Labor-saving bicycle
A bicycle and flywheel technology, which is applied in the field of rickshaws, can solve the problem of inconvenient effort when pedaling and driving, and achieve the effect of good labor-saving effect.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
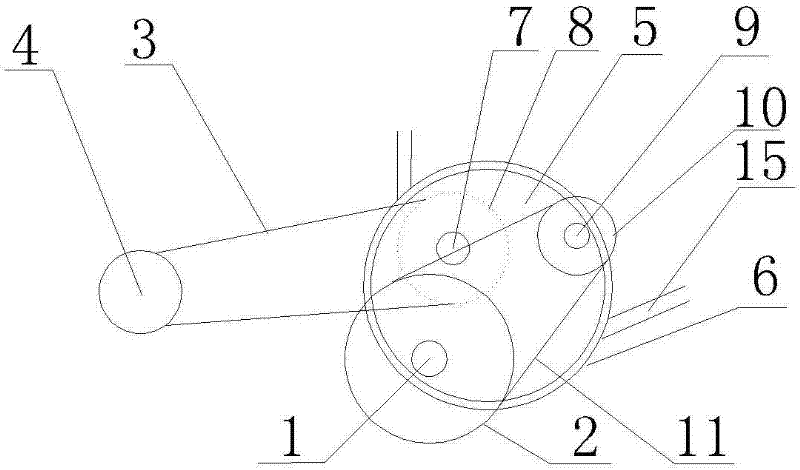
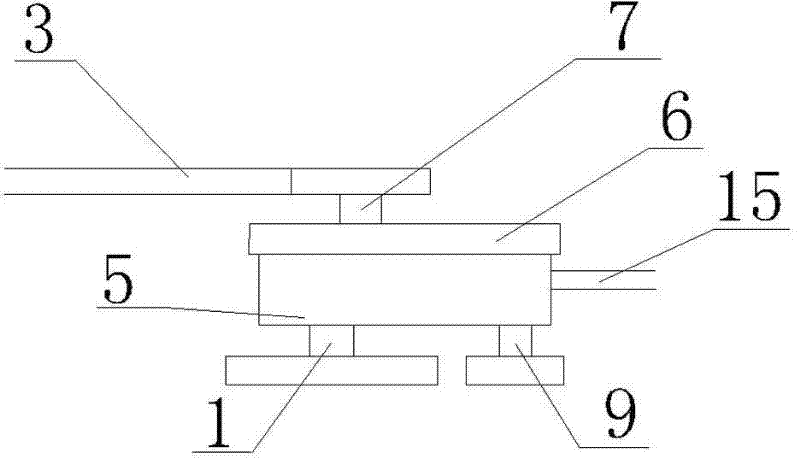
[0012] Such as figure 1 and figure 2 As shown, a labor-saving bicycle includes a pedal axis 1, a tooth plate 2, a chain I3, a rear axle 4, a box body 5 and a box body shell 6, and is characterized in that: the box body 5 is also provided with an output shaft 7, Flywheel Ⅰ 8, input shaft 9, flywheel Ⅱ 10, chain Ⅱ 11 and transmission assembly 12, output shaft 7 has flywheel Ⅰ 8, input shaft 9 has flywheel Ⅱ 10, pedal center shaft 1 is linked with input shaft 9 through chain Ⅱ 11, and input shaft 9 is linked with the output shaft 7 through the transmission assembly 12.
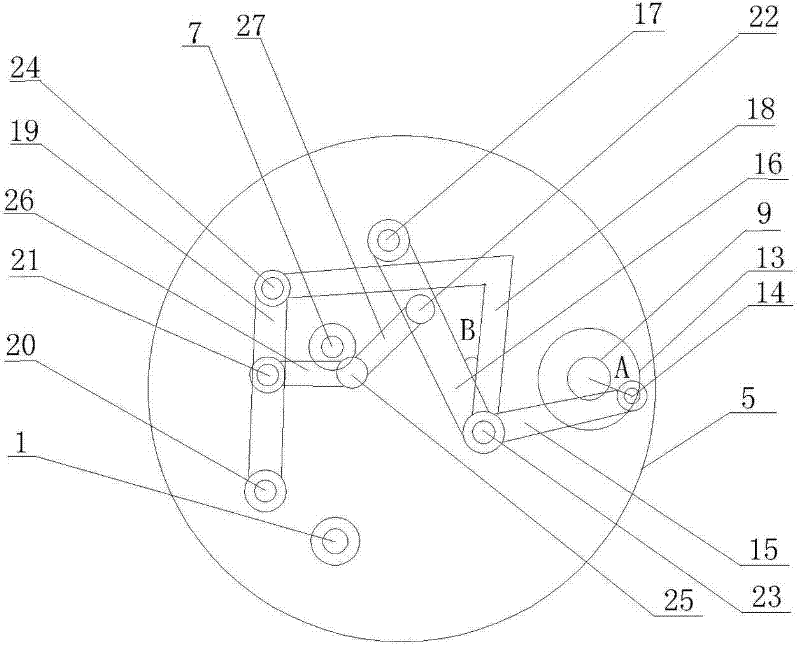
[0013] Such as image 3 As shown, the structure of the transmission assembly 12 is: there is a disc 13 on the input shaft 9, and a rotating shaft I14 on the disc 13. The rotating shaft I14 is connected to the movable shaft III23 through the transmission rod I15, and the movable shaft III23 is connected to the fixed shaft through the rod II16. I17 is connected, the fixed shaft I17 is fixed on the box body 5, o...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com