Uses of anti-CD40 antibodies
A technology of antibody and monoclonal antibody, applied in the application field of anti-CD40 antibody, can solve the problem of wasting patients
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0191] Basic guidelines for the preparation and use of polypeptide variants are provided in the art. In preparing variants of anti-CD40 antibodies, one skilled in the art will readily determine which modifications to the nucleotide or amino acid sequence of the native protein will result in a therapeutically active ingredient suitable for use in the pharmaceutical compositions of the methods of the invention variant of .
[0192] The anti-CD40 antibody used in the method of the present invention preferably has at least one of the following biological activities in vitro and / or in vivo: inhibition of T cell-stimulated normal human peripheral B cells to secrete immunoglobulin; inhibition of CD40L expressing cells or soluble CD40 ligand ( sCD40L)-stimulated survival and / or proliferation of normal human peripheral B cells; inhibition of Jurkat T-cell-stimulated normal human peripheral B cell survival and / or proliferation; inhibition of sCD40L or solid-phase CD40L-stimulated any ce...
Embodiment 1
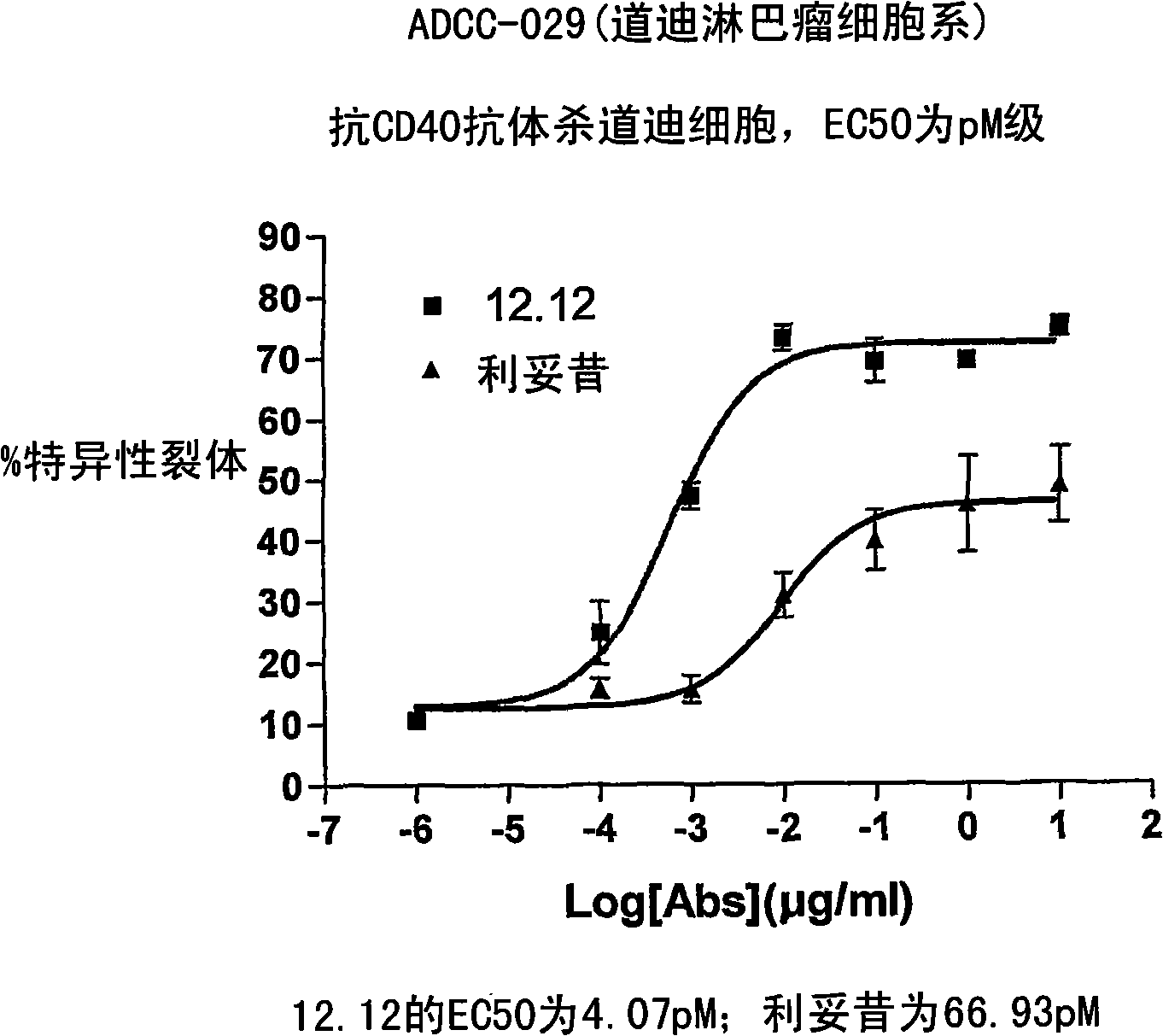
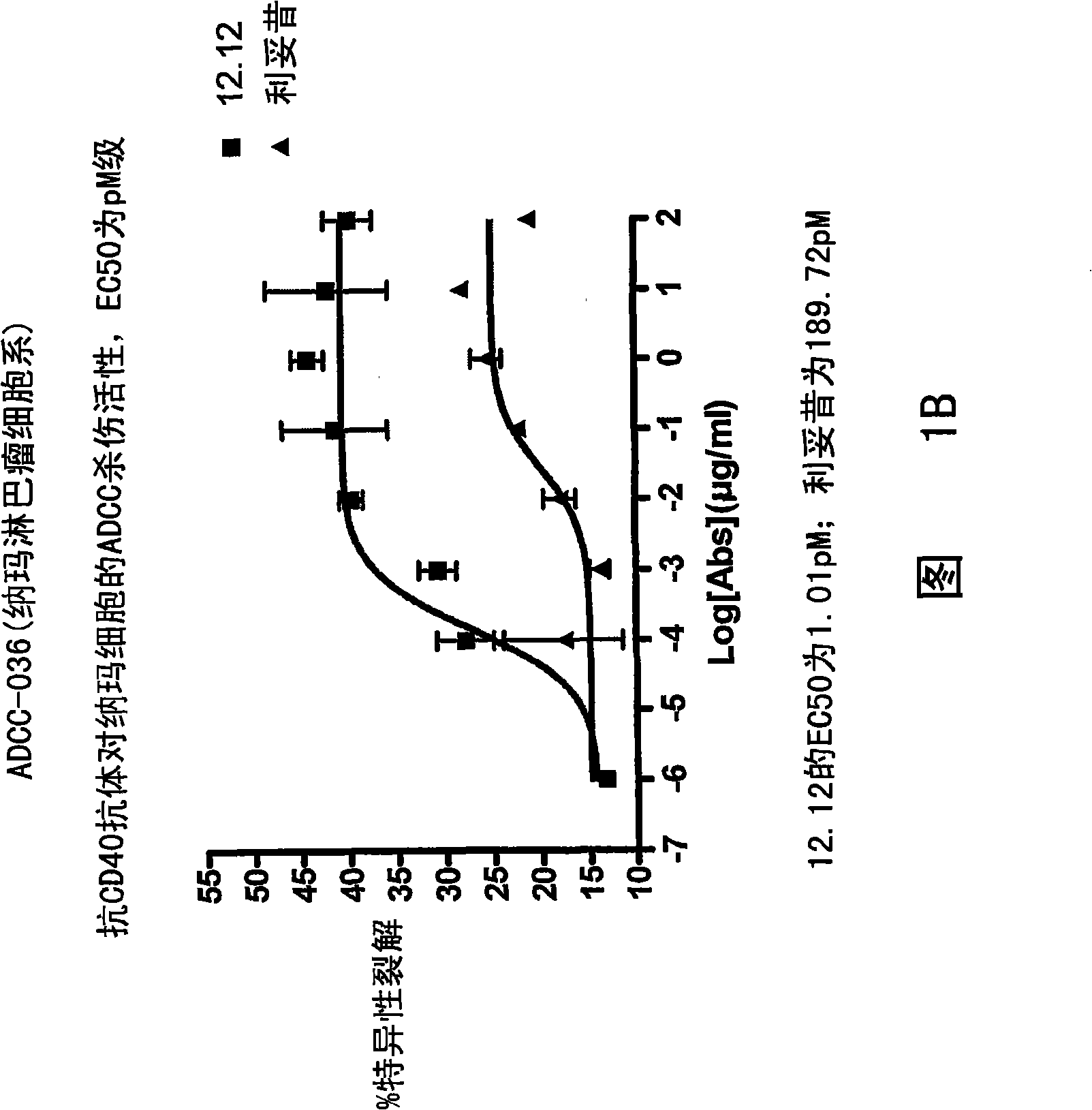
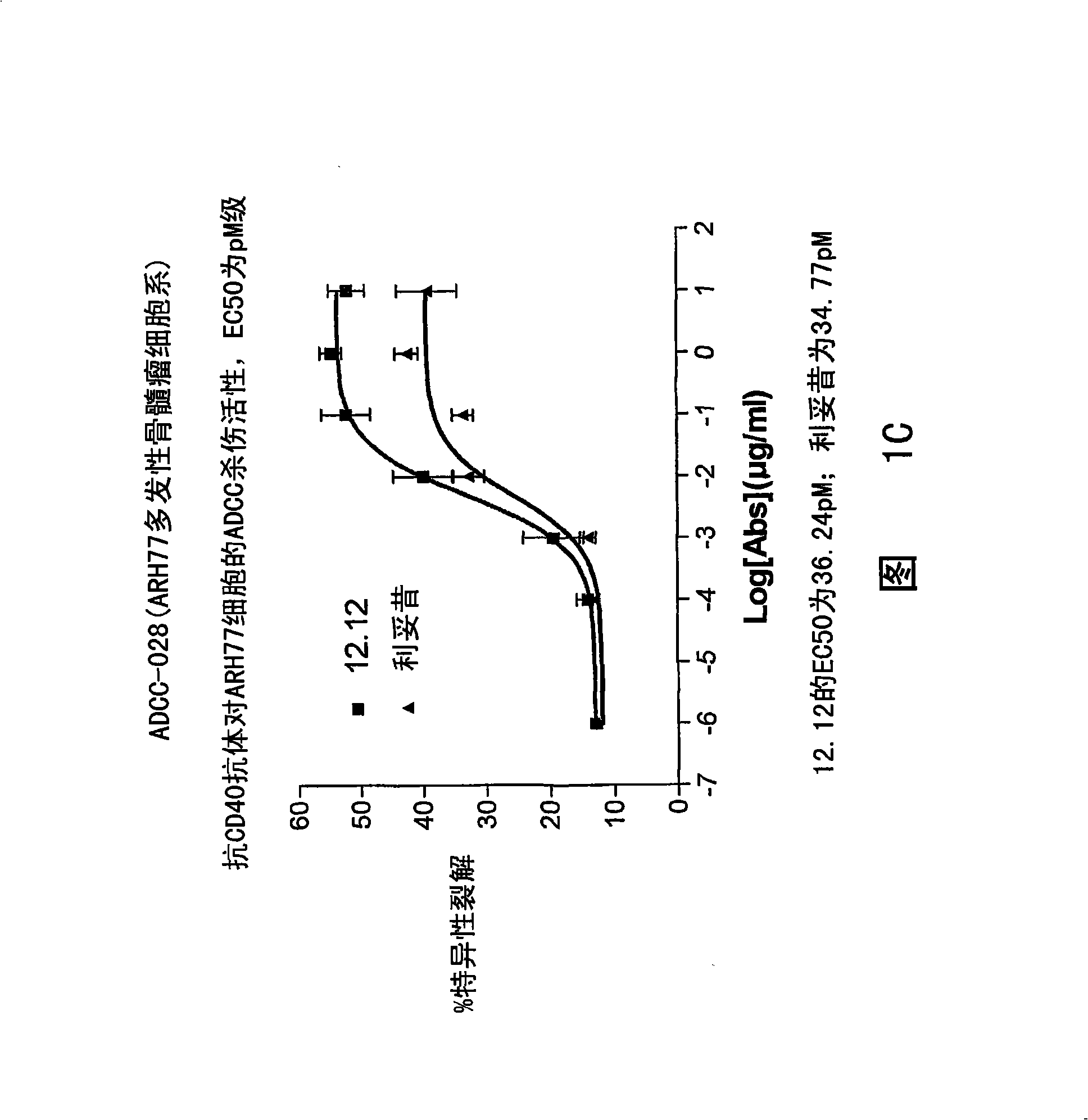
[0295] Example 1: Analysis of ADCC of Cell Lines
[0296] The relative ADCC activities of CHIR-12.12 and rituximab were compared against various malignant B cell lines expressing both CD40 and CD20 antigens, including lymphoma cell lines (Daudi, Namar cell lines), multiple Myeloma cell lines (ARH77, IM-9), B-ALL cell line (CCRF-SB) and B-CLL cell line (EHEB).
[0297] Determination of percent maximum lysis and ED, respectively 50 , comparing the ADCC potency and strength of CHIR-12.12 and rituximab. The results of these trials can be found in Figure 1A -1F. In all target cell lines, CHIR-12.12 was a more potent and potent mediator of ADCC compared to rituximab. In the six cell lines examined, the number of CD20 molecules per cell surface was 2.6-30.8 times higher than the number of CD40 molecules. These data demonstrate that CHIR-12.12 lyses malignant B-cell lines more efficiently than rituximab, despite displaying fewer CD40 molecules compared to CD20.
Embodiment 2
[0298] Example 2: Analysis of ADCC in CLL patient cells
[0299] The relative ADCC activities of CHIR-12.12 and rituximab on ex vivo primary CLL cells from 8 patients were compared. Compared to rituximab, CHIR-12.12 had higher ADCC activity against CLL in all patients (see Figures 2A-D and Figure 3). The results are shown in Figure 3. CHIR-12.12 was more potent than rituximab.
[0300] Antibody-Dependent Cytotoxicity (ADCC) Assay Design
[0301] Target cells: CLL patient cells, 5000 cells / well. Effector cells: purified normal human NK cells, 50,000 cells / well. E:T ratio: 10. Antibody concentrations: 0.00001, 0.0001, 0.001, 0.01, 0.1, 1 and 10 μg / ml. Incubation time: 4 hours. Medium: RPMI (without phenol red) + 10% FBS + 1% P / S. Culture device: 96-well round bottom plate. Readout: Released Calcein fluorescence AM was measured in Arbitrary Fluorescence Units (AFU) with excitation at 485 nm / emission at 535 nm. Calculation: % specific lysis=100×(AFU detection value-AFU...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| affinity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| affinity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| affinity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com