SM2 signature algorithm security verification method based on random number unknown
A verification method and random number technology, applied in the field of information security, which can solve problems such as difficult algorithms and inability to protect and protect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
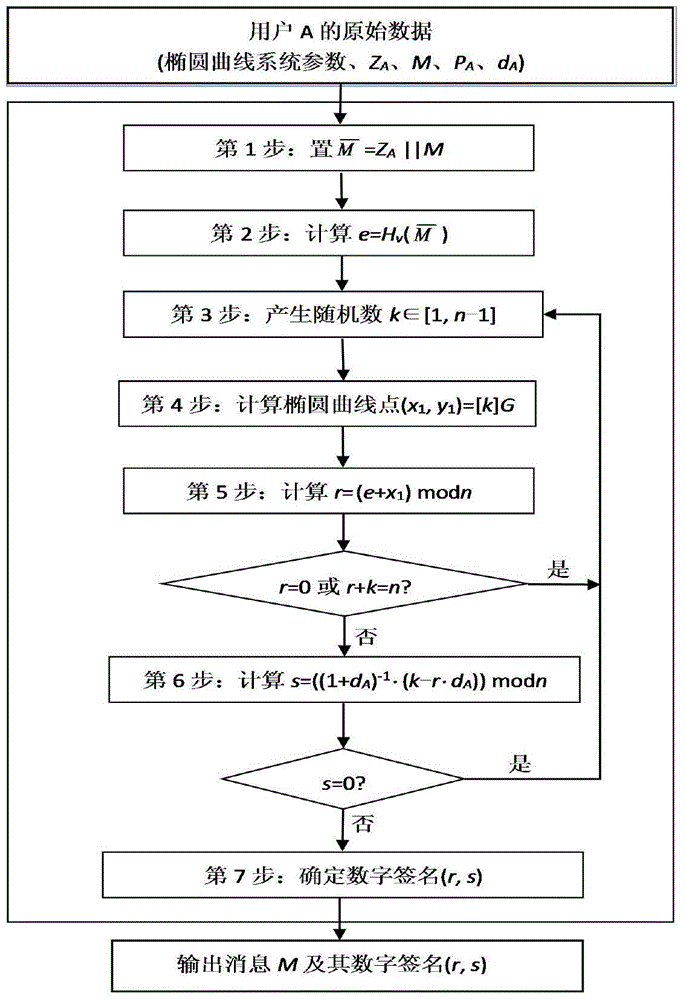
[0081] The following describes the present invention in further detail with reference to the accompanying drawings and an example, but the scope of the present invention is not limited in any way. In the embodiment, an experiment in which the error attack method of the present invention performs a lattice attack on the SM2 signature algorithm is used as an example to illustrate the effectiveness of the present invention.
[0082] 1) Injecting an error into the random number k causes the same error in the lower part of the bit. In a 32-bit SM2 signature algorithm chip, a total of 50 signatures are performed. When the random number of machines generated in each signature operation is written into the memory, an error is injected into the EPPROM (store COS instruction) area, and k i = B i 2 l +a i (0≤i≤49) the lower 32 bits a i All are equal to a, where l=32, as shown in the following table, the lower 32 bits of all random numbers are the same, all are a, a=0xf5e333d0, and an incorre...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com