A dual-bias passive control method for sun-synchronous orbit descending node local time
A technology of sun-synchronous orbit and descending node, which is applied in the direction of motor vehicles, space navigation vehicle guidance devices, space navigation equipment, etc., to achieve the effect of passive control principle and calculation process optimization, fuel saving, and less calculation.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
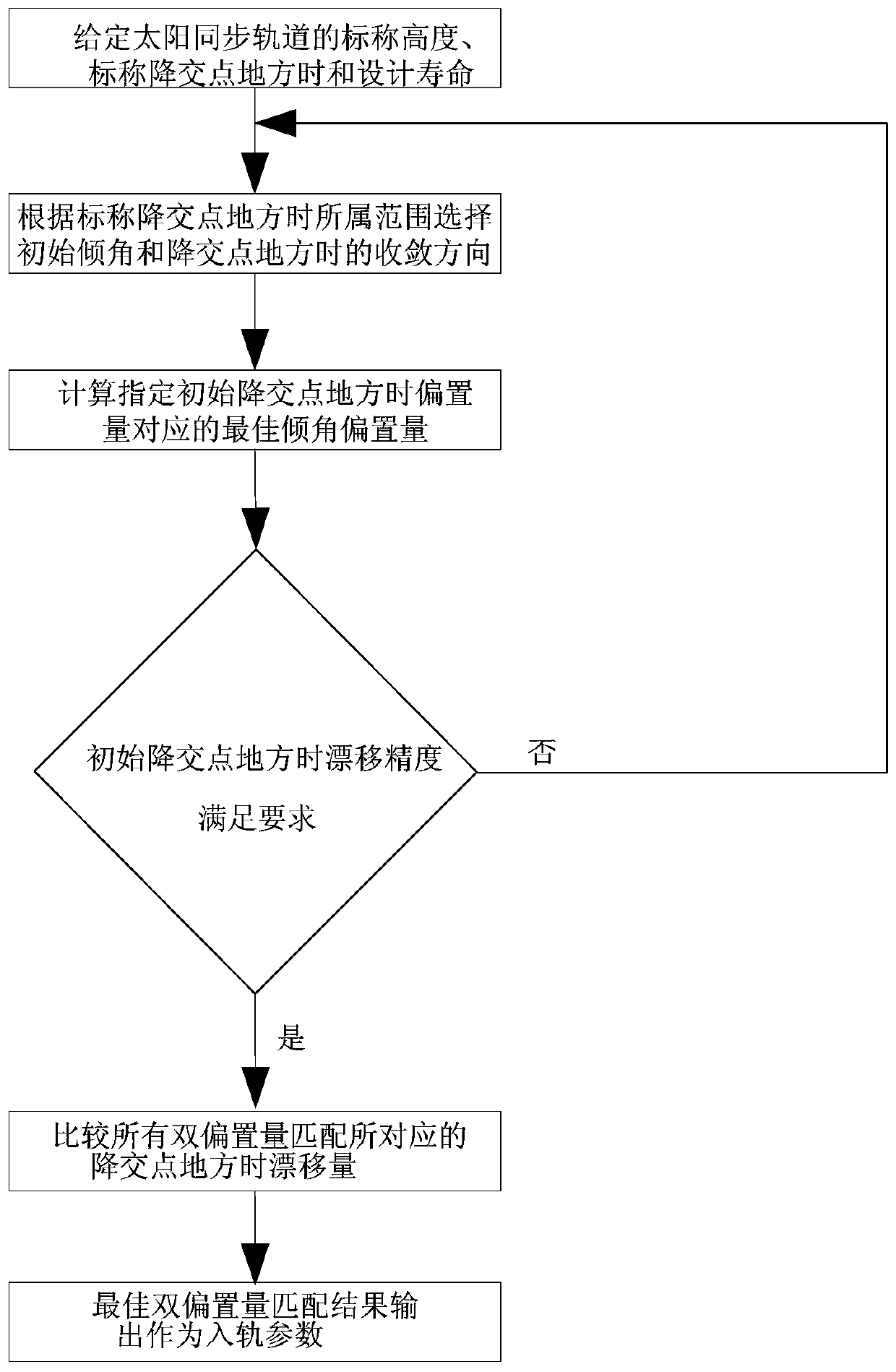
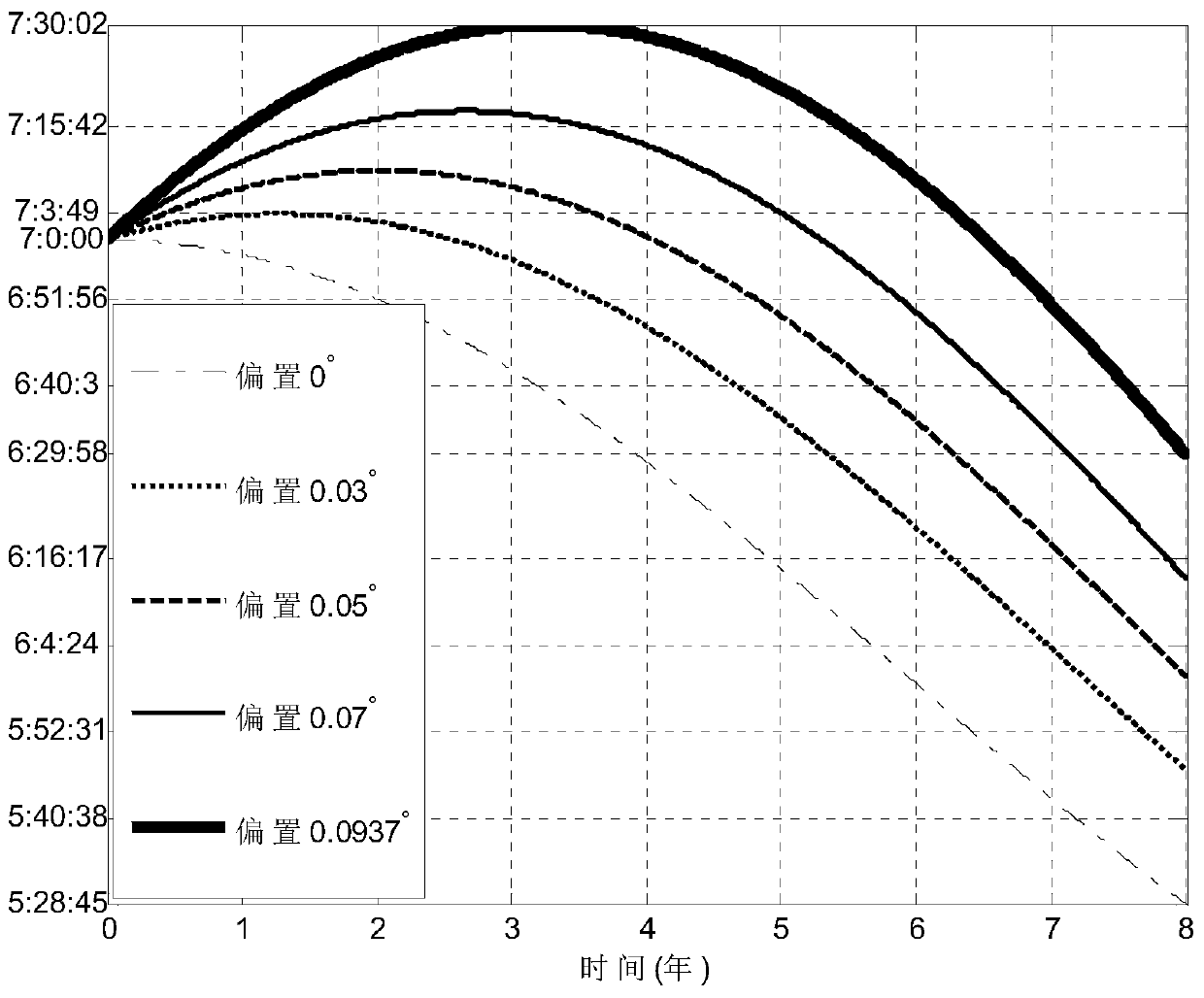
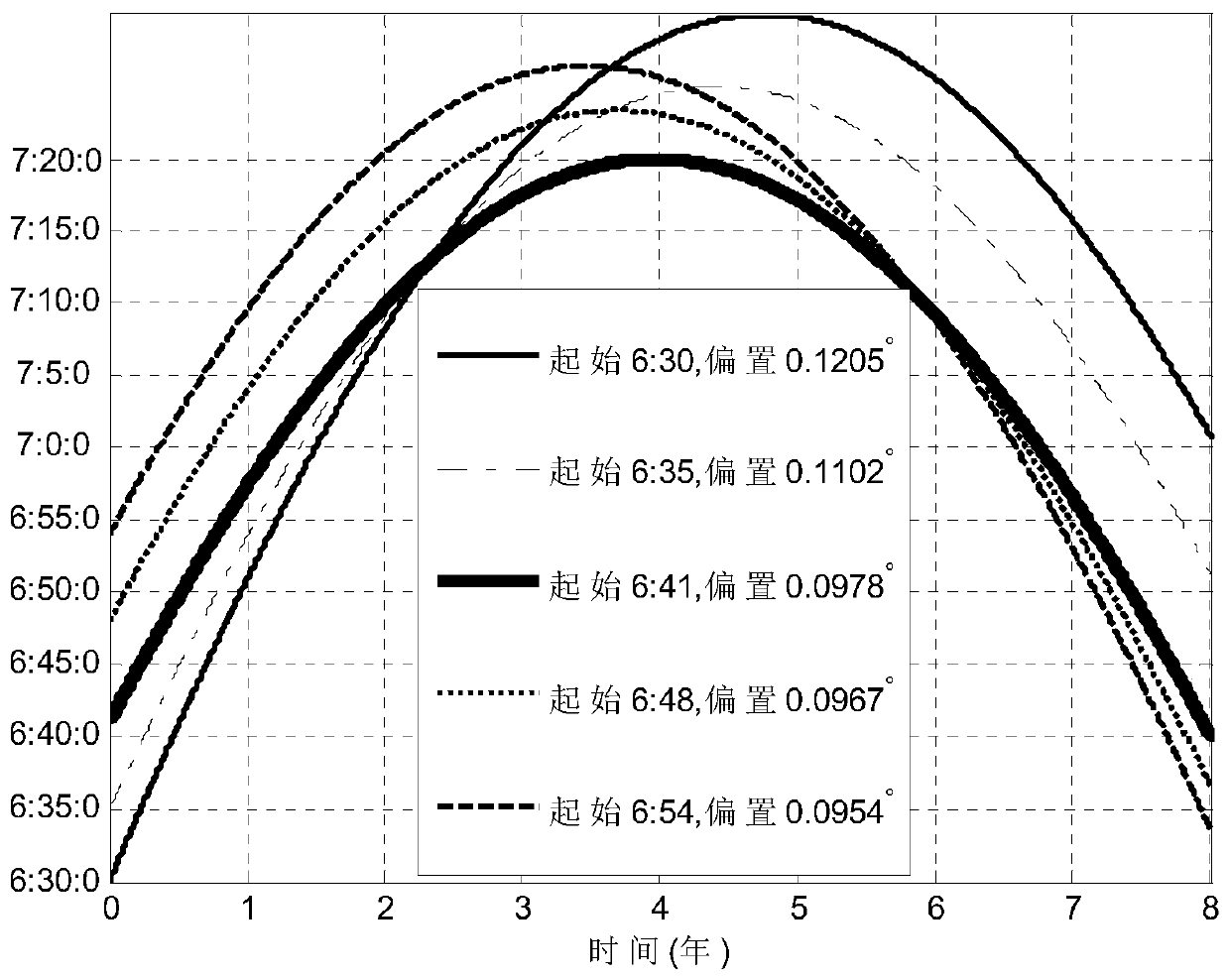
[0027] A dual-bias passive control method at the descending node of the sun-synchronous orbit, such as figure 1 As shown, the specific steps are as follows:
[0028] (1) When obtaining the sun-synchronous orbital position, adjust the mission's preset sun-synchronous orbital altitude H, and when the nominal descending node position is LTDN 0 And the satellite design life T;
[0029] According to the patent: "Sun-synchronous Orbital Inclination Offset Method Considering Multi-task Altitude", ZL201310108729.6, formula (1) calculates the nominal inclination i corresponding to the working height H 0 , The relationship between the two meets the following conditions:
[0030]
[0031] Where p=a(1-e 2 ), a=R e +H, R e Is the semi-major axis of the earth, e is the orbital eccentricity, μ is the earth's gravitational constant, J 2 Is the second-order harmonic coefficient of the earth's gravity, J 4 Is the fourth-order harmonic coefficient of the earth's gravity, n s Is the angular velocity of ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com