A discriminant sparse preserving embedding method for unconstrained face recognition
A face recognition, non-constrained technology, applied in character and pattern recognition, instruments, computer parts, etc., can solve the problem of not considering the global distribution characteristics of samples, the performance of the algorithm is degraded, and the low-dimensional essential information cannot be accurately mined.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
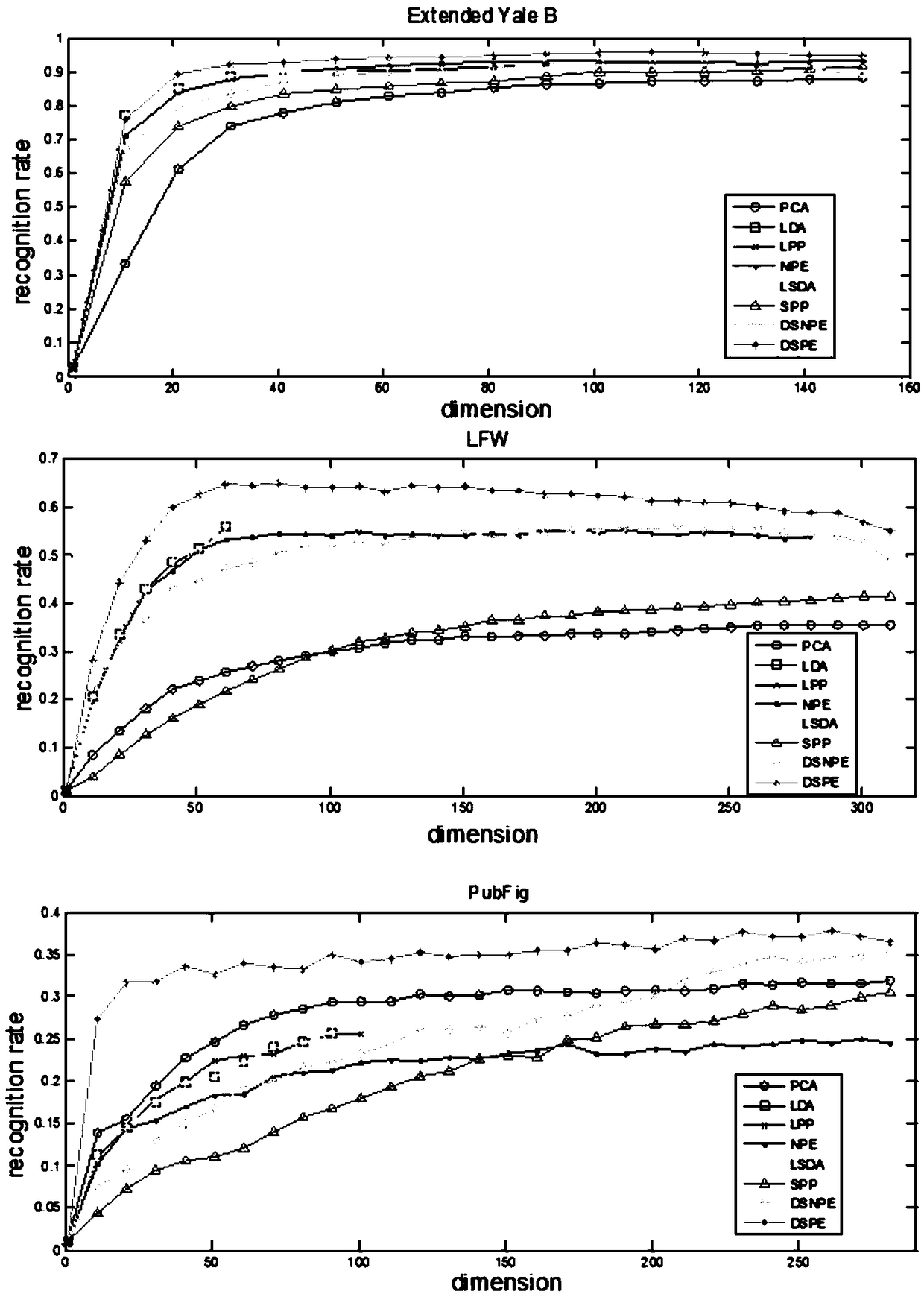
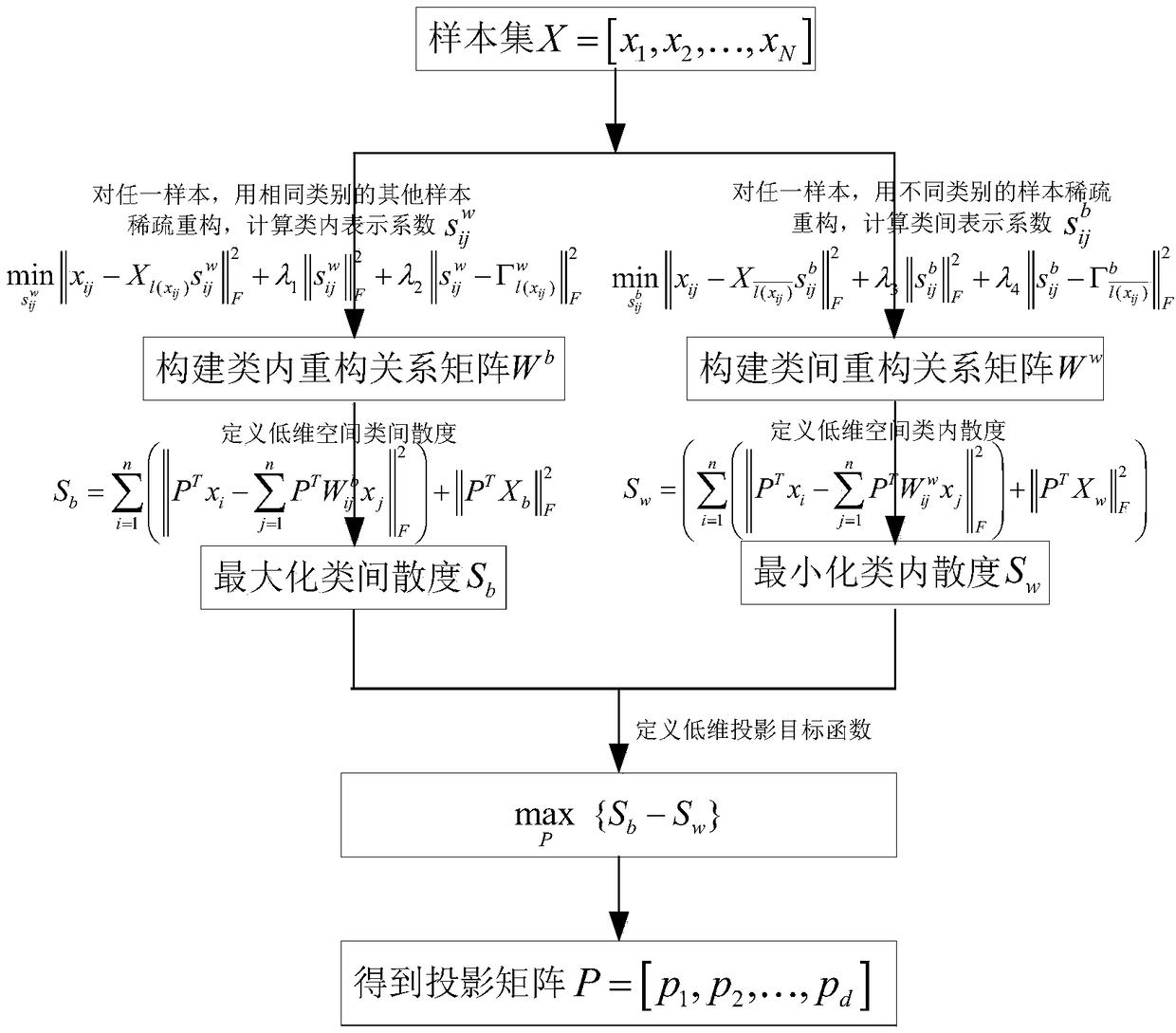
[0064] Aiming at the problem that in the Sparsity Preserving Projections (SPP) algorithm (Sparsity Preserving Projections, SPP) uses a global dictionary to represent the sparse reconstruction relationship between samples and the projection process does not analyze the structural characteristics of samples from a global perspective, the present invention proposes a supervised discriminative sparse-preserving embedding Algorithm (Discriminative Sparsity Preserving Embedding, DSPE), designed to achieve the following invention objectives:
[0065] (1) By introducing category labels, establish a local intra-class dictionary and an inter-class dictionary, so that the samples to be tested are sparsely represented by similar samples and heterogeneous samples, and increase intra-class compactness constraints and inter-class compactness constraints on the basis of sparse representation , to enhance the reconstruction relationship between the sample to be tested and similar samples in the...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com