner, as appropriate, so that the “far” locations on the terrain would take more time to reach than the “near” locations, similar to a “twitch” type of video game.
[0013] The icons would preferably have unique configurations which could be chosen by the visitor from a selection or created based on the prof...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com