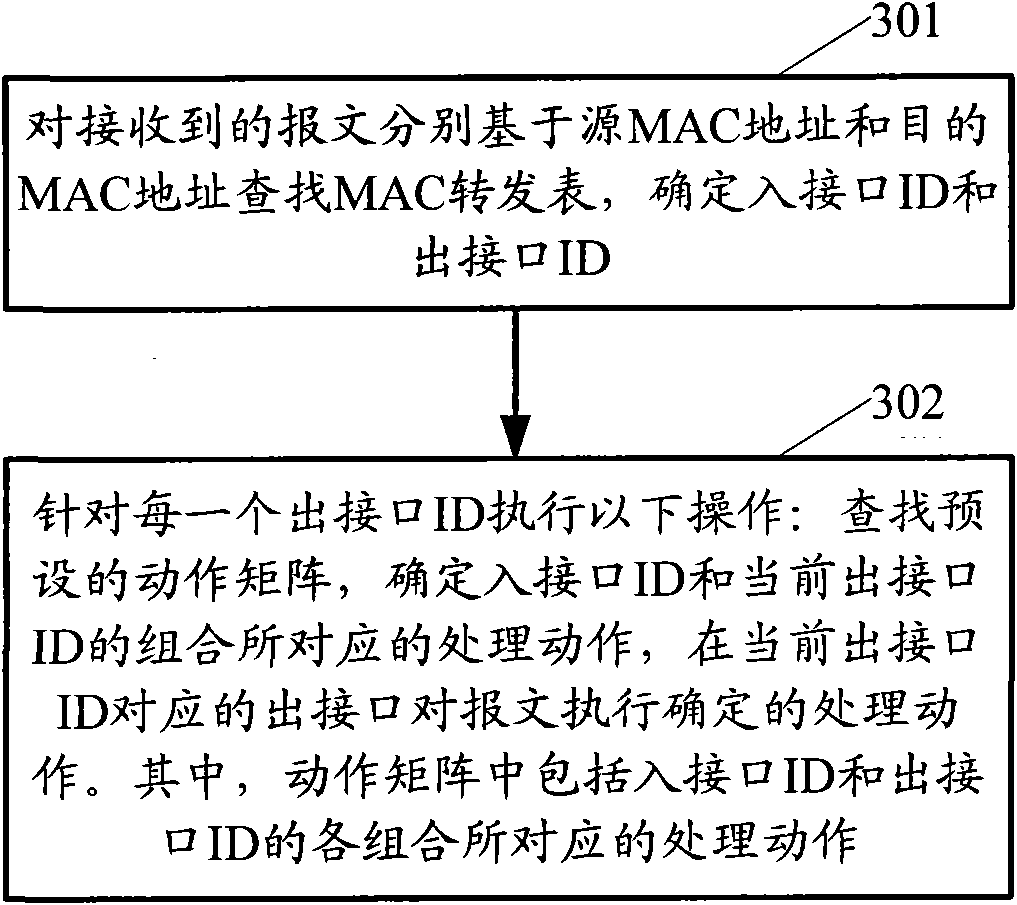
Method and device for processing message
A message processing and message technology, which is applied in the field of network communication, can solve problems such as invalid broadcast flow and inability to realize source filtering, and achieve the effect of suppressing invalid broadcast problems
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
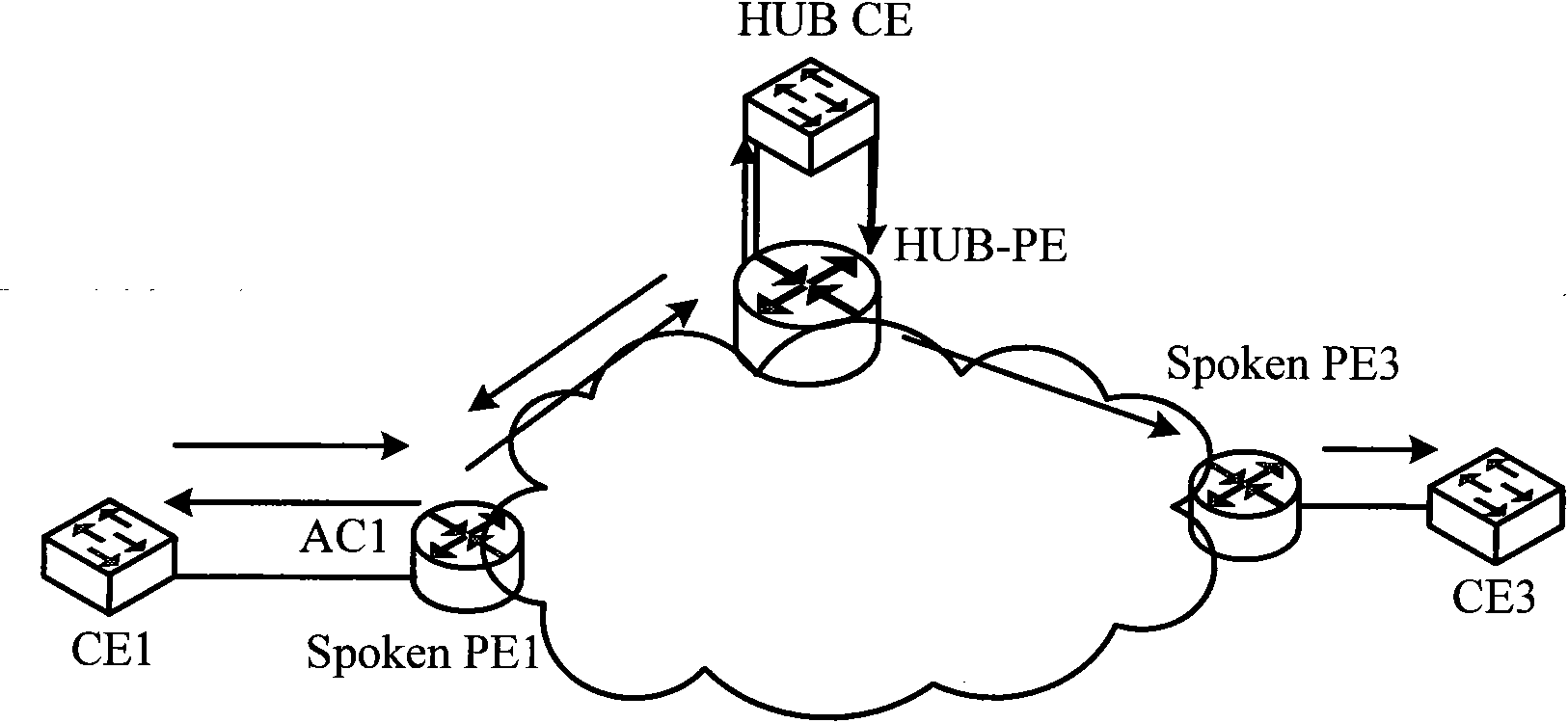
[0039] Example 1: Hub-Spoken networking applied to VPLS, such as Figure 5 shown.
[0040] On the Spoken PE1 device, the incoming broadcast packet from the CE1 device has an inbound interface ID of AC1. The Spoken PE1 device learns the source MAC address from AC1 to the interface ID corresponding to the source MAC address in the MAC address forwarding table. At the same time, add the VC label to the broadcast message and forward it to the HUB PE device. The HUB PE strips off the VC label and forwards the broadcast message to the HUB CE, and the HUB CE returns it to the HUB PE after processing. After the HUB PE receives the message, it adds a VC label and broadcasts it in the VSI again. At this time, both Spoken PE1 and Spoken PE3 will receive the broadcast message.
[0041] After receiving the broadcast message, Spoken PE1 strips off the VC label. Search the MAC forwarding table based on the destination MAC address and the source MAC address respectively. The destination M...
example 2
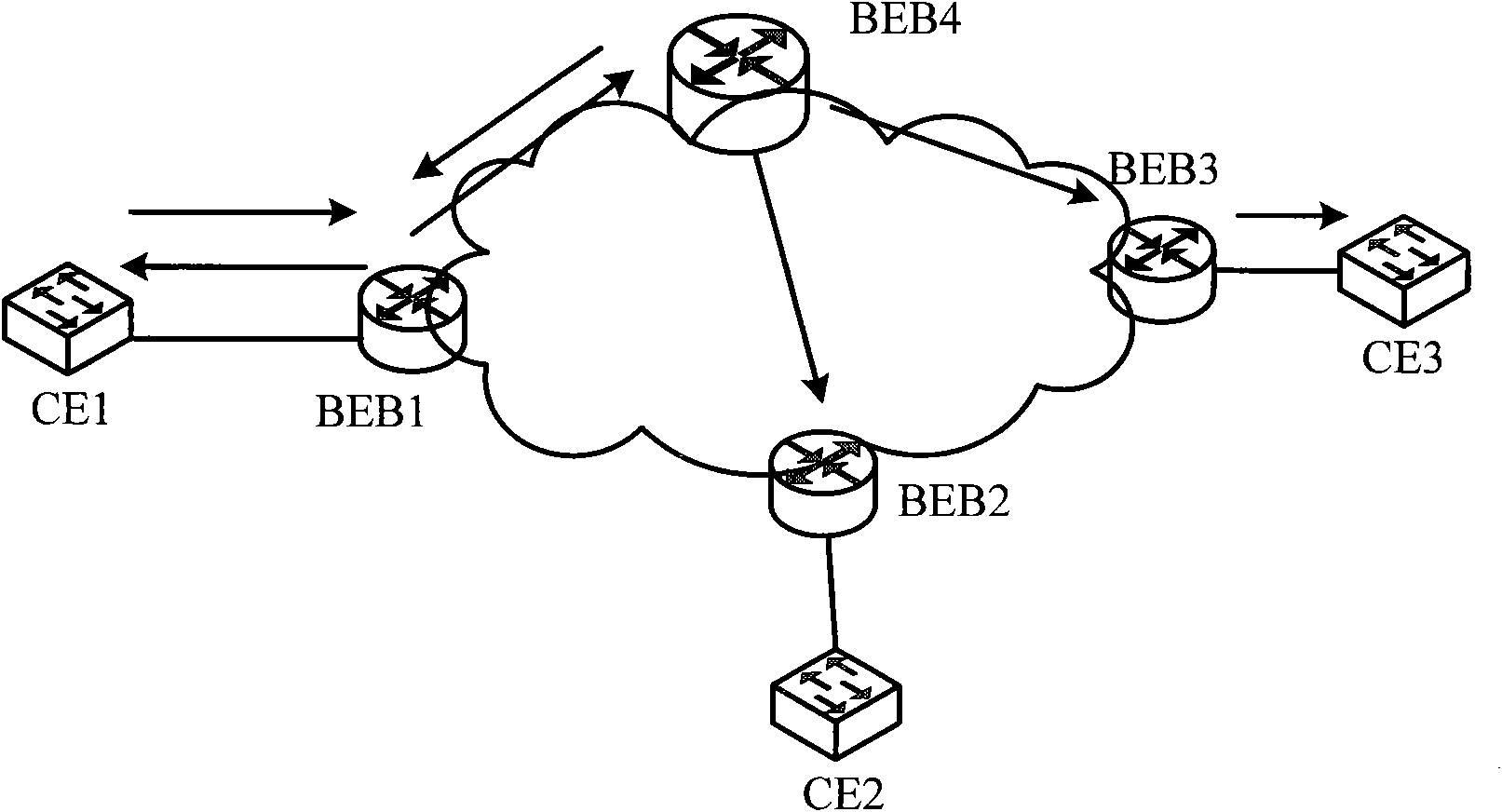
[0049] Example 2: Applied to star PBB networking, such as Figure 6 shown.
[0050] The broadcast message entering from CE1, after passing through the BEB1 device, adds the MinM tunnel header and broadcasts to BEB4 along the uplink port 1. At this time, BEB4 pops off the MinM tunnel header after receiving the MinM message from the uplink port 1 of the public network side, and The source MAC address is learned in the I-SID domain. At this time, the inbound interface of the source MAC address is uplink port 1, and is recorded in the MAC forwarding table.
[0051] When the packet entering BEB4 is searched based on the destination MAC address, it also searches based on the source MAC address. Since the destination MAC address of the broadcast message is the broadcast address, the MAC forwarding table cannot be matched. The default outbound interface ID is used, that is, multiple broadcast outbound interface IDs: uplink port 1, uplink port 2, and uplink port 3. Although the broad...
example 3
[0061] Example 3: Access restrictions applied to different VLAN domains in the same VSI instance, such as Figure 7 shown.
[0062] exist Figure 7 In the shown network, the ACs where CE1, CE2, CE3, and CE4 are located belong to the same VSI instance, but this VSI domain is divided into multiple VLAN domains, and each VLAN domain is distinguished by VLANTag, that is, CE1 and CE3 The AC where CE2 and CE4 reside is bound to VLAN1, and the AC where CE2 and CE4 reside is bound to VLAN2. When each PE device learns the source MAC address, it sends the VLAN Tag of the packet as the interface ID to the MAC forwarding table.
[0063] In this example, it is assumed that VLAN1 is restricted to only have access to this VLAN domain, and VLAN2 is allowed to access all VLAN domains. Then it can be set in advance in the action matrix as shown in Table 3.
[0064] table 3
[0065]
[0066] The packet whose destination MAC address is sent by CE1 is the MAC address of the user on CE4 is ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com