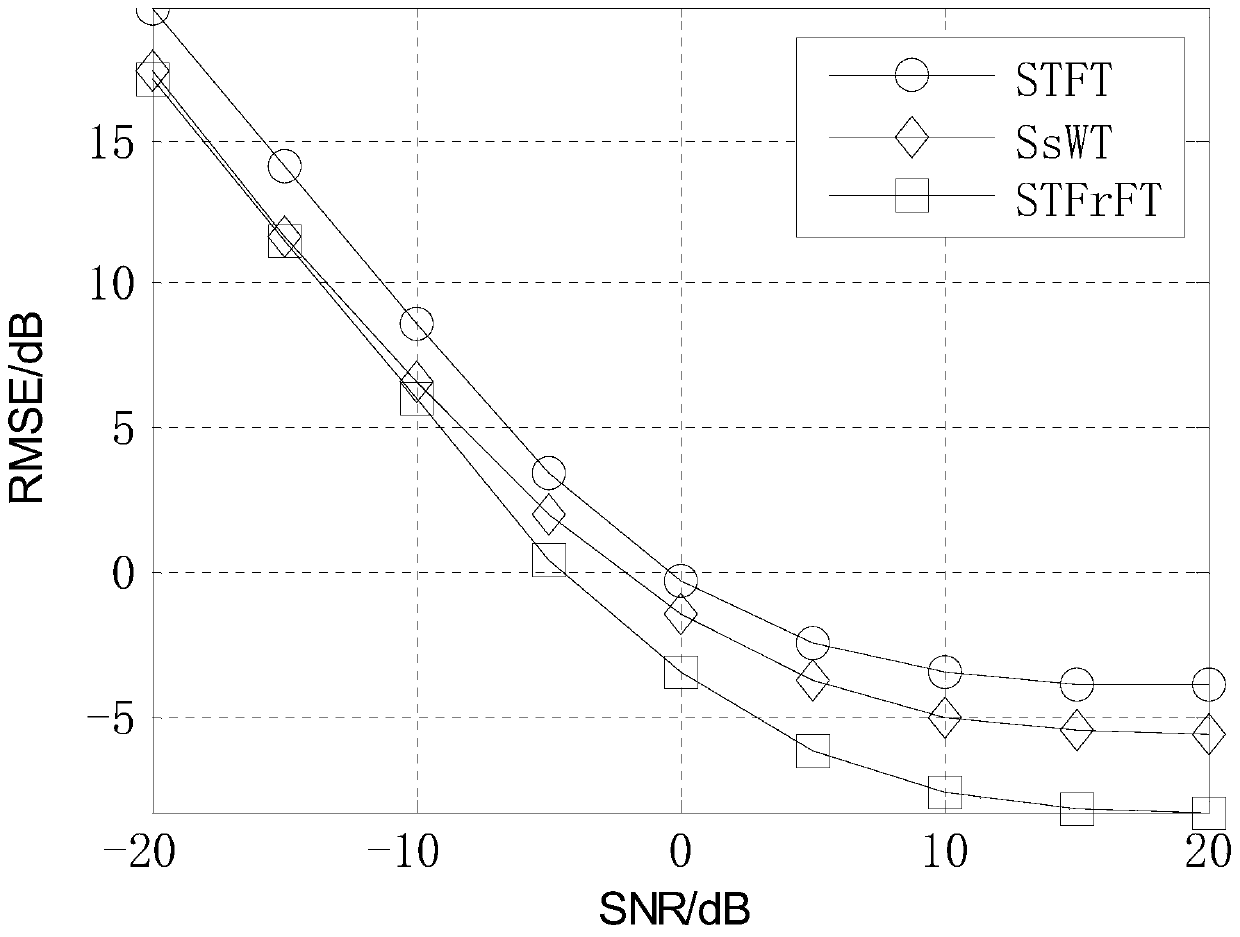
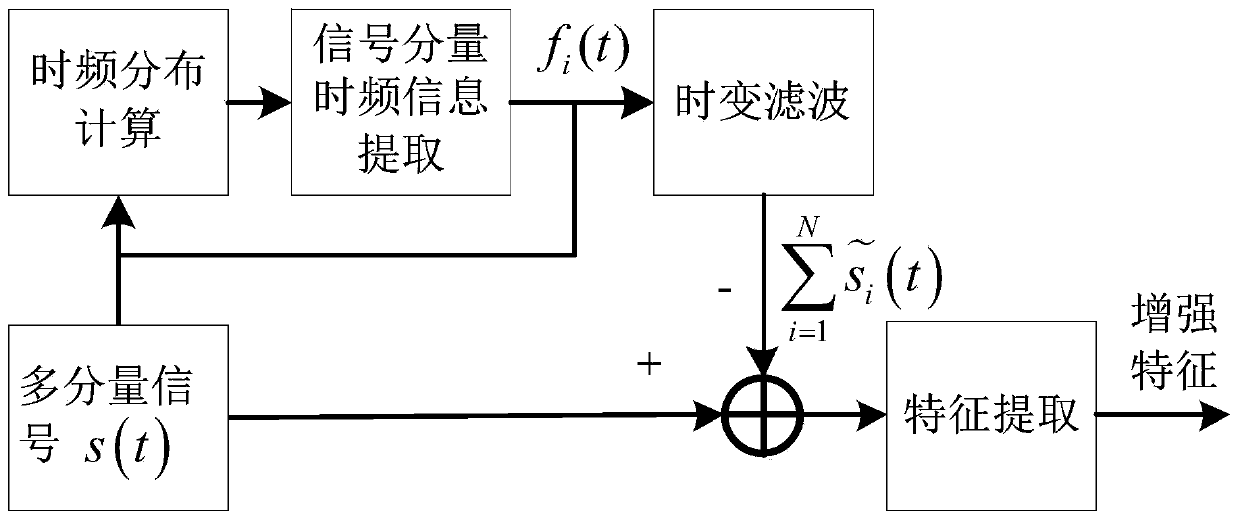
Radiation source individual characteristic enhancement method based on time-varying filtering theory
A technology of time-varying filtering and feature enhancement, which is applied in the direction of instruments, character and pattern recognition, computer components, etc., can solve the problems of identification failure and low identification accuracy of radiation source individuals, and achieve the effect of enhancing the characteristics of radiation source individuals
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
[0041] Specific implementation mode one: combine figure 1 Describe this embodiment. In this embodiment, a method for enhancing individual characteristics of a radiation source based on time-varying filtering theory has a specific process as follows:
[0042] Step 1. The receiver receives the radiation source signal. The radiation source signal is a multi-component signal s(t), which includes multiple signal components and can be divided into three parts. First, the signal of the target radiation source itself and the interference signals of other radiation sources are both Belonging to the main signal, the energy of this part is relatively high, and the component can be directly extracted from the time-frequency distribution; second, the individual radiation source adds the modulation signal component, which is the part to be enhanced and feature extracted by this algorithm, and the energy of this part Low, it cannot be directly extracted from the time-frequency distribution; ...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0074] Specific embodiment 2: The difference between this embodiment and specific embodiment 1 is that in the first step, the time-frequency distribution calculation is performed on the multi-component signal, and the time-frequency information is extracted to obtain the time-frequency of each signal component in the main signal component information; the specific process is:
[0075] The instantaneous frequency estimation algorithm based on the adaptive fractional spectrogram method calculates the time-frequency distribution of the multi-component signal, and extracts the time-frequency information to obtain the time-frequency information of each signal component in the main signal component.
[0076] Time-frequency distribution calculation and time-frequency information extraction can refer to literature (Khan N A, BoashashB.Instantaneous Frequency Estimation of Multicomponent Nonstationary Signals Using Multiview Time-Frequency Distributions Based on the Adaptive Fractional ...
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0078] Specific embodiment 3: The difference between this embodiment and specific embodiment 1 or 2 is that the radiation source signal in step 2 or 2 is based on the time-varying short-time fractional Fourier order of the i-th signal component time-frequency information in the main signal. Transformation Kernel During Leaf Transformation The expression is:
[0079]
[0080] Among them, α i (τ) = πp i (τ) / 2 is the rotation angle of FrFT; j is the imaginary unit, j 2 =-1; k is an integer; δ(·) is an impact function; p i (τ) is the order time-varying function of the i-th signal component in the main signal component.
[0081] Other steps and parameters are the same as those in Embodiment 1 or Embodiment 2.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com