Construction method and application of a conditional yap1 gene knock-in mouse
A construction method and conditional technology, applied in application, genetic engineering, plant gene improvement, etc., can solve problems such as unfavorable experimental research, impure pathological type of spontaneous tumor tissue, and non-specificity of lung squamous cell carcinoma
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0074] The preparation method of the linearized plasmid is not particularly limited in the present invention, preferably including: transforming Escherichia coli with a carrier plasmid; extracting the plasmid by shaking bacteria; purifying the plasmid; verifying the plasmid by enzyme digestion; linearizing the plasmid by enzyme digestion; verifying linearization by enzyme digestion Plasmid; linearize the plasmid by electrophoresis, cut the gel to recover the target fragment; verify the recovered linearized product by enzyme digestion, and obtain the linearized vector plasmid. In the present invention, there are no special limitations on the experimental methods and reagents involved in the above-mentioned preparation method of the linearized plastid, and conventional methods and reagents in the art can be used.
[0075] The method of the present invention is not particularly limited to the ES targeting method, and conventional methods in the field can be used, preferably includ...
Embodiment 1
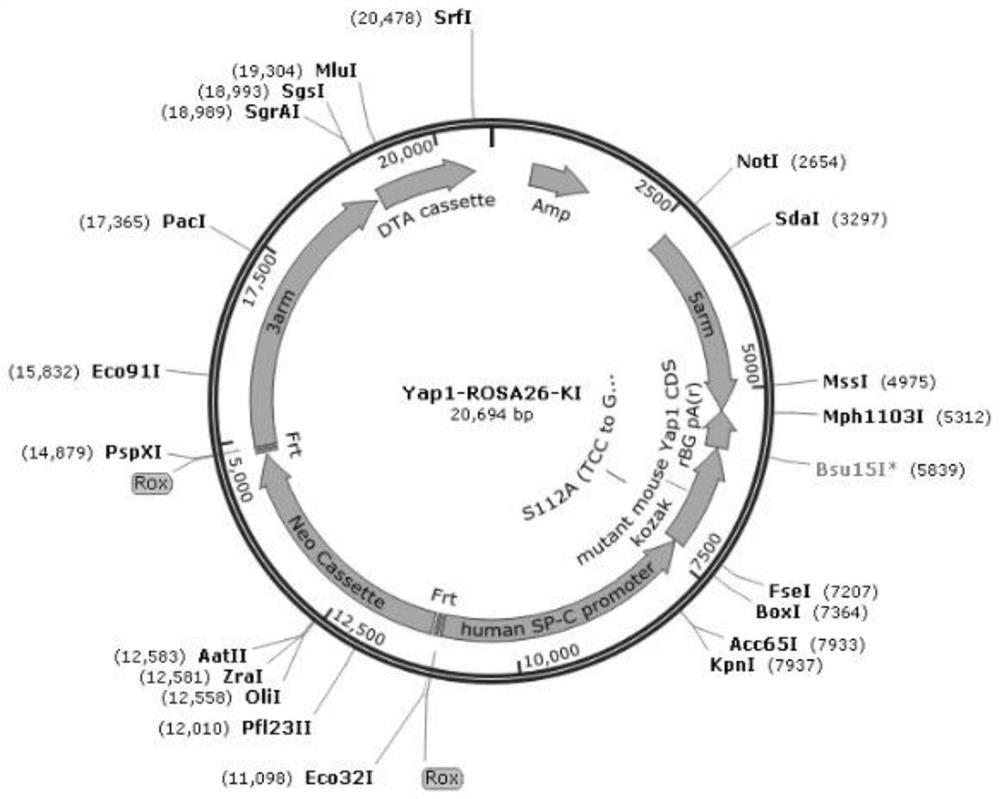
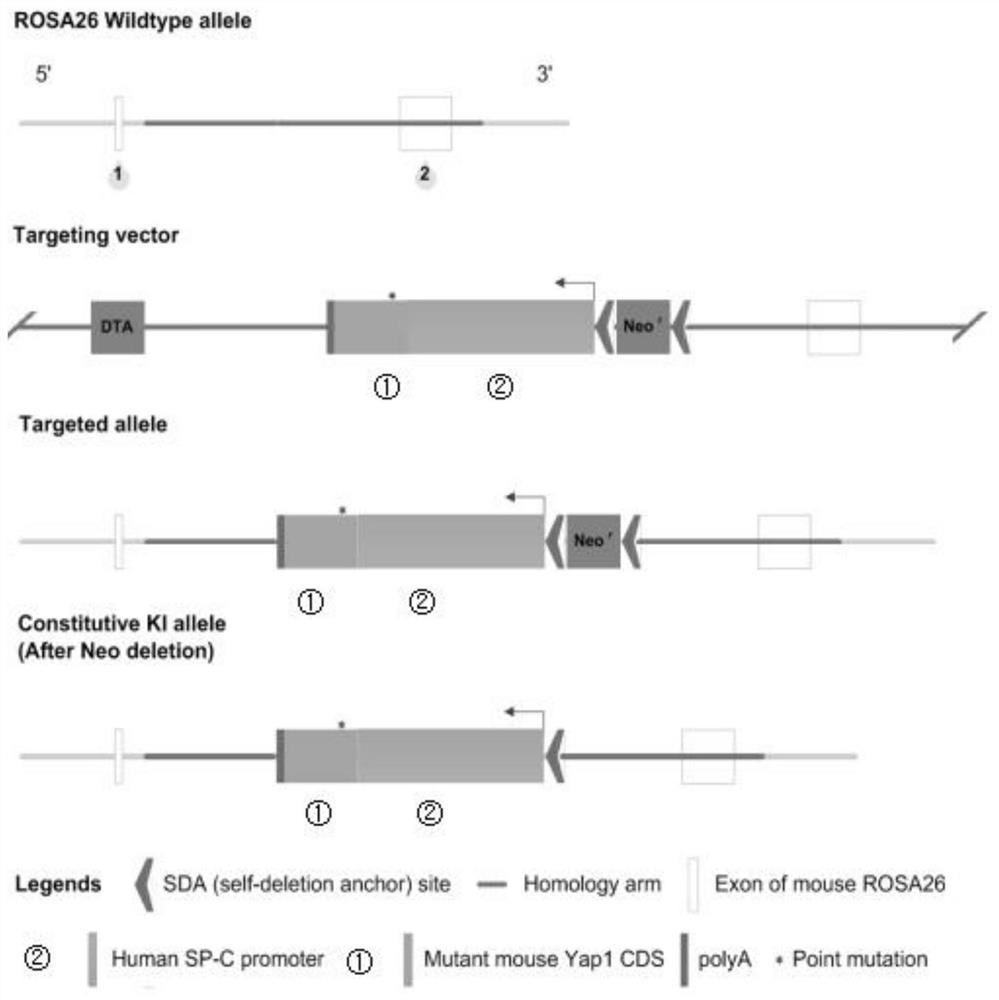
[0104] Construction of targeting vector:
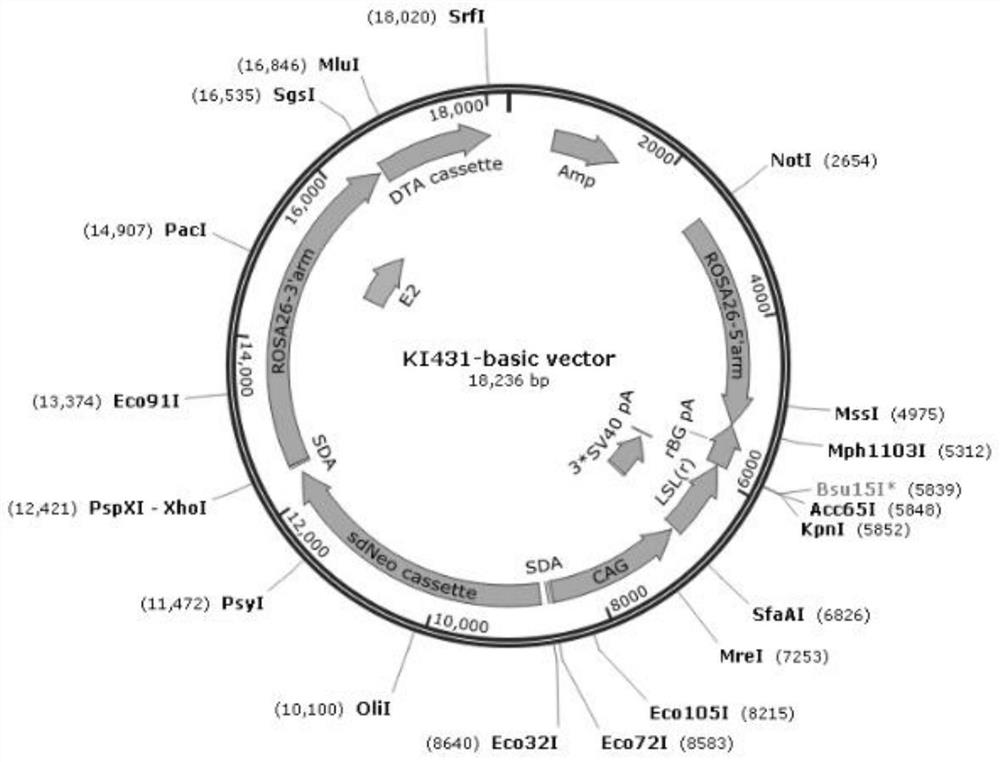
[0105] (1) Use KpnI / PmII to digest the basic skeleton containing the ROSA26 gene: ROSA26-5'arm-rBGpA(r)-MSC-SDA-sdNeo cassette-SDA-ROSA26-3'arm;
[0106] (2) Directly synthesize the plasmid human SP-C promoter-mutant mouse Yap1 CDS, clone it into the pUC57 vector, use EcoRV to digest the pUC57-Human SP-C promoter-mutant mouse Yap1 CDS vector, and recover the 5252bp band, namely For Human SP-C promoter-mutant mouse Yap1 CDS;
[0107] (3) The target fragment: Human SP-C promoter-mutant mouse Yap1 CDS was ligated into the enzyme-cut backbone using In-fusion ligase to obtain the SP-C promoter-Yap1-ROSA26-KI431 targeting vector .
Embodiment 2
[0109] Determination of targeted clones: Delivery of linearized vectors to ES cells (C57BL / 6) by electroporation, followed by G418 drug selection, selection Figure 5 The indicated regions were screened by PCR, and a total of 91 drug-resistant clones were obtained, and the samples labeled 1F2, 1D4, 1B5, 1G6, 1H5, 1D8 and 1D9 were identified as potential target ES clones, and the results were as follows Figure 6 As shown; select the same region, perform SouthernBlot on 1B5, 1D4, 1D8, 1F2, 1G6 and 1H5 samples, and the predicted fragment sizes are:
[0110] Neo Probe (containing 5’HA)–9.7Kbp–Hind III;
[0111] Neo Probe(containing 3’HA)–12.7Kbp–Kpn I; the results are as follows Figure 7 As shown, all six ES clones (1B5, 1D4, 1D8, 1F2, 1G6 and 1H5) were confirmed to be correct.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| volume | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com