Insect genetical population simulating method based on natrual reproduction process
A genetic population and insect technology, applied in the field of insect genetic population simulation based on the natural reproductive process, can solve the problems of inability to use selected populations, unclear biological meaning, and no establishment of insect genetic population simulation methods, so as to improve efficiency, easy to achieve effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
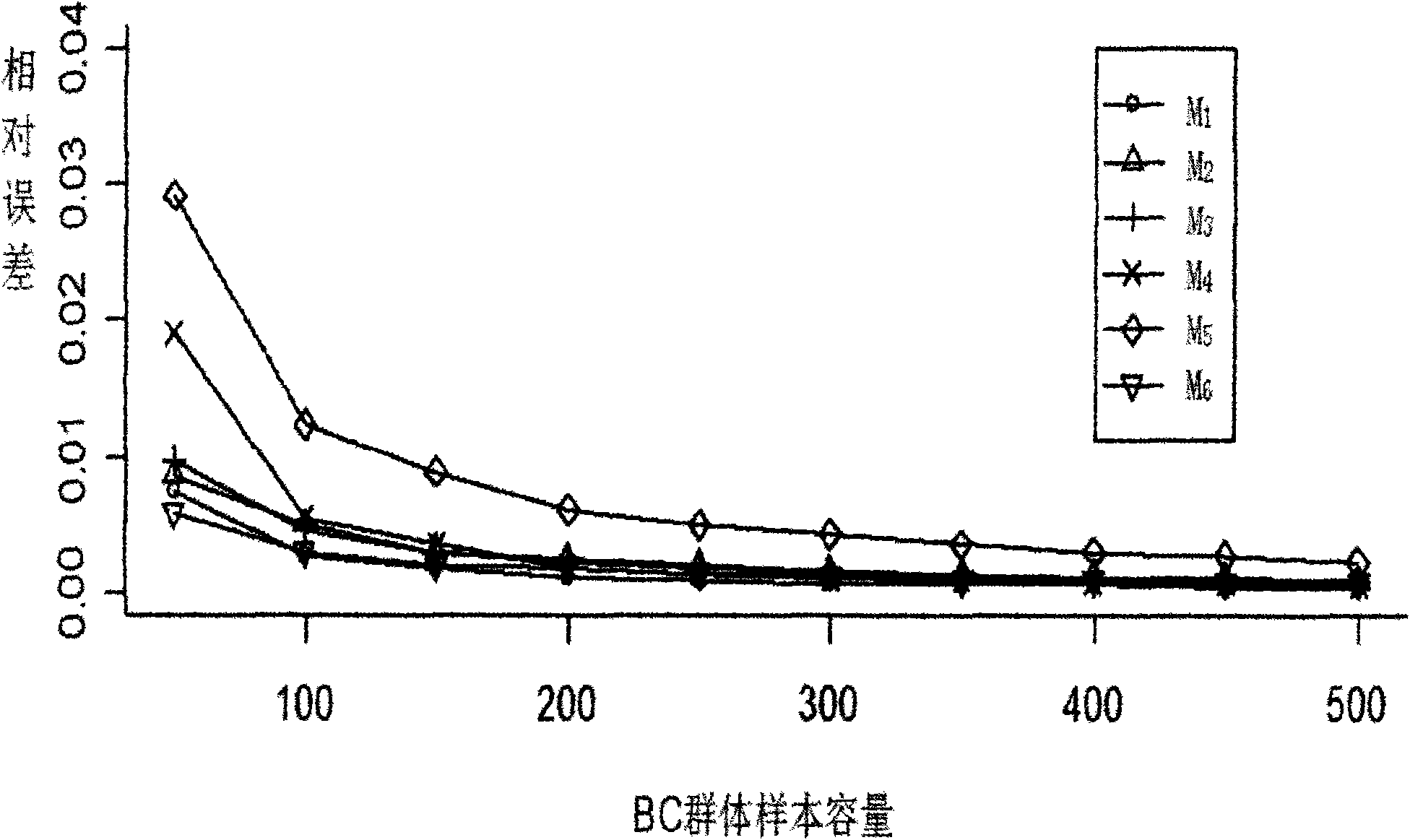
[0024] Example 1: Take the genetic analysis of resistance genes of rice stem borer to Bt insecticide as an example. Let resistance gene be R bt , the corresponding recessive gene is r bt . Here, only the chromosome Chrl carrying the resistance gene needs to be considered, and other chromosomes need not be considered. After the parents are selected, the marker data of the parents (M 1 0, M 2 2, M 3 67, M 4 70, M 5 141, M 6 160) and (m 1 0,m 2 2,m 3 67, m 4 70, m 5 141, m 6 160), where M 1 ,M 2 ,...,M 6 and m 1 , m 2 ,...,m 6 Represent the 6 molecular markers on Chrl of the maternal and paternal chromosomes, 0, 2, ..., 160 represent the position of each marker on the chromosome, expressed by the accumulated genetic distance, and the unit of distance is centimorgans (cM) . The actual backcross population contains 100 individuals. Simulate as follows:
[0025] (1) Express the original sample sequence of molecular markers of the parents of Chilo s...
Embodiment 2
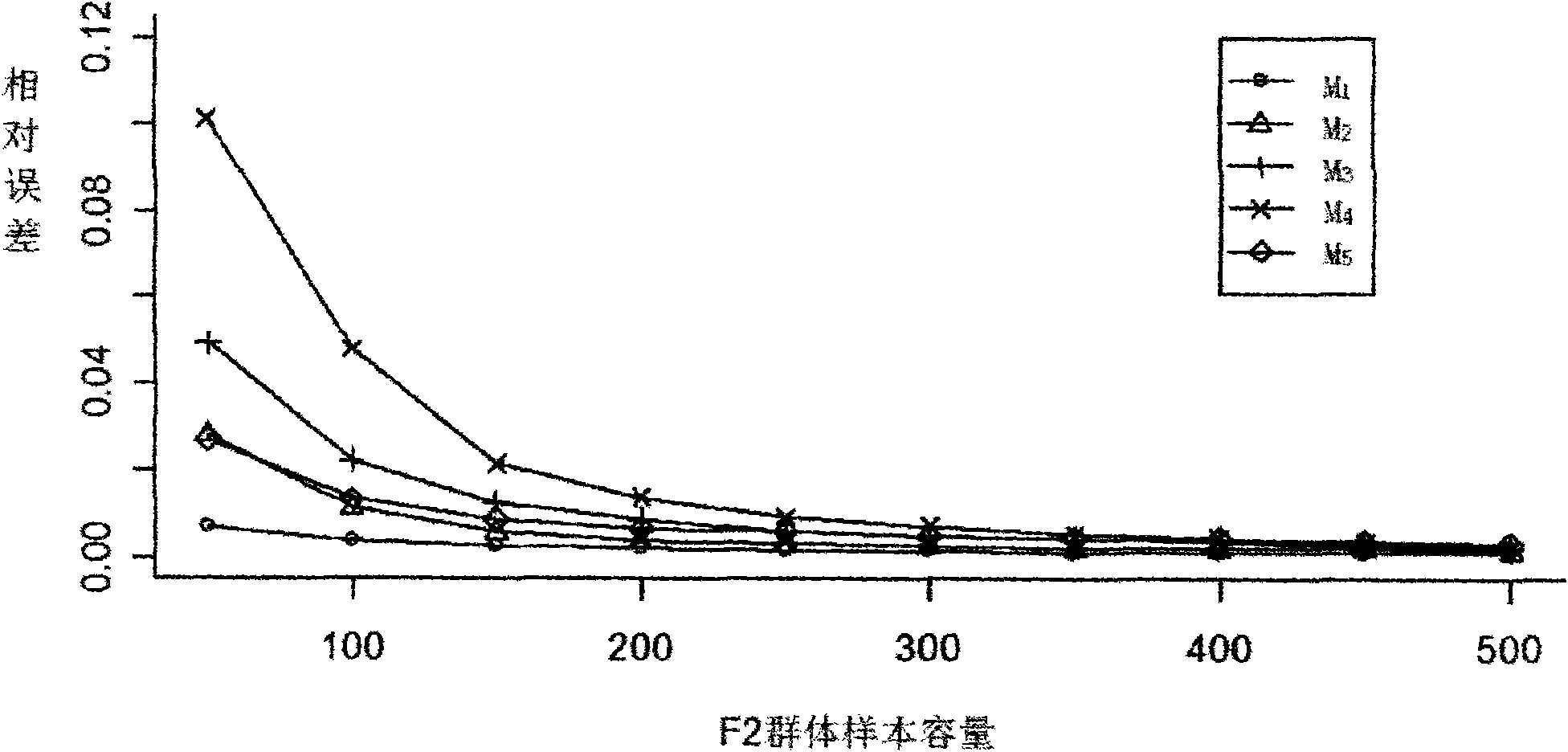
[0031] Example 2: Take the genetic analysis of the Drosophila F2 population as an example. Drosophila has 4 pairs of chromosomes, one pair of sex chromosomes and 3 pairs of autosomes. Assuming that we need to map autosomal genes genome-wide, we need to simulate F2 populations with different numbers of individuals. After the parents are selected, the marker data of the parents are obtained by molecular biology methods, here are five molecular markers on the maternal and paternal chromosome 1 (M 1 0, M 2 11, M 3 101, M 4 111, M 5 118) and (m 1 0,m 2 11, m 3 101,m 4 111,m 5 118). Simulate as follows:
[0032] (1) Represent the original sample sequence of parental molecular markers of Drosophila as a digital array X composed of 1 and 0 (i) ={X (i) (1) , X (i) (2) , X (i) (3)}, where i=1 represents the female parent, i=2 represents the male parent, X (i) (1) , X (i) (2) , X (i) (3) Represent the molecular marker vectors on chromosomes 1, 2, and 3, ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com